Phytopsia: treatment
Those. Since photopsia are only symptoms and not an independent disease, this condition will go away on its own if the causes that caused it are eliminated.
As already noted, the appearance of photopsia is caused by various eye diseases that require the participation of an ophthalmologist
Therefore, it is extremely important to choose an eye clinic where you will really be treated professionally, without “dismissing” existing problems, and especially without “extracting” money
For multiple sclerosis and myasthenia, immunosuppressants, glucocorticoid hormones, and immunoglobulins are used. Endocrine ophthalmopathy with photopsia requires hormonal replacement therapy (for hypothyroidism, insulin-dependent diabetes). Hyperthyroidism is treated with Mercazolil. To improve vision, vitamins A and group B (pyridoxine, thiamine, cobalamin) are used. Surgery is performed for glaucoma and cataracts.
Photopsia is not a disease, but a symptom that can go away on its own. However, its chronic appearance indicates serious problems that require consultation with a doctor.
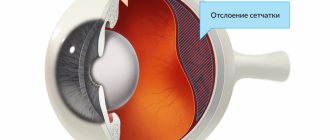
Therapy involves combating the primary pathology. The most widespread among ophthalmological pathologies is retinal detachment, which is treated using laser coagulation of the eye to fix the detached tissue.
Cataract involves removal of the damaged lens and implantation of an intraocular lens as a replacement.
Treatment of diseases such as hypertension, diabetes and chronic migraines requires the supervision of a specialized specialist.
Due to the fact that they are not an independent disease, they must be eliminated by getting rid of the root cause of their occurrence. There are no methods to help eliminate photopsia directly. Sometimes even treatment of the diseases that provoked them does not lead to getting rid of flickering.
Treatment methods in such cases may include the following measures:
- If extensive hemorrhages or massive retinal lesions are observed, vitrectomy is performed. This is a method of surgical intervention that involves the removal of blood clots or clouded areas of the vitreous body, fibrovascular cords;
- If a cataract is diagnosed, the clouded lens is removed and replaced with an artificial lens;
- If the cause of photopsia is chryoiditis, symptomatic therapy is carried out, which involves the use of antibiotics. As a rule, treatment is carried out in an inpatient setting;
- Macular edema, which provokes the appearance of flickering before the eyes, can be removed by conservative methods, for which anti-inflammatory drugs are used (for example, Kenalog). In some cases, laser therapy is resorted to, and sometimes surgery cannot be avoided;
- If photopsia is caused by migraines, it is necessary to stop their attacks, for which serotonin receptor agonists are used;
- If atrial scotoma is detected, the use of sedatives and medications that help normalize blood flow in the vessels of the brain is indicated. The representative of the latter is Cavinton;
- When diagnosing vertebral artery syndrome, drugs are used for treatment that help eliminate venous edema (for example, Nimesulide, Troxerutin). Medicines are also used to improve blood flow (Nicergoline, Cinnarizine, Vinpocetine). To prevent the occurrence of chronic ischemia in brain tissue, muscle relaxants (for example, Tolperisone) are used. Vitamin B, Ceraxon, and Actovegin are used for the same purpose.
During treatment, it is recommended to avoid excessive physical activity and stress.
It is extremely important to provide the patient with a favorable emotional atmosphere
In this case, special attention should be paid to the prevention and timely treatment of eye diseases, since they are the most common causes of photopsia. It is impossible to ignore photopsia - they can be a signal of the development of quite serious pathologies in the body or directly in the organs of vision
To determine the exact cause of the phenomenon and begin correct treatment, it is necessary to visit a doctor
You cannot ignore photopsia - they can be a signal of the development of quite serious pathologies in the body or directly in the organs of vision. To determine the exact cause of the phenomenon and begin correct treatment, it is necessary to visit a doctor
Provoking factors
Unpleasant manifestations are not an independent disease. Midges, sparks and other signs may be only a major or minor symptom.
The main provoking factors are the following.
- Vascular pathologies. Unpleasant flashes before the eyes can be observed with a disease such as choroiditis. The anomaly is an inflammation of the choroid of the organs of vision. Photopsia can also be provoked by blockage of the arteries or VSD.
- Inflammatory pathologies. Inflammatory processes: retinitis, chorioretinitis, and retinal rupture or detachment can lead to floaters and flashes before the eyes.
- Diseases of the cornea. Fuchs' dystrophy keratitis and other ophthalmological diseases can also serve as a provoking factor.
- Progressive glaucoma. Due to increased intraocular pressure, damage to the optic nerve occurs, which is the cause of visual abnormality.
- Cataract. The process of clouding the lens of the organ of vision leads to unpleasant manifestations of photopsia; the more the disease progresses, the more pronounced the visual abnormalities are.
- Neuritis. The inflammatory process of the optic nerve can be of two types. In the first (retrobulbar), the pathology affects the optic nerve head; in the second (intrabulbar), such damage is not observed. Neuritis can be caused by autoimmune, infectious or demyelinating pathologies.
- Hemorrhage in the retina of the organs of vision. Most often observed with mechanical damage to the organs of vision, hypertension, excessive physical exertion and elevated blood glucose levels.
- Various injuries to the organs of vision and brain. A foreign body in the eye and various brain injuries can provoke photopsia in various manifestations.
- Destruction of the vitreous body. Pathology is observed with vascular anomalies, dysfunction of the endocrine system, as well as metabolic disorders.
- Vitreous detachment.
- Toxic poisoning. Exposure to organophosphorus compounds negatively affects the organs of vision.
- Migraine. The duration of the outbreaks can vary from several minutes to 1 hour. Classic migraine is characterized by bilateral manifestations of photopsia.
- Atrial scotoma. Another name for this disease is ocular migraine. The main symptom of the pathology is the absence of a picture in some parts of the visual field and photopsia at the border of these areas.
- Diabetic renitopathy. This disease is a complication of diabetes mellitus and is characterized by an abnormal condition of the vessels of the eyeball.
- Cancerous tumors, mainly in the brain.
- Hypertonic disease. As a result of this disease, vascular spasm is observed, which leads to visual abnormalities.
- Macular edema. Pathology occurs as a consequence of surgical interventions in the organs of vision.
- Vertebral artery syndrome. This diagnosis is given to persons with developmental pathologies or dystrophic processes in the cervical spine. Photopsia can be observed with osteochondrosis (most often these are floaters and lightning, flashes are observed less frequently).
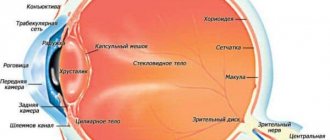
Most often, photopsia is observed due to damage to the retina and vitreous body. Visual abnormalities of cortical origin are observed much less frequently.
Treatment
Medication
Retinal detachment is accompanied by the death of photosensitive receptor cells that are responsible for visual acuity. Treatment with drugs will not work here, so you have to resort to surgery.
Surgical methods
The result of the operation depends on the stage at which it was performed. Currently, there are several options for surgical intervention, which are selected by a specialist depending on the situation.
Surgical methods:
- Photocoagulation using laser. A stream of laser beams is directed into the eye. The rays cause micro burns in those places where retinal detachment occurred. Scars form at the site of burns, which prevent fluid from accumulating and getting under the retina.
- Cryopexy. This method is also called freezing. To perform the operation, probes are used that freeze the retina at the sites of detachment.
- Vitrectomy (removal of the vitreous body). In order for the surgeon to gain convenient access to the retina, he can remove the destruction of the vitreous body. Thus, he will be able to eliminate damage to the retina.
- Pneumatic retinopexy. A small bubble of air is injected into the eye. It moves to the site of the retinal detachment and closes the tears and damage. This prevents liquid from accumulating there. To connect the detachment sites, the doctor can use laser photocoagulation or cryopexy.
- Sclerosis. For this purpose, a special elastic plastic or silicone is used, which is placed in the area of the outer layer of the eye. This method allows you to prevent further detachment and preserve the retina in its original state.
Surgical intervention (surgery)
Before resorting to surgical intervention, it is necessary to take tests (blood, urine, x-ray, electrocardiogram) and undergo diagnostics. You will need to check the condition of the retina and fundus of the eye. The ophthalmologist should check visual acuity and, if necessary, order additional tests.
Six hours before surgery you should not eat, but only if there are no contraindications.
Features of the procedure:
- During surgery. The patient is injected with anesthesia, which can be either local or general. It all depends on the method of surgery and the characteristics of the health condition. The operation lasts from two to four hours. When the patient wakes up after surgery, he will feel slight pain and nausea. In most cases, he can go home almost immediately.
- After operation. To recover, you must follow all the specialist’s recommendations. After the operation, a bandage is put on the eye, which cannot be removed until the doctor’s permission. Most often, the bandage is removed a day or a day and a half after the operation.
- For the next month after the operation, you should not go to the bathhouse or sauna, and try not to visit places with high humidity and temperature. Avoid getting water in your eyes, lifting heavy objects, and engaging in strenuous exercise. To monitor the recovery process or, if problems arise, to detect them in a timely manner, you must visit an ophthalmologist and follow all his recommendations.
Read about cataract surgery in the article.
Photopsia symptoms
Symptoms of photopsia include the appearance of light figures of various shapes and colors. The violation may also be accompanied by:
- headaches;
- increased blood pressure;
- fatigue;
- severe eye fatigue;
- dizziness;
- problems with the functioning of the autonomic and cardiovascular systems;
- pain in the eyes.
Most of these manifestations bring severe discomfort and create inconvenience in performing daily activities.
Diagnostics
Flashes in the eyes may be a consequence of developing neurological, vascular or ophthalmological disease.
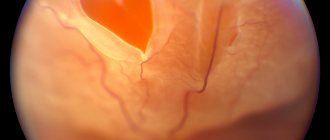
Typically, the examination begins with an ophthalmologist, who will examine all aspects of the visual system. The following procedures are expected to be carried out:
- initial examination using a slit lamp;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- computed tomography of the eye;
- Ultrasound;
- tonometry;
- fluorescence tomography;
- visual acuity test;
- coherence optical tomography.
This study provides a detailed, comprehensive clinical picture of the elements of the visual system and can confirm or exclude the development of ophthalmological pathology. Next, the necessary therapy is prescribed or the patient is redirected to a specialist in another field.
As a rule, an ophthalmological examination is only part of the diagnosis, which includes a wider range of procedures to determine possible concomitant diseases.
What diseases have this symptom?
Flashes, lightning and other unpleasant sensations in the eyes can indicate the presence of various diseases in the human body:
Arterial hypertension. High blood pressure causes spasms of blood vessels located in the retina of the eye. Hemorrhage occurs, causing visual function to decrease.
Hypotension. An insufficient amount of blood enters the vessels, which leads to flickering.
Cervical osteochondrosis. Due to the displacement of the vertebrae, the nerve endings are pinched and do not receive the required amount of blood.
Anemia. A decrease in hemoglobin provokes continuous flickering, dizziness, and blurred vision.
Diabetes mellitus. Due to increased glucose levels, the retina of the eye is affected, causing flicker. Vision diseases. Flickering can be caused by cataracts, glaucoma, and myopia.
Migraine. Flashes before the eyes are harbingers of the imminent appearance of a severe headache.
Eclampsia. This is late toxicosis, which occurs in late pregnancy.
At the first sign of a symptom, it is important not to delay visiting a gynecologist, as there is a high probability of a hypertensive crisis.
Vitamin deficiency or unbalanced diet. The flickering goes away after taking vitamin supplements and adjusting the diet.
Intoxication of the body
The optic nerve is damaged.
Causes of photopsia
Photopsia can be caused by various reasons. Moreover, against the background of one disease, various forms of photopsia can occur. Among the pathologies leading to the formation of this visual phenomenon, the following should be mentioned:
- Retinal pathology (retinitis, rupture or detachment);
- Disruption of the vascular system (arterial occlusion, choroiditis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.);
- Progressive course of glaucoma;
- Changes in the corneal lens;
- Cataract;
- Hemorrhage into the retinal substance;
- Optic neuritis;
- Migraine;
- Intoxication with various poisons;
- Detachment of the vitreous substance;
- Destruction of the vitreous body;
- Traumatic damage to the eye or brain itself;
- Infections of the vitreous or retina;
- Penetration of foreign bodies into the eyeball;
- Diabetic retinopathy;
- Hypertension;
- Tumor lesion of the eye;
- Macular swelling.
Phytopsia: treatment
Due to the fact that they are not an independent disease, they must be eliminated by getting rid of the root cause of their occurrence. There are no methods to help eliminate photopsia directly. Sometimes even treatment of the diseases that provoked them does not lead to getting rid of flickering.
Treatment methods in such cases may include the following measures:
- If extensive hemorrhages or massive retinal lesions are observed, vitrectomy is performed. This is a method of surgical intervention that involves the removal of blood clots or clouded areas of the vitreous body, fibrovascular cords;
- If a cataract is diagnosed, the clouded lens is removed and replaced with an artificial lens;
- If the cause of photopsia is chryoiditis, symptomatic therapy is carried out, which involves the use of antibiotics. As a rule, treatment is carried out in an inpatient setting;
- Macular edema, which provokes the appearance of flickering before the eyes, can be removed by conservative methods, for which anti-inflammatory drugs are used (for example, Kenalog). In some cases, laser therapy is resorted to, and sometimes surgery cannot be avoided;
- If photopsia is caused by migraines, it is necessary to stop their attacks, for which serotonin receptor agonists are used;
- If atrial scotoma is detected, the use of sedatives and medications that help normalize blood flow in the vessels of the brain is indicated. The representative of the latter is Cavinton;
- When diagnosing vertebral artery syndrome, drugs are used for treatment that help eliminate venous edema (for example, Nimesulide, Troxerutin). Medicines are also used to improve blood flow (Nicergoline, Cinnarizine, Vinpocetine). To prevent the occurrence of chronic ischemia in brain tissue, muscle relaxants (for example, Tolperisone) are used. Vitamin B, Ceraxon, and Actovegin are used for the same purpose.
It hurts to move your eyes: is it worth worrying about?
During treatment, it is recommended to avoid excessive physical activity and stress.
It is extremely important to provide the patient with a favorable emotional atmosphere
How to treat retinal detachment at home
Following a diet, performing eye exercises, and including infusions, vitamins, and herbal decoctions in the diet helps treat the disease at an early stage.
Gymnastics for the eyes
The purpose of the training is to increase blood flow to the center of the pathological process. The effect of the exercises is observed with daily exercise. Gymnastics example:
- While sitting or standing, move your gaze from one object to another, which is distant from the first by a considerable distance.
- Rotate your eyes in different directions.
- Move your gaze from one corner to another, outlining a diagonal.
- Look left and right, changing direction.
Do repetitions 5-7 times.
To increase blood circulation in the retina of the eye, you need to go outside and do gymnastics in the fresh air.
- Cover your eyes with your hands to reduce the effect of sunlight on the retina.
- Blinking frequently, gradually open your eyes.
The exercise repetition time is 3-5 minutes.
Foods and vitamins that improve vision
Green foods are rich in lutein and zeaxatin. These are important nutrients that act as light filters. To a greater or lesser extent, they are found in spinach, mango, broccoli, beans, grapes, and other vegetables. Orange products (sea buckthorn oil, apricots, tomatoes, pumpkin, sorrel, zucchini, carrots, chicory) contain carotene. This is a substance that has an antioxidant effect.
Reference. If you have visual impairment, it is helpful to eat orange and dark green foods.
Among the abundance of vitamins, the following are considered important for the visual organs:
- A - does not allow the development of dystrophy in the nervous tissue of the eyes.
- E - is responsible for cellular and oxygen metabolism, protein synthesis.
- C - does not allow the development of cataracts, serves as a shield against the action of free radicals.
- B1 - necessary for neuro-reflex regulation and metabolism.
- B2 - actively protects the retina of the eyes from UV rays.
- B6 - helps improve hematopoiesis and the functioning of the central nervous system.
- B12 - participates in metabolism and the construction of nucleic acids.
- Nicotinic acid is responsible for tissue respiration and the course of redox reactions.
Photopsia: causes of eye disease, symptoms and possible treatment, what it is, prevention
435 10/22/2019 5 min.
All people get spots before their eyes if they look at the sun or an artificial light source, such as a table lamp, without looking away for more than five seconds. This is one of the visual phenomena in which the visual organs incorrectly process information from the surrounding world. But it is not a disease.
It’s another matter when pointless objects (dots, lines, rings, etc.) arise due to pressure on the eyes with fingertips, sudden movement of the eyes in any direction, accommodation, or, in general, just like that.
In this case, they talk about the presence of problems with the retina or vitreous body (most often). Photopsia, as the pathology is called, makes itself felt both in daylight and at night.
Read below about the causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of photopsia.
Causes of pathology
The causes of photopsia may include ophthalmological pathologies, general diseases or external factors.
Visual ones include:
- Neuritis is an inflammatory process in the optic nerve.
- Cataract in the later stages is a partial or complete decrease in the transparency of the lens.
- Primary and secondary glaucoma in later stages – increased intraocular pressure.
- Ocular migraine.
- Neoplasms in the eyes.
As for the common causes, they include the following diseases:
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Osteochondrosis is changes in the cartilage of joints, mainly intervertebral discs of various parts of the spine.
- High blood sugar, diabetes mellitus.
- Injuries (mechanical damage) to the eyes or brain.
- Very serious, literally exhausting, physical activity.
- Headache. The duration of manifestation of objectless objects ranges from 5 to 45 minutes.
- Hypertension is high blood pressure. When it occurs, the microvessels of the retina or vitreous are blocked, which leads to “garbage” in front of the eyes.
These are not all causes of photopsia, just the most common ones. You can learn about the causes of double vision in this material.
Kinds
There are several types of photopsia:
- front sights, which are several dots and stripes that interfere with the normal perception of the surrounding world;
- sparks - illuminated points that quickly move from place to place;
- flashes - just like sparks, are illuminated and quickly move from place to place, these are shapes without clear boundaries, something like the consequences of a strong blow to the head on a hard object;
- lightning - zigzags of various sizes, brightness and location;
- a veil is like a curtain, making everything around barely visible.
This disease can also be divided into two groups:
- unilateral (on one of the eyes);
- bilateral (in both eyes).
The specificity of this pathology is that it can occur in a person with good, bad or no vision at all, day or night.
conclusions
- Photopsia is a phenomenon of the visual organs in which the patient sees spots in front of the eyes.
- This pathology can occur for ophthalmological or general reasons. It can also appear due to injury, retinal detachment, or excessive physical exertion.
- There is no cure for this disease as such. To eliminate symptoms, it is necessary to identify and eliminate its root cause.
Associated phenomena with photopsia
In many cases, lighting effects can also be accompanied by other signs, for example:
- headache and dizziness;
- fatigue, as well as intolerance to loud sounds;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- vascular dystonia;
- pain in the eyes when blinking.
At your appointment, the doctor will definitely ask you about all the manifestations that occur during photopsia in order to get a complete clinical picture. In addition, he will prescribe a full examination using modern equipment in order to most accurately determine the cause. As we can see, there can be quite a lot of them.