The mechanism of the pupil is reminiscent of a camera diaphragm, the diameter of which decreases in bright light or strong lighting, which gives a clearer image after cutting off blinding light rays. Insufficient light, on the contrary, requires expanding the aperture. Actually, this function of the pupil is really called diaphragmatic and is provided by the pupillary reflex. The pupillary reflex is the reaction of the organ of vision to changes in the illumination of the retina, or rather, the rods and cones (photoreceptors) transmitting visual information to the nerve centers: to the center of the parasympathetic department of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for the work of the sphincter of the pupil and to the center of the sympathetic department, responsible for the work of the dilator . Regulation of the size of the pupils thus occurs completely unconsciously and depends on the level of illumination.
Pupillary reflex
Any reflex has 2 development paths: the first is sensitive, when information about any impact is transmitted to the nerve centers, and the second is motor, when impulses are sent from the nerve centers to the tissue, which causes a certain reaction as a response to the impact.
Illumination of the pupil causes the pupil to constrict, which limits the entry of bright light into the eye, and vision becomes better.
The pupillary reaction to light is direct, when one eye is directly illuminated, or cooperative, observed in the paired unlit eye. The friendly pupillary reaction to light can be explained by partial decussation of the nerve fibers of the pupillary reflex in the area of the chiasm.
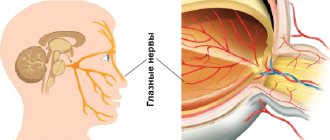
Along with the reaction to light, a change in the size of the pupils is also possible during the work of convergence - tension of the rectus internal muscles of the organ of vision, or accommodation - tension of the ciliary muscle. This is observed when the point of fixation changes - the gaze shifts from a distant object to a closer one. Both of these reflexes arise from tension, the so-called proprioceptors of the muscles, and are provided by fibers that enter the apple of the eye with the oculomotor nerve.
Emotional excitement, pain and fear can also cause a change in the size of the pupils, namely their dilation. Irritation of the trigeminal nerve, on the contrary, causes constriction of the pupil. Constriction or dilation of the pupils is also caused by the use of medications that affect the receptors of the pupillary muscles.
What is a pupil?
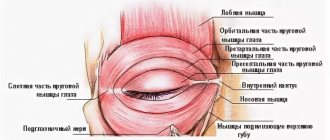
The pupil is a round hole in the center of the iris of the eye. Thanks to the ability to change its diameter, the pupil regulates the flow of light rays entering the eye and falling on the retina. Thanks to the work of the muscles of the pupil: the sphincter, the tension of which leads to a narrowing of the pupil, and the dilator, which leads to its expansion during contraction, the degree of illumination of the retina is controlled.
The principle of this operation is similar to the diaphragm of a camera: in bright light and strong lighting, the diameter of the diaphragm decreases, resulting in a clearer image by cutting off blinding light rays. In low light, on the contrary, an expanded aperture is required. Indeed, this function of the pupil is called diaphragm. It is this function that is provided by the pupillary reflex.
The reflex occurs when the illumination of the retina, namely the rods and cones, changes, transmitting information further to the nerve centers: the center of the parasympathetic department of the autonomic nervous system for the sphincter of the pupil and the sympathetic department for the dilator. Thus, regulation of the size of the pupils occurs unconsciously depending on the degree of external illumination.
Polycoria
This is a congenital defect in which there are several pupillary holes in the iris. It may be present in one or both eyes. As a rule, this disorder is combined with other defects and accompanies congenital syndromes.
True polycoria:
There are true and false polycoria:
- True polycoria - when all the pupils have sphincters and react to light, dilate when appropriate drugs are instilled;
- Pseudopolycoria - when “false” pupils do not respond to light and mydriatic medications, lacking a sphincter;
Visual acuity in such patients depends on the diameter of the pupillary openings - the smaller it is, the worse the vision.
Treatment of polycoria can be surgical. Patients are also prescribed contact lenses, which correct the appearance of the eye and correct vision.
Wikipedia about pupula duplex
The extensive virtual encyclopedia does not contain individual materials about this condition. There is a short article about polycoria here.
Modern medicine clearly distinguishes between an anomaly of a double pupil and the formation of two irises of the eye.
What functions does the pupil of the eye perform?
The main function of the pupil is to regulate the light flux penetrating into the organs of vision. It is realized through the ability to change the diameter: expand and contract. If the lighting is insufficient, the size of the hole increases, so that a person can clearly see objects. Bright light triggers a special reflex, the pupil narrows. This mechanism protects the visual apparatus from the harmful effects of light.
Interesting! The color of the pupil is black, and there are reasons for this too. The fact is that little light penetrates into it. The inside of the eyeball is dark, so it appears as if the pupil is also black.
The pupil is responsible for filtering out streams that penetrate the lens. Thanks to this ability, spherical distortions are compensated. At dusk, the diameter of the hole increases, color perception and visual acuity deteriorate, but under such conditions the retina is able to perceive low-intensity light, due to which a person can easily distinguish large objects and navigate in space.
What to do?
If your eyes hurt from daylight or artificial light and the pain does not go away within 3-4 days, you should not self-medicate, but consult a doctor. If the cause of the pain is an eye infection, such as conjunctivitis, improper self-treatment can lead to deterioration of the eye condition, sometimes even leading to loss of vision. The doctor will conduct the necessary diagnostic examinations and prescribe the correct therapy.
After making a diagnosis, a neurologist will prescribe medication and physiotherapeutic treatment.
Photophobia itself is a symptom of another disease. And to solve this problem, you need to know the cause of photophobia. The appearance of accompanying symptoms such as nausea, weakness and dizziness may indicate a serious neurological disease. In this case, it is necessary to consult with a neurologist who will prescribe medication and physiotherapeutic treatment, as well as eye exercises. In severe situations, surgery is used.
If an ophthalmological disease and its symptoms significantly worsen the quality of life, then the following methods can be used to diagnose the disease:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- fundus examination;
- laboratory and clinical tests.
If the eyes are afraid of light and react painfully to it with myopia, the doctor will prescribe contact lenses or glasses and help you choose them. If an inflammatory eye disease is detected, the ophthalmologist prescribes eye drops and ointments, and for severe headaches and migraines, painkillers. Traditional medicine will help alleviate the condition. If the eye hurts, waters and cuts even with a weak light source, you should wear high-quality sunglasses throughout the entire treatment period.
Drugs
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics in the form of tablets, injections, ointments, or drops. For ophthalmological ailments, when the eyes hurt in the sun and have difficulty seeing, the doctor may prescribe symptomatic treatment, including the following types of medications:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- anesthetics;
- antibiotics in the form of ointments, tablets, injections, drops;
- interferon-based drugs;
- solution for washing the eye area.
Folk remedies
To eliminate pain in the eyes from light, medicinal plants, for example, plantain, are used. To prepare the product you need the following ingredients:
- plantain - 20 g;
- boiling water - 300 ml.
Procedure:
- Pour boiling water over plantain in a thermos.
- Leave for 3 hours.
- Strain.
- Rinse eyes in the morning and evening.
Sea buckthorn compress
For a sea buckthorn compress, mix crushed berries with one teaspoon of honey. Ingredients:
- chopped fresh sea buckthorn pulp - 2 tablespoons;
- honey - 1 teaspoon.
Procedure:
- Mix sea buckthorn with honey.
- Apply compresses from the mixture for 7 days in the morning and evening for 15 minutes, evenly distributing 1 teaspoon of the product on cotton pads.
When you are bothered by a sore and cutting eye, these useful tips will help:
- If there is no fever, you can take a warm bath by adding chamomile infusion to the water. The pain should subside.
- To relieve pain, rub a raw potato onto a gauze cloth and apply it to your forehead.
- It is recommended to drink warm milk with honey, hot tea with lemon balm or chamomile. These drinks promote relaxation, as a result of which the pain will subside.
Common pupil pathologies
The pupil is located in the center of the iris. In normal condition, it performs its functions properly. But there are factors that negatively affect its performance. These include injuries, eye surgeries, and various pathological changes. The onset of pupillary disease can be determined by the following signs:
- the shape of the hole is distorted;
- Anisocoria is observed;
- adhesions formed on the iris.
It is important to detect the onset of the development of the pathological process in time in order to eliminate the provoking factors and restore the full functionality of the visual apparatus.
Midriaz
Pupil dilation provides good visibility at dusk, the ability to distinguish objects and navigate in space when it is dark. The hole also enlarges when a person experiences pain, is very frightened or is happy. But if the pupil is constantly dilated, we can talk about the development of a disease known as mydriasis. It occurs against the background of such pathologies:
- asphyxia (suffocation);
- glaucoma;
- migraine accompanied by severe headaches;
- injury to the oculomotor nerve;
- presence of neoplasms;
- encephalitis;
- cysts.
The pupils increase in size in people who are in a state of alcoholic delirium. The same is observed when taking medications from certain pharmacokinetic categories, as well as when narcotic substances enter the body.
Interesting! Why do emergency doctors immediately check the visual reflex and evaluate the size of the pupil after arriving on the scene? If the deviations are insignificant, this means that the person is in a state of fainting, but if the victim has so-called “glassy” eyes, this indicates a serious condition.
Miosis
A decrease in the size of the hole can be physiological or pathological. Narrowing of the hole is observed when the lighting in the room is too bright, severe fatigue, during sleep, and with hypermetropia. The pupil is narrow in older people and newborn babies. The same condition occurs as a result of taking medications that affect the eye muscles. The hole decreases with sphincter spasm, which accompanies diseases such as meningitis, epilepsy, and encephalitis.
Anisocoria
The pupils of the eye are normally the same. If their size differs, they speak of the development of anisocoria. By the way, it does not always indicate pathology; some people have unequal pupils - a structural feature of the visual apparatus. In this case, the deviations are very minor and cannot be noticed with the naked eye.
Pupils of different diameters can signal the occurrence of complex pathological processes in the body:
- injury to the optic nerve;
- the presence of tumors in the brain;
- neurological diseases;
- aneurysm.
If a person is found to have a deviation, he is prescribed a number of diagnostic techniques to determine the causes of this condition of the pupils.
Polycoria
Polycoria is very rare. This is an anomaly in which a person has not one pupil, but two or more in one eye. Congenital pathology exists in two forms: true and false. In the first case, all holes react to light; they can have different shapes and sizes; in the second, the visual reflex is present only in one pupil.
An ophthalmological anomaly causes serious discomfort to a person, because the visual acuity of the defective eye is much lower compared to a healthy one. If the patient has more than 3 holes measuring more than 2 mm, surgery is prescribed. It is advisable to carry out the correction in early childhood (up to 1 year). Adults are not operated on; they are prescribed special lenses.
Other pathological changes
In ophthalmology, there are several other pathological conditions associated with the pupil. The shape of the hole changes due to surgery or eye injury. In blindness, the pupils are motionless and do not respond to light.
Prerequisites for asymmetry
It is inappropriate to judge how much the pupil weighs, since it is just a hole in the iris, although it looks like a dark structure located in the center of the eyeball.
Pupillary asymmetry occurs mainly when a person sees worse in the right or left eye. But a sharp difference between the diameters of the pupils can also appear in many severe brain lesions. These include traumatic brain injury, hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke, transient vascular attacks and malignant neoplasms. All of these ailments affect the eyeballs, as intracranial pressure increases. For example, when a large tumor grows or a hemorrhage occurs in the right hemisphere, the eye on the corresponding side suffers.
Treatment
If meningitis or encephalitis is diagnosed, then antibacterial or glucocorticoid therapy is mandatory. If any problems with the eyes are determined, eye drops are prescribed, and, if necessary, tablets or injections.
An effective remedy for restoring vision without surgery or doctors, recommended by our readers!
Often, when leaving a dark room on a sunny day, tears begin to flow from your eyes. I really want to close them with my hands. This is the weakest manifestation of photophobia. In more severe pathologies, pain, pain, and lacrimation occur at the slightest ray of light. Photophobia is one of the most common ophthalmological diseases.