Causes of pupil dilation
Of course, any anomaly in a person’s physiological state is perceived as a manifestation of a disease, but dilated pupils are not such a sign. According to scientific research, pupils can dilate when a person is in a good mood or is excited. In addition, the pupils dilate due to a reaction to light.
Stress or just a bad mood causes the pupils to constrict, but with positive emotions, a person’s pupils instantly dilate. For example, a woman’s pupils dilate as soon as a man who is truly interesting to her appears in her field of vision. This is a physiological reaction of the body.
In general, there are very specific reasons for pupil dilation, such as:
1. Insufficient lighting. 2. Lesions of the nervous system. 3. Mental conditions 4. Reaction to taking certain medications. 5. Retinal pathologies. 6. Brain tumors. 7. Glaucoma disease.
Glaucoma: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Glaucoma is an eye disease associated with increased intraocular pressure and impaired outflow of aqueous humor. As a result, visual field defects and marginal excavation (displacement, depression) of the optic nerve head develop.
We will try to answer in more detail the questions “What is glaucoma” and “How to treat it”, and also consider the main symptoms, causes and types of prevention of the disease.
Classification
Open-angle and closed-angle glaucoma
Depending on the angle of the anterior chamber, located between the cornea and the iris of the eye, there are:
- open angle;
- closed angle shape.
By origin:
- primary: formed due to deterioration of the outflow of aqueous humor.
- secondary: becomes a consequence of other eye diseases, such as cataracts, thrombosis of the central vein.
- combined: develops after ocular developmental anomalies or other body structures.
According to the age:
- congenital: occurs before age 3;
- infantile: child age 3-10 years;
- juvenile: up to 35 years;
- adult glaucoma.
Depending on the IOP (intraocular pressure) values:
- with increased IOP;
- normal pressure glaucoma.
Symptoms
The open-angle form does not appear in any way for a long time. It is often diagnosed during IOP measurement. And only in the later stages of the disease do symptoms characteristic of glaucoma appear.
The angle-closure form is characterized by the appearance of an acute attack, during which severe eye pain, nausea, vision becomes blurred, and the eye becomes extremely hard.
Symptoms of glaucoma in adults at an early stage
There are signs that should definitely alert a person.
They are divided into 3 groups:
- Characteristic of all eye diseases: the appearance of floaters before the eyes, rapid eye fatigue during visual stress.
- Inherent in glaucoma:
- vision becomes blurred at times;
- migraine-like headache,
- the appearance of rainbow circles when looking at the light.
- Early reliable symptoms:
- increased lacrimation;
- imaginary eye moistening: this sensation depends on an increase in IOP.
Causes
The cause of glaucoma is excessive accumulation of intraocular fluid (intraocular fluid). This leads to the fact that the pressure increases, and the optic nerve experiences compression, and its fibers die. Thus, vision is gradually lost over several years.
With angle-closure glaucoma, there is a sudden blockage of the iris channels, which prevents fluid from moving into the trabeculae. The pressure in the eyeball rapidly increases, taking on very high values, causing an acute attack. This is dangerous due to sudden loss of vision within 1-2 days.
Diseases such as diabetes and myopia can increase the likelihood of developing this disease. Taking corticosteroids increases the risk of optic nerve damage from glaucoma.
Treatment: can glaucoma be cured?
Unfortunately, this disease cannot be completely corrected. It causes irreversible damage to the optic nerve and remains with the person throughout his life. But high IOP must be combated, otherwise it will lead to blindness. In older people, such consequences are most likely, since with age the elasticity of tissues and their ability to recover are lost.
Most often, medical conservative therapy is used or various operations are performed.
Conservative therapy
It is most useful only in the early stages of the open-angle form, and is not so effective in the closed-angle form.
There are 2 groups of drugs with different mechanisms of action:
Group I: reduce the production of aqueous humor: miotics (Pilocarpine), α-adrenergic agonists (Epinephrine) and prostaglandins (Latanoprost).
Group II: improving its outflow: β-blockers (Timolol, Betaxolol) and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Dorzolamide, Brinzolamide).
In addition, in the case of advanced stages of the disease, combined agents are used: Fotil Forte, Glauprost, Kosopt.
Main stages of treatment:
- In the initial stages, the first choice medication is used. In case of ineffectiveness, change to another drug of first choice or may prescribe a combination drug.
- If the patient has contraindications to the use of the 1st choice drug, the 2nd choice drug is used.
- If a doctor prescribes combination therapy, the drugs must have different mechanisms of action.
- In case of long-term treatment, it is advisable to periodically change drugs.
Pupil dilation as a reaction to light
The human body has the function of protecting the retina from exposure to ultraviolet radiation, as well as various damages, because more than 80% of all information about the world around us is perceived through vision. Bright sun or strong artificial light causes the pupil to constrict. And vice versa, in twilight, the pupils begin to dilate. This happens due to the need to ensure clarity of vision.
In the dark, it is quite difficult for a person to assess the surrounding environment, so the eye muscles begin to focus, and the eyeball itself becomes somewhat wider. Interestingly, in the dark the pupil can expand up to 9 mm, although in normal conditions its diameter is 3 mm.
Classification of pathology
There are several classifications in which coloboma exists.
By time of occurrence:
- Congenital anomaly is the most common option. It may be hereditary or occur when the fetus is exposed to damaging factors. In this case, the embryonic palpebral fissure does not close and the integrity of the eye membranes is disrupted. A peculiarity is the combination with other eye defects and systemic lesions.
- Acquired coloboma. In this case, part of the membrane of the eye is removed surgically, for example, due to a tumor, destroyed due to injury, or replaced with scar tissue after inflammation.
The anomaly can be detected in different parts of the eye, and therefore varies in location:
- iris (most often);
- choroid (choroid of the eye); Chorioretinal coloboma is common, in which the anomaly also affects the retina;
- retina;
- ciliary (ciliary) body;
- lens (rare);
- vitreous body;
- optic nerve (rare);
- eyelids.
By prevalence:
- isolated – affects a specific department (iris, nerve, etc.);
- combined – several parts of the eye are involved;
- penetrating (or complete) - all eye membranes are affected;
- unilateral or bilateral defects (one or both eyes are damaged).
According to the classic description of coloboma, it happens:
- typical;
- atypical (a defect in the eye shell does not fit into the traditional description in nature or location).
Pathological causes of dilated pupils
The causes of dilated pupils are often symptoms of various diseases. As a rule, these are head injuries or some malfunction of the thyroid gland. When, in addition to dilated pupils, other symptoms of deterioration in well-being appear, for example, increased blood pressure, headaches accompanied by nausea or vomiting, you should immediately seek medical help. Only a specialist will determine the true cause of these symptoms and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The cause of temporary dilation of the pupils can be damage to the central nervous system - stroke or epilepsy.
Injuries to the eyes or head, with damage to the eye muscle, which is responsible for the correct functioning of the pupil, also causes its persistent dilation. In these cases, we are talking about a violation of the process of contraction and expansion. Pupil dilation also occurs under the influence of alcohol, narcotic substances, and psychotropic drugs. If these factors influence the dilation of the pupils, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment: physical and psychological.
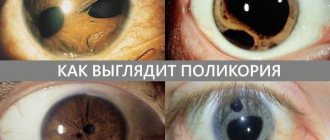
Prevention of polycoria
There are no specific methods for preventing polycoria. Nonspecific measures involve eliminating the influence of harmful factors during pregnancy and preventing infection of the fetus by pathogenic agents that can cross the hematoplacental barrier. Polycoria is a serious pathology that is predominantly congenital. The only way to cope with the disease is surgery. If surgical intervention is not possible, symptomatic therapy is performed.
Chronic dilated pupils
The causes of chronic dilated pupils are partial lesions of the optic nerves, after which the nerves lose the ability to adequately respond to light. People with a similar pathology experience pain when the light is too high. And in the dark they have problems with vision, which is why they have to be especially careful at night.
In addition to natural causes of dilated pupils, health problems often lead to this condition. That is why if your pupils remain dilated for quite a long time, you need to seek medical help without resorting to self-medication. And yet, the causes of dilated pupils in most cases are certain human characteristics, as well as the body’s physiological reactions to the external environment, as well as ongoing events.
In the medical department, everyone can undergo examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on the results, receive advice from a highly qualified specialist. The clinic is open seven days a week and operates daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Our specialists will help identify the cause of vision loss and provide competent treatment for identified pathologies.
You can make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by calling 8 and 8 (499) 322-36-36 (daily from 9:00 to 21:00) or using the online registration form.
Fomenko Natalia Ivanovna
Effective treatments
If the pathology is severe, a person may develop strabismus.
There may be no progression of pathology provided that the disease does not have complications. Due to the strong shift, which only causes discomfort, it is recommended to use lenses to correct the shape of the pupil. With a shift, vision often remains normal. But with severe forms of corectopia and the presence of other disorders, visual functions can be significantly affected, and there is a threat of the formation of amblyopia and strabismus. In such cases, surgery is performed. Corectopia often occurs with significant genetic pathologies and, within the framework of such deviations, has a progressive appearance. Then the patient is scheduled for a consultation with a geneticist.
If the shift occurs against the background of other diseases, the patient must undergo examinations to identify the root cause of this pathology. After diagnostic measures, adequate therapy is selected based on the results obtained. Such treatment depends entirely on the disease that causes the displacement. It includes both the use of medications and surgery.