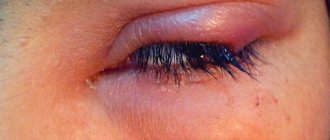
Photophobia is the increased sensitivity of the eyes to bright light. It can be caused by certain diseases, or by a person staying in a dark room for a long time or by the action of special medications. Usually, the pupils are dilated, which is what causes the rays to hit the retina.
The oculomotor nerve regulates the diameter of the pupil to ensure normal vision of objects in different degrees of illumination. The entry of light through the refractive system to the retina is limited by the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. The action of the first leads to expansion, the second - to narrowing of the pupil. In the dark, the pupil increases in diameter, and in light it decreases.
Causes of photophobia
Photophobia is a sign that too much light from the external environment enters through the pupil, which irritates the central nervous system. Bright rays can cause headaches, epilepsy, and other unpleasant sensations.
Causes of photophobia of the eyes:
- An impending migraine attack, increased intracranial pressure due to hypertension, epilepsy, eclampsia in pregnant women.
- Alcohol intoxication, drug intoxication, hangover.
- The effect of drugs that dilate the pupil.
- Damage to the central nervous system due to traumatic brain injuries, tumors, strokes, neuroinfections, multiple sclerosis.
- ARVI, allergic reactions.
- Albinism.
- Eye diseases: pathologies of the cornea, iris, conjunctiva.
- Damage to the circular muscle, which constricts the pupil after injuries, tumors.
It is useful to read about surgical treatment of cerebral aneurysm and rehabilitation after surgery.
Why there is a veil before the eyes: causes, provoking diseases.
This is an incomplete list of the diseases that cause photophobia. Photophobia is characteristic of epilepsy, traumatic brain injury, meningitis, encephalitis and other diseases accompanied by cerebral edema. Eye injuries and damage can also cause intolerance to bright rays.
Types of cataracts and their signs
The first sign that allows a doctor to suspect a person has cataracts is the patient’s age over 60 years. In this case, the clinical picture has characteristic features. During examination, the ophthalmologist observes opacities that can be located in different parts of the eye: in the peripheral lobe of the lens, or opposite the pupil. The opacities are grayish in nature, sometimes with a white tint.
Depending on what type of cataract it is, the ophthalmologist will observe a varied clinical picture, accompanied by the following signs:
- An anterior cataract appears as a white spot with clearly defined boundaries. When it is slightly pushed forward and pointed, such a cataract is called anterior pyramidal.
- If the clouding is located at the posterior pole of the lens and is presented in the form of a round white ball, then it is said to be a posterior polar cataract.
- Central cataract is determined by such characteristics as: spherical appearance, location - center of the lens, diameter - 2 mm.
- A fusiform cataract can be judged by its shape. This clouding is presented in the form of a thin spindle, it is located along the entire length of the lens.
- Zonular congenital cataract has the appearance of a cloudy core with transparent layers.
- Cloudiness of the entire lens, liquefaction of its masses and further formation of a dense bag are signs of a dense soft cataract.
- Diabetic cataracts are characterized by the appearance of white opacities in the form of flakes. They are located over the entire surface of the lens, and changes in the iris often occur.
- Tetanic cataract is characterized by the same symptoms as its diabetic variety and is determined by the signs of the disease that caused it (hypofunction of the parathyroid glands).
- Toxic cataract most often manifests itself in the form of opacities located under the lens capsule, with subsequent spread to the cortical layers.
- Senile cataract has many symptoms and depends on the degree of progression of the disease: initial, swelling, mature and overripe.
These are the most common signs that allow us to characterize cataracts and attribute them to one type or another.
Symptoms
Sunlight and other bright light causes pain in the eyes and head. In photosensitive epilepsy, it can provoke seizures. Photophobia of the eyes may be accompanied by symptoms such as:
- Tearing.
- Itching of the conjunctiva.
- Visual impairment, white flies.
- Dizziness, palpitations.
- Excretion of saliva, with epilepsy - with foam.
With eclampsia, photosensitive epilepsy, and traumatic brain injuries, convulsive seizures are possible, provoked by bright rays, sharp sounds, and odors.
Causes and symptoms of pathology development
First, it is important to note the fact that cataracts are characterized not only by a gradual loss of visual vision, but also as a result, if a person does not treat the disease, he may lose his vision altogether. Finding out on your own at home whether the disease exists is quite possible, but you need to know about the causes of the disease:
- old age;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- innate character;
- head injuries;
- poisoning with various substances such as mercury, thallium, naphthalene, etc.;
- manifestation of myopia and glaucoma;
- severe myopia;
- radioactive exposure.
If you don’t know how to find out about incipient cataracts, then this series of reasons will definitely help. In addition, another cause of cataracts is the sun. Long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation will negatively affect the visual system.
Cataract symptoms tend to progress, so it is simply impossible not to pay attention to the following aspects:
- The sharpness of vision decreases (double vision, black dots are visible, you want to wipe your eyes, remove the fog - all these are the first sensations).
- Reading in the twilight is very easy and relaxed. If you have this symptom, then think about why it has become more comfortable to read in the dark, but there is no reaction to lighting fixtures.
- Irritated by the brightness of lighting fixtures. When the light is too bright at home or at work, think about why it annoys you.
Important! You can identify the signs of cataracts even with the help of banal conversations! So, if you notice that you started talking about how the world around you has become somehow foggy, lost its bright colors and turned pale, then something is clearly wrong with your eyes.
Read on the topic: What is eye cataract and how to treat it?
Diseases that cause photophobia
Swelling of the brain due to compression of the ventricles by tumors leads to disruption of the activity of the oculomotor nerve nucleus. The accumulation of excess fluid in the cavities (ventricles) leads to inadequate functioning of the central nervous system, in particular the third pair of cranial nerves.
Increased intracranial pressure is observed in hypertension, kidney disease, and heart disease due to fluid retention in the body. The excess is secreted through the choroid plexuses at the bottom of the lateral ventricles. Influenza infection, meningitis, tick-borne encephalitis lead to swelling.
Eclampsia in pregnant women is caused by renal failure, as a complication of gestosis. Leads to epileptic seizures preceded by abnormal sensitivity to light.
Important! In case of fear or intoxication, the sympathetic nervous system dominates, which leads to increased photosensitivity. People with a mental illness called heliophobia have a fear of bright sunlight.
Albinism is a genetic disease characterized by impaired synthesis of melanin, which protects the retina from too bright rays. With this pathology, photophobia is observed in the child.
The sensitivity of one eye to light may increase when the apex of the lung of the same name is affected by the tuberculous process. The pupil is dilated, which leads to photophobia.
Treatment
Today, curing cataracts is not difficult. This can be done in an eye clinic by replacing the affected lens with an artificial intraocular lens. The cataract removal procedure is performed using ultrasound or using a femtosecond laser. The operation is called phacoemulsification and is performed using local drip anesthesia, which is usually well tolerated.
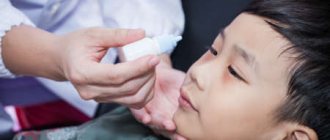
There are also medications for the treatment of cataracts, but they mainly act in the initial stages and only slow down the disease process. Most often these are drops that contain vitamins (PP, B, C), antioxidants, potassium iodide, amino acids and other substances. These remedies are ineffective in eliminating cataracts and will not replace conservative treatment.
Diagnostics
To exclude serious organic brain lesions (tumors, intracranial hematomas, hydrocephalus), MRI is used. If you suspect a pregnancy complication, such as eclampsia, you should donate blood for a biochemical test (creatinine, urea) and urine, which often contains protein, which indicates a disorder of the kidneys.
An electroencephalogram is needed to assess the excitation of the cerebral cortex, finding ectopic foci that cause epileptiform seizures and photophobia.
If heliophobia is suspected, the patient is sent to a psychiatrist.
Drug and alcohol intoxication must be excluded by testing for the presence of these substances in the blood and urine.
All about hemianopsia: classification, causes, characteristic signs, treatment.
Why vision loss occurs due to optic nerve atrophy: causes and treatment.
It is important to learn what to do with intracranial pressure in order to prevent compression and oxygen starvation of brain tissue.
Prevention of cataracts
Cataracts are the aging of the lens of the eye, so prevention is achieved through general health measures that relate to lifestyle, nutrition and regimen. People who maintain physical activity and proper nutrition can, if not avoid, then significantly delay the aging of the lens and the body as a whole.
There are special recommendations. Cataract formation occurs under the direct influence of ultraviolet rays as a catalyst for free radicals. Sun damage to the cells of the lens is a trigger for lens clouding.
Hormonal drugs, corticosteroids and agents that increase sensitivity to UV rays have a similar effect on the eye. Tablet contraceptives and caffeine-containing drinks have a negative effect. After 40 years of age, blood glucose monitoring and a preventive examination by an ophthalmologist are mandatory.
Photophobia - all about the symptom - Ochkov.net encyclopedia
Photophobia manifests itself as increased sensitivity to daylight or artificial light. Most often, a person’s eyes react to bright light sources, but in especially severe cases, unpleasant symptoms also occur in moderate lighting.
Photophobia symptoms
Photophobia can manifest itself in the following signals:
Photophobia is often accompanied by headache and dizziness, the effect of sand in the eyes, and a gradual deterioration in visual function. The presence of photophobia can be determined independently by these symptoms, but you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and prescription of corrective therapy.
Causes
- Photophobia can occur for non-pathological reasons:
- a congenital structural feature of the eye with the absence of coloring pigment;
- dilated pupils when using eye drops;
- use of certain medications;
- prolonged work at the computer, which overloads the eyesight and causes dry mucous membranes;
- prolonged stay in the dark;
- the presence of a foreign body in the organs of vision (in this case, photophobia usually affects one eye and is accompanied by cutting sensations);
- exposure to excess sunlight on the retina.
For such reasons, fear of bright light does not indicate the presence of a disease.
But in some cases, photophobia is a sign of the disease, which, in combination with other signs, indicates the true cause of the pathology:
- the presence of an ophthalmological disease (keratitis, conjunctivitis, etc.);
- acute infectious diseases (measles, rubella, meningitis);
- cold viral infections;
- in rare cases - neurological disorders, depressive disorders, chronic fatigue.
Getting rid of photophobia in such situations can only be done by identifying and treating the underlying disease.
Photophobia as a symptom
By analyzing the compatibility of symptoms, you can guess what pathology caused the appearance of photophobia, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
- Photophobia and lacrimation
Their simultaneous appearance may indicate a mechanical injury, a foreign body or substance entering the eye; inflammation or erosion of the cornea; conjunctivitis; influenza or acute respiratory disease; aniridia and other developmental anomalies of the eyeball; inflammation, melanoma or retinal detachment; retinopathy; hemophthalmos; hyperthyroidism; uveitis; migraine; encephalitis, meningitis.
In addition to lacrimation and photophobia, each of these diseases is characterized by a whole list of other symptoms that help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe competent treatment.
- Photophobia and eye pain
They can be combined with burns, ulcers, mechanical damage to the cornea, spring catarrh, acute glaucoma, endophthalmitis.
- Photophobia and redness of the eyes
The simultaneous appearance of these signs may indicate injury or burn of the cornea, keratitis, uveitis, conjunctivitis.
- Sun sensitivity and fever
Increased sensitivity to light in combination with a rise in body temperature may indicate meningitis, endophthalmitis, encephalitis, trigeminal neuralgia, hemorrhagic stroke, brain abscess, purulent uveitis.
- Photophobia and headache
This combination is typical for brain abscess, migraine, encephalitis and meningitis, stroke, tension headaches, acute attacks of glaucoma, acromegaly.
Typically, nausea combined with photophobia indicates increased pressure inside the eyes or skull, which is typical for diseases such as meningitis, migraines, hemorrhagic stroke, and brain abscess.
- Photophobia and pain in the eyes
Cutting sensations in the eyes with fear of bright light are characteristic of conjunctivitis, keratitis, astigmatism, trigeminal neuralgia, uveitis, blepharitis, ulcers and burns of the cornea.
Diagnosis and treatment of photophobia
Therapy for photophobia is based on finding and eliminating the cause of this symptom. The following types of studies help to detect a disease that has manifested itself as photophobia:
- ophthalmoscopy - when performed, the doctor examines the fundus of the eye using a special device;
- biomicroscopy - an ophthalmologist examines areas of the fundus and the vitreous body through a slit lamp for changes;
- perimetry - this method allows you to establish the boundaries of the patient’s field of vision;
- tonometry - a test during which the doctor measures the pressure inside the eyes;
- gonioscopy - involves examining the corner of the eye where the iris borders the cornea;
- pachymetry is a diagnostic test in which the doctor determines the thickness of the cornea;
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision - helps to examine areas of the eye when ophthalmoscopy is not possible;
- fluorescein angiography - during this, the doctor examines the patency of the vessels that feed the ocular structures;
- optical tomography - it is used to detect changes in the tissues of the retina;
- electroretinography is a research method aimed at analyzing the functioning of the retina;
- culture for viruses, bacteria - helps to establish the source of the eye infection.
These diagnostic methods allow the ophthalmologist to name the exact cause of the development of photophobia and other associated symptoms.
If ophthalmological examinations show the absence of eye diseases, but photophobia is present, consultation with a neurologist is required.
This specialist may prescribe additional diagnostic tests: MRI of the brain, Dopplerography of the cervical vessels, electroencephalography.
If, along with photophobia, signs of hyperfunction of the thyroid gland or diabetic retinopathy were detected, an endocrinologist is involved in treatment. For symptoms indicating a tuberculosis process in the cornea, call a phthisiatrician.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist in case of photophobia is mandatory, but prophylactic wearing of sunglasses, which will significantly reduce the dose of ultraviolet radiation affecting the organs of vision, will help ease its course.
Possible complications
One of the most likely complications of photophobia is the worsening or chronicity of the disease that caused its occurrence. In severe cases, ignoring photosensitivity can even lead to complete loss of vision.
In addition to significantly reducing the patient’s quality of life, photophobia can cause the development of such a serious psychological condition as heliophobia. The pathology is accompanied by a strong, often panicky fear of the sun's rays. People with heliophobia (and even those patients who have already gotten rid of photosensitivity) experience severe emotional shock before going out into sunlight, fearing that it will again cause pain, pain and discomfort in their eyes.
Fear of sunlight is accompanied by:
- increased heart rate and breathing;
- trembling in the limbs;
- attacks of arrhythmia;
- nausea, sometimes with vomiting;
- dizziness with the possibility of short-term loss of consciousness (syncope);
- panic attacks;
- hysteria.
If hypersensitivity to light occurs, do not neglect the alarming symptoms. To avoid dangerous consequences, it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible, since in some cases photophobia may be one of the signs of the presence of a brain tumor.
Basic principles of cataract treatment
In the conditions of ophthalmological centers, of course, cataracts of the eye are much easier to diagnose. All treatment is carried out by professionals and in 99% of cases, the patient’s vision is restored. Difficulties with diagnosis arise when the examination is carried out in a regular public hospital. The lack of equipment and lack of personnel lead to the fact that in the periphery there are many times more patients registered with an ophthalmologist than in the cities.
A characteristic complaint with mature cataracts regarding loss of vision is typical for every second patient who has reached the age of 70 years. Modern doctors can offer two directions for treating the disease: surgical or conservative. Eye drop therapy is prescribed to prevent the development of new diseases. It is impossible to relieve a patient from clouding of the lens with drops alone. After all, the pathological process has complex physiological lesions. The best option when there are cataract symptoms and treatment is surgical. The essence of the surgical intervention is based on the installation of a lens similar to the lens. All materials used in such operations are as close as possible to the natural tissues of the eye. Therefore, patients after such correction do not feel strong changes, only mild discomfort during adaptation. Restored vision returns, and the patient is thus freed from eye cataracts forever. Laser vision correction allows manipulations to be carried out absolutely safely, quickly and with a short rehabilitation period. A unique removal of formations in the area of the diseased eye is carried out by modern specialists using ultrasound. The operation takes 10 minutes and does not require general anesthesia. Proper therapy consists of administering local anesthesia, and after removing the cataract, prescribing eye drops.