Psychologists define the cognitive sphere as a set of mental processes designed to perform the function of rational cognition. This term was introduced in the 60s of the last century. Then, in the wake of the large-scale development of cybernetics and the widespread passion for this science, the comparison of a person with a complex biocomputer became popular. Attempts have been made to model human psychological processes with varying degrees of success.
The cognitive sphere is something that can be modeled. The area with which this technique did not work was called affective.
The concept and essence of the cognitive sphere
Today in psychological practice, by the phrase “cognitive sphere of personality,” experts understand several psychological processes that occur in accordance with a logical and meaningful sequence, the purpose of which is to process information.
That is, we can talk about this area only if data processing is characterized by logic and rationality.
Traditionally, this area is associated with memory, attention, perception, understanding, thinking, decision-making, action and influence (however, only when it concerns cognitive processes and not entertainment or attraction). With a certain simplification, it can be argued that the cognitive sphere is a set of competence and knowledge, skills and abilities.
Examples of cognitive processes
Each person has a specific set of cognitive abilities that allows them to perform daily tasks. Thanks to perception and sensations, an individual can easily experience the world without visible effort.
For example:
- Thanks to vision, people are able to observe a large number of visual objects, which include people, houses, and road signs.
- When a student looks at a book, he or she can remember a literature lesson.
- With the help of hearing, a person is able to hear a huge range of sounds and tones.
- With the help of memory, people are able to find answers to many questions, as well as reproduce any important information at the required moment in time.
For example:
- thanks to memory, people know their date of birth, address and telephone number;
- a person is able to reproduce information from the past;
- various smells, sights and sounds can remind people of some significant event;
- Listening to a song, a person can remember his childhood or his beloved.
Thanks to attention, people capture the signals, information, knowledge and skills they need.
For example:
- when a person wants to say something, his interlocutor tries to focus attention on him so as not to miss important words;
- If at school a teacher asks a student to make a report, then, thanks to his attention, the student will be able to complete it.
Without the cognitive sphere, a person would not be able to enjoy all the delights of the world around him. Communication with other people would be impossible. Therefore, people should take care of their cognitive processes, constantly develop them and maintain them in good condition. If age-related problems are identified, consult a doctor immediately.
Learn more about rational and emotional mechanisms of perception
The cognitive sphere is a kind of synonym for rational perception, which manifests itself as a critical, analytical assessment.
The direct opposite of the rational type of knowledge is intuition, that is, a pure, living impression. Any term becomes more understandable when the definition is supported by illustrations: despite the fact that ice cream is delicious and you really want to buy it, a person does not eat these sweets on the street in winter, as he may get sick. This conclusion is the result of rational reflection.
When the rational mechanism of understanding is activated, it involves concepts and logic. While emotional, bodily and experiential ways of understanding involve empathy, empathy and sensitivity.
Therefore, in order to exert a rational influence, they use various methods of persuasion and explanation (referring to reason and logic). Irrational methods are used for suggestion, emotional contagion, anchoring and other techniques.
Interaction and interdependence of the two spheres
Considering that each personality has integrity, its main spheres (emotional, cognitive) perform their specific functions, complementing each other.
In everyday life, most people get used to making do with feelings and established habits; they trust automatisms. However, if necessary, rational thinking with its logic and concepts is activated.
Scientists are still studying the development of the cognitive, emotional sphere and the features of their functioning. As for rational methods of cognition, science has advanced quite far in their classification and description.
Affective processes are extremely difficult to model due to their unpredictability. These include emotions that accompany a sensual attitude towards life, interaction with the world, with oneself and society. True, there are a number of mental processes, the occurrence of which is regulated by specific laws. Then they talk about studying the cognitive component of these emotions.
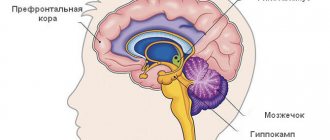
Characteristics and definition of memory
Memory is the human ability to preserve and accumulate information about the world around us. If this mechanism did not exist, people would constantly have to perceive all events and phenomena as if they were happening for the first time. Memory allows you to reduce the energy costs of the brain to evaluate constant or repetitive factors, as well as adapt to circumstances with minimal stress.
Thus, memory is responsible for the fact that a person stores, remembers and then, if necessary, reproduces his individual experiences.
Cognitive functions. What is this?
All cognitive functions are divided into memory, attention, speech, praxis (purposeful activity), gnosis (orientation, recognition of place and time), thinking. The capabilities of cognitive functions form the personality of an individual, determine success in education, professional activities, and other areas of life.
There are 4 main interacting components of cognitive functions : 1. perception of information (visual, auditory, tactile gnosis, smell, taste, etc.); 2. processing and analysis of information (“executive” functions), which include voluntary attention, generalization, identification of similarities and differences, formal logical operations, establishment of associative connections, drawing conclusions. This also includes thinking and intelligence, which imply, among other things, the ability to adapt in society, behave adequately in a changing environment, building a program of behavior, adjusting one’s actions based on the appropriateness of the moment; 3. memorization and storage of information (memory) and 4. exchange of information, construction and implementation of a program of action - “expressive” functions, which include speech, skills of targeted motor activity (praxis) Memory is the ability of the central nervous system to assimilate new information, store it and repeatedly use in the process of life. Memory consists of stages: memorization (retention), storage of information and reproduction of information. In vascular cognitive disorders, information reproduction suffers to a greater extent, while memorization and storage may be preserved. Semantically mediated “cues” during testing help patients reproduce information. In neurodegenerative diseases (AD), memory is primarily affected. There are individuals with hypo- or hypermnesia, with innate “mnestic giftedness”. There are patients who are sensitive to interference (distractions), and there is a primary weakness of memory even without interference. When the reproduction of information is impaired, pseudo-reminiscences (minor inaccuracies in details), contamination (inclusion of some memories in the structure of others), confabulations (events that do not take place are remembered) are distinguished. HYPOMNESIS is divided into: Fixation (the period of time corresponding to a certain event is forgotten), antero- and retrograde; progressive and non-progressive
Memory types
Depending on which parts of the brain and organs of the human body are involved in the process of memorization, there are:
- Motor memory - automatic movements. She is responsible for developing useful skills that are used quite often. The purpose of this mechanism is to increase efficiency and speed up motor processes. People use motor memory to drive cars, write words, play musical instruments, and even walk.
- The emotional type of memory is the memorization of emotional states accompanying certain situations. This mechanism is designed to complement other types of memory. The retention of emotions and reactions allows a person to strive for certain events and avoid others.
- Figurative memory, in which data on visual, auditory, gustatory, olfactory and other images is stored. This type of memory is considered professional, since the intensity of its development depends on human activity.
- Verbal-logical, the object of which is thoughts. It is carried out thanks to the presence of words.
- Voluntary and involuntary memory. Their difference is that while storing information, a person can understand why he needs this information, or remember it in random order.
- Short-term, operational and long-term memory. The first ensures the storage of information literally in a fraction of a second, the second provides access to intermediate results in the course of solving current problems, and the last represents the accumulation of data for the future.
The listed types of memory, as features of the cognitive sphere, function in close interrelation with each other.
The concept of "cognitive sphere"
Definition 1
The cognitive sphere is the sphere of human psychology associated with cognitive processes and consciousness and includes a person’s knowledge about the world and about himself.
The term cognitive sphere appeared against the backdrop of the development of cybernetics in the second half of the 20th century, when for the first time a person was compared to a biorobot of a complex structure. During this period, scientists modeled the mental processes occurring in the human brain, but attempts were not always successful. The simulated mental process is called cognitive.
Human mental functions aimed at cognition and learning form the cognitive sphere of a person. The basis of the processes is the consistent and logical perception of information and its processing.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Cognitive sphere in psychology 420 ₽ Essay Cognitive sphere in psychology 280 ₽ Examination Cognitive sphere in psychology 220 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
The cognitive sphere is distinguished by logic and rationality. Attention, memory, perception of new information, thinking, logically determined actions belong to the cognitive sphere. Cognitive processes are not associated with entertainment, emotional disturbances, or attachments.
Cognitive processes manifest themselves, for example, at the moment of reading, when opening a book, a person perceives words, letters, information and relates it to his existing knowledge. When it comes to a work of art, a person can imagine the picture described in the book.
Cognitive processes are also activated when writing; a writer, for example, imagines what he will write about, using his imagination. To write a coherent and beautiful text, you need to remember what you wrote earlier, and this activates your memory quite well.
The acquisition of skills and abilities during the learning process is not complete without certain cognitive processes.
Attention also belongs to the cognitive process, because when receiving new information it is important to focus on it without being distracted by something else. Thus, memory is necessary in order to remember the information received, and imagination allows you to visualize what we are talking about.
Have questions about this topic? Ask a question to the teacher and get an answer in 15 minutes! Ask a Question
Cognitive processes also manifest themselves in a person’s everyday life, for example, the desire to lose weight, on the one hand, and a piece of delicious cake, on the other hand, make a woman think: she can satisfy her desire, or she can stop in time.
The development of cognitive processes occurs gradually and over a long period of time. The child learns these processes from the first days of life and it is important to ensure that the level of their development corresponds to age. In children, the level of development of this area is determined using structured, depending on age, diagnostic materials presented with different tasks.
Imagination is a truly human ability
One of the most important differences in the activities of humans and animals is that people project (imagine) the end result of their actions before doing anything. This happens thanks to such an ability as imagination. It provides people with the ability to create an image of an object that does not exist in the real world, hold it, and even moreover, manipulate it.
The development of the cognitive sphere in general and imagination in particular is important for generating solutions in the absence of complete information. With the ability to design theoretical models, people can not only imagine the final result of actions, but also “see” the intermediate products.
Types of imagination and their characteristics
The main parameters that describe imagination are activity and effectiveness.
Often it acts as an integral element of creative activity, that is, it participates in the transformation of the surrounding reality. This is active imagination.
In contrast, there is a passive type, which is characterized by unrealistic or impracticable projects. People who want to escape from reality resort to passive imagination. They can create images and outline behavior programs that can never be implemented.
Unintentional imagination is activated at the moment of weakening control over consciousness (dreams, hallucinations).
Attention and its varieties
Characteristics of the cognitive sphere would be incomplete without a description of such a phenomenon as attention. It accompanies almost all types of human activity: it ensures clear and effective perception, memory or thinking.
The main task of attention is that it selects and limits current stimuli. It also ensures focus and concentration of mental activity. In other words, it helps the subject to focus on the object.
There are several types of attention:
- Involuntary. It is the simplest and most natural, as it appears without effort on the part of a person.
- Arbitrary. It requires the manifestation of will to concentrate on the chosen goal, as well as to repress interfering thoughts and impulses.
- Post-voluntary. Its peculiarity is that it is a consequence of voluntary attention, but is maintained consciously.
As a rule, the post-voluntary type is caused by a deep and persistent interest in what is happening and what will be obtained as a result.
Like different types of memory, types of attention are usually tightly interconnected; they can move and flow into each other.
The relationship between emotional and cognitive spheres
Personality orientation - what is it in psychology, its types
If a person is mentally developed, both his cognitive and emotional spheres are fully activated. Thanks to them, he is a complete person.
Additional Information. Some people often succumb to emotional impulses, but despite this, in difficult and responsible situations they use the cognitive side of the personality.
The relationship between the rational and emotional spheres lies in the fact that, no matter what a person does, no matter what work he does, he does not cease to feel. If his emotional impulses begin to intensify, he makes every effort to logically comprehend his subsequent actions and the consequences of them.