Clinical picture
- Severe pain in the outer part of the upper eyelid.
- Swelling of the eyelid.
- Restricted mobility of the eyeball outward and upward.
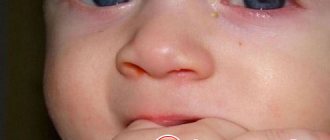
- The upper eyelid takes the shape of the English letter S in a horizontal position.
- Sharp pain when palpating the eye area.
- Retracting the upper eyelid allows you to see the enlarged lacrimal gland.
- Swelling of the conjunctiva of the eyeball.
- Diplopia.
- Headache.
- Fever, chills.
- Lymphadenopathy.
Diagnostics
Important for making a diagnosis:
- Anamnesis. Collection of complaints and analysis of the general health of patients, identification of traumatic injuries preceding the disease, chronic or hormonal pathologies.
- Inspection. Detection of characteristic external signs of inflammation of the lacrimal gland.
- Consultations with a general practitioner, venereologist, endocrinologist, hematologist, and infectious disease specialist regarding the course of underlying diseases.
- Instrumental studies: visometry, perimetry, biomicroscopy, ophthalmoscopy, computed tomography, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI.
- Laboratory tests: general detailed and biochemical blood tests, testing for tuberculosis, syphilis and other infections, blood for angiotensin (for sarcoidosis), blood for sugar, for coagulation, etc.
Treatment of acute dacryoadenitis
It is carried out only in a hospital setting and includes local and general treatment. Local treatment: antibacterial drops and ointments, glucocorticosteroids, NSAID drops. General therapy: oral and parenteral antibiotics, antiviral drugs, painkillers as needed. Aspirin is contraindicated in children with a viral infection due to the risk of developing Reye's syndrome. When acute phenomena subside, physiotherapeutic techniques begin to be used. Sometimes, to improve outflow, the lacrimal gland is drained with an incision through the conjunctiva. If an abscess or abscess forms, they are opened and drained without fail.
Timely seeking qualified medical help makes the prognosis favorable.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Diclofenac sodium 0.1% solution (Diclo-F, Naklof) is an NSAID for topical use in ophthalmology. Dosage regimen: the drug is instilled into the conjunctival sac, 1 drop 4-5 times a day. The duration of treatment with the drug is no more than 28 days.
- Indomethacin 0.1% solution (Indocollir) is an NSAID for topical use in ophthalmology. Dosage regimen: prescribe 1 drop into the conjunctival sac 3-4 times a day. depending on the severity of the condition. The course of treatment can last from 1 to 4 weeks.
- Sulfacyl sodium 10-20% solution.
- Chloramphenicol 0.25% solution (Levomycetin).
- Gentamicin 0.3% solution.
- Moxifloxacin 0.5% solution (Vigamox) is an antibacterial drug of the fluoroquinolone group for topical use in ophthalmology. Dosage regimen: adults and children over 1 year of age, instill 1 drop into the affected eye 3 times a day. Typically, improvement occurs within 5 days, but treatment should be continued for the next 2-3 days. If the condition does not improve after 5 days, the question of the correctness of the diagnosis and/or prescribed treatment should be raised. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the clinical and bacteriological course of the disease.
- Tobramycin 0.3% solution (Tobrex, Tobrex 2X) is an antibiotic from the group of aminoglycosides for topical use in ophthalmology. Dosage regimen: in case of a mild infectious process, the drug is instilled 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye (or eyes) every 4 hours. In the case of an acute severe infectious process, the drug is instilled every 30-60 minutes, as inflammation decreases, the frequency of instillations is reduced. drug.
- Tetracyclic 1% ointment (broad-spectrum antibiotic with bacteriostatic properties). Dosage regimen: a small amount of eye ointment is placed behind the lower eyelid 3-5 times a day.
Dacryoadenitis (inflammation of the lacrimal glands)
Dacryoadenitis is an ophthalmological disease characterized by inflammation of the lacrimal gland. As a rule, the disease rarely occurs independently; usually inflammation of the lacrimal gland is a complication of another disease. In ophthalmology, acute and chronic dacryoadenitis is distinguished.
The acute form is more common in children, the chronic form is observed in people of mature age. Treatment of dacryoadenitis is usually conservative, using anti-inflammatory drugs and physiotherapy. In severe cases, surgical intervention is required when an abscess forms.
Description and features
The lacrimal glands are one of the main elements of the accessory elements of the human visual apparatus. They belong to the tubular glands and visually resemble a horseshoe of two segments.
It is thanks to the lacrimal gland that the normal functioning of the eyeball is ensured.
They produce tear fluid, which cleans the surface of the cornea, lubricates it, moisturizes it, ensures clear images and protects it from minor damage.
Inflammation of the lacrimal glands usually occurs against the background of infectious processes of the visual apparatus. Dacryoadenitis is diagnosed in people of any age and gender.
Acute dacryoadenitis usually occurs in young children with weakened immune systems. The provoking factors in this case are:
- sore throat, scarlet fever;
- parotitis;
- flu;
- intestinal infections.
Acute dacryoadenitis, as a rule, develops against the background of other infectious diseases
Several other reasons for the development of chronic dacryoadenitis. A sluggish inflammatory process of the lacrimal gland can develop in the following cases:
- active tuberculosis;
- syphilitic lesions, gonorrhea;
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia;
- sarcoidosis;
- reactive arthritis;
- Wegener's granulomatosis.
In recent years, thanks to numerous studies, a connection has been established between dacryoadenitis and lymphomatous hyperplasia, which also affects the salivary, parotid and submandibular glands.
Symptoms and development
Symptoms of inflammation of the lacrimal glands in the acute stage appear clearly, it is impossible not to notice them. Typical complaints of patients with dacryoadenitis:
- redness and swelling of the eyelid;
- pain on palpation in the area of the lacrimal gland;
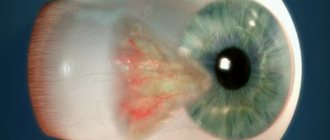
- as inflammation progresses, pronounced ptosis of the upper eyelid appears in the shape of the letter “S”;
- limited movement of the eyeball in all directions;
- “dry eye” syndrome due to decreased production of tear fluid by the inflamed gland.
It is almost impossible to miss the symptoms of acute inflammation of the lacrimal gland in a child.
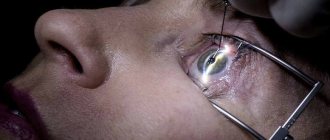
In the photo you can see exactly what an eye affected by acute dacryoadenitis looks like. In most cases, only one gland becomes inflamed; in the acute phase, general symptoms of intoxication are also noted:
- Increase in body temperature, sometimes very significant.
- Headache.
- Severe enlargement and pain of the lymph nodes.
Upper eyelid abscess
In the chronic form of the disease, the symptoms are the same, but they are less pronounced.
The eyelid over the affected lacrimal gland is moderately hyperemic, dense and hot to the touch, but the patient does not feel painful sensations on palpation.
Ptosis can be very mild; in some cases, there is a slight narrowing of the palpebral fissure. The movements of the eyeball are not impaired, tear fluid is produced in sufficient quantities.
It is noteworthy that in the chronic form of the disease, two eyes are most often affected.
Symptoms can be very mild for a long time, sometimes months and even years pass before the patient consults an ophthalmologist and begins treatment.
The most dangerous complication is the development of an abscess or phlegmon. In this case, the infection can spread to the brain tissue and cause meningitis.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
Inflammation of the lacrimal gland is easy to pre-diagnose through visual examination and questioning of the patient. Modern laboratory and instrumental methods are also used to collect a complete history:
- viziometry;
- tonometry;
- biomicroscopy of the eye.
For successful treatment of the inflammatory process, local and systemic drugs, as well as physiotherapy, should be used in combination
All these manipulations are needed more to identify the cause of dacryoadenitis and determine optimal treatment methods. Usually external symptoms are enough to diagnose an acute form of the disease. The diagnosis of chronic inflammation of the lacrimal gland is somewhat complicated. In this case, the following procedures may additionally be carried out:
- Ultrasound of the eyeball.
- MRI or CT, if differential diagnosis is required for suspected neoplasms in the structures of the eyeball.
- Fluorography or chest x-ray if tuberculosis is suspected to be the cause of dacryoadenitis.
- Mantoux test or Diaskintest for the same reason.
- Biopsy of lung tissue for suspected sarcoidosis.
- Serological tests.
- Biochemical study of saliva in cases of suspected Mikulicz disease.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the form of the disease and its etiology. Acute forms of dacryoadenitis are usually treated with conservative methods. What can an ophthalmologist prescribe in such cases:
- a course of antibiotic therapy, using products for external use (ointments, rinsing solutions), tablets for oral administration, intramuscular injections;
- physiotherapy – warming with dry heat, UHF;
- anti-inflammatory drugs in various forms;
- analgesics for severe pain.
Treatment of dacryoadenitis alone does not make sense if the underlying disease that provoked it is not treated. A comprehensive scheme is selected by an ophthalmologist together with a specialist - pediatrician, immunologist, phthisiatrician, venereologist, etc. As a rule, doctors recommend going to a hospital during treatment.
Surgery is required if inflammation has led to the formation of an abscess. In this case, under local anesthesia, the abscess is opened, the wound is cleaned, washed with an antiseptic, after which drainage is installed to ensure the outflow of residual pus and prevent re-suppuration. Next, treatment is carried out according to the standard regimen, always using antibiotics.
Important: if the chronic form of dacryoadenitis is difficult to treat, X-rays are used to irradiate the affected eyeball. This method is considered outdated, as it has a number of contraindications and side effects; it is not suitable for treating young children. But if there is no choice, then irradiation is carried out, strictly controlling the irradiation dosage.
Incidence (per 100,000 people)
| Men | Women | |||||||||||||
| Age, years | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + | 0-1 | 1-3 | 3-14 | 14-25 | 25-40 | 40-60 | 60 + |
| Number of sick people | 0.1 | 1 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 0.1 | 1 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
Symptoms of dacryocystitis in adults and diagnosis
In general, the manifestations of the disease in both children and adults are similar. The area of the lacrimal sac becomes noticeably red and swollen, and after some time purulent discharge begins from the eyes, as the nasolacrimal duct becomes clogged. When pressing on the inflamed area, a person experiences pain.
If the disease occurs in an acute form, the pain can be very sensitive. The tumor becomes denser, and after a few days it begins to soften and the swelling subsides. At this time, an abscess is formed, which can spontaneously open, and due to the outflow of pus from it, the swelling will decrease.
To diagnose dacryocystitis in adults, the doctor prescribes a general analysis of urine and blood, and a smear for bacterial culture. Rhinoscopy is required, which is necessary to exclude diseases associated with abnormalities in the structure of the nose. A canalicular test may also be prescribed, during which a Collargol dye solution is instilled into the patient’s eyes. After this, they look to see if the solution goes into the tubules. If this does not happen, then this is a clear sign of blockage of the ducts.