Pupil functions
In this article
- Pupil functions
- One pupil is larger than the other: reasons
- The child has different pupils - what to do?
- Methods for diagnosing diseases of the pupillary reflex
- Anisocoria in myopia: features of pathology
- Anomaly of the pupils due to myopia - treatment and prevention
The pupil is located in the center of the iris of the eye, and its size can vary depending on lighting conditions. Its main function is to protect the retina from large amounts of light rays. Therefore, in bright light the pupil contracts, and in dim light it dilates. The constriction of the pupil is reflexive - a person does not need to think for any action to occur with the pupil. The pupils of both eyes can simultaneously dilate not only in response to dim light, but also to stress, strong emotional arousal, anger, or due to the use of medications.
The size of a person’s pupil depends on the individual characteristics of the optical system of the eye. People with large eyes tend to have large pupils. It is important that they are the same size and can reflexively respond to changes in light levels. If one eye has a larger pupil than the other, this indicates that changes have occurred in the visual system. Which ones?
Dangerous pathological
If the patient's condition is caused by any disease or disorder in the body, the pupils will not only not correspond to each other. The affected organ of vision also does not respond to bright light, that is, the pupil is in a constant state of dilation.
The other eye functions normally, that is, it narrows when exposed to bright light and widens in the dark.
Protection against coronavirus
How to boost immunity and protect loved ones
>
There are many reasons why this anomaly may appear:
- A disorder in the structure of the iris, as a result of which the muscle tissue of the eye is not properly stretched. Therefore, one pupil narrows sharply, while the other does not contract completely.
- Brain disease, underdevelopment during embryogenesis. As a result, nerve impulses do not enter the tissues of one of the eyes, so the pupil becomes permanently dilated.
- Birth injury. These could be blows, bruises, or curvature of the cervical spine.
- Traumatic brain injury. The symptom appears immediately after a child falls or gets a head injury. It can be used to determine which part of the brain is damaged.
- Benign or malignant neoplasm in the brain. If it is localized near the visual analyzer, it affects the conduction of impulses from the brain to the eyes. As a result, one of the organs of vision suffers, its pupil does not narrow.
- Infectious diseases. A discrepancy in the size of the pupils may occur if the infection has reached the brain and is localized in the visual analyzer. This often occurs with encephalitis and meningitis.
- Mechanical damage to the eyeball. Anisocoria occurs if the sphincter of the pupil has been damaged.
- Neurological disorders. This symptom is caused by pathologies of the autonomic nervous system, especially if the cranial nerves in the area of the third pair are affected.
- Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure, which is formed due to a violation of the outflow of secreted fluid. As a result, the camera of the eye compresses the sphincter of the pupil, which leads to disruption of its function.
- Hereditary pathologies. These include Parinaud, Horner, and Argyle-Robertson syndrome. These are mutations in genes that lead not only to anisocoria, but also to other clinical manifestations.
One pupil is larger than the other: reasons
Very often, myopic people notice that their eyes are not the same, and the pupil of one eye is larger than the pupil of the other.
The likelihood of this condition increases if the refraction of the eyes is very different. An eye with greater myopia may have a dilated pupil due to excessive visual strain. This condition is temporary and passes quickly. If you notice that the pupils of both eyes are too different, and one of them does not reflexively react to light, then you need to visit not only an ophthalmologist, but also a neurologist to get an accurate picture of your health, since the causes of the pathology can be serious.
One pupil is larger than the other - reasons:
- Physiological - the pupil of one eye may be larger if a child or adult has experienced a stressful situation or the dilation of the pupil has been affected by taking medications.
- Congenital pathologies - it happens that the pupil is large in only one eye, while the other is of normal size, and this may be due to disturbances in the structure of the iris, dysfunction of the nerves that control the extraocular muscles, etc.
- Ophthalmological pathologies - the pupil can become large as a result of severe eye fatigue, especially if there is a strong difference in refraction, myopia, astigmatism.
- Others include tumor processes, eye and brain injuries, infectious diseases, and diseases of the nervous system.
Since there are many reasons why one pupil is small and the other is large, a comprehensive diagnosis will be required. You should not hesitate to visit a doctor, as some dangerous diseases manifest themselves asymptomatically. Vision may remain normal for a long time, but it will quickly become poor if treatment for the disease is not started in a timely manner.
Features of treatment
The specific course of treatment will depend on what exactly caused this deviation - unequal pupil size. Read more in the table below.
Table. How is anisocoria treated?
Reason: List of necessary measures
| Poisoning | Gastric lavage is performed and enterosorbent drugs are prescribed (activated carbon, for example, or Smecta). |
| Herpetic infection | In this case, interferons and Acyclovir are usually used for treatment. |
| Trauma to the nervous system | Here, first, the hematoma is removed, which caused the compression of the stem section. During the operation, craniotomy is performed. |
| Multiple sclerosis | To treat this disease, immunosuppressants are used, as well as donor immunoglobulins and glucocorticoid drugs. |
Important information! If one pupil is larger than the other, then it is necessary to consult a qualified doctor as soon as possible. In most cases, this symptom indicates a serious pathology that can potentially be life-threatening. For example, in case of brain injury, anisocoria does not mean anything good, since it is a consequence of herniation of the brain stem.
The child has different pupils - what to do?
A slight difference in the size of the pupils in adults and children is a physiological norm. If the difference is significant, then it may be associated with congenital anomalies, and not only the pupil, but also visual acuity may differ. Different pupil sizes in children also occur due to underdevelopment of the eye apparatus and are often accompanied by strabismus. Such diseases are diagnosed in early childhood. If you notice that one pupil of a schoolchild is larger or significantly smaller than the other, you should urgently visit a doctor, since such a pathology may be associated with brain injury, tumor, retinal diseases, or damage to the optic nerve.
To exclude dangerous pathologies, comprehensive diagnostics is necessary.
Methods for diagnosing diseases of the pupillary reflex
Since diseases of the pupillary reflex, in which the size of one pupil may be smaller or larger than the other, are often associated with the functioning of the brain, the diagnosis is carried out by both an ophthalmologist and a neurologist. First of all, it is determined whether the pupils react to bright lighting. If one pupil does not have such a reaction, this may indicate damage to the midbrain or tension of the oculomotor nerve.
The main methods for diagnosing diseases in which one pupil becomes large:
- study of pupillary reactions using an intense light source;
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- CT scan;
- studies of the reaction to accommodation with convergence.
During the examination, it is clinically important to establish which eye is in a pathological condition. Anisocoria (different pupils) can be observed when taking medications, traumatic hematomas and hemorrhages that put pressure on the visual centers.
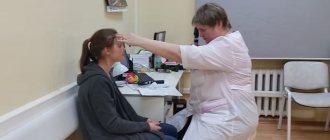
Diagnostics
If you notice anisocoria in a child, you should contact an ophthalmologist. The doctor should check the reaction of the pupils to light, examine the eyes for injuries and inflammation, and assess intraocular pressure using tonometry. He can also conduct pharmacological tests - instill certain medications and assess the condition.
If the ophthalmologist suspects the development of a neurological disease, he will refer the baby for examination to a neurologist, which may include:
- reflex testing;
- Ultrasound of the brain (until the fontanelle closes);
- CT, MRI or X-ray of the brain, chest, cervical spine.
If signs of an infectious disease are detected, blood tests are performed (general, bacteriological, antibody). In addition, a lumbar puncture may be necessary to obtain cerebrospinal fluid (in the case of meningitis).
Anisocoria in myopia: features of pathology
The pupils can have different sizes - one pupil is significantly larger than the other if a person has an ophthalmological problem such as anisometropia. With this pathology, the refraction of the left and right eyes is very different, and therefore the visual organs are subject to excessive stress even when corrected with glasses and contact lenses. Correction with contact lenses is the most preferable, as it is possible to achieve the highest possible visual acuity with an optimal level of patient comfort. If you have myopia with a pronounced difference in the refraction of the eyes and you notice that the pupils differ in size, for example, one is larger than the other, be sure to visit an ophthalmologist for advice. It is possible that it will be possible to get rid of the problem with the correct selection of corrective optics.
Due to eye strain due to myopia, against the background of insufficient or incorrect correction, many ophthalmological problems arise, including spasm of accommodation, impaired outflow of intraocular fluid, increased eye pressure, etc. The main task of a person diagnosed with myopia is to constantly take care of the health of the visual organs, which consists of performing a set of therapeutic and preventive measures.
Anomaly of the pupils due to myopia - treatment and prevention
The development of anisocoria in myopia can be prevented by paying due attention to the prevention of the disease. To prevent the pupil of one eye from becoming larger than the other, it is necessary to reduce the strain on the eyes, improve blood circulation and metabolism in the organs of vision. How to do it? Treatment and prevention of anisocoria, if one pupil becomes larger than the second due to myopia:
- taking eye vitamins with lutein;
- eye drops, the action of which is aimed at restoring the protective functions of the eye, improving metabolic processes, and nourishing the tissues of important eye structures;
- daily exercises for the eyes - a special set of exercises will help relieve spasm of accommodation, improve visual acuity and strengthen the accommodative muscle;
- hiking, swimming, exercise bikes and other useful physical activities allowed for myopia.
If the pupil of an eye with severe myopia is larger than the second one, this may indicate insufficient or incorrectly selected correction. A consultation with an ophthalmologist will help you understand the cause of this condition and find a solution to the problem. The main thing is not to delay visiting a specialist, even if your vision has not become worse, so that the health of your eyes cannot be harmed by disorders that can be successfully treated with timely diagnosis.