Causes of pain
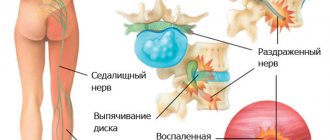
5 pairs of nerve roots in the lumbosacral region combine to create the sciatic nerve. Beginning at the back of the pelvis (sacrum), the sciatic nerve travels behind the buttocks and down through the hip joint into the lower extremities. Nerve roots are not separate structures, but part of the body's overall nervous system, capable of transmitting pain and sensations to other parts of the body. Radiculopathy is caused by nerve root compression, disc rupture, or bone growth between the nerve root and the sciatic nerve.
Lumboischialgia symptoms and treatment.
Lumboischialgia is a powerful pain attack that radiates to the lower back, radiating to one or both limbs. More often, the pain syndrome spreads along the buttock and back of the thigh. Symptoms are localized mainly due to damage to the sciatic nerve and spinal processes. In this case, the person feels a feeling of chills or heat. Typically, an attack begins with sudden sharp pain, limited movements in the lumbar region and the affected limb. It can be provoked by a sudden movement of the body, a previous spinal injury, arthritis, fibromyalgia, or hypothermia in the back area. There are also predisposing factors to vertebrogenic sciatica. The key ones are: stressful and depressive conditions, pregnant women, age exceeding 25-35 years, low pain tolerance range, poor posture, heavy physical work, increased weight. But the main cause of the disease is a hernia, that is, a herniated disc or protrusion. The diagnosis is based on the typical manifestation of complaints of pain in the lumbar region, back and lower extremities.
How to treat sciatica of the sciatic nerve.
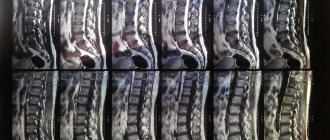
During a clinical examination, a neurologist checks the nature of muscle contraction, which is divided into statistical and dynamic examination of the spine. Using palpation, checks the symptoms of tension in the sciatic nerve roots. Eliminates the presence of signs of malignancy and infection. An accurate diagnosis and determination of the cause of the pain syndrome is established after an instrumental examination: x-ray examination of the pelvic and lumbar region, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, myelography. Treatment of sciatic nerve sciatica is characterized by the benign nature of the disease, thanks to which it can be treated quite successfully.
Most often, symptoms appear during prolonged physical activity, mainly provoked against the background of degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the spine, in which the intervertebral disc suffers, that is, osteochondrosis. The main thing is to start treatment as soon as possible in order to prevent the progression of the inflammation process. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances. First of all, in neurology, measures are taken to eliminate acute pain syndrome, aimed at combating the cause of the disease. That is: herniated discs, osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region, etc.
The treatment of lumboischialgia is carried out by a neurologist or chiropractor. In the initial acute stage, the patient needs to be provided with proper care. The patient must sleep on a special hard mattress; pain is relieved with analgesics and non-steroidal drugs. If painkillers do not provide the desired effect, then novocaine blockades, blockades with anti-inflammatory and analgesic solutions are applied directly to the affected area. Local irritating manipulations give good results. (special ointments, compresses with warming solutions, warm baths and bath procedures). If drug and therapeutic treatment is ineffective, traction traction of the spine is prescribed.
The greatest effect is achieved in the treatment of chronic pain in the lumbosacral spine using physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetic therapy, TENS therapy, professional massage, manual therapy, special gymnastics and sleep).
Disc protrusion or herniation
Disc protrusion is a condition when the central gel-like part of the disc (nucleus pulposus) protrudes towards the spinal canal, while the integrity of the outer wall of the disc (annulus fibrosus) is not compromised. A disc herniation occurs when the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the annulus fibrosus. With protrusion or herniation of the disc, the protruding part of the disc can compress the adjacent nerve root and cause sciatica. The consequences of a herniated disc are worse. In this case, the prolapsed disc core not only causes direct compression of the nerve root, but at the same time the disc substance contains an acid, a chemical irritant (hyaluronic acid), which causes inflammation of the nerve. Nerve compression and irritation cause inflammation and pain, often leading to limb numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness.
Lumbar spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis manifests itself as nerve compression and most often affects older adults. Pain in the lower extremities, similar to sciatica, may be the result of spinal stenosis of the lumbar spine. The pain is usually positional, occurring with changes in body position, standing or walking, and relieved by sitting. The nerve roots branch from the spinal cord and exit through the foramen, bounded by bones and ligaments. Nerve roots emerge from these foramina and innervate other parts of the body. When these openings become narrow and cause compression of the nerve, the term foraminal stenosis is used.
Types of lumboischialgia
There are several classifications of pathology.
There are:
- acute lumbar ischialgia (primarily occurring pain syndrome);
- chronic lumbago with sciatica (acute phases followed by remissions).
Because of its appearance, lumboischialgia is differentiated into types:
Vertebrogenic or vertebral (associated with diseases of the spine),
including:
- discogenic (caused by a herniated disc);
- spondylogenic (due to osteochondrosis of the spine).
Nonvertebrogenic,
including:
- angiopathic (manifests itself when the vessels of the lower extremities and lower back are affected);
- myofascial (observed in diseases of muscles and fascia);
- lumboischialgia with damage to the peritoneal organs;
- lumbago with sciatica due to pathologies of the hip joint.
To study Treatment of lumbar radiculitis at home
According to the degree of distribution of the pain syndrome, lumboischialgia can be:
- unilateral - radiates to one limb, more pronounced on one side of the lower back: left or right);
- bilateral (bilateral) - appears on both sides of the spine, often radiating to both limbs.
Piriformis syndrome
This syndrome is named after the piriformis muscle and pain is caused when this muscle irritates the sciatic nerve. The piriformis muscle is localized in the pelvic region, connects the femur and is involved in hip rotation. The sciatic nerve passes under the piriformis muscle. Piriformis syndrome occurs when this muscle spasms, thereby compressing the sciatic nerve. Due to the insufficient information content of X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging, diagnosing this pathology is difficult.
Causes of neuralgia syndrome, sciatica and pain
Sciatica is pain caused by damage to the tissue of the sciatic nerve. This is one of the most pronounced pain syndromes that a person experiences in his life. Therefore, when pain appears, it is necessary to begin to relieve it as quickly as possible. And this cannot be done unless all possible causes of sciatica syndrome are eliminated. Therefore, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the most likely risk factors. Before starting treatment, it is recommended to avoid their exposure if possible.
The first group of reasons why neuralgia and sciatica can develop is a disease, it includes:
- degenerative dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs of the lumbosacral spine (protrusion, extrusion, hernia);
- viral and bacterial infections in the human body, as a result of which a huge amount of toxins are released, they affect the sciatic nerve;
- poisoning, including alcoholic and drug poisoning (with uncontrolled use of medications without a doctor’s prescription);
- metabolic disorders, as a result of which decay products are not removed from the area where the sciatic nerve passes;
- impaired blood supply to the sciatic nerve (most often caused by diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis and chronic cardiovascular failure);
- ankylosing spondylitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid spondylitis and other pathologies of the autoimmune type;
- spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis;
- instability of the position of the vertebral bodies and their periodic sliding forward (antelisthesis) and backward (retrolisthesis);
- stretching of the ligamentous apparatus of the vertebral column and the subsequent formation of scar tissue;
- benign and malignant neoplasms of soft paravertebral tissues, bone tissue of the vertebrae and their processes, the spinal cord and the surrounding membranes;
- poor posture and curvature of the spinal column;
- piriformis syndrome;
- deforming osteoarthritis of the sacroiliac joint;
- compression fracture of the vertebral body or fissure of the spinous process.
This is not a complete list of potential causes of sciatica. There are a number of predisposing factors. These are excess body weight, violation of ergonomic rules when organizing sleeping and working spaces, a sedentary lifestyle, lifting heavy objects, weightlifting, and falling from a height onto the gluteal region. Approximately 5% of cases of sciatica are due to the consequences of unprofessionally performed intramuscular injection. If you administer the medicine in close proximity to the passing sciatic nerve, then there is a high probability of its inflammation and subsequent necrosis.
Treatment of sciatica
To create a treatment plan, diagnostics are required, including a neurological examination, x-ray and magnetic resonance imaging. Depending on the cause of sciatica, there are several treatment options. Conservative therapy includes changes in activity, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory therapy and various types of blockade to relieve inflammation of the nerve root. Surgical treatment includes removal of the disc herniation through a small incision (microdiscectomy), and in case of stenosis, decompressive surgery with partial or complete removal of the vertebral arch (laminectomy).
Get qualified specialist advice by contacting the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Do not delay making an appointment with a neurologist if any alarming symptoms appear. We remind you that early diagnosis allows you to stop the problem at an embryonic level. You can make an appointment at the central clinical hospital of the capital by phone or using the form on the website.
How to treat lumbar ischialgia in Russia, in Saratov? How to get rid of leg pain?
What should you do if you have pain in your back and leg, if the pain radiates to your left leg, to your right leg, to both legs, if it hurts to turn around? How to get rid of excruciating pain in the spine after lifting weights or after working in the country? Sarclinic in Saratov has been treating pain syndrome and pain associated with neurological manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis for many years. Treatment of subacute and chronic lumboischialgia has an analgesic, trophic, desensitizing effect. Impulsation from the pathological focus is blocked, a new dominant is created in the cerebral cortex, muscle spasm is relieved, and blood circulation in the sciatic nerve is improved. If you have pain radiating to your leg , lower back pain radiating to your left (left) or right (right) leg, pain in your legs, call Sarklinik. Sarklinik knows how to get rid of pain in the leg and buttock, how to treat lumbar ischialgia.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Dizm | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Intervertebral disc, treatment in Saratov, hernia, protrusion of the intervertebral disc, intervertebral disc
Deforming spondylosis of the spine, spine, treatment of spondylosis in Saratov
Poor posture in children, treatment in Saratov, prevention, causes, types of spinal curvature
Vertebrogenic lumboischialgia: treatment, pain in the leg and back, back pain, radiates to the leg
Osteochondrosis of the spine, treatment in Saratov, chondrosis