Causes of the disease
The inflammatory process in the iris of the eye is characterized by a variety of factors that cause it. A separate group consists of iritis caused by infections - viruses, bacteria, fungi. Infections affect the eye from the outside or are located inside the body.
Another group consists of inflammation of the iris associated with chronic diseases:
- rheumatism;
- diabetes;
- hyperthyroidism;
- gout.
The inflammatory process occurs against the background of injury, intoxication of the body, or an allergic reaction.
Provoking factors are decreased immunity, nervous or physical fatigue, and starvation.
What does the treatment consist of?
Some drugs are administered to the patient subconjunctivally.
Treating acute inflammation of the iris is not easy. The difficulty lies in determining the etiological factor that caused this pathology. As part of drug therapy, drugs that dilate the pupils are used locally. Antibacterial drops, glucocorticosteroids, and nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs are widely used. Antibiotics are also administered subconjunctivally.
How does the disease manifest itself?
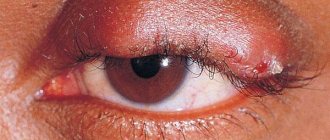
Symptoms of eye iritis primarily depend on its cause and the nature of its course. Inflammation of the iris is usually unilateral, with the exception of diabetic iritis.
Acute iritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the eyeball, aggravated by pressure;
- decreased visual acuity;
- the appearance of flies or veils before the eyes;
- heightened reaction to light;
- change in the color of the iris.
The subacute form is characterized by the same symptoms, but less pronounced. In a chronic process, there is a change in periods of remission and exacerbation.
Diagnostics
To identify inflammation of the iris, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. After the initial examination, the doctor prescribes laboratory research methods. Their description is presented in the following table.
| Name of the procedure. | Description. |
| Biomicroscopy of the eye. | The study reveals swelling, posterior synechiae, and dystrophic changes in the iris. |
| Gonioscopy. | Changes in the drainage system of the eye, the presence of turbid fluid, sometimes mixed with pus, in the anterior chamber of the eye are determined. |
| Study of pupil reaction to light. | With iritis, the pupil reacts slowly to the flow of light. |
| Reaction to mydriatics. | One percent platiphylline or homatropine hydrobromide is instilled into the eye. Under their influence, the pupil dilates. When iritis is present, it takes on an irregular shape. If the eye is healthy, the pupil will dilate, but will have a natural, round shape. |
| Ultrasound examination of the eye. | Ultrasound is used to determine secondary eye lesions (lens opacification, anterior and posterior synechiae). |
| Checking visual acuity. | There is a decrease in it caused by a change in the refraction of the light beam. |
| Measuring intraocular pressure. | Inflammation of the iris is accompanied by a change in pressure inside the eye due to impaired hydrodynamics. |
During diagnosis, it is important to differentiate iritis and glaucoma.
In both cases there is no reaction of the pupil to light. But with glaucoma the pupil is dilated, and with iritis it is narrowed. In case of chronic inflammation of the iris, an examination by an endocrinologist, dentist, ENT specialist, therapist, phthisiatrician, or rheumatologist is required.
Read in a separate article: Aniridia of the eye: symptoms and treatment of the disease
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of eye iritis comes down to treating the cause of the disease and eliminating the symptoms. Drug treatment includes the following drugs:
- antibiotics - “Ceftriaxone”, “Amoxiclav”;
- NSAIDs - “Ibuprofen”, “Diclofenac”;
- antihistamines - “Cetrin”, “Claritin”;
- absorbable - “Trypsin”, “Lidaza”.
Drops with antibiotics are used locally - “Tobrex”, “Normax”. When adhesions form between the iris and the lens, surgical intervention is required.
Treatment tactics for iritis
- In order to avoid the main danger of the disease - fusion of the ocular elements, it is recommended to use mydriatic agents as early as possible, which can stop the adhesive process. For this purpose, atropine is prescribed in ointments and solution for installations.
- The use of dry heat on the eye and leeches on the skin of the temple on the same side is indicated. Leech saliva has a pronounced disinfecting effect and helps normalize blood circulation at the local level. Sometimes leeches are placed on the suboccipital area and on both sides of the seventh cervical vertebra.
- During the height of the disease, the use of steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (hydrocartisone, prednisolone), as well as antihistamines, is justified.
- If purulent iridocyclitis occurs, then antibiotics and sulfonamide drugs, vitamins B and C, as well as PP are added to the treatment regimen. If the process is tuberculous or syphilitic in nature, then specific treatment is prescribed.
- When the pupil becomes infected, the defect is eliminated by removing the formed film from the surface part of the lens, using multiple magnification under a microscope. This is a complex operation, dangerous due to the possibility of damage to the lens bag. In this case, the lens will have to be removed completely.
With timely and adequate treatment, acute iritis resolves within three to six weeks. The chronic process is difficult to treat, and therapy can last for several months, while maintaining the potential for periodic relapses associated with seasonal cooling. The degree of decrease in visual acuity in this case is directly dependent on the severity of the inflammatory process and qualitative changes in the refractive media of the visual organ.
Prevention
Without treatment, the disease leads to the development of severe complications:
- impaired mobility of the lens, which causes farsightedness or nearsightedness;
- deformation of the pupillary opening;
- secondary glaucoma.
Inflammation of the iris has mild symptoms, which makes diagnosis difficult. Treatment is carried out as early as possible, using an integrated therapeutic approach. Lack of treatment increases the risk of complications.
Leave comments on the article, tell us about your experience, and share information with your friends on social networks. All the best and stay healthy.
Symptoms and causes of the disease
This disease can occur due to infection or toxic-allergic damage.
The following diseases lead to infection of the iris:
- chronic caries;
- inflammation of the tonsils and sinuses;
- tuberculosis;
- brucellosis;
- gonococcal infection;
- leptospirosis;
- flu;
- syphilis;
- purulent abscess of the cornea.
Toxic-allergic causes of the disease include various rheumatoid pathologies, metabolic disorders, exposure to toxins during tissue breakdown in patients with eye tumors and retinal detachment.
Negative factors that provoke the development of inflammation:
- hypothermia;
- long-term depression and serious stress conditions;
- excessive physical and visual stress.
The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. The first option is cured within a month to two months. The chronic process lasts for several months, with periodic exacerbations, especially in cold weather, and subsidence.
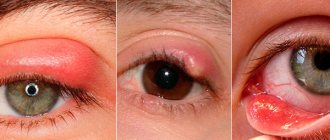
Complications of iritis
In the absence of adequate therapy, iritis can cause various complications.
Possible consequences of the disease include the following:
- Cataract.
With this disease, clouding of the lens is observed. The likelihood of problems is especially high after prolonged inflammation. - Incorrect pupil.
Scar tissue can cause the iris to adhere to the lens or peripheral part of the cornea. As a result, the pupil takes on an irregular shape, and the iris reacts slowly to light. - Glaucoma.
Recurrent iritis can provoke glaucoma, a dangerous pathology of the organ of vision. This disorder is characterized by increased pressure in the eye. The disease can cause complete loss of vision. - Accumulation of calcium salts on the cornea.
This disorder is called band keratopathy. This abnormal condition causes corneal necrosis and can cause visual impairment. - Retinal swelling.
This term refers to cystoid macular edema. There is a risk of blurred or reduced central vision.
How to treat inflammation and redness of the eye
The health of the visual apparatus must be constantly taken care of, since a failure in its operation will certainly affect the quality of life. Inflammation of the eyes is a disorder that almost everyone has had to deal with. Full recovery can only be expected if treatment is started immediately.
At the first signs of an inflammatory process, you need to make an appointment with a doctor. After making a diagnosis, he will determine the origin of the disease and prescribe effective medications to treat inflammation of the eyes when they are red.
Effective and proven medications
How to treat eye inflammation? Medicines are selected taking into account the reasons that caused the disorder:
- If inflammation occurs as a result of a foreign object entering the eye, it is removed. The doctor will prescribe medications to prevent infection.
- For pathologies of bacterial origin, treatment is indicated with agents that have an antimicrobial effect - tetracycline ointment, Dex-Gentamicin, Betagenot and others.
- For viral diseases, medications with antiviral properties are prescribed, among which Acyclovir is popular.
- Allergic inflammation is managed through the use of Allergodil, Lecrolin, Zaditen.
Correct treatment at home
It is imperative to consult a doctor regarding treatment. To temporarily eliminate discomfort in the organs of vision, you can use simple methods at home.
First, the eyes are washed with cool water, which will relieve inflammation for a while. Using sterile cotton wool, a handkerchief or a napkin, you need to carefully examine the area of the cornea and conjunctival sac; tea leaves or chamomile decoction are suitable for washing the eyes.
In the absence of a foreign body or barley, the use of Visine or Visomitin, as well as natural tear preparations that help moisturize and nourish the dry cornea, is allowed.
If the inflammation has formed as a result of “dry eye syndrome,” these remedies will be enough to make the symptoms disappear. Otherwise, you should contact a specialist.
Folk remedies to help
All kinds of decoctions and tinctures from plants, as well as medicinal compresses, cope well with inflammation. The main thing is to first agree on the use of folk remedies with your doctor.
The following recipes will help ease the symptoms:
- For redness, painful discomfort and burning in the eyes, it is necessary to chop raw potatoes, apples or cucumbers, wrap them in cloth and place them on the sore spot. The area below the back of the head is covered with a hot and damp towel.
- Chamomile (3 tablespoons) is brewed with boiling water (200 ml), infused for an hour and filtered. The solution is used for washing.
- Boiling water (1 glass) is poured into calendula (1 tsp) and left to infuse for half an hour. It is useful to wash the organs of vision, make lotions and compresses.
- If inflammation is accompanied by suppuration, an infusion made from plantain will be useful. Raw materials in the amount of 50 g must be poured with a liter of boiling water and left overnight. During the daytime, rinsing is done with the help of infusion, and a compress can be made before going to bed.