Osteochondrosis - definition and mechanism of development
Osteochondrosis is a chronic progressive disease of the spine. During the examination, gradual destruction of cartilage and deformation of bone segments are observed. The cervical spine consists of six vertebrae - bone segments connected by ligaments. For shock absorption during movement, turns and tilts of the head, intervertebral cartilage is located between adjacent vertebrae. Special openings contain vertebral arteries and nerves that go to the brain, and protecting them from damage is one of the functions of the cervical spine.
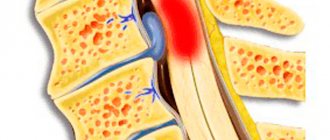
With osteochondrosis, the cartilage tissue of the intervertebral discs loses its elasticity. Its main reason is insufficient supply of blood and nutrients to the cartilage tissues of the intervertebral discs. This process may be associated with age-related changes, insufficient blood supply to cartilage, as well as the consequences of injuries and inflammatory diseases of the joints. The intervertebral discs become thin and insufficiently elastic, so they cannot absorb shock during movement. This leads to decreased neck mobility, painful sensations, and compression of the nerves and blood vessels that pass through this area. The process progresses because the cervical spine is the most mobile and has a weak muscle corset.
Causes of headaches with cervical osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis is a common disease among both elderly and young people. It is accompanied by limited mobility of the neck in all or in a certain direction, deterioration of hearing or vision, as well as acute headache. These symptoms appear already at the initial stage of the disease and only progress over time.
Headache with cervical osteochondrosis is associated with a number of pathological changes:
- decreased clearance between adjacent cervical vertebrae;
- compression of nerves and blood vessels that go to the brain;
- insufficient blood supply to brain cells;
- deformation of bone tissue, formation of growths, fusion of vertebrae - a mechanism of adaptation of the body against abrasion of bones during movement.
Headaches with osteochondrosis can only occur when the cervical spine is affected. This area contains arteries and nerves that carry blood to the brain and participate in its innervation. When the thoracic and lumbar regions are affected, pain in the head does not occur. However, the disease is most often diagnosed in this area, since it is the most mobile and the supporting muscle corset is poorly developed. Incorrect posture, prolonged sitting, lack of physical activity, or, conversely, too intense exercise without sufficient warm-up contribute to the rapid development of osteochondrosis at any age.
Causes of headaches
Headache is a symptom of osteochondrosis, but it is provoked only by certain pathological reactions. It would not be a mistake to identify the reasons why a patient experiences headaches due to osteochondrosis:
- Muscle spasm
. The muscle contracts sharply and remains in this state for a long time. Spasms occur under the influence of osteophytes (formations in the intervertebral discs) or as a result of the development of autonomic dysfunction. In simple words, when failures occur, the human body turns on the “braking mode,” especially during stress and heavy loads. - Vertebral artery syndrome
. The vertebral artery, which is located in a narrow canal of the spine, is compressed or narrowed. This reaction sharply reduces the volume of oxygen transported by the blood and oxygen starvation of the brain occurs. The disorder occurs as a result of mixing of the vertebrae or due to the growth of osteophytes inward. Sometimes, the cause is a hernia. - Pinched occipital nerves
. The processes can be compressed, resulting in the patient not only experiencing severe pain, but also experiencing decreased hearing and vision. - Hypertension or high HF blood pressure
. The blood vessels narrow, and oxygen starvation of the brain occurs. - External factors
. Often the cause of pain is injury, hypothermia and stress, nervous conditions and hard work, sudden movements of the head.
The last group of factors is not the direct cause of the onset of the disease, but can become a stimulus for the deterioration of the patient’s condition, including the appearance of headaches.
The nature of pain caused by osteochondrosis
Headaches with osteochondrosis are a symptom by which the disease can be identified even in the absence of any damage to the neck area. However, it is impossible to make a final diagnosis based on examination alone. There are several options for what types of headaches there are with osteochondrosis, depending on the cause of their occurrence:
- when the vertebral artery is compressed, the pain resembles a migraine, often spreading to only one half of the head;
- when the roots of the spinal nerves are pinched - pulsating, sharp, intensified during turns and tilts of the head;
- chronic headaches are associated with ischemia, a lack of oxygen and nutrients in certain areas of the brain.
With osteochondrosis, headache is often accompanied by additional symptoms. The main one is stiffness in the neck, muscle spasm and discomfort. In addition, the patient may experience numbness in his hands and a tingling sensation in the skin of his palms. If there is insufficient blood flow to the brain, hearing and vision deteriorate, and difficulties with coordination of movements appear. There is also increased sensitivity to bright light and loud sounds and tactile stimuli. These signs disappear after blood circulation is restored.
Diagnostic methods
Headaches with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are a symptom for which it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis. To begin treatment, it is necessary to determine the location of the problem area, the stage of the disease and the pathological changes caused by the disease. To do this, a set of examinations is prescribed, including:
- MRI of the head is one of the most informative and accurate diagnostic methods, thanks to which you can assess the condition of brain tissue;
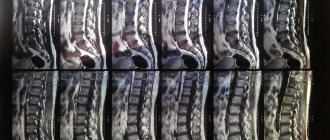
- MRI of the cervical spine is a simple way to get an accurate picture of all the disorders that appear in this area (thinning and decreased elasticity of the interarticular cartilage, proliferation of the articular surfaces of the bones.
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the neck and head - performed with the addition of a contrast agent to monitor cerebral blood flow and determine areas of the brain that suffer from ischemia.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a full examination, determine the stage of the disease and monitor the dynamics of treatment. For this, only modern techniques and precise equipment are used, which allows us to obtain a detailed image of the area under study in any projection. In addition, experienced specialists will be able to accurately determine the causes and stage of the disease, thanks to which the patient quickly receives competent and effective prescriptions.
Treatment of headaches with cervical osteochondrosis
Treatment of headaches with cervical osteochondrosis is symptomatic. The attacks can be relieved at home, but they will continue to occur. It is important to understand that osteochondrosis is a chronic, progressive disease, and it is impossible to completely restore the structure of the affected part of the spine. The goal of therapy is to slow down further destruction of the vertebrae, restore normal blood supply and innervation, and also get rid of pain and other unpleasant symptoms.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, individual treatment regimens are selected. They depend on the stage of osteochondrosis, the age of the patient and the characteristics of the course of the disease, as well as on additional symptoms. Most patients are treated at home, but it is important to periodically return for re-examination to track the dynamics of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy. However, during the period of diagnosis and undergoing a course of procedures, there is the possibility of staying in a hospital.
Drug treatment
Most patients are prescribed a comprehensive treatment regimen for osteochondrosis. You can take a pain reliever at home, but the headache will return. It is important to choose an effective set of medications that will affect not only the symptoms, but also the causes of headaches. Timely initiation of treatment will help maintain the condition of the spine at the same level and prevent further deterioration of well-being.
Doctors can prescribe several types of medications to relieve headaches with cervical osteochondrosis:
- non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs - eliminate pain and relieve inflammation in the joints (Nurofen, Solpadein);
- muscle relaxants - a group of drugs that relieve muscle spasms, thereby improving blood circulation in the vertebral artery (Mydocalm);
- vasodilators - necessary for high blood pressure, as well as to eliminate vascular spasm (magnesium sulfate);
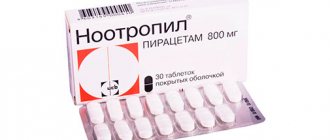
- nootropics are an additional category of medications that are selected to improve blood circulation in brain cells.
If your head and neck hurt with osteochondrosis, medications can be prescribed either in the form of tablets or injections, or as an ointment. To improve blood circulation and nourish cartilage, gels with a warming component and anti-inflammatory effect are useful. They stimulate blood circulation and regeneration processes, therefore supporting the condition of the spine during periods of exacerbation of the disease.
Additional techniques
Treatment of headaches due to osteochondrosis includes a number of techniques that strengthen the cervical spine and prevent compression of important nerves and arteries. They represent special exercises for the formation of a muscle corset, as well as physical and other methods of influencing the affected area. They are prescribed in combination with drug therapy and are carried out in a course of several sessions.
- Therapeutic exercises are simple exercises to strengthen muscles and ligaments and increase their elasticity. Warm-up consists of turns and bends, circular movements of the head. Next, you should alternately place your palm on your forehead, temple and back of your head. The head is tilted towards the hand, and the palm offers resistance. At home, you can perform exercises in the morning and evening, devoting at least 20-30 minutes a day to physical exercise.
- Massage is an effective technique that will help relieve severe headaches with osteochondrosis, as well as prevent the progression of the disease. At home, you can do self-massage, which kneads the muscles of the back and sides of the neck, as well as the trapezius muscles. It is useful to attend therapeutic massage sessions, which are carried out in a course of 5–10 procedures. The course is repeated every 4–5 months.
- Physiotherapy is a set of techniques that a doctor can prescribe to improve well-being in case of cervical osteochondrosis. This can be magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin baths and other methods of influence. Under external influence, blood flows faster to the damaged area, nutrition of damaged intervertebral discs and their oxygen saturation improves. In addition, restoration processes are activated at the cellular level, due to which the disease does not develop further.
Regular exercise, attending massage sessions and physiotherapy will help get rid of severe headaches due to osteochondrosis. The main condition is to complete the full course of procedures. They are carried out at intervals of several days to a week, and up to 10 sessions may be needed to achieve maximum effect. During treatment, ease of movement, absence of headaches and other symptoms, improvement in concentration and performance are noted. However, it is important to remember that osteochondrosis is a chronic disease, so the course of procedures is repeated every 4-6 months.
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis
Surgery is prescribed only in cases where conservative treatment is ineffective. This occurs in advanced cases, if the patient experiences fusion of adjacent vertebrae or the formation of osteophytes - bone growths on the articular surfaces of bones. These changes lead to constant headaches, neck stiffness, and chronic ischemia of some areas of the brain. The operation can be performed in several ways:
- removal of pathological growths on the surfaces of the vertebrae that prevent them from participating in movement;
- connecting adjacent vertebrae to reduce compression of nerves and blood vessels;
- replacement of the damaged segment with an implant.
The decision regarding surgical intervention is made individually. It is worth understanding that this is a complex operation that will require a long recovery period. In the early stages it is not carried out, since there is no threat to the patient’s health. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain will be able to choose the optimal method for treating osteochondrosis and headaches caused by these diseases, based on the results of a full examination.
Headaches with cervical osteochondrosis: treatment and prevention
Headaches due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can be relieved in different ways: tablets, ointments, vitamins, blockades, exercises and physiotherapy... However, there is always a risk of a sudden return of pain. What to do to prevent the pain from returning, and is it possible to find a “magic” remedy that will help you forget about cervical migraine?
Drug treatment
To relieve headaches with cervical osteochondrosis, conventional painkillers are often unsuitable - then antispasmodics aimed at muscle spasms, analgesics that relieve pain, and sedatives (calming) drugs designed to eliminate irritability and bring general relief come to the rescue.
Vasodilators are often prescribed to improve blood circulation.
Important! Self-medication is extremely dangerous! Only a doctor should select medications - after a complete examination of the patient.
Warming ointments
Special warming ointments are applied to the neck area - they help relieve inflammation, strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood flow in the cervical spine.
However, you need to be very careful - if you use it carelessly or excessively (warming up for too long, using the wrong drug, etc.), you can easily get burned!
Blockades
For unbearable headaches due to cervical osteochondrosis, a course of blockades may be prescribed - anesthetic pain-relieving injections that simultaneously relieve pain and relieve inflammation. In essence, during the blockade process, the doctor literally “blocks” the damaged nerve, causing the patient to feel noticeable relief.
It is important to understand that blockades give a temporary effect and allow you to forget about cervical osteochondrosis only for a limited time. This is an effective method at the time of exacerbation, but for proper treatment it must be combined with restorative and preventive procedures.
Vitamins to improve arterial health
To strengthen muscles and improve blood circulation, doctors prescribe a complex of vitamins (tablets or injections). As a rule, vitamins B, E and C provide the best results.
Exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy
Finally, one of the most important treatment methods that directly affects a positive result is therapeutic exercises, which the patient performs independently or under the supervision of a specialist (depending on the stage and “severity” of the disease).
Exercise therapy is a special set of exercises aimed at stretching the spine, relieving tension and generally strengthening the muscular frame. If the patient’s condition allows, physical education can be supplemented with physiotherapy and massage of the head and collar area.
Prevention methods
Symptoms and treatment of headaches with cervical osteochondrosis are associated with the mechanism of development of this disease. Injuries are one of its causes, but the pathological process can also manifest itself in a healthy person. Doctors recommend instilling the right habits from an early age that will help maintain the health of the cervical spine and prevent the development of dangerous diseases:
- correct posture both when walking and while working at the monitor is the main condition for an even load on the spine;
- moderate physical activity - even a healthy person can benefit from performing simple exercises daily to strengthen and increase the elasticity of the muscles and ligaments of the neck;
- a properly selected mattress and pillow will help avoid pinched nerves and ischemia of brain cells during sleep;
- avoiding heavy loads in everyday life - do not try to carry heavy loads in uncomfortable bags and packages;
- for those who do sedentary work - regular breaks for a short warm-up;
- in the cold season, wearing a scarf is mandatory.
Patients of the Clinical Institute of the Brain are often interested in whether a headache can occur from cervical osteochondrosis and how to prevent this unpleasant symptom. Pain in the head area, especially the occipital part, indeed often manifests itself even in the early stages. It is important not only to get rid of discomfort, but also to influence the pathological process and stop further tissue destruction.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 23 votes
Share article on social networks
Characteristic features of headache in osteochondrosis
Make an appointment Zakharova Alexandra Vadimovna Osteopathic doctor Specialization - Somatic dysfunctions; - diseases of the musculoskeletal system; -work and location of internal organs, developmental disorders; - osteopathic otoringology; - osteopathic support for pregnant women; - osteopathic facial modeling. Consultation from 2000 rub.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in the form of a headache may be the first manifestations of this disease even before the appearance of discomfort in the spine. It is characterized by localization in the crown, temples and back of the head. Headache with cervical osteochondrosis has an aching, bursting, pressing character. Patients complain of concomitant nausea, dizziness, malaise, pressure surges, congestion and ringing in the ears. Patients suffering from arterial hypertension often experience pain in the back of the head. For them, this is a common sign of increased blood pressure. But if the pressure is normal, and there are complaints of pain, then one of the reasons may be degenerative changes in osteochondrosis. However, spinal osteochondrosis can cause not only headaches, but also arterial hypertension. Important! With osteochondrosis, taking drugs with an analgesic effect is not effective enough, and the pain increases when moving the head.