The welding profession is included in the group of dangerous and harmful to human health. However, eye burns from welding occur not only in production.
Now that purchasing your own welding machine is not a problem, you can “catch bunnies” anywhere. But regardless of where the injury occurred, the result is the same: in the late afternoon, the burned person literally washes himself with tears, household members have no idea about the causes of the strange symptom, and precious time is running out.
But in some cases, a minute of delay leads to irreversible impairment of visual functions. To save a victim from blindness, it is important to know the symptoms of an eye burn and the basic rules of first aid.
The main causes of eye burns from welding
Neglecting the rules for working with a welding machine can result in a burn to the cornea of the eye. Often the organs of vision are affected in the following cases:
- Assembling metal structures without the help of a partner and fasteners. Without wearing a mask, the welder holds the parts with his own hands and places tacks.
- Using a low-quality mask. Ultraviolet rays penetrate into the gaps between the filters and the mask frame.
- Using the wrong mask. To perform some tasks, an automatically darkening chameleon mask is required. In a mask with a regular shield, a worker simply will not have time to cover his face.
Presence during welding work (forced or accidental). The risk of injury increases on bright sunny days. Having succumbed to the deceptive sensation of the faint glow of the arc, a person loses his vigilance and by the evening he receives a full bouquet of burn symptoms.
What causes electroophthalmia?
Electrophthalmia is a burn of the eyes caused by welding, quartz or other powerful light source in medical language. The main cause of injury is the effect of ultraviolet rays on the mucous membrane, involving the cornea and retina.
The depth of damage depends on the scale of irradiation. A burn to the mucous membrane occurs when:
- a particle of hot metal or a spark gets into an unprotected eye;
- open contact with fumes of metals and gases;
- ultraviolet/infrared radiation;
- failure to comply with safety regulations (described above);
- exposure to thick toxic smoke (from a melted electrode) in the eye.
Classification of injuries received
All burns received during welding are divided into the following groups:
- thermal (heat) burns;
- light damage to the eyes, manifested in the visible range of the spectrum emitted by the arc;
- chemical burns resulting from exposure to harmful substances contained in the melt vapor.
The first group of factors dangerous to humans, in addition to direct burns from molten slag, includes ultraviolet and infrared rays, which are an invisible source of heat.
The characteristic glow of the welding arc is quite dangerous for the operator’s eyes, especially for their cornea, which has increased sensitivity to the visible part of the spectrum. This type of burn is unpleasant due to its difficult to predict consequences and requires immediate pre-medical care.
The last group of possible damage includes dangerous fumes generated when working with special metals (zinc fumes, for example).
The impact of oxides of known metals that are part of welding aerosols (chromium, manganese, nickel, iron and others) is classified in a similar way.
This should also include toxic gases released during the welding process (carbon monoxide, ozone, hydrogen fluoride, nitrogen dioxide, etc.).
Statistics of burns received during the welding process convincingly show that the most vulnerable part of the operator is poorly protected hands. However, due to violation of TB requirements, facial burns are also common. For this reason, this case requires separate consideration.
Symptoms of a welding burn
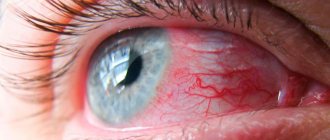
Immediately after a welding burn to the eyes, there are practically no symptoms. They grow within 6–12 hours. During this time, a person who has “picked up bunnies” can prepare everything necessary to provide first aid. If the burn is deep, it is better to see a specialist when the first symptoms appear.
Let's look at the general signs that help identify electroophthalmia:
- The first sign of a welding burn is a strong or mild burning sensation in the eyes, developing into a sharp pain. If you close your eyes tightly, it becomes easier. However, this is a deceptive feeling, because when you open your eyes, the pain returns.
- Tears constantly flow from the eyes, it hurts the victim to look at the light.
- With deep damage and involvement of the retina, a person sees nothing. However, there is no need to panic; in most cases, vision returns after 48 hours.
- When looking at the light, spots of light “stand” before the eyes. The duration of the symptom is determined by the duration of contact with the traumatic factor.
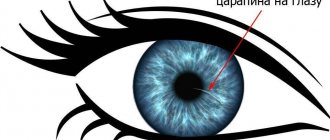
- You can feel the sand under your eyelids. Do not rub your eyes under any circumstances! This can accelerate the development of the inflammatory process and lead to swelling of injured tissues.
- The eye pain gradually spreads to the head, intensifying when you try to move your gaze to the side.
Signs of eye damage depend on the severity of the burns. In medicine there are:
- I degree (mild) – a burn of the cornea of the eye is expressed by decreased transparency, darkening of the cornea, and redness of the conjunctival membrane. In some cases, there is a slight burning sensation and itching. The victim can be helped at home.
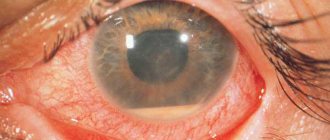
- II degree (medium) – after an injury, the eye becomes covered with a film, the cornea is damaged, becomes loose and erosive. Victims experience photophobia and severe pain.
- III degree (severe) – visual functions sharply decrease, the eyelids swell, and severe aching pain occurs. There is a constant sensation of a foreign body under the eyelids (as if sand had been poured into the eyes). You cannot do without medical help.
- IV degree (extremely severe) – the injured tissue begins to die, the cornea becomes whitish, the victim screams in pain and cannot open his eyelids. Without timely medical assistance, a person becomes blind.
In case of a mild or moderate eye burn and proper first aid, the victim’s condition improves after a few hours. If deeper tissues are injured, the burned person should be taken to the emergency room as soon as possible.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of electroophthalmia should be used with great caution so as not to cause additional irritation to damaged eye tissue. Experts advise resorting to them no earlier than a day later and only after the inflammation has subsided. As healing drops, you can use a solution of honey in water in a ratio of three parts water to one honey, or additionally add one part fresh aloe juice.
Compresses made from chamomile infusion, potato lotions made from raw tubers, and cabbage pulp applied to the eyelids have proven themselves to be effective. It is important to know: even if your eyes stop hurting, you need to visit an ophthalmologist to check your vision and the condition of the eye tissues using laboratory methods. This will help avoid future problems such as corneal erosion and detachment, damage and clouding of the retina. After diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe medications and vitamins to quickly restore damaged areas of the eyes. If the damage is extremely severe, surgery and hospital treatment may be required.
First aid
What to do in case of a 1st, 2nd or 3rd degree welding burn to the eyes in order to alleviate the suffering of the victim and not harm him even more?
Experienced welders immediately sense if the cornea of the eye has been burned and immediately stop working. If this is not done, the damage will affect deeper tissues. Then follows a set of first aid measures:
- Wash and rinse your eyes thoroughly with clean drinking water, potassium permanganate, tea leaves or chamomile decoction (all in low concentration). Do not skimp on liquid; copious rinsing is indicated.
- Cover the windows with dark curtains or remove the victim to a place protected from light.
- Eye drops will help relieve pain and swelling from burns: “Vizin”, “Visoptin”, “Proculin” (for eye burns, drip 1 drop while lying down). Special products will speed up the healing of affected tissues, reduce itching and pain intensity. For mild trauma to the mucous membranes, therapy continues for 3 days until the discomfort is completely eliminated. If the pain is very severe, the burned eyes are instilled with Lidocaine 2% or Tetracaine every 12 hours.
- Take a painkiller tablet (“Spazmalgona”, “Analgina”). If it’s really bad, you can inject Ketanov intramuscularly.
- To relieve inflammation, drink Nimesil, Diclofenac, Nimesulide.
- Using a sterile napkin or a clean handkerchief, remove metal particles and other foreign bodies from the eyes. If this is not possible, seek medical help immediately.
- To relieve inflammation, cover your eyes with a cloth moistened with cool water. Do not use ice!
- Squeeze a little antiseptic ointment (Tetracycline, Solcoseryl) into the conjunctival sac.
- In case of stage 4 burns, it is necessary to call an ambulance and relieve the suffering of the burned person with an anesthetic injection.
Attention! Long-term use of these drugs leads to a decrease in visual functions.
Further therapy
After providing professional medical care, the patient is discharged with recommendations for further therapy:
- Bed rest for deep wounds. It is necessary to stay in a dark room to reduce eye strain.
- The use of ointments for burns (Bepanten, Eplan) for healing the skin.
- Local antibacterial drugs for the skin (Erythromycin) and eyes (Tsiprolet, Tobrex). Application time is 7-10 days.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are dropped into the eyes to relieve swelling and redness (Indocollir). Vasoconstrictor drops (Visomitin, Octilia) complement the anti-inflammatory effect. They are used for no more than 5-7 days.
- For rapid tissue regeneration, agents are used that accelerate metabolism in cells (Solcoseryl) and improve blood circulation (Actovegin).
- After burns, the eye sclera begins to dry out. To prevent this, moisturizing drops (Artificial tears) are prescribed.
- For any damage in the affected areas. Interstitial fluid begins to accumulate. Cells of the immune system flock to the lesion. This is manifested by swelling, inflammation, and redness. To eliminate them, antihistamines (Suprastin, Zodak) are prescribed.
A burn from welding can cause irreparable damage to health. You cannot ignore your doctor's instructions. Assignments must be strictly followed.
When to see a doctor
It is important to understand that a burn to the retina can lead to blindness. This means that the victim’s quality of life will deteriorate: he will lose the ability to self-care, become incapacitated, etc., so you need to see a doctor for any degree of damage.
Special indications for sending a victim to a medical facility or calling an ambulance are:
- increasing pain that does not respond to pain relief with medications;
- noticeable deep tissue damage;
- the presence of metal particles that cannot be removed;
- state of shock.
Possible complications
Severe degrees of damage can lead to scarring on the surface of the eyes, chronic inflammation, and clouding of the cornea. Without proper treatment, there is a high risk of vision loss, because the burned tissue begins to die. If the cornea is burned, the following consequences develop:
- perforation of the eyeball;
- erosive processes;
- increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma);
- degenerative clouding of the lens (cataract);
- chronic form of conjunctivitis;
- scars on the eyelids.
Types and degrees of possible welding burns
The burn received when performing welding work is similar in its effects to ultraviolet radiation. First signs:
- whitish fog before the eyes;
- short-term blurred vision;
- severe burning sensation;
- photophobia.
Types of damage to the organs of vision:
- Chemical burns from welding - usually occurs in enclosed spaces due to exposure to caustic fumes.
- Light injury is an occupational disease among welders that occurs during a sufficiently long period of exposure to bright light on the eyes, which accompanies the entire welding process.
- Thermal burn - occurs when exposed to high temperatures from the flame of a welding tool.
- Complex injury is when a welder receives several types of burns at the same time.
According to the degree of damage, burns are distinguished:
- Lungs - redness of the eyelids, clouding of the cornea, pain in the ocular conjunctiva, slight erosion of the cornea is observed.
- Medium – the skin of the eyelids bubbles, films have formed on the conjunctiva, which are removed with a tampon.
- Severe - the cornea is completely clouded, films stick to the conjunctiva, and the affected areas of the skin die off.
- Super severe - deep necrosis of the tissues of the cornea, eyelids, and retina.