A scratch on the eye (on the cornea) is not as dangerous as, for example, burns, erosions, and penetrating injuries. It has virtually no effect on vision, but causes very strong unpleasant sensations and should not be ignored under any circumstances.
At the first signs, you should immediately contact a specialist. These injuries occur in 70% of all eye injuries.
First aid
If you notice the above symptoms, then before going to the doctor, you should do the following:
- If the scratch appears due to a foreign body, you must try to remove it, to do this you need to blink the injured eye frequently. Such actions stimulate the release of tears, which can wash away the unnecessary object.
- Also, use your fingers to push back the upper eyelid of the affected eye and pull it onto the lower eyelid; the eyelashes will try to remove a grain of sand if it is stuck on the inside of the upper eyelid.
- If the previous steps do not work, rinse your eyes with room temperature water or saline solution.
- Apply artificial tears (special eye drops).
- Take painkillers.
- If you manage to remove the interfering object, then a light scratch may go away on its own within some time.
There is a scratch on the cornea of the eye - what to do and how to treat it
Our main organ of vision is reliably protected from any mechanical or physical influence. At the slightest threat from the outside, the nerve endings send a signal to the muscle fibers, causing the eyelids to instantly close. But dealing with minor damage is more difficult. Eyelashes, midges, and dust particles often get into the eyes. They can damage the organ of vision.
A scratch on the cornea of the eye creates great inconvenience. Such damage occurs due to external influences; they do not cause serious damage to vision, but cause pain and significant discomfort. The problem cannot be ignored.
In most cases, the scratch heals without intervention or treatment, but there is a possibility of it becoming infected, in which case serious complications develop.
If you feel discomfort that does not disappear with frequent blinking, it is advisable to consult a doctor. Explain the essence of the problem to the ophthalmologist so that he can draw preliminary conclusions. This is followed by a mandatory examination to determine the extent of corneal damage. Next, the specialist will prescribe the necessary measures aimed at healing the scratch. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Functions of the cornea
The cornea performs several important functions. It has the shape of a convex lens that “covers” the lens of the eye. Thanks to this, it collects the rays, directs them, forming a clear image, making it possible to focus it.
The cornea also performs a protective function by covering the lens. The smallest foreign bodies that enter the eye settle on the cornea and are then washed away with the help of tear fluid. Such specks of dust and cilia can injure the surface of the eye.
Scratches appear on it that are invisible to the naked eye.
Significant damage to the cornea is possible with chemical burns and serious injuries. Then the organ ceases to perform its functions. Modern ophthalmology is constantly evolving. Science and medicine have come a long way over the past few decades.
Today, all over the world, cornea transplant operations are actively carried out in case of serious damage. In this way, it is possible to restore the lost functions of the cornea.
If the damage is minor, then modern treatment can eliminate all the negative consequences of the injury.
Causes of scratches
Scratches on the cornea appear for a number of reasons:
- Getting dust or grains of sand into the eyes;
- Loss of eyelashes with further contact with the iris;
- Using contact lenses for too long;
- Cracks on the surface of contact lenses;
- Active influence of water;
- Other injuries.
You can damage your cornea by swimming in a pool or sea for a long time. Bleach, like an excess of salt, negatively affects the mucous membrane of the eye and dries it out. Because of this, the cornea becomes less protected. Micro scratches appear on it.
People who work in wood processing plants often suffer from small chips getting into their eyes.
The same thing happens when cutting metal using a grinder, chainsaw, and other tools. Tiny pieces of hard materials can get into your eyes. That is why such work must be carried out with special glasses or a mask.
In strong winds, grains of sand often fly into the eyes, which can injure the cornea. Our eyelashes are constantly renewed. When they fall out, they can get into the eye. Such minor microtraumas can lead to a lot of negative consequences.
Associated symptoms
Microtraumas of the cornea of the eye are accompanied by numerous unpleasant symptoms:
- Burning sensation;
- Pain when blinking;
- Unpleasant sensations when moving the eye sideways, up and down;
- Lack of clarity of vision;
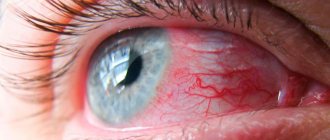
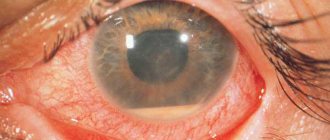
- Redness of the eye;
- Upper eyelid spasm;
- Tearing;
- Sensitivity to light.
A person feels the presence of a foreign body in the eye. Blinking creates a feeling of discomfort and sometimes severe pain. Because of this, the upper eyelid is constrained by spasm. If you try to blink less often, the surface of the eye is poorly moistened with tear fluid, which is why other problems develop.
Your vision drops sharply and you cannot focus. The picture becomes blurry and unclear. The sclera of the eye takes on a pinkish tint due to the fact that the small capillaries inside burst. The tender skin around also becomes red and swollen. The eyes look very inflamed.
Excessive sensitivity to light occurs. As soon as a person goes outside, he involuntarily begins to squint, causing a significant release of tear fluid. Tears blur everything before my eyes, the clarity of the image drops even more.
Vision is one of the basic human senses. If it falls, it will negatively affect your safety. That is why the smallest disruptions in the functioning of this system, microtraumas, require urgent diagnosis and treatment.
Consequences
If you do not start treating a scratch on the cornea in a timely manner, this is fraught with many negative consequences. The slightest violation of the integrity of tissues leads to the active reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms here. Inflammatory processes are launched that are difficult to stop. In some cases, returning normal vision becomes problematic.
The cornea of the eye can no longer perform its basic functions, and the person faces serious problems. The most common of them is doubling of any image, its blurred boundaries. Microtrauma triggers other pathological processes in the visual system. All its components begin to work incorrectly.
Timely treatment is the only possible way to get rid of the negative consequences of injury and prevent their development in the future. Therapeutic activities are carried out at home or in an outpatient clinic. Inpatient treatment for microtrauma is not required.
Treatment methods
Therapy is carried out in several stages. First, it is necessary to remove the foreign body from the eye if it is present.
It is strictly forbidden to remove a grain of sand or an eyelash with your hands, tweezers, or other devices. You risk causing further injury to yourself or infection in your eye.
It is advisable to immediately contact the emergency ophthalmology department or the doctor on duty at the outpatient clinic.
If you remove a foreign body at home, the actions depend on the size of the object. A small grain of sand, a midge or an eyelash can be removed simply by actively blinking. At the same time, a significant volume of tear fluid is released, which washes away all impurities.
If a foreign body has penetrated deeply into the cornea, then you cannot remove it yourself. This procedure is performed only by a doctor. At home, you can also do rinsing by putting drops in your eyes, lying on your side, in the direction from the outer to the inner corner. For these purposes, special drops based on artificial tears or sterile cool water are used.
When the foreign body is removed, the doctor assesses the degree of damage to the cornea and prescribes further measures. For speedy healing, moisturizing and anti-inflammatory eye drops are used. In rare cases, topical steroids are prescribed. They give a quick positive effect, but cannot be used for a long time.
It is strictly forbidden to apply a blindfold. Previously, this method of treatment was common, but recent studies have confirmed that such measures only slow down the recovery process. The patient should blink regularly to naturally moisturize the surface of the eyeball. When the eye is closed, this task is not performed.
Girls will have to give up eye makeup for a while. All patients are recommended to wear sunglasses until complete recovery, so as not to further injure the organs of vision. For severe pain, the doctor prescribes painkillers.
Only such an integrated approach gives positive results and allows you to get rid of the unpleasant consequences of scratches on the cornea forever.
Examination by a doctor
In any case, you should immediately consult a doctor to avoid any complications and prevent infection.
To determine whether a patient has a scratch on the cornea of the eye, the doctor simply examines the eye. In addition, he must also:
- Understand how dangerous the damage is, whether it is penetrating. To do this, the doctor instills a local anesthetic (Alcaine eye drops) into the eye. After some time, when the drug takes effect, the specialist examines the eye using an ophthalmoscope - a special lamp (slit).
- To more accurately determine a scratch, a special substance (one percent fluorescein) is used, which colors the scratch or any damage to the cornea green.
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Scratch on the eyeball
If the eyeball is exposed to a damaging factor, a scratch may appear on it. It can be superficial and deep. As the external structures of the eye interact with the environment, pathogenic microorganisms multiply on it and can penetrate the wound.
Therefore, it is recommended to immediately consult an ophthalmologist. He will examine the damaged surface and prescribe conservative or more serious treatment, which will facilitate the rapid restoration of damaged tissue.
Causes of a scratch on the eye
The main causes of damage are the following conditions and diseases:
- mechanical impact due to careless use of any object by a person, contact with foreign substances in the eyes, exposure to chemical reagents;
- prolonged use of contact lenses;
- postoperative complications;
- diseases affecting the outer surfaces of the eyes, such as erosions.
The doctor must identify the root cause. So, if this is not done, the risk of re-formation of damage increases.
The child scratched the cornea of his eye
If a child scratches the outer surface of the eyes, self-medication is not recommended. Parents or close relatives may further harm the affected area. It is prohibited to apply any bandages, ice, tinctures, or lotions. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance or take the injured child to the traumatology department yourself.
Symptoms
When scratches occur on the superficial membranes of the eyes, the following characteristic clinical symptoms appear:
- increased sensitivity in the eye area, which causes severe acute pain and the inability to open the eyelids;
- increased production of tear fluid;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- inflammatory process that causes swelling;
- increased sensitivity to bright light;
- sensation of a foreign object under the eyelids.
If the above symptoms occur after a damaging factor, this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
First aid
There are first aid rules that a patient can apply before being examined by a doctor:
- if a foreign object gets into the eye, it is recommended to rinse it with running warm water;
- instillation of drugs into the eyes that provide hydration of the mucous membrane (Slezin, Defislez, Artificial tear);
- rinsing actions should be carried out from the outer to the inner corner of the eyes;
- if the damaging factor was a mechanical or chemical effect, it is recommended not to resort to self-medication;
- wear sunglasses to reduce exposure to bright light;
- take an age-appropriate pain reliever.
There are important rules about what measures should not be taken in case of damage to the superficial structures of the eyes:
- apply herbal, medicinal lotions to the eyelids, the active ingredient of the drug may cause irritation;
- rub your eyes, touch them with cotton swabs or napkins;
- apply a bandage that will prevent the flow of oxygen to the wound and eyes;
- if the victim wears contact lenses, it is recommended to remove them for the duration of the injury and wear glasses during treatment;
- if the patient was wearing makeup at the time of the injury, it is recommended to remove it only after visiting a doctor;
- If the damage is deep, it is recommended not to apply cosmetics at the time of treatment.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the condition of the superficial structures of the eyes, the doctor uses several methods:
- Applying a local anesthetic in the form of drops, which will numb the eye and eliminate photophobia.
- Examine the damaged area using a slit lamp. The doctor will identify the location of the scratch and determine its depth.
- If visual inspection fails to detect damage, a fluorescein solution is used. It colors the mucous membrane green, so damaged areas appear.
After an examination, the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Treatment
Comprehensive treatment is carried out to prevent the development of complications:
- Treatment with an antiseptic (Furacilin) or antibacterial (Tobrex, Vigamox) to eliminate the risk of spreading infection and suppuration.
- Applying an ointment that promotes the regeneration of damaged tissue. These include Solcoseryl, Korneregel. They are used before bedtime, since applying the drug under the eyelid causes blurred vision.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in case of severe swelling.
- Applying a flap soaked in an antibacterial drug to the cornea.
It is recommended to fully adhere to the prescribed treatment to avoid possible complications. Self-medication can lead to irreparable consequences and adverse reactions.
Complications
Without consulting a doctor or if treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the following complications may occur:
- spread of infection, suppuration;
- penetration of infection into the deeper tissues of the eyes;
- ulcers and erosions of the mucous membrane;
- damage to the cornea, which reduces visual acuity.
Forecast
If the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner, the risk of complications is reduced.
In this case, the prognosis of the disease will be favorable. Failure to consult a specialist, self-medication, or changing the dosage of medications can cause extensive damage to the superficial structures of the eyes. In this case, a person can spread the infection to deeper tissues.
Prevention
To avoid damage to surface structures and eyes, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- if a person works in an enterprise where it is possible to introduce an object or chemical into the eye area, it is recommended to use protective equipment, glasses, masks;
- remove all dangerous objects that could harm the child in the room where he is constantly located;
- wear contact lenses for a limited amount of time;
- If dry eyes develop, apply moisturizing drops that prevent the formation of microtraumas on the mucous membrane and cornea.
The formation of scratches on the surface structures of the eyes is an unpleasant and dangerous condition. If all medical procedures are performed in a timely manner under the supervision of a doctor, the prognosis for the patient’s condition will be favorable.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale! (
1 3,00
Treatment options
Depending on the degree of damage, the specialist prescribes treatment:
Minor scratches
The doctor prescribes antibacterial drops for instillation three to four times a day.
Albucid is often prescribed, but it is not enough, so for greater effect, Floxal, Miramistin, and Tobrex are used.
Before going to bed, antibacterial gels and ointments are applied to the eyelids: “Solcoseryl-gel”, “Korneregel” and so on.
Scratch of the cornea of the eye
A scratch on the cornea of the eye can appear when the mucous membrane is damaged by a nail, branch or other sharp object.
It is often possible to scratch the white of the pupil, the mucous membrane of the pupil, or the sclera even with a lens if it is used carelessly.
In children and adults, a scratched cornea can take a long time to heal; during this period, the person’s vision is cloudy and blurry, and they are often bothered by soreness and redness.
If you accidentally or intentionally poke a fingernail or a branch into the cornea, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, since such damage can lead to complete or partial loss of vision.
Why does it appear and what are the risk factors?
A child or an adult can accidentally scratch the cornea when rubbing the eye too hard. The stratum corneum is especially often injured when a foreign body penetrates. A scratch often occurs when sand, small gravel, dust, dirt or shavings get into your eyes when cutting metal.
In the latter case, the eyeball takes longer to heal and is much more painful. A scratch on the eyelid often occurs in people who wear contact lenses for a long period of time. Careless surgical intervention can damage the conjunctiva, the area of the white and the pupil.
At this time, the cornea is most vulnerable and scratch marks easily appear on it. The following factors are identified that influence the occurrence of a violation:
The membrane of the visual organ can be damaged due to wearing contact lenses.
- drying or thin layer of the cornea;
- use of contact lenses;
- work activity in which there is a high risk of eye damage;
- professional sports, during which the eyeball may be injured.
How to recognize the symptoms?
If a scratch occurs on the pupil, white, cornea, or inside the eyeball, then the person will be worried about pathological symptoms. The pathological condition can be recognized by the following signs:
- increased tearfulness;
- severe closure of the eyelid, known as blepharospasm;
- photophobia;
- increased attack of pain in the eye;
- reflex narrowing of the gap;
- pronounced redness;
- formation of a mixed or pericorneal injection on the eyeball.
Due to trauma, a person begins to see the surrounding space blurred.
If the cornea is scratched by a lens, nail or other foreign object, then the person complains of a feeling of a foreign body in the eye. Against the background of damage, impaired visual function may appear; the patient begins to see everything blurry or as if “in a fog.” If the scratch is not noticed in time and the necessary treatment is not carried out, the victim will experience frequent headaches.
Dangerous consequences
If a child or adult is not provided with timely treatment after a scratched cornea, serious complications may arise. You should not expect the resulting wound to heal on its own. A neglected scratch on the cornea of the eye can provoke an inflammatory reaction, which is medically known as keratitis.
When the disease occurs, a person's visual function is impaired, and a strong fear of light arises. The stronger the injury, the more pronounced the signs of keratitis. In especially severe cases, the patient is unable to open his eyes. If the cornea or the central part of the eye is inflamed, then visual acuity rapidly decreases.
When the inflammatory reaction extends to the periphery of the cornea, there is no negative effect on visual function.
Keratitis that occurs when the cornea is scratched requires timely treatment, since the pathology leads to persistent clouding of the membrane, as a result of which a person is not able to distinguish objects, but sees only light or darkness.
Diagnostic procedures
Usually, using a slit lamp, the doctor is able to identify the cause of the patient’s discomfort.
If a child or adult scratches the cornea area, you should urgently consult an ophthalmologist. To better examine the damaged area, an anesthetic substance is injected into the conjunctival sac twice or three times with a short break.
After 10 minutes, a diagnostic examination is performed using lateral illumination and a slit lamp. If in this way it was not possible to discern a scratch on the cornea, then a fluorescent substance is used, which is illuminated. The drug is also injected into the conjunctival sac.
Thanks to this diagnostic technique, the damaged areas are tinted green and it is easier for the doctor to assess their area.
What to do and how to treat?
To avoid negative consequences when the cornea is scratched, you need to know what measures to take. First of all, it is necessary to remove the foreign body that has damaged the cornea of the eye. For this purpose, the organs of vision are thoroughly washed using running water.
Quick blinking also helps to remove a foreign object, which allows you to eliminate a speck, a grain of sand, or trapped dust. Special drops that can be bought at a pharmacy without a doctor's prescription also help get rid of a foreign body in the eye.
Such products are aimed at washing the eyeball and eliminating unpleasant symptoms when scratched. During therapy, follow these recommendations:
Until the organ recovers, it is necessary to stop using cosmetics.
- To reduce the pain of injury, it is recommended to take a tablet with an anesthetic effect.
- It is strictly forbidden to wear an eye patch, since it does not speed up the healing process, but, on the contrary, contributes to the spread of infection and aggravation of the situation.
- During the treatment of a scratch in the cornea, you should refrain from using cosmetics and wearing contact lenses.
- During therapy, it is recommended to use glasses that protect the eyes from ultraviolet rays.
Treatment for a minor scratch
For minor damage, it is necessary to apply compresses to the damaged cornea, which will speed up the healing process. The specialist also prescribes special drops to the patient, which are used three times a day. The table shows effective remedies for a small scratch of the cornea:
| Release form | Name |
| Drops | "Albucid" |
| "Floxal" | |
| "Miramistin" | |
| "Tobrex" | |
| Eye ointments and gels with antibacterial effects | "Solcoseryl-gel" |
| "Korneregel" |
Therapy for large lesions
Before the intervention, the affected area is numbed with anesthetic drops.
A severe scratch on the eye requires more radical therapeutic measures. If a corneal flap has been scalped, the following manipulations are performed alternately:
- Anesthesia through eye drops.
- Treating the scratched surface of the eye with antibacterial medications.
- Putting the flap in place.
- Another instillation of drops.
- Using an antiseptic dressing.
If the flap cannot be placed due to a scratch on the cornea, then surgery is performed in which sutures are placed using monofilament fibers.
Prognosis and prevention
If a patient with a scratch on the cornea is treated promptly, the risks of complications are minimal. When the disease is advanced, complete or partial loss of vision is possible.
In order not to scratch the cornea, it is necessary to use special protective equipment during traumatic activities to prevent eye injury.
It is not recommended to wear contact lenses for a long time, as drying out and damage to the mucous membrane is likely.
Help with scratches
If the reason is a foreign body, then you need to try to remove it. To do this, you need to rinse your eye with warm water or saline solution (water with salt). Under no circumstances should you rinse your eyes with water straight from the tap, as it can cause infection. The rinsing time depends on the cause of the eye injury.
You can also blink for two minutes to help remove the foreign body from the eye. In this way, the tear will wash the eye and unnecessary particles will come out of it. Do not pull out foreign bodies using tweezers or other objects. This can cause additional injury.
If the above steps do not help, you can pull the upper eyelid onto the lower eyelid. This way you can get rid of a traumatic object if it is located on the inside of the eyelid.
After removing the foreign body, you need to instill eye drops. Moreover, they are sometimes used to flush out a foreign object from the eye. The necessary drops are available at any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription.
- You can bury it yourself or ask a person nearby.
- Often people choose artificial tears eye drops, which have a moisturizing and lubricating effect.
- If you need to drip more than four times a day, then you need to choose products without preservatives. They are irritating and the eye will become even more inflamed.
- After all procedures, you need to take painkillers.
- Healing time depends on the depth of the lesion.
The doctor can tell you what to do with a scratch on the eye that does not heal for a long time. To do this, you need to seek advice from a clinic and they will correctly diagnose the disease.
Symptoms
If the organ of vision is damaged, a person begins to complain of the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the eye;
- increased lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- blepharospasm or severe closure of the eyelid;
- reflex narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- headache;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
All of these symptoms may indicate dangerous damage to the cornea of the eye, so if they appear, you should see an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. If a child scratches the cornea of the eye, parents do not need to self-medicate. You should seek medical help sooner
Diagnostic procedures
If a child or adult scratches the cornea area, you should urgently consult an ophthalmologist. To better examine the damaged area, an anesthetic substance is injected into the conjunctival sac twice or three times with a short break. After 10 minutes, a diagnostic examination is performed using lateral illumination and a slit lamp. If in this way it was not possible to discern a scratch on the cornea, then a fluorescent substance is used, which is illuminated. The drug is also injected into the conjunctival sac. Thanks to this diagnostic technique, the damaged areas are tinted green and it is easier for the doctor to assess their area.
How to recognize the symptoms?
If a scratch occurs on the pupil, white, cornea, or inside the eyeball, then the person will be worried about pathological symptoms. The pathological condition can be recognized by the following signs:
- increased tearfulness;
- severe closure of the eyelid, known as blepharospasm;
- photophobia;
- increased attack of pain in the eye;
- reflex narrowing of the gap;
- pronounced redness;
- formation of a mixed or pericorneal injection on the eyeball.
Due to trauma, a person begins to see the surrounding space blurred.
If the cornea is scratched by a lens, nail or other foreign object, then the person complains of a feeling of a foreign body in the eye. Against the background of damage, impaired visual function may appear; the patient begins to see everything blurry or as if “in a fog.” If the scratch is not noticed in time and the necessary treatment is not carried out, the victim will experience frequent headaches.
Treatment
Therapy depends on the severity of the damage to the stratum corneum. For minor injuries, your doctor will prescribe antibiotic eye drops. They need to be dropped into the eyes four times a day. For example:
- Albucid;
- Tobrex;
- Miramistin.
Also apply antibacterial gel before going to bed. For example:
- Solcoseryl gel;
- Korneregel.
If the damage is more severe and the corneal flap has been scalped, anesthesia is used. It is treated with an antibacterial agent, the flap is placed in its location and again treated with antibacterial drugs. Then a bandage is put on. You will need to put drops in your eyes 4 times a day and apply the gel before bed. Do not remove the bandage under any circumstances until the doctor gives permission to do so.
Sometimes it is not possible to put the flap in its place. In this case, the seams are made with monofilament fiber. For example, nylon fibers or supramid are used.
Nowadays it is not recommended to adjust the bandage. Since oxygen does not reach the eye, and the cornea is very dependent on this. At the same time, the eye is tense and the pain intensifies, healing slows down. Therefore, the doctor will be able to suggest an alternative to the blindfold. A doctor's prescription of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drops in combination with soft contact lenses can easily replace a bandage. In this case, a person sees with two eyes, which receive oxygen and the wound heals faster.
Scratches on the eyes are very common, and the majority of them are scratches.
Abrasions and scratches on the cornea of the eye
Corneal abrasions and are superficial injuries to the eye's cornea, the clear membrane located at the front of the eye that covers the iris and pupil, allowing light to pass to the inner structures of the eye. Accidental contact with dust, sand, wood chips or metal particles can scratch or cut the cornea, damaging it.
When the cornea is damaged, the eye experiences severe pain, redness, burning, tearing, photophobia, blurred vision and headache. Corneal abrasions can heal within 24 to 72 hours and rarely progress to ulceration, erosion, or infection.
Initial treatment should be symptomatic and include removal of foreign bodies, analgesia with topical or oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , and antibiotics. Corneal scratches and abrasions can often be avoided by wearing protective eyewear when performing activities that expose the eyes to injury.
Functions and structure of the cornea
The cornea is an organized group of cells that is structurally related to the sclera (the white part of the eye). This thin membrane performs three important functions of vision: protection, filtering some ultraviolet waves, and refraction (the cornea is responsible for 65-75% of the eye's ability to focus light on the retina).
To ensure proper passage of light to the internal structures of the eye, the cornea must be completely transparent. For this reason, it is not vascularized and consumes oxygen and is nourished from tears (superficial epithelial cells), and from aqueous humor that fills the anterior chamber (deep cells).
In addition, there are many more free nerve endings, so the cornea is one of the most sensitive parts of the entire eye. All these aspects are of great importance, since severe damage to the cornea can cause blindness, even if other parts of the eye are completely normal.
Causes and risk factors
Typically, corneal abrasions are the result of direct trauma.
The most common reasons why the cornea of the eye can be scratched include:
- foreign bodies entering the eye from the upper eyelid (for example, eyelashes, dust, sand or ash);
- getting something larger into the eyes (example: tree branches, edge of a piece of paper, nail, etc.);
- long-term wearing of contact lenses;
- rough rubbing of the eyes;
- some eye diseases, including trachoma or other infections.
People of all ages can suffer from corneal damage. In some cases, occupational activities may increase risk, as in the case of farmers, carpenters and construction workers exposed to environments containing airborne particles such as dust, sawdust and sand.
Even materials that reach slightly larger sizes can penetrate the eyes and cause even deeper injuries: for example, a small metal fragment can strike a person's eye when operating a shredder without safety glasses.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms vary from person to person, depending on the extent of the injury. Corneal abrasions, unless caused by extensive chemical burns or ultraviolet radiation, usually affect only one eye.
In case of scratches on the cornea, the following symptoms and signs may occur:
- pain, which may increase with movement of extraocular muscles;
- photophobia (photosensitivity);
- headache;
- blepharospasm;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- dilation of the pupils;
- excessively watery eyes;
- blurred or changed vision;
- pain in the eyes when exposed to bright light;
- redness of the sclera;
- feeling that there is something inside the eye. This sensation sometimes develops several hours later rather than immediately after the injury.
Why does it appear and what are the risk factors?
A child or an adult can accidentally scratch the cornea when rubbing the eye too hard. The stratum corneum is especially often injured when a foreign body penetrates. A scratch often occurs when sand, small gravel, dust, dirt or shavings get into your eyes when cutting metal. In the latter case, the eyeball takes longer to heal and is much more painful. A scratch on the eyelid often occurs in people who wear contact lenses for a long period of time. Careless surgical intervention can damage the conjunctiva, the area of the white and the pupil. At this time, the cornea is most vulnerable and scratch marks easily appear on it. The following factors are identified that influence the occurrence of a violation: