Causes of blepharitis
Blepharitis can manifest itself as an independent disease or as a consequence of general diseases of the body. The main reason for its occurrence is a decrease in local immunity. The disease can develop as a result of such factors:
- Anemia (anemia).
- Lack of vitamins.
- Infections of a chronic type, the focus of which is found in the nasopharynx or in the oral cavity.
- Allergic manifestations.
- Dust gets on the mucous membranes, causing them to become irritated.
- Disorders in the digestive system.
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays while in the sun or under other circumstances.
- Contact with various types of chemicals.
- Diseases of the visual organs (astigmatism, farsightedness, dry eye syndrome).
Blepharitis can be caused by staphylococcus aureus (aureus in adults and epidermal in children), lice, or improper eyelash growth.
Classification of blepharitis
Blepharitis varies in terms of development and characteristics. The following types of disease are distinguished:
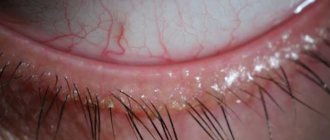
- Scaly (simple). Eyelashes stick together, sebaceous glands are secreted. The eyelids turn red. Their edges thicken.
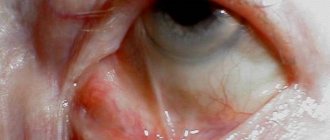
- Ulcerative. The eyelash bulbs are surrounded by pus. Ulcers form on the eyelids.
- Rosacea blepharitis. Gray-red nodules form on the skin in the eyelid area, containing a purulent rash (pustules). In some cases, the disease is accompanied by pink acne.
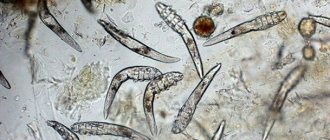
- Demodectic. Its cause is mites.
- Allergic. Formed as a consequence of an allergic reaction.
- Meibomian. Characterized by inflammation of the sebaceous glands located on the eyelids.
Depending on the area of the lesion, angular (in the corners of the eyelids), anterior marginal (edge of the eyelashes) and posterior marginal (deep lesion) blepharitis is distinguished.
It is worth noting: Posterior marginal blepharitis can cause damage to the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye.
Symptoms of the disease in photographs
Blepharitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
| White spots under the eyes | Redness | Purulent discharge |
| Discomfort in the eye area | Eyelash loss | Copious secretion of tears |
| Swelling of the eyelids | Peeling skin |
Sometimes, as a result of blepharitis, small blood vessels dilate. Because of this, nets or stars form on the skin. About 50% of cases of the disease are accompanied not by excessive production of tears, but by their lack. This manifestation is called dry eye syndrome. The disease may be accompanied by a fear of light.
It is worth noting: Symptoms of blepharitis are not always permanent. Periods of improvement (remission) may alternate with exacerbations of symptoms of the disease.
Let us consider the symptoms of the disease for some types of blepharitis separately.
Allergic
As a result of allergies, not only the eyelids become inflamed, but also the conjunctiva. The disease is accompanied by itching, pain in the eyes, swelling, flow of tears, and secretion of mucus from the eyes.
Demodectic
The first symptoms are itching and mucous discharge in the affected area. Later, inflammation, thickening of the eyelids and redness of the eyes appear. Dried mucus turns into scales.
Scaly
Sometimes accompanied by seborrheic type dermatitis in certain areas of the skin. The eyelids turn red. Their edges thicken. The skin does not bleed after removing the resulting scales. Dried sebaceous glands form yellowish crusts.
Ulcerative
Drying pus forms crusts. If they are removed, ulcers with blood and pus form. After some time, they are replaced by scars. Loss of eyelashes is observed.
Blepharitis rosacea
The eyelid becomes covered with pink blisters and pustules.
Paying attention to the symptoms, the ophthalmologist makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Allergic blepharitis - how dangerous is the disease?
The inflammatory process affecting the integrity of the skin of the eyelid negatively affects the condition of the epidermis. Constant tension on the skin of the eyelids, traumatizing it, leads to scarring. Scars and nodules appear on the surface of the eyelids, which will interfere with the normal growth of eyelashes. In addition to purely aesthetic problems, impaired eyelash growth can lead to constant irritation of the cornea, therefore, when treating eyelid blepharitis, it is important to perform the entire range of prescribed procedures.
What are the dangers of blepharitis and eyelid edema - possible complications:
- scarring of the eyelid skin, scars, thickening of the epidermis;
- chronic keratitis, conjunctivitis;
- fragility, loss of eyelashes;
- weakened vision due to excessive eye fatigue.
How to treat blepharitis to prevent complications of the disease? It is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions: take medications and use ointments, do not finish treatment ahead of schedule, even if the symptoms of an allergic disease are no longer felt. The treatment regimen for allergic blepharitis includes a set of measures aimed at alleviating symptoms and preventing various complications.
Treatment of the disease
Depending on the spread and causes of blepharitis, its treatment is prescribed. In any case, the process aimed at recovery involves the following stages of action:
- Cleansing the ducts of gland secretions.
- Eyelid hygiene.
To achieve results, at the first stage of treatment, warm compresses are applied to the eyes. The procedure is carried out 4 times a day for 10 minutes. The second stage of treatment involves cleansing the eyelids of crusts and dirt. The resulting scales and dirt are removed using cotton swabs soaked in diluted baby shampoo. Such measures help reduce the risk of possible complications.
For any type of blepharitis, the ophthalmologist prescribes topical antibacterial drugs. If these are drops, then they are used 3 to 6 times a day. They contain the antibiotic gentamicin. The ointment is applied to the affected areas no more than 4 times a day. Among its components should be erythromycin or tetracycline and chloramphenicol liniment.
The possible clinical picture and treatment of blepharitis are presented in this commentary:
Separate treatment is indicated for the following types of blepharitis:
- Demodectic. Treat for at least 1.5 months. The eyelids are treated for parasites. Measures are being taken to increase immunity and maintain hygiene rules. The eyelids are treated with alcohol tinctures from herbs such as calendula and eucalyptus.
- Infectious-allergic. It is treated with an eye ointment consisting of antibiotics and glucocorticosteroids.
- Angular. Treatment with zinc-based ointments and solutions is effective.
- Chronic nonbacterial blepharoconjunctivitis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for treatment. The most popular of them are Indocollir and Diclofenac.
- Scaly. The eyelids are treated with green paint. Syntomycin emulsions and fish oil are used for treatment.
During blepharitis, you should not use cosmetics until the disease is completely eliminated.
It is worth noting: Blepharitis requires a long course of treatment. Medicines are used throughout the entire path to recovery and for another month after the disease has been eliminated. This helps avoid recurrence of inflammation. Blepharitis is often accompanied by conjunctivitis, which must be treated separately.
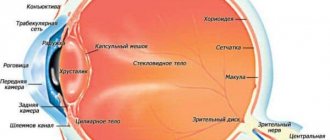
Diagnostics
Special studies • Bacteriological examination of eyelid discharge in atypical blepharitis • Biopsy for suspected cancer.
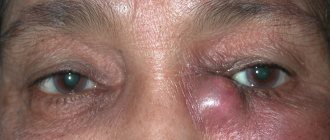
Differential diagnosis • Demodicosis of the eyelids - damage to the hair follicles of the eyelashes, sebaceous glands of the eyelids, caused by acne gland mites (Demodex folliculorum). For diagnosis, it is necessary to study the native drug (eyelash) immediately after collecting the material • Long-term inflammation and thickening of the edges of the eyelids suggest that the patient has squamous cell, basal cell carcinoma or cancer of the sebaceous glands, resembling blepharitis in appearance. The above tumors can also look like a stye or chalazion. The mortality rate for sebaceous gland cancer is 23%, and more than half of the patients have a clinical picture of benign inflammatory processes (chalazion and chronic blepharoconjunctivitis) • For any swelling or inflammation of the eyelids that has not resolved within a month with adequate therapy, an examination is necessary to detect a possible cancer • Stye and chalazion often complicate blepharitis. In this case, the manifestations of blepharitis recede into the background.
Contact lenses for blepharitis
In some cases, you will have to stop wearing lenses. Among them:
- Eye irritation and itching.
- Paraffin content in eye ointment used for treatment.
- The use of tear replacement medications that contain preservatives.
- Accompanying blepharitis with other diseases of the visual organs.
If such conditions exist, then wearing lenses may be accompanied by pain, discomfort, and irritation. In this case, it is better to give preference to glasses during treatment.
Treatment at home
To ensure a speedy recovery, in most cases it is enough to organize proper eye care. It involves following these rules:
- A warm compress is applied to the eyelids 4 times a day for 20 minutes. Each procedure involves using a clean material to apply to the eyes.
- Before and after bedtime, the eyelids should be cleaned with a swab dipped in a solution of baby shampoo.
- Artificial tears can be used to relieve discomfort.
At home, the following recipes are effective for treating blepharitis:
Blepharitis is not a contagious disease, but precautions should be taken when it occurs. You need to wash your hands more often and more thoroughly. You cannot use other people's towels. Such measures will not only help protect others from danger, but also reduce the harmful effects for the patient.
How to avoid relapse of allergic blepharitis
Why can allergic blepharitis recur? This will happen if there is contact with a past allergen or a new agent starts the process. To prevent the spectrum of allergens from expanding, it is necessary to increase immunity and maintain hypoallergenic hygiene. A new stage of the disease can be provoked by:
- cessation of therapy at the stage of weakening of symptoms;
- contact with an allergen, the emergence of a new allergen due to weakened immunity, unfavorable environmental conditions;
- intoxication due to an infectious disease, exacerbation of chronic diseases, systemic pathologies;
- stressful situations, hypothermia, overheating.
It is not worthwhile to constantly take antihistamines or use special drops to avoid relapse of the disease, since medications can also act as a new agent. But it is necessary to pay attention to the prevention of such a disease, since this really reduces the likelihood of recurrence of blepharitis.