How does photophobia of the eyes manifest?
Photophobia is commonly understood as a painful reaction of the eyes upon direct contact with a source of natural or artificial light. The most pronounced symptoms of this pathological condition are closing of the eyelids and increased lacrimation. In addition, accompanying symptoms are often observed - pain, burning and itching. Sometimes photophobia of the eyes is accompanied by headache, nausea, vomiting, and in severe cases, even loss of consciousness. All of the above symptoms are typical for both children and adults. Discomfort occurs only with direct contact with a light source. When you are in a darkened room, it disappears.
Photophobia can be temporary or long-lasting. In the first case, it occurs due to exposure to external factors, for example, prolonged contact with ultraviolet rays or taking certain medications. This reaction usually goes away on its own, so the person does not require medical attention. If increased sensitivity of the eyes to light is observed for more than two days, we can talk about a long-term nature of the manifestation. In such a situation, you should consult a specialist and undergo a comprehensive examination to identify the cause of the pathology.
From a physiological point of view, photophobia is an excessive manifestation of the protective reaction of the eyes to exposure to a light source. In a normal state, when exposed to high-intensity light rays, the unconditioned reflex of involuntary squinting is triggered. Each person has his own threshold of permissible brightness, which the organs of vision can perceive. But in general, this indicator has an average statistical value. If the intensity of the light source exceeds the permissible norm, involuntary squinting of the eyes occurs, caused by blinding. This reaction is normal. In the case when the closure of the eyelids and increased lacrimation are observed at a normal level of brightness of the light source, we can talk about photophobia.
The appearance of such a reaction may be associated with a disruption in the functioning of the visual, nervous or endocrine system. Also, increased eye sensitivity to light occurs as a result of serious pathological conditions in the human body, including intoxication, an acute attack of glaucoma and migraine. Therefore, many are interested in photophobia: a symptom of what disease? To reliably answer this question, you need to take a general blood test and undergo a comprehensive examination.
In some cases, high eye sensitivity to light may be associated with a serious psychiatric illness such as heliophobia (fear of being in the sun). This reaction should not be confused with photophobia, since it has nothing to do with the functioning of the visual system. The cause of this pathological condition is associated with a malfunction of the human nervous system.
Signs of photophobia:
- Increased lacrimation;
- Involuntary squinting of the eyelids;
- Pain, itching, burning and stinging;
- In some situations - dizziness and headache;
- In severe cases - nausea, vomiting, loss of consciousness.
Symptoms
The symptoms of photophobia are:
- Pain in the eyes;
- Tearing;
- Forced squinting;
- Headache.
Photophobia is a complete intolerance to bright light in one or both eyes, and the light can be either natural or artificial. A person suffering from photophobia, when exposed to an illuminated space, closes his eyes, squints, and tries to protect his organs of vision with his hands. When wearing sunglasses the situation improves somewhat.
Increased photosensitivity may be accompanied by:
- headache;
- lacrimation;
- dilated pupils;
- redness of the eyes;
- a feeling of “sand” or “soreness” in the eyes;
- impaired visual acuity;
- unclear outlines of objects.
Photophobia is a sign of eye diseases if, in addition to it, there is decreased vision, redness of the eyes, swelling of the eyelids, and purulent discharge from them. If there are no such symptoms, most likely it is a pathology of the nervous system.
Depending on the accompanying manifestations of photophobia, one can roughly guess which diseases photophobia is a symptom of. This is what we will look at next.
Treatment of photophobia is entirely based on the cause of this symptom. This requires ophthalmological diagnosis, since many eye diseases are similar to each other. To make a diagnosis, the following studies are needed:
- Ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus through a previously dilated pupil.
- Biomicroscopy - examination in a special slit lamp for changes in the vitreous body and areas of the fundus.
- Perimetry - checking visual fields.
- Tonometry is the measurement of intraocular pressure.
- Gonioscopy is an examination of the corner of the eye where the iris borders the cornea.
- Pachymetry is the measurement of corneal thickness.
- Ultrasound of the eye helps to examine the transparent media of the eye when it is impossible to perform ophthalmoscopy.
- Fluorescein angiography is a study of the patency of blood vessels that supply the structures of the eye.
- Optical coherence tomography - helps to identify changes in retinal tissue.
- Electroretinography - helps to carefully study the functioning of the retina.
- Sowing the discharge from the conjunctival sac for viruses (using the PCR method), bacteria and fungi.
Photophobia of the eyes in an adult: why it occurs
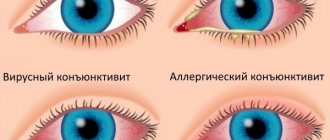
One of the most common causes of photophobia are various infectious, inflammatory and other diseases of the visual organs. Often people suffering from conjunctivitis (inflammation of the uvea), keratitis (inflammation of the cornea), and iritis (inflammation of the iris) turn to ophthalmologists with this problem.
In some cases, photophobia of the eyes in adults manifests itself due to adverse environmental influences, for example, with prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays reflected from snow. Also, photophobia can result from damage to the eyes from excessively bright light during welding work without protective glasses. Sometimes the occurrence of this reaction is associated with some common diseases, such as migraine, acute respiratory infections, influenza, and an acute attack of glaucoma may also be the cause.
People on forums often ask what serious disease symptom is photophobia. Experts say that this reaction may indicate problems with the thyroid gland or signal a tumor in the brain. The patient will be prescribed additional examinations, such as ultrasound, MRI or CT. The causes of photophobia are sometimes associated with damage to the visual organs of various types, including wearing incorrectly selected contact lenses or penetration of a foreign body. Sunburn, as well as ulcers, erosion and mechanical damage to the cornea can also cause involuntary squinting of the eyes when in direct contact with a light source.
What diseases does increased light sensitivity of the eyes indicate? The appearance of this reaction is often not associated with pathological processes. Sometimes constant drying of the cornea and increased visual stress also become the causes of photophobia. This is especially true for people who spend a long time in front of a computer monitor.
In rare cases, symptoms of photophobia occur in people due to the complete absence or insufficient amount of a special pigment in the body (melanin). At the same time, the eyes react too actively to any light source. In this case, the pathology is congenital. It should be noted that this form of sphetophobia is quite rare.
Photophobia can be a symptom of what disease?
- Various diseases of the organs of vision (inflammatory, infectious, etc.);
- Malfunctions of the nervous system;
- Pathologies of the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- General diseases (flu, acute respiratory infections, glaucoma);
- Hereditary diseases associated with insufficient melanin in the body.
Photophobia in children
Increased sensitivity of the visual organs to light can occur in any person, regardless of age. Photophobia in children appears due to lack of sleep, excessive time spent at the computer, stress, as well as various pathologies of the visual organs. Children are more often susceptible to viral and infectious conjunctivitis and other diseases, so there is a risk of increased photosensitivity of the eyes. Sometimes incorrectly selected correction means can become a provoking factor. Therefore, it is important that the selection of optical products is carried out by a qualified ophthalmologist after conducting a comprehensive examination of the visual system.
Quite rarely, photophobia of the eyes in a child is associated with the so-called “pink disease”. This is an autoimmune disease accompanied by increased blood pressure, photophobia, increased sweating, anorexia, and pinking of the skin of the palms and soles with prolonged contact with a light source.
Diagnosis of photophobia of the eyes
If symptoms of photophobia persist for more than two days, you should seek medical help. Initially, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination of your vision organs in the office of an ophthalmologist. As a rule, it includes various diagnostic methods aimed at identifying the cause of the pathology: examination of the condition of the cornea, ophthalmoscopy, and others. If the specialist determines that the cause of photophobia is not related to a dysfunction of the visual system, the patient will be scheduled for further examination by a neurologist, who will most likely give a referral for an MRI or CT scan of the brain. In some cases, an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and other examinations may be required. This approach is aimed at identifying the primary cause of photophobia. Only in this case can the patient be provided with qualified medical care to eliminate high sensitivity to light.
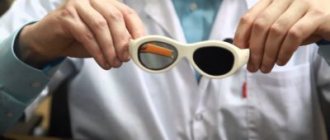
If it is impossible to eliminate the cause of the primary pathology, for example, with autoimmune thyroiditis, a person is recommended to make small adjustments to his daily life to prevent photophobia. On sunny days, direct contact with ultraviolet rays should be avoided. To do this, you should go outside wearing a wide-brimmed hat and safety glasses. These recommendations are also relevant if photophobia is in no way related to any pathological processes and is an individual feature of the human body.
If photophobia occurs temporarily, for example, due to a foreign body entering the eye, you should use a moisturizing ophthalmic solution, antiseptic or anti-inflammatory drops. This will help alleviate the symptoms somewhat. However, the use of medications is permissible only under the supervision of a physician.
Symptoms of photophobia for which you should consult a doctor:
- Increased lacrimation and pain in the eyes are observed even with low lighting levels;
- Vision becomes blurred when in contact with a light source;
- Discomfort persists for 2 or more days;
- Headaches and dizziness appear;
- There is a need to wear sunglasses indoors.
Causes
Reasons may be:
- Psychological stress, stress, fatigue, lack of sleep;
- Pathologies of acquired and congenital nature;
- Taking medications, often provoked by antibiotics - doxycycline, tetracycline and diuretics - furosemide;
- Heavy strain on the eyes when a child sits at the computer for a long time and often;
- Wearing contact lenses that are incorrectly fitted;
- Tumors, traumatic eye injuries, foreign bodies.
The primary cause of photophobia will be congenital. A child with this pathology has no or low amounts of melanin - the disease is called albinism. Photophobia can develop with various eye diseases - conjunctivitis, keratitis, iritis.
If a child has acrodynia, the symptoms of photophobia will be pronounced. Acrodynia is a disease of the nervous system in which the following symptoms appear: the feet and hands turn pink and become sticky due to profuse sweating.
The child becomes sensitive to bright light. The next disease in which we observe symptoms of photophobia is endocrine ophthalmopathy.
Autoimmune type disease.
In case of injury or previous infectious diseases, paralysis of the motor nerve may develop. The symptoms of this disease are easy to recognize: the upper eyelid is drooping and the eye looks to the side, while the pupil is dilated and does not react to light, so a reaction to light occurs.
If photophobia is a concern on both sides, then we can state the fact of the cause of common diseases, for example, measles or rubella, and besides, with these diseases the temperature rises. If there are no other visible symptoms, then be wary, because in children such diseases can begin with these symptoms.
Photophobia is a painful reaction of the eyes to sunlight or artificially created light. In medicine, this condition is called photophobia.
The pathology is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the visual organs. A person constantly squints his eyes in any light, but in the dark the feeling of discomfort disappears. There are certain reasons for this.
In adults
Disturbances in the functioning of the body provoke photophobia of the eyes; the causes in an adult may lie in the following problems:
- eye diseases;
- albinism;
- eye injury;
- viral and infectious diseases;
- presence of a foreign body in the eye;
- mental disorders;
- brain damage;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- taking medications;
- stress, lack of sleep.
Working at a computer monitor for long periods of time is bad for your eyes. The mucous membrane dries out, increasing the load on the visual organ. All this provokes a fear of light.
Serious pathologies are indicated by severe pain in the eyes, headache, redness of the whites, and blurred vision. If you have these symptoms, you should immediately consult a specialist.
How to prevent the appearance of photophobia?
To prevent the occurrence of increased eye sensitivity to light, doctors advise following a daily routine. It is important that sleep is stable and complete: at least 7 hours for adults and at least 8 hours for children. Daily walks in the fresh air are also recommended, preferably at least 1-1.5 hours a day.
Maintaining personal hygiene of the organs of vision is also an important factor in preventing the occurrence of photophobia. This will eliminate the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory processes in the eyes. Another important component of prevention is a balanced diet. It is important that a person receives the required amount of vitamins, macro- and microelements from food.
With increased visual stress, it is worth regularly performing simple eye exercises every 30-40 minutes of working at the computer. Builders, drivers and representatives of other professions who are often outdoors during the daytime need to wear sunglasses with a UV filter.
On the Ochkov.Net website you can profitably buy contact correction products to improve vision clarity for myopia, farsightedness and other refractive errors.
Diagnosis and treatment
Since photophobia is just a symptom, if the disease that caused it is cured, the signs of photophobia will disappear. Never try to treat the disease yourself! Only a qualified specialist can diagnose and prescribe treatment. For infectious diseases, drops are usually prescribed that will help eliminate the problem in a few days.
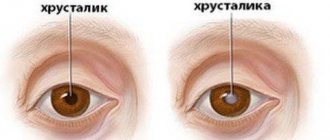
In case of poisoning with medications, the attending physician replaces them with other, weaker ones. Ophthalmologists diagnose the appearance of cataracts at the earliest stages, when a person is not yet aware of its presence. It can only be treated with surgery. The unsuitable lens is replaced with a transparent artificial one.
When going outside, wear sunglasses, try not to be in the sun for too long, do not sit at the computer for a long time, buy special contact lenses with a dark iris. They will transmit only the amount of light waves necessary for the human eye.
To exclude all organic brain injuries (intracranial hematomas, tumors and hydrocephalus), the patient uses MRI. If you suspect complications when bearing a child, it is important to donate blood for a biochemical test (urea and creatine) and urine, in which protein can often be detected, which indicates disturbances in the normal functioning of the kidneys.
The electroencephalogram is very important for assessing the rate of excitation of the cerebral cortex, determining the location of the ectopic lesion that causes epileptic seizures and fear of light. If a doctor diagnoses heleophobia, the patient visits a psychiatrist.
When conducting diagnostics, it is very important to exclude alcohol intoxication and drugs, as well as conduct tests for the presence of such substances in the patient’s blood.
There is no need to suffer from bright daylight at all before going to the doctor. To alleviate your general condition, you need to purchase special polarized sunglasses that will help reduce the amount of ultraviolet radiation reaching the retina. You also need:
- reduce the number of hours per day working at the computer;
- stop rubbing your eyes too much;
- use Vidixic drops, which are considered a good means of artificial tears;
- if there is purulent discharge in the eyes, it is best to use special drops with antibiotics or antiseptics Tobradex, Okomistin, chloramphenicol drops. With all this, the attending physician must carefully examine the patient, since purulent processes can also affect the deeper layers of the eye, to which the local agent simply will not reach;
- If photophobia appears due to a burn, bruise or injury to the eye, then the patient should be immediately provided with ophthalmological care. First, you should drip the eyeball with drops containing an antiseptic effect, and apply sterile gauze to the eye.
There is no need to wait long before seeking help from a treating specialist, otherwise such a seemingly insignificant reason can provoke the development of a malignant tumor in the brain, which will begin to progress rapidly.