Inflammatory eye diseases in children
The eye is a complex organ, and inflammation can have different localizations. At the same time, the appearance is often little different, and only a specialist can figure out the reason. The inflammatory process can affect the mucous membranes, eyelids, cornea and other parts of the organ, or may be a consequence of common diseases, such as allergies.
Infectious conjunctivitis
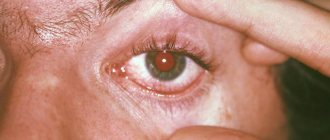
The most common cause of inflammation is an infectious lesion of the mucous membrane - the conjunctiva. In this case, redness occurs due to the emerging network of small capillaries.
Other symptoms of infection:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- itching;
- photophobia;
- sometimes a slight increase in temperature;
- purulent discharge of a yellowish-green color, eyelids stick together in the morning.
With a herpetic infection, a blistering rash is noticeable on the mucous membrane. A viral infection is usually accompanied by a strong discharge of fluid similar to tears.
Depending on the nature of the infection:
- bacterial;
- viral.
Infection is often caused by dirty hands that children rub their eyes with on the street. It is often transmitted by contact or droplets from infected people. The initial impetus is sometimes microtrauma due to the entry of a foreign body and damage to the mucosa. Since the eye is a paired organ, it usually affects both.
Conjunctivitis accounts for 30% of eye diseases in young children. With poor treatment, they often result in more serious diseases - keratitis, dacryocystitis, decreased vision. Infectious conjunctivitis is often associated with other viral and bacterial infections - otitis media, influenza, rhinitis, tonsillitis.
Video from Dr. Komarovsky:
Blennorea
The disease is a type of infectious conjunctivitis, which in most cases is caused by gonococcus (gonoblenorrhea). It is observed in newborns, usually 2-3 days after birth. Infection occurs during prolonged labor in utero or in the genital tract when the mother becomes infected.
Symptoms in an infant:
- tight eyelids that cannot be opened;
- redness, swelling;
- discharge of pus for 2-3 weeks.
In severe cases, trophic changes in the cornea and scars are possible. Currently, it is uncommon due to preventive measures in maternity hospitals.
Allergic conjunctivitis
This type of inflammation of the mucous membrane is similar only in external manifestations to infectious conjunctivitis.
The disease occurs due to sensitization of the body by an allergen and is one of the possible symptoms of an allergy. Most often, it first appears at the age of 3-4 years when the baby has allergic reactions.
The most common allergens are:
- dust;
- animals;
- flowering plants;
- medicines;
- food products - citrus fruits, chocolate, honey, fruits and berries.
The main difference from infectious conjunctivitis is the absence of purulent discharge. This type of conjunctivitis is accompanied by severe itching; children scratch their eyes, which promotes infection.
In children of any age, it is often accompanied by other signs of allergy:
- skin rashes and itching;
- intestinal disorders;
- respiratory manifestations - nasal congestion, sneezing, sore throat.
Irritated mucous membranes often lead to the addition of an infectious infection, then purulent discharge may appear. The severity of symptoms depends on how much contact there is with the allergen. The onset of the disease can be sudden and acute. With the constant presence of a dangerous substance, inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs in a chronic manner.
If allergic conjunctivitis is suspected, the child is referred to an allergist to clarify the diagnosis and conduct diagnostics. A blood test for immunoglobulin E, tear testing and allergen tests are prescribed.
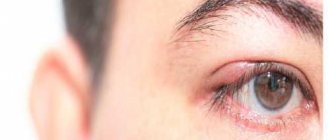
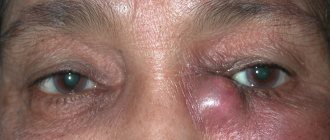
Barley
This is the popular name for inflammation of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle of the eyelid. The medical name is hordeolum. The resulting redness and swelling of the eyelid ends with the appearance of a head with pus. Accompanied by itching and burning. In children under one year of age, the temperature may rise and their general health may deteriorate.
The infection is usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus, which affects children with weakened immune systems. Therefore, in frequently ill children, stye often follows one after another. With this phenomenon, you need to accustom your baby to hygiene and take care of strengthening the immune system.
Dacryocystitis
This inflammation develops in a part of the eye called the lacrimal sac. It is located between the nose and the beginning of the eyelids. There is dacryocystitis of newborns, which occurs due to the congenital narrowness of the lacrimal canal or the membrane that closes the exit. This type of disease causes great discomfort to infants, inflammation and suppuration of the eyes. Usually goes away without serious treatment as it grows.
In older children, inflammation is often preceded by viral or bacterial infections - rhinitis, ARVI, sinusitis. Typically, inflammation of the lacrimal sac develops in one eye and is therefore different from other infections. Inflammation can be difficult to determine, since the swelling spreads to the entire organ, including the nose and cheek.
In this case, a febrile state with a rise in temperature may be observed. When the swelling subsides, an abscess forms. Dacryocystitis can cause other infectious lesions. You need to see a doctor.
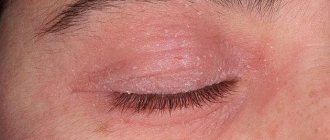
Blepharitis and uveitis
This is the name of the inflammatory process on the eyelids. It is accompanied by redness of the eyelids, swelling, loss of eyelashes, and the formation of small wounds on the edges of the eyelashes.
Inflammation of the blood vessels in the eye is called uveitis. It can be of an allergic or infectious nature, and is also caused by general diseases of the body and injuries.
Trauma - foreign body
Small dust particles that do not immediately come out with tears can cause eye inflammation in children.
In this case, the foreign body may remain under the eyelids and continue to injure the mucous membrane. Only a doctor can get it. Facial bruising can also cause severe swelling.
Video from Dr. Malysheva:
Traditional medicine methods
Treatment of inflammatory phenomena in children can be carried out not only with medications. You can use folk recipes, but first you should definitely talk about this with a specialist. Washing and various compresses will help speed up the recovery process.
Children's eyes need to be treated with extreme caution. With the help of rinses you can achieve good results. For example, pharmaceutical chamomile will be useful.
You will need:
- chamomile (4 tbsp);
- hot water (1 glass).
The product is infused for about one hour, after which the eyes are washed.
The following recipe is no less effective:
- first the onion is cooked;
- a small amount of honey and boric acid are added to the decoction;
- number of procedures – about 5 times per day.
Under no circumstances should you use breast milk or saliva. Although various sources often recommend such treatment, doctors are categorical. After all, both milk and saliva can contain bacteria, which will worsen the condition of the baby, especially a newborn.
As for compresses, the following recipes will be useful:
- Finely chopped parsley is wrapped in gauze. Then it should be immersed in boiling water. Apply the product warm to the eyes after the water has completely drained. The duration of the procedure is several minutes.
- You can't do without tea compresses. They should be made from tea that has been brewed, cooled and steeped for half an hour, which is filtered before use.
- Jasmine, rose hips, and clover eliminate inflammation well. The leaves of the listed plants are poured with boiling water, mixed with honey, infused for 20 minutes and filtered.
It is very important to take care of the health of the visual apparatus of children. The baby should be protected from possible negative influences. But the main thing is not to resort to any independent treatment. Such actions often provoke unexpected and extremely unpleasant complications.
As soon as the slightest manifestations of an inflammatory nature appear in the eyes, the baby should immediately be shown to an ophthalmologist. If detected in time, the disease can be eliminated, in most cases, without any serious consequences.
What causes eye diseases in children and what treatment is most effective for the development of diseases of the cornea, eyelids, and membranes of the eye? to relieve eye inflammation in a child at home and how to organize treatment for the development of conjunctivitis? We will discuss these and other issues related to eye diseases in children in this material. Conjunctivitis refers to a number of inflammatory eye diseases. They are the most common among eye ailments. A child can encounter them at any age. Pathogens are divided into two groups: endogenous (autoallergic reaction, complications of other diseases) and exogenous (allergies, infection, chemical factors, physical influence). When conjunctivitis develops in a child, the eyeball becomes red, small blood vessels are visible, and the eyelids and conjunctiva swell. Patients often experience: high fever, lack of appetite, restless sleep and excessive moodiness. When inflammation develops in a child, the eyes itch and cut. When the baby wakes up, crusts or a film of pus are visible in the corners of the eyes, which sometimes sticks the eyelashes together.
Relieving eye inflammation in a child Treatment at home: Pus is removed from the eyes with a wet cotton swab. Wet it in plain water; decoctions of various medicinal herbs or tea are ineffective. Do not press the wet cotton on your eyelids while removing pus. After the procedure, rub a dry piece of cotton wool around the eyes.
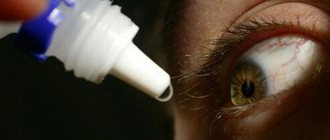
If your child is itchy, use anti-inflammatory eye drops that inhibit the production of histamine or prevent it from affecting receptors. Cold water in a compress eliminates significant swelling and itching, relieves inflammation of the cornea and eye membranes.
In advanced cases of eye inflammation, antibiotics are used: chloramphenicol, ciprolet, vigamox. The drugs are available in the form of eye drops for inflammation and ointments. In the first case, pus is removed from the surface of the eyelids several times a day, after which the medicine is dripped. The medicinal substance will remain in the palpebral fissure longer if ointments are used against inflammation of the eyelids and eyes.
the most common eye diseases in children Astigmatism, farsightedness and nearsightedness are often congenital eye defects and are sometimes diagnosed only when a child starts going to school. The consequence of an advanced disease can be amblyopia - decreased vision due to poor functioning of the eye, insufficient development of the visual system (another name is lazy eye).
One in 40-50 children is diagnosed with strabismus (paralytic, atypical, or concomitant). With the monolateral type of the disease, one eye is affected, with the alternating type - both.
There are many types of congenital defects and eye diseases: paralysis of some muscles, insufficient intrauterine development (up to the absence of an eye), changes in the shape of any elements of the organ. All this can occur due to genetic disorders, problematic pregnancy and a host of other factors.
Not all parents know how to properly treat inflammation of the eye or eyelid in a child when characteristic symptoms of eye disease are detected - tearing, redness of the eyelids or eyeball, swelling, discharge of pus from the corners of the eyes. Next, we will talk in detail about what symptoms are characteristic of conjunctivitis, how and with what to wash the eyes and
how to put drops in a child’s inflamed eyes, treatment of common eye diseases in children.
INFLAMMATION OF THE EYES IN CHILDREN
Now you know how and with what to treat a child’s inflamed eyes, and you have also familiarized yourself with information about what treatment is most effective for inflammation of the membrane or cornea of the eye . If your child has symptoms of eye inflammation and our recommendations for treating the disease do not help at all, be sure to contact a pediatric ophthalmologist to find out the source of the child’s eye disease.
Next article: How to treat kidney inflammation in a child
Go back to main page
INTERESTING FOR WOMEN:
In children, inflammatory eye diseases occur no less often, if not more often, than in adults. But their diagnosis is complicated by the fact that the little patient is not able to talk about what is bothering him. Therefore, treatment without the recommendations of an eye doctor is dangerous: an incorrectly selected drug can worsen the clinical picture and cause irreversible consequences. What to do if a child’s eyes are inflamed?
What to do if a child has an inflamed eye?
If signs of inflammation appear - swelling and redness, itching and foreign body sensation, you should call a pediatrician. If your condition allows, you need to go to the clinic to see an ophthalmologist.
At home while waiting for a doctor you should:
- Rinse eyes with lukewarm boiled water. Each organ is washed with a separate cotton pad.
- Put the child to bed, wash your hands and face well beforehand.
- In case of severe itching and swelling, apply cool compresses to the eyelids for 10-15 minutes.
- If you suspect an allergy, do not feed the dangerous product and remove the animals.
Further actions to combat inflammation are carried out after diagnosis.
Dacryocystitis
The development of the pathological process is based on obstruction of the lacrimal canal. Children with the following pathologies are at risk for dacryocystitis:
- rhinitis;
- deviated nasal septum;
- dropsy of the lacrimal sac;
- birth injury;
- narrowed nasal passage.
Blockage of the nasolacrimal duct creates favorable conditions for the active reproduction of pathogenic microflora. As a result, the pathological process can lead to the development of dangerous complications leading to loss of vision.
What can't you do?
If a child has an inflamed eye, you cannot independently determine the diagnosis and begin treatment. There is no need to rely on photographs on the Internet and figure out how to treat it.
You should also not:
- Rinse with tea, as grandmothers advise. Modern tea contains many foreign components, and the quality of the leaves is unknown.
- Try to remove the foreign body yourself.
- Instill drops that adults have used for a similar problem. Only a doctor can determine the causes of inflammation.
- Infants should not be given breast milk instillations, as this can serve as an additional source of infection.
- You can't expect everything to go away on its own. Inflammation can spread to other parts of the organ, making it more difficult to treat.
You should not send your child to school or kindergarten, as he can be a source of infection. In addition, his condition may worsen.
Tablets and ointments
In case of eye inflammation in children, a diagnosis is carried out to identify the part of the organ involved in the process and the nature of the disease.
Allergy
When treating allergic inflammation, it is necessary to identify and eliminate a dangerous substance. Elimination measures, skin tests or blood serum tests are carried out.
For treatment the following are prescribed:
- antihistamines to alleviate the condition - local remedies - Levocabastine, Azelastine, tablets for internal use - Claritin, Suprastin;
- eye drops – Oftalmoferon, Allergodil, Cyclosporin A, Olopatadine, Visin, Emoxipin, Cromohexal;
- corticosteroids - for long-term and severe disease and the ineffectiveness of other drugs - Hydrocortisone.
Eye drops have a vasoconstrictor, antihistamine, and anti-inflammatory effect. In case of prolonged inflammation of an allergic nature, antibacterial drugs are sometimes used, especially if there is a risk of infection.
Treatment of infections
In case of infectious lesions, sensitivity to the antibiotic is determined by a smear from the conjunctiva. After this, antiviral or antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Used for treatment:
- washing with antiseptic solutions - Boric acid, Furacillin;
- applying ointments or drops - Levomycetin, Lincomycin, Albucid, Vitabact, Tetracycline;
- antiviral ointments – Acyclovir, Florenal;
- for severe itching, antihistamines may be used.
In severe cases, appropriate intravenous or internal antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the infection systemically. It is mandatory to carry out a full course of antibiotics, even after the signs of inflammation have passed. The course is 10-12 days, its duration is determined by the doctor.
Treatment rules
When treating, you must follow the rules for the products to be effective:
- even if one eye is affected, it is necessary to rinse and instill in both;
- a separate swab is taken for each eye to process and remove secretions;
- pipettes should be boiled after use or new ones should be taken for the next use;
- treatment is carried out according to the prescribed regimen, without decreasing or increasing the dose or number of applications;
- Before handling, you should wash your hands thoroughly;
- drops are placed behind the lower eyelid, pulling it back slightly;
- it is necessary to ensure that the baby does not rub his eye and the medicine does not come out;
- ointments are also placed behind the lower eyelid, ask the child to close the eye and lightly massage the upper eyelid.
Children do not like treatment; it will take patience to complete the course. It should be remembered that you cannot blindfold yourself so that the exit for secretions is open.
Medicines for the treatment of eye inflammation in children
When a child has an eye infection, treatment usually involves the use of medications prescribed by a doctor. Let's make a brief overview of drugs widely used in pediatrics to treat the eyes of young patients.
| A drug | Group | Active substance | Indications | Mode of application |
| Fucithalmic (drops); 0+ | Antibiotics. | Fusidic acid. | Conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis and other bacterial eye lesions. | 1 drop twice a day for 7 days. |
| Albucid (drops); 0+ | Sulfacyl ntaria. | To prevent blenorrhea: 2 drops after birth and the same amount after 2 hours. For the treatment of bacterial eye diseases - 1-2 drops every 4-6 hours until symptoms disappear. | ||
| Tsiprolet;(drops); 1+ | Ciprofloxacin. | The first two days - 1 drop every 2 hours. Then for five days - every 4 hours, 1 drop. | ||
| Ophthalmoferon; 0+ | Antiviral, immunomodulatory, antihistamine. | Human interferon. | Allergic and viral inflammatory eye diseases. | In acute cases - 1-2 drops every 3-4 hours. As the symptoms weaken, the number of instillations is reduced to 2-3 times a day. Treatment is continued until signs of inflammation completely disappear. |
| Aktipol; 0+ | Antiviral. | Para-aminobenzoic acid. | Viral eye infections. | 1-2 drops 2-8 times a day until symptoms disappear. Continue for another 7 days, instilling 2 drops twice a day. |
| Allegordil; 4+ | Antiallergic. | Phthalazinone derivatives | Allergic conjunctivitis. | 1 drop 2 to 4 times a day. |
Attention! To give the drops to your child, wash your hands with soap. Then place your baby on a pillow and gently pull down the lower eyelid. Apply a few drops (as prescribed by your doctor). Make sure your child does not toss and turn for several minutes. Then the medicine will have time to be absorbed and will not leak out.
Traditional methods
Before using folk remedies, you should consult your doctor. They should be used only if you are completely confident in the quality of the raw materials.
Chopped fresh parsley is tied in a bandage and dipped in boiling water. When it drains and cools down, apply to closed eyes for 10 minutes.
Mix equal amounts of clover, calendula and chamomile. A tablespoon of herbs is poured into a glass of boiling water. Leave for 1 hour. Wet the tampons and apply for 10-15 minutes.
The activity and curiosity of children makes them easy prey for various infections. To avoid inflammation, children should be taught to practice good hygiene. We need to teach children not to touch their eyes on the street and to wash their hands after returning home. These habits and strengthening your immune system will help you avoid many dangerous infections.