The situation when a person has a headache, and the eyes are a source of additional discomfort, is not uncommon. You should not ignore the condition or immediately begin self-therapy. It is better to assess the full picture of the situation and seek advice from a specialist. An experienced doctor, based on one clinical picture, may suspect why attacks of headache and pain around the eyes appear simultaneously. In most cases, anxiety symptoms can be easily relieved with simple manipulations.
Definition and types of symptom
Simultaneous pain in the head and eye is a condition that usually occurs suddenly in a patient. This symptom most often has a high intensity, acute piercing nature. May have various manifestations:
- Episodic attacks. As a rule, such attacks are short-term, appear regularly, and are observed in the patient for about a year.
- Chronic attacks. They appear rarely in the patient, lasting less than a month. Difficult to treat.
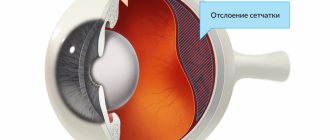
Pain in the eyes and head is not always the only symptom that worries a person. It is often accompanied by additional manifestations of certain diseases: nausea, vomiting, the appearance of spots before the eyes (especially with increased intracranial pressure), impaired consciousness, increased pressure. Read more about the reasons for the appearance of floaters before your eyes in this material.
This is how “floaters” appear before the eyes
Intracranial pressure
Poor circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is typical for the following diseases:
- necrotizing encephalitis;
- epilepsy;
- subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- meningitis;
- flu
Headache in the temple area, radiating to the left eye, is associated with increasing signs of intracranial hypertension and congestion in the corners of the optic nerves in acute encephalitis.
In the case of the development of periaxial Schilder encephalitis (diffuse sclerosis), the patient experiences pressing pain, impaired accommodation, and atrophy of the optic nerves. In the acute phase, the patient feels discomfort in the temporal region, intracranial pressure is increased.
Partial simple seizures in epilepsy are characterized by impaired visual sensations, pain in the eye and temple, and dizziness. As a result of a mild concussion, pain appears in the temporal region and oculomotor disturbances are observed.
After a hemorrhagic stroke, patients complain of cephalalgia, swelling and pressure in the eye area. With hydrocephalus, the patient feels an unpleasant feeling of pressure in the cranial area, which intensifies after mental stress.
Other causes of eye pain
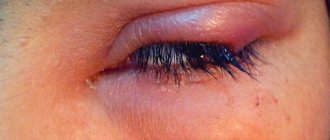
A speck or eyelash caught in the eye Eyes can also hurt for other reasons that are not related to health. Since the eyes are the most easily vulnerable organ. A simple, light or accidental injury to the eye (for example, a speck or an eyelash caught in the eye) can cause severe and cutting pain. If you spend a long time in the sun, in windy weather without protective glasses, or swim for a long time in salt water, painful sensations in the eye area may also occur.
People who wear glasses with incorrectly selected lenses may experience discomfort and pain in their eyes throughout the day. As a rule, you should immediately consult a doctor who will help you check your vision and select the required diopter. Treatment may not be necessary if the pain goes away with properly selected glasses.
Why does my head hurt and put pressure on my eyes?
A headache that radiates to the eye can occur from tension due to prolonged work at the computer. But pain in the eyeballs and head can also be a manifestation of more serious conditions, including intracranial hemorrhage.
A severe headache that presses into the eyes can be a symptom of fatigue. But it also occurs in many dangerous diseases and conditions:
- high intracranial pressure with pain in the eyes develops against the background of a general increase in pressure in the vessels of the head and cavities of the brain. It makes itself felt when moving or static muscle tension. This is manifested by discomfort in the eyes, headache, fever, slow heartbeat. Disorders of the vomiting center occur. Over time, the face and body swell significantly.
- Concussion, especially if it is accompanied by the development of a hematoma. The accumulation of blood in the brain interferes with surrounding tissues, causing headaches that radiate to the eyes. This is a dangerous condition, as the hematoma can burst and be fatal.
- Vascular dysfunction and risk of stroke. The worse the condition of the blood vessels, the harder it is for the brain. When their damage reaches a critical level, a stroke attack will occur.
- Aneurysm. Sac-like dilatation of blood vessels threatens rupture and hemorrhage at the slightest strain. Urgent surgical intervention is required.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. Constant spasm of the neck muscles and immobility of the joints cause pinching of the vessels of the head. This leads to oxygen starvation of the brain, which is accompanied by pain in the head. The pain can radiate to the eyes, shoulders and chest. Most often occurs with a sedentary lifestyle.
- Accommodation spasm and visual impairment in patients with myopia. It occurs when the right or left eye is overstrained and is not corrected by rest. Vision may be lost if there is prolonged contraction of the eye muscles. It hurts to move your head and eyes. Sometimes swelling of the eyes causes the same effect.
Most often, pain in the head in the forehead area radiates to the eyes. They may indicate unexpected problems in the body.
Poisoning
For your information! Toxins in industrial products may cause this symptom. Often found among sellers and warehouse workers.
To avoid permanent poisoning, it is advisable to avoid furniture or household appliances with a strong chemical odor. If you experience any discomfort, pay attention to your recent purchases - they may have caused your discomfort.
A similar reason is a reaction to components of food additives: nitrates, monosodium glutamate, etc.
The symptom also occurs with an allergy to citrus fruits.
ENT diseases
Possible diseases that are characterized by this symptom:
- Sinusitis. The disease is accompanied by headache and eye pain, runny nose, and fever. The sensations can be very strong, and the condition is regarded as dangerous due to the proximity of the inflammatory process to the brain.
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the frontal sinuses - Frontitis. Characterized by pain after waking up.
- Inflammation of the ethmoid sinus in the skull - Ethmoiditis. Occurs in children, as well as adults with weak immunity.
Eye diseases
The described symptom can be accompanied by all common eye diseases: astigmatism, conjunctivitis, myopia, etc.
Remember! If you notice such defects, as well as with constant migraines due to overexertion at the computer, you should contact an ophthalmologist.
Headache in the temple area
You need to immediately understand that there can be many reasons for headaches in the temple area. Even weak sensations signal a disruption in normal functioning and can be symptoms of diseases of varying severity. It is better to immediately contact a specialist.
Problems with blood circulation in the brain are the most common cause of pain in the temples. There are many diseases that affect blood vessels, causing spasms and constrictions. This leads to increased intracranial pressure and the appearance of migraines and other diseases:
- Temporal arteritis.
- Trinitarian neuralgia.
- Giant cell arteritis.
- Cervicogenic headache.
People over 40 years . They can already be classified as a risk group. On the other hand, the environmental situation is steadily deteriorating and this age limit is constantly falling lower.
There are already many known cases of identifying “age-related” diseases in young people. The pressure in the vessels of the cerebral group can jump even due to changes in weather conditions.
Another cause of pain in the temples is infections, which, along with the usual symptoms, cause headaches. If these sensations are accompanied by fever, then there is a high probability of meningitis or encephalitis.
Hormonal changes and menstruation can cause serious headaches in the temples in women. Typically, they are aching in nature and cause spontaneous irritability and inadequate perception.
Excessive alcohol consumption causes intoxication of the body. Just like self-medication, which is common among the Slavic people, after which a large amount of medicine accumulates. It is intoxication that contributes to the rapid development and intensification of pain in the temples.
If you are exposed to constant stress and exhaust your body with physical activity, this can cause headaches. The most vulnerable are people employed in jobs involving mental work.
Don't forget about foods that contain monosodium glutamate. It can be a source of pain in the temples. Here are some “harmful” foods:
- Smoked fish.
- Bacon and nuts.
- Sauces and hot dogs.
- Canned soups.
- Chinese cuisine.
Naturally, if you experience a headache in the temple area, it is better to consult a specialist and get a professional opinion. If the causes are known and the diagnosis has been established, then you need to take the prescribed medications.
If pharmaceutical intervention does not work quickly enough, the condition can be improved by performing a massage. Simple circular movements around the temples and forehead can significantly relieve pain.
Causes of discomfort
Headache and eye pain can occur in patients for various reasons. These could be:
- Overwork. Most often, it appears in those people who work for a long time in front of a monitor or perform tasks that require very high concentration.
- Incorrect selection of contact lenses or glasses. Most often, pain occurs if a person wears lenses of greater optical power than he needs. Unpleasant sensations with this factor usually appear in the afternoon.
Selection of optical lenses
- Concussion, traumatic brain injury. Even a small injury is enough to cause headaches and eye pain. Find out what causes headaches in the forehead and eyes here.
- Infectious diseases affecting the nervous system. This group includes meningitis and encephalitis.
- Glaucoma. With this disease, intraocular pressure increases, causing pain first in the affected eye and then in the head.
- Increased intracranial pressure. Usually this condition is accompanied by the appearance of spots before the eyes, rapid heartbeat, and nausea.
The cause of the headache itself is not entirely clear. Inheritance and various factors that can cause discomfort are taken into account. Headache, in which it is painful to move the eyes, has the following etiologies:
- physical, mental stress, exhaustion;
- dehydration;
- weather changes;
- musculoskeletal disorders;
- non-compliance with sleep patterns;
- some food, drinks;
- some medications;
- infections (most often headaches, sore eyes, stuffy nose during colds);
- other diseases.
Overwork
Many health problems related to diseases of civilization are caused by humans themselves. Many daily tasks take away the time needed for rest and sleep. Headaches, pain, and tenderness when turning the eyes can be caused by other diseases, and a wide range of pathophysiological mechanisms are involved in the development of these symptoms. Regular adequate sleep can reduce the risk of their occurrence.
Migraine
The disease manifests itself as throbbing pain on top of the head or unilateral pain (the right half of the head hurts or the left), the pain radiates to the right eye or presses behind the left eye. Sometimes visual disturbances are added (flickering in the eyes). The attack usually lasts 4–6 hours, accompanied by intolerance to light, noise, smells, tearfulness, nausea, leading to vomiting.
Symptoms include a dull ache, often pressing on the inside of the eyes, and increased tension in the neck. There are no other somatic symptoms, the discomfort does not increase with movement, but may slightly worsen when raising the eyes up. The cause of tension-type headache is mainly stress, depression, computer work, prolonged writing and reading (when you see double). These factors cause changes in tension and blood circulation in the neck muscles.
Hypertension
High blood pressure may not appear at all for a long time. Sometimes fatigue, nosebleeds and headaches occur in the area of the eyes, temples, and back of the head.
Increased ICP usually accompanies conditions associated with brain tumors. An increase in ICP invariably leads to headaches, during which it is painful to move your eyes and blink. High blood pressure can occur for many reasons, including:
- brain tumors and metastases of other tumors to the brain;
- infections;
- intracranial hemorrhage.
Reduced or increased eye pressure may indicate serious illness.
Most often, an increase in eye pressure is accompanied by redness, swelling of the eyes, and it is painful for a person to rotate the eyes. Critically high IOP values have dramatic manifestations, such as:
- frequent headaches, especially when turning the eyes;
- vomit;
- blurred vision (blurred vision);
- perception of various light phenomena (dazzles before the eyes);
- gradual loss of visual field.
An unpleasant dull pain caused by inflammation of the nasal sinuses appears on the forehead, in the bridge of the nose. When you tilt your head, you feel pressure from the inside of your eyes. Headache caused by inflammation of the cavities is accompanied by fever, runny nose, patients are often tired, and their eyes turn red. The discomfort intensifies in the 2nd half of the day, when pressing on the sore area or the bridge of the nose.
The most common cause of headaches over the right eye or over the left is quite commonplace. In particular, discomfort is caused by incorrectly selected prescription lenses or an ingrained dislike of wearing glasses. A person's vision becomes blurry and dark, mainly after long periods of reading or hours of work at the computer. A similar effect can be caused by a tendency to squint (the eye muscles try to correct the defect, which leads to their overstrain).
The cause of eye pain that radiates to the head can be ophthalmological diseases - barley, inflammation of the lacrimal glands, conjunctivitis. A common reason for a burning, reddened eye is a lack of hydration due to a deficiency of eye fluid.
The following conditions require urgent medical attention:
- severe headache and eye pain;
- blurred vision occurred.
Glaucoma associated with increased IOP may occur, putting the person at risk of blindness.
Brain diseases
The most serious condition of this group is headache associated with brain tumors. Headache and twitching (right eye or left eye twitching) occur in approximately 60% of cases of intracranial carcinoma. Often these symptoms are the first manifestations of pituitary tumors.
Insignificant pain occurs with slow-growing tumors and carcinomas located in asymptomatic areas (especially the frontal lobes). In particular, meningiomas can remain without clinical symptoms for a long time.
Of the dangerous vascular diseases of the brain, the most severe is subarachnoid hemorrhage. This is bleeding from a cerebral artery aneurysm (a vessel bursts and blood pours into the cavity).
Poisoning
Most poisonings manifest as headaches that radiate to the eyes and bruises under the eyes. The same symptoms are present when metabolites or toxic substances accumulate in the body. This group also includes hangover headaches, which occur due to the accumulation of toxins and dehydration. Headache is one of the signs of lead or carbon monoxide poisoning.
Medicines
When drugs are abused, as a rule, tolerance to the active substance occurs, so the patient increases the dose of the drug and the frequency of its administration. Psychological and physical dependence may occur. If a person does not take “his” medications for headaches, withdrawal symptoms appear and the headache gets worse. Withdrawal symptoms are varied: the eyes turn red, there is pain over the right or left eye, vomiting.
The most frequently reported dependence is on Sumatriptan, Ibuprofen, Eletriptan, Ergotamine drugs, and combined analgesics (painkillers containing several active substances).
Oculomotor nerve neuropathy
After trauma, neuroinfection, stroke or due to the development of a malignant tumor, the oculomotor nerve is affected. Diabetic neuropathy occurs with intense headaches in the temporal region. The palpebral fissure narrows almost completely. There are lumbagoes that occur spontaneously or in a certain position of the head.
Changes in muscles and nerves contribute to the development of crises limited to the temporal region. Tumor processes cause disturbances in the pathways, pain radiates to the eyes, and the frequency of paroxysms varies.
With collagenosis and vasculitis, ischemic optic neuropathy develops. The patient experiences a sudden feeling of discomfort and pressure in the eyeball, loss of the upper and lower half of the visual field.
Neuropathy of the third pair of cranial nerves in a patient with diabetes mellitus occurs with increased intracranial pressure and intense pain in half of the head. He experiences severe spasms in the right side of his face, spreading from the temple up to the eye, and then down to the place where the jaws close. The doctor determines neuropathy of the abducens nerve due to a neuroinfection.
Optic neuritis
Treatment at home
Home remedies for headaches cannot replace full-fledged therapy prescribed by a doctor. In addition, prolonged and uncontrolled use of certain painkillers can cause serious health problems.
The recommendations and advice that will be given below are intended only for one-time relief of headaches associated with overwork or geomagnetic conditions. If you have headaches on an ongoing basis, then consulting a doctor is mandatory.
The first thing you can do to relieve pain is to place a cool, wet towel on your forehead, lie down, relax, turn off the lights and be quiet for a while.
If the pain does not go away, then you can take an analgesic or antispasmodic. Essential oils cope well with headaches: lemon, lavender, peppermint. You can simply apply them to your temples, or you can do a light massage with your fingertips, onto which you drop a drop of oil.
Honey is often used to treat headaches at home.
Balm “Zvezdochka” also helps relieve headaches. You can make a lotion with cinnamon, apply a cabbage leaf to your forehead, and wipe your temples with lemon juice. Some people find that pulling a tight bandage around their head helps, but this can only be done if you are sure that your blood pressure is not high.
Possible diseases
A headache that appears simultaneously with pain in the eyes may indicate that a person has various serious diseases. These could be:
- Sarcoma of the brain. This pathology is accompanied by constant headaches, nausea and vomiting.
- Meningitis. If the patient has this particular disease, the headache will be accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting, and in some cases, a disorder of consciousness.
- Migraine. This disease can occur if a person suffers from headaches for a long time. Accompanying symptoms include nausea and vomiting. Migraine symptoms may worsen when weather conditions change, which requires special attention.
- Aneurysm. With this pathology, a person will experience severe intense pain that does not subside for several days. Requires immediate hospitalization as it threatens the patient's life.
- Encephalitis. With such a disease, the pain will have a constant pulsating nature.
- Glaucoma. With this disease, severe pain will first appear in one of the eyes, and then move to the head. The following accompanying symptoms may appear: pupil enlargement, photophobia, nausea, vomiting, decreased vision. More about the signs of glaucoma here.
Migraine is a common cause of temporal pain
With migraine, headaches in the temples and eyes are paroxysmal, pulsating in nature. They are concentrated in the ocular and frontotemporal region. Usually their localization is noted on one side, although there are also bilateral pain sensations. Sometimes they are accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
The face may turn pale or red as an attack occurs. The pain intensifies in the presence of sound, light and olfactory stimuli. Mental and physical stress is difficult to bear, and sometimes completely impossible. The period of the attack varies. It can last several hours and 2-3 days. The pain is often relieved during sleep.
In some cases, headaches in the temples and eyes during migraine appear with enviable frequency. They are interspersed with short periods of mild pain. Such attacks are called migraine attacks. Against their background, meningeal syndrome develops.
Diagnosis and treatment
If your head hurts too often, you should consult a doctor. Only a specialist can correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment. The scheme is determined individually in each case. The following medications may be prescribed:
- improving cerebral circulation;
- to normalize blood pressure;
- painkillers.
The duration of the course of treatment is determined by the doctor. In some cases, it is necessary to undergo treatment in a hospital setting.
In order to find out the cause of pain in the left side of the head and eye area, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination. The following procedures may be prescribed to the patient:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- X-ray examination of the neck and spine;
- ECG;
- coagulogram;
- Ultrasound and rheovasography of neck vessels;
- analysis for the determination of bilirubin, creatinine and urea in the blood.
In addition, you should measure your blood pressure for several days, which will allow you to establish the relationship between headaches and hypertension. For a more accurate diagnosis, an MRI of the head may be prescribed, and if thrombosis or tumor is suspected, angiography of the cervical arteries may be prescribed.
Treatment of deviation
The therapeutic method, treatment regimen, course duration and dosage are selected only by the attending physician after a detailed examination of the patient. To normalize blood pressure, Enam, Captopril, Renitek are prescribed, and the neurologist will also recommend therapy with drugs whose action is aimed at strengthening blood vessels (Verapamil, Amlodipine, Verapamil). To eliminate pain, analgesics such as Ketanov, Baralgin, Tempalgin are recommended; Paracetamol, Aspirin, Ibuprofen are prescribed to relieve inflammation.
If the cause of the pain is traumatic injury to the head or eye, it is recommended to resort to surgery to eliminate the problem. Some alternative medicine techniques and traditional recipes can be used as adjuvant therapy. It is important to remember that self-medication can greatly harm the patient and aggravate the course of the disease, therefore, before trying auxiliary methods, you must first consult with a doctor.
What to do if your eyes and head hurt
First of all, analgesics are prescribed. At the same time, the cause of the pain is determined. Based on the findings of the examinations, an individual therapeutic approach is selected.
Eye exercises
Do your eyes burn, have difficulty seeing, or have other problems arise when working at the computer for a long time? Stop and do eye exercises suitable for both adults and children. Look left, right, up, down. Repeat several times. Breathe freely and regularly. Do gymnastics once every few hours.
Another option for help is if there is blur in the eyes, the eyelids are swollen and itchy - the eyes open and slowly close. Then place your palms on your eyes so that they do not let in light and do not squeeze your eyelids. In the dark, with calm breathing, create a feeling of inner peace.
How to avoid pain in your temples and eyes
To prevent pain, it is necessary to normalize your daily routine. You definitely need to rest and get enough sleep.
Prevention methods:
- If possible, sleep during the day, but no more than an hour;
- perform gymnastics for the eyes, neck and head;
- take breaks to rest every hour when working at the computer or watching TV;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- stop being nervous, avoid conflicts, hypothermia, overwork;
- ventilate the room 3-4 times a day, always before going to bed;
- promptly cure eye diseases and head injuries;
- undergo regular preventive medical examinations;
- eat right, don’t overeat at night, take vitamin complexes;
- drink 1.5 liters of clean water per day;
- exclude fatty, unhealthy and heavy foods from the diet;
- walk in the fresh air every day for at least 30-40 minutes.
If there are frequent relapses during remission, you should undergo a course of relaxing massage or reflexology.