3 January 2021
12977
0
4.3 out of 5
Some diseases of the spine, vascular disorders and even endocrine pathologies can provoke the occurrence of such an unpleasant and very detrimental condition as cervical myelopathy. It is accompanied by disturbances in sensitivity and mobility, and can also lead to serious complications. Therefore, it is important to diagnose it in the early stages of development, establish the cause of its occurrence and effectively influence it in order to avoid worsening the condition.
Etiology and pathogenesis of myelopathy
In the overwhelming majority of cases of myelopathy, its location is the cervical spine, which occurs as a result of the development of osteochondrosis or spondylosis. In the latter case, we are talking about vertebrogenic cervical myelopathy.
Myelopathy can also develop due to diseases such as congenital spinal stenosis, craniovertebral anomaly, damage to spinal tissue as a result of injuries and deformations, cirrhosis of the liver, deficiency of vitamins E and group B, borreliosis, rheumatoid arthritis, paraneoplastic syndrome. There is myelopathy that develops as a result of therapeutic measures, which can be chemical and radiation therapy, epidural anesthesia.
There are other types of myelopathy, the causes of which can be atherosclerosis, various inflammations, received doses of radiation, osteoporosis, diabetes, etc.
Among the causes of the vertebrogenic form are herniated intervertebral discs, congenital stenosis of the spinal canal and osteochondrosis. Myelopathy of this type develops when the spine regularly experiences loads falling on its upper zones, where the pathology is localized. The acute version of myelopathy is the result of injuries that patients usually receive in car accidents due to whiplash. This is a special movement of the head and neck when the car suddenly stops, for example, when colliding with an object. Typically, this injury occurs to an unbelted driver or front seat passenger. In this case, the spinal cord is damaged as a result of displacement.
Why does cervical myelopathy develop?
There are a large number of factors that can cause the development of this disease. Among the most common reasons are the following:
- spinal column injuries;
- surgical manipulations, in particular spinal cord punctures;
- the occurrence of infectious and inflammatory processes;
- too much stress on the spinal column in the cervical region;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- the occurrence of tumor-like formations or hernias that cause compression of the spinal cord;
- destruction of bone tissue and drying of discs due to natural aging;
- dysfunction of the metabolic system and deficiency of essential vitamins.
To study Diffuse protrusion of the L4 disc
Cervical myelopathy can even occur due to muscle inflammation caused by adverse conditions. Then patients experience swelling and spasms of muscle tissue, causing pain. With the development of cervical myelopathy, patients experience disturbances in the functioning of the entire body, while protective and reflex functions are reduced.
Epidural myelopathy
Epidural myelopathy is the most dangerous. It forms after a hemorrhage in the spinal canal and, as it develops, disrupts the structure of the nervous tissue. Severe bleeding can completely destroy the canal.
Various kinds of neurotropic toxins that reduce the number of nerve cells also cause myelopathy, which is classified as other types. As a result, the transmission of signals to the brain from individual parts of the body becomes either difficult or completely impossible.
Classification of myelopathy
Myelopathy is divided into eight types. The classification is based on the reasons that cause changes in the tissues of the spinal cord.
- Spondylogenic myelopathy is a consequence of various types of degenerative pathologies affecting the spine;
- The atherosclerotic type of this disease occurs when cholesterol deposits form on the walls of the vessels supplying blood to the spinal cord. Most often, this type of myelopathy develops due to systemic atherosclerosis, genetic metabolic disorders, and malformations of the cardiovascular system;
- Vertebrogenic myelopathy is the result of disorders such as osteochondrosis, stenosis, and intervertebral hernia. There are two types of this type of myelopathy: chronic, which occurs in the absence of timely treatment of these diseases, and post-traumatic, also called acute, which develops due to injuries. In the first case, the disease occurs as a result of the proliferation of osteophytes, compressing tissues and blood vessels. In the second - as a consequence of whiplash and displacement of intervertebral discs;
- The toxic type is a complication of the toxic effect on the central nervous system in diseases such as diphtheria and similar diseases;
- Radiation. The cause of its development may be radiation therapy carried out in the treatment of malignant neoplasms;
- Infectious - a frequently observed pathology provoked by Lyme disease, neurosyphilis, HIV infection, enterovirus infection that affects the body in childhood;
- Carcinomatous myelopathy. This pathology is caused by paraneoplastic damage to the central nervous system: oncological process, lymphoma, leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis;
- Demyelinating is a myelopathy that develops due to demyelinating disorders of the central nervous system of hereditary etiology.
Basic treatment methods
It is possible to cope with cervical myelopathy only by carrying out competent treatment of the underlying disease that caused its development. Directly to eliminate muscle weakness and circulatory disorders of the spinal cord, drugs of various clinical and pharmacological groups are used. To enhance their effect, physiotherapy, manual therapy, and acupuncture are performed.
Pharmacological drugs
Treatment of cervical myelopathy is aimed at the maximum possible restoration of damaged discs, vertebrae, blood vessels, and spinal roots. For this, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with anti-edematous and analgesic effects. To relieve acute pain, injection solutions are used: Ketorolac, Ortofen, Xefocam; for moderate pain, Nimesulide, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen tablets; for mild pain, Finalgel, Voltaren, Artrosilene gels;
- muscle relaxants to relax spasmodic skeletal muscles. Therapy with Mydocalm, Sirdalud Baklosan, Tolperisone has proven itself especially well;
- antihypoxants to increase the brain's resistance to oxygen deficiency - Solcoseryl, Cerebrolysin, Piracetam.
We advise you to study - Spinal cancer symptoms and manifestations
Diclofenac-based drugs are in demand in the treatment of cervical myelopathy
Injections of Eufillin, Xanthinol nicotinate, Pentoxifylline, and Nicotinic acid help improve blood circulation in the cervical spine. Then the result is secured by taking tablets of the same name. To improve the functioning of the central nervous system and prevent the death of spinal cord and brain cells, Cavinton, Nootropil, and Piracetam are included in treatment regimens.
Be sure to use drugs with B vitamins in treatment - Milgamma, Combilipen, Neurobion. They have a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses and trigger regeneration processes in the discs and vertebrae. Combilipen for injection contains lidocaine, an anesthetic that quickly relieves pain.
If myelopathy has developed against the background of osteochondrosis, then the patient is prescribed long-term (up to 2 years) treatment with chondroprotectors - Teraflex, Arthra, Structum. The drugs prevent further destruction of the discs and narrowing of the spinal canal.
Non-drug treatment
Patients with myelopathy are recommended to attend physiotherapeutic procedures - magnetic therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, galvanotherapy, as well as applications with paraffin and (or) ozokerite. Their action is aimed at increasing the temperature in the area of damaged areas of the spinal cord in order to improve blood supply to the tissues. Neurologists prescribe up to 15 sessions of electrophoresis with B vitamins, calcium solutions, and antispasmodics to speed up reparative processes.
The best method of non-drug therapy is considered to be dry or underwater traction of the spine. Under the influence of physical forces, the distance between the vertebral bodies increases, promoting better blood circulation. With small intervertebral hernias, it is possible to return the disc to its anatomical position.
In the complex treatment of cervical myelopathy, acupuncture, classical, acupressure, and vacuum massage are also used. To strengthen weakened muscles, patients are advised to exercise regularly. Yoga and swimming are also helpful.
Symptoms of myelopathy
Myelopathy can manifest itself in different ways. There are signs of a general nature and signs that are characteristic exclusively of a specific type of disease. Common symptoms that occur with any form of myelopathy include:
- Paralysis of the arms or legs depending on the location of the pathology;
- Paresis of limbs;
- Imbalance in bowel and bladder function;
- Numbness in the limbs;
- Severe pain in the area of the outbreak;
- Reduced tissue sensitivity in the area below the area in which the change is observed.
- The ischemic type of myelopathy is a disease that is most often localized in the neck and only in rare cases in the lumbar area. The course of the disease is long, with progression of the process. Regardless of the affected area, ischemic myelopathy causes radicular and joint pain, numbness, and awkward movements of the arms and legs. There is atrophy and muscle weakness, starting in the limbs closest to the pathology and spreading to the rest. In the later stages, disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs become pronounced.
- The post-traumatic type of this disease is characterized by segmental sensory disturbances and conduction defects. Segmental disorders in this case are peripheral paresis, accompanied by hyporeflexia and muscle hypotonia, and conduction defects are sensitivity below normal and central paresis, which occurs simultaneously with spastic muscle tone and an increased level of reflexes. In addition, the following may be observed: bulbar syndrome, vestibular ataxia, impaired sensitivity of tissues in the facial area, complications of urination, incontinence, constipation, and genitourinary tract infections. The presence of certain signs depends on the location in which the spinal cord is damaged.
- Radiation myelopathy affects the spinal cord at least six months after the end of radiation therapy. The maximum period in which it can manifest itself is 3 years. The development of the disease occurs slowly with gradual tissue necrosis without changes in the cerebrospinal fluid. In rare cases, it may be accompanied by Brown-Séquard syndrome.
- Carcinomatous myelopathy is characterized by such signs as necrotic changes in the structure of the spinal cord. In the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with this type of disease, moderate hyperalbuminosis or pleocytosis is detected.
Description of species
Since the pathology is multifaceted, there are several types into which the disease is usually divided.
Myelopathy can be of several types
Table. Types of myelopathy and their characteristics.
| Species name | Characteristics |
| Spondylogenic | It is formed due to degenerative-dystrophic vertebral changes, which are a consequence of the destruction of discs during the aging process. They are caused by a lack of moisture in the cartilage, since as the body ages, it irreparably loses it. |
| Compression | It develops as a result of an abnormal configuration of the vertebral bodies that occurs after traumatic injuries. |
| Vertebrogenic | Here the cause is widespread osteochondrosis of the spine, as well as stenosis of the cervical canal. In some cases it can be caused by injury. |
| Ischemic | Due to the compression of the blood-vascular lumen that occurs during ischemia, the brain begins to experience a lack of nutrition, including oxygen not reaching it in the required quantities. |
| Infectious | It is a consequence of tuberculosis, syphilis, complicated Lyme disease. Severe enterovirus infection and AIDS may also be the cause. |
| Metabolic | Development occurs against the background of destruction of metabolic processes and in pathological conditions of the pancreas, which can arise, including due to diabetes mellitus. |
To study: Is it possible to cure osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
Symptoms and causes of vertebrogenic myelopathy
Weakness in the leg muscles, increased tone and decreased sensitivity are the main manifestations of alcoholic myelopathy
If at the beginning of the disease the clinical symptoms are mild, then gradually the affected area of the neck begins to experience more and more pain, which is not relieved by analgesic drugs. This characterizes any form of manifestation. Also obligatory are numbness (numbness) and weakening of the limbs, convulsive spasms, poor tactility and coordination. Perhaps, especially in the metabolic form, there may be a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, sweating, and urinary dysfunction. With a complicated course, the patient may experience paresis and paralysis.
Neck massager
Diagnosis of myelopathy
First of all, to determine the disease, the patient is examined by a neurologist, who, if necessary, prescribes further examination. As a rule, the patient is referred for both laboratory and instrumental studies.
The first include:
- general and detailed blood test;
- studying the level of immunoglobulins and inflammatory proteins in the blood;
- lumbar puncture;
- biopsy of spinal cord tissue;
- blood or cerebrospinal fluid culture.
These tests help identify spinal cord infections and autoimmune disorders. In addition, they provide information about possible circulatory defects in the spinal cord.
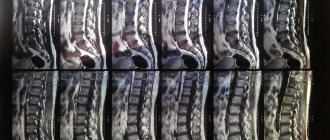
Among the instrumental diagnostic methods, computer and magnetic resonance imaging and electromyography are mandatory. CT allows you to visualize the bones of the spinal column, and CT angiography allows you to visualize blood vessels into which a contrast agent is previously injected.
Using MRI, specialists look at the spinal cord, brain, intervertebral discs, and possible tumors in their areas. If a spinal stroke is present, it can also be easily examined using this test.
Electromyography provides information about the level of electrical excitation along the peripheral nerves and throughout the spinal cord. In some cases, densitometry and radiography are prescribed to examine the spine for the density of its tissues.
How is cervical myelopathy treated?
After carrying out all diagnostic measures, the doctor prescribes the most effective therapy, based on the intensity and cause of the disease. Treatment of myelopathy of the cervical spine can be carried out using both conservative and surgical methods.
The patient’s age and the presence or absence of concomitant diseases are also taken into account. If the disease is detected in a timely manner during the treatment process, it is possible to do without surgical intervention, while the patient is prescribed complete rest for the cervical spine, which can be ensured with the help of a cervical collar
We advise you to study – Intercostal neuralgia
Surgery for cervical myelopathy
If complex myelopathy is diagnosed and conservative treatment methods do not provide the desired result, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment. Surgical procedures can be performed only if the patient does not have any contraindications and the risk of brain damage. The main purpose of the operation is to eliminate the risk of paralysis of the limbs, which can lead to disability of the patient.
In case of partial destruction of the spinal column, the patient needs to have implants installed. After the operation, the patient is prescribed medication and a rehabilitation course designed to restore the functionality of the injured area.
What medications are indicated for cervical myelopathy
Drug therapy for cervical spine myelopathy depends on the cause of the disease. Patients are almost always prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs designed to eliminate characteristic symptoms, reduce swelling and inflammatory processes. Patients can also be prescribed medications that improve metabolic processes.
For infectious cervical myelopathy, treatment may include taking antibiotics to eliminate the underlying disease causing the pathology. The patient is also required to be prescribed medications to strengthen the overall immune system, vitamins and minerals necessary for the body.
Treatment of myelopathy
Despite the fact that myelopathy is a very complex disease, modern medicine has several effective ways to treat it. General therapeutic measures include not only eliminating the symptoms of myelopathy, but also combating the cause of this disease.
Treatment includes a course of B vitamins, antioxidants, vasodilators and neuroprotective drugs necessary to stop further death of nerve cells.
In addition to general measures, patients undergo treatment prescribed for certain forms of myelopathy. So, for a disease caused by osteochondrosis, patients take analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed for the period of exacerbation. In the period between these critical conditions, massages, a course of exercise therapy and physiotherapy are necessary.
For myelopathy caused by multiple sclerosis, steroid drugs may be prescribed. Antipyretics and antibiotics are used to neutralize infection. Steroids are used, but not always, depending on a number of features of the patient's condition.
The compression type of myelopathy often requires surgery to remove a tumor or hernia that is interfering with the normal functioning of the spine.
Treatment
Therapy for myelopathy depends on the underlying disease. It is carried out comprehensively, including medications, surgical methods, and physical therapy.
Drug treatment is based on the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Their use is aimed at reducing pain. Tablets, ointments, and injection solutions (Movalis, Revmoxicam) are used. To reduce inflammation, glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone) and Dexamethasone are prescribed.
Muscle relaxants help relieve muscle tone, cope with cramps and spasms, and reduce pain. This is Mydocalm, Sirdalud. To activate metabolism, Actovegin and Piracetam are prescribed.
To study "Milgamma" injections: reviews for osteochondrosis
Anticonvulsant medications reduce the occurrence of muscle cramps. These are drugs valproic acid, Phenytoin, Clonazepam. The action of neuroprojectors helps normalize blood flow and improve nutrition of brain tissue. Tanakan is used.
In case of severe pathology, increasing symptoms, or lack of effect from the use of medications, surgical intervention is prescribed: disectomy, laminectomy.
For physiotherapy, paraffin therapy, electrophoresis, mud therapy, UHF, electrical stimulation, and reflexology are used. Massage and exercise therapy are prescribed.
Prognosis and prevention of myelopathy
The patient's future condition is determined by the degree of preservation of the spinal cord substance after the end of treatment. It can be determined only after blood flow is completely restored and tissue compression has stopped. The sooner doctors manage to eliminate the damaging factor, the more optimistic the prognosis for myelopathy is, therefore, at the first suspicion of its presence, you should take all tests prescribed by a specialist and undergo a full diagnosis as soon as possible. The doctor makes the first preliminary conclusions based on the MRI results, but in the field of therapy they may take a different form.
Prevention of myelopathy, as such, does not exist in medicine, since it is a consequence of other diseases. Measures to prevent this pathology include the prevention of infectious diseases, cancer, atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias, diphtheria and other diseases that may in the future cause the development of myelopathy in the spinal cord.
Separately, care must be taken to minimize the likelihood of injury and severe overload. People who work physically and athletes need to regularly visit their doctor for examination and timely detection of signs of pathology of spinal cord tissue. The same applies to people with hereditary demyelinating disorders of the central nervous system. Scientists do not yet know guaranteed protection against myelopathy.