Diplopia belongs to the pathologies of an ophthalmological nature.
The disease is characterized by bifurcation of the image and disturbances in the functionality of the muscles of the visual apparatus.
The displacement of the image received by the visual apparatus occurs in several directions, according to the vertical, horizontal and diagonal axes.
The splitting is observed due to a failure in the projection of the resulting image by the visual apparatus. Often the pathology is accompanied by additional diseases, the elimination of which helps to cure the split. Progression of congenital diplopia is possible.
Reasons for development
The primary cause of diplopia is the displacement of the apple of the organ of vision in the orbital cavity. Factors that provoke the disease include:
- hematomas in the area of the eyeball;
- pinched muscle fibers;
- refraction of the wall of the orbit;
- tuberculosis-type meningitis;
- formations inside the skull;
- decreased functionality of the optic nerve;
- brain stem lesions;
- infectious pathological conditions;
- intoxication due to increased alcohol intake;
- anisometropia;
- carotid artery aneurysm;
- heterotrophy;
- neuroses;
- cardiopsychoneurosis;
- attacks of hysteria;
- botulism;
- Wernicke's syndrome;
- polio;
- complications after neurosurgical operations;
- myasthenia gravis;
- diabetes;
- botulism;
- anziometry;
- Lyme diseases;
- multiple sclerosis;
- congenital eye abnormalities;
- taking medications or antibiotics;
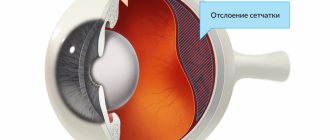
- retinal disinsertion;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- strabismus;
- due to surgical removal of cataracts.
Factors lead to pathological conditions causing diplopia:
- injuries to the visual apparatus;
- dysfunction of the brain;
- decreased tone of the eye muscles;
- changes in eye mobility;
- displacement of the eyeball.
Causes
Persistent double vision indicates visual impairment at the brain level. That is why the provocateurs of diplopia are head injuries, paralysis and paresis, myasthenia gravis, and previous neurosurgical operations.
Causes of binocular diplopia also include:
- endocrine myopathies;
- operations in the epibulbar region;
- developing strabismus;
- multiple sclerosis;
- infectious diseases with toxic development;
- cerebrovascular accident.
Ophthalmological diseases can lead to double vision. Frequent provocateurs of diplopia include astigmatism, corneal clouding, retinal rupture, and pathological changes in the lens. But ophthalmological problems usually provoke monocular diplopia - diseases rarely affect both eyes, although this also occurs in ophthalmological practice.
Temporary double vision can be caused by epilepsy, alcohol or drug intoxication, stroke, and infectious pathologies of an ophthalmological nature. With temporary diplopia, the prognosis is favorable. Sometimes it is possible to do without special treatment - vision is restored on its own after the provoking factor is eliminated.
Between the ages of one and five years, double vision can signal polio. Early vaccination prevents the spread of the disease, but children who are not vaccinated on time may be exposed to polio enterovirus. In addition to vision problems, other clinical manifestations of the disease occur that make it possible to quickly recognize the disease.
Possible complications
If diplopia is not treated, then over time the functions of the eyes are suppressed and vision is impaired, and cataracts may occur. Therefore, you need to promptly contact specialists to find out the causes of double vision and eliminate harmful consequences.
What is a cataract? It is a disease that obscures the lens. It is one of the most important structural components of the eye. In its normal state it is transparent. Streams of light pass through it without obstacles and are displayed on the retina. From there, the picture travels along the nerve to the brain.
The simplest explanation of what a cataract is is a disease in which the lens becomes opaque and vision is seriously impaired. If complications occur, complete blindness may occur.
The main symptom of this disease is a condition when a person sees all objects as if through foggy glass. Other manifestations are:
- Poor visibility in the evening.
- Impaired color identification.
- Double vision.
- High sensitivity to bright light.
Cataracts can only be cured through surgery. The cloudy lens is removed. Instead, a special transparent lens is inserted.
Without treatment, complications almost always develop. The most likely and common will be the transition of the disease to an advanced stage, when only surgical intervention can presumably correct the situation. However, even performing several operations at an advanced stage does not guarantee normalization of visual function.
In most cases, a complication of diplopia is a violation of the psycho-emotional state of pain. This is due to a deterioration in the quality of life and the inability to perform ordinary manipulations without help. The patient is unable to work, read, or write. In addition, at an advanced stage, the risk of injury increases due to severe vision loss.
Diplopia is a common ophthalmological disease, the causes of which are associated with many predisposing factors. Timely contact with a specialist and completion of a course of treatment helps eliminate the problem and prevent the progression of the disease.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Strabismus is a type of binocular vision disorder.
According to experts, the most common disorder of binocular vision today is strabismus. It consists in the deviation of the visual axes of one or simultaneously both visual organs from the point of direction of the object in question. Due to strabismus, there is a mismatch in the functioning of the eyes, and binocular vision needs correction. The most common type of pathology today is the so-called monocular strabismus, which doctors can also call dysbinocular amblyopia.
With this visual impairment, usually only one eye squints, the optical power of which is often reduced, and therefore it is not used by the brain, since it is practically impossible to read information from it. The second type of this disorder is called alternating strabismus, or, more simply, alternating. In this case, both organs of vision squint with the same deviation and can look in turn. Simply put, both eyes are used in the visual process, but alternately.
Classification
Depending on the root causes of diplopia and the course of the pathology, several of its varieties are distinguished:
Binocular diplopia
The most common disease. Due to the lack of parallelism of the visual axes, images overlap each other. As a result, a feeling of duality appears. When one of the eyes is closed, a clear picture is observed.
The causes of such diplopia are strabismus or displaced position of the eyeball. When children get sick, the brain turns off one of the organs of vision, which leads to an improvement in the picture. But at the same time, only one eye functions. In adult patients, such adaptation is observed very rarely.
Additionally, this type of disease is divided into:
- sensory orbital;
- mixed;
- strabogenic;
- motor.
Monocular diplopia
The resulting image is displayed by the brain in two different parts of the retina. When one eye is closed, the double vision does not disappear. This form is most often caused by congenital disorders or injuries of the visual apparatus. There are several subtypes of this disease:
- retinal;
- refractive;
- pupillary;
- aberrational.
What are the reasons for dizziness and double vision?
Depending on the symptoms of the disease, it is customary to distinguish between monocular and binocular types of diplopia.
Monocular diplopia
In this case, double vision persists, even if you look with only one eye and close the other. Often this process is associated with damage to the cornea or lens, as a result of which the image is projected twice onto the retina. In addition, it can occur with various inflammatory eye diseases, as well as cataracts, astigmatism and dry keratitis. Monocular double vision is less common than binocular double vision and has characteristic symptoms, so it can be diagnosed quite easily and quickly by specialists.
What eye diseases lead to monocular diplopia?
- Problems associated with the cornea: scarring, infectious diseases (keratitis), keratoconus (thinning and curvature of the cornea), pterygium (pterygium in the area of the inner canthus).
- Cataract. The most common cause of double vision is clouding of the lens. In this case, the symptom is especially pronounced when reading. Lens luxation. This pathology leads to visual distortions and double vision. In this case, surgical treatment is usually required.
- High degree of astigmatism.
- Dry keratitis. Drying of the cornea sometimes leads to monocular double vision. In this case, the use of special moisturizing drops is indicated.
Binocular diplopia
The most common is binocular diplopia, in which a person sees several images of one object only if he looks with both eyes at once. As a rule, if you close one eye, the double vision immediately disappears. Binocular double vision can occur due to various visual pathologies, one of which is strabismus. In this case, the patient experiences a deviation in the visual axis of one of the eyes, caused by weakening of the muscles that are responsible for the correct movement of the eyeball. If the oblique muscles do not work correctly, vertical double vision occurs, and if the rectus muscles work abnormally, horizontal double vision occurs. Many people are interested in what disease can cause binocular diplopia. Let's look at the common causes of this double vision.
Why can you see double?
- Strabismus;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland, which contribute to the weakening of the motor eye muscles;
- Hypertension and other vascular disorders - a sharp change in blood pressure or cerebral circulatory disorders (stroke);
- Diabetes mellitus - can cause damage to the nerves responsible for proper eye movement;
- Myasthenia gravis is weakening and wasting of the eye muscles due to a neuromuscular autoimmune disease;
- Multiple sclerosis is a pathology in the functioning of the central nervous system (CNS), in which the cells of a person’s spinal cord and brain are “attacked” by his immune system.
- An aneurysm is a pathology that occurs when part of an artery (blood vessel) dissects;
- Brain injuries (including concussion);
- Feverish conditions caused by various viral infections;
- Eye surgeries.
The image also doubles in cases of severe intoxication of the body caused by excessive alcohol consumption or nitrate poisoning. In addition, the symptom may occur due to taking certain medications (anticonvulsants, antiepileptics) and visual fatigue. In these situations, diplopia is temporary and goes away on its own over time.
Vertical and horizontal
The localization of the pathology determines the directions of image ghosting. The two most common options here are horizontal or vertical. There is another type - diagonal. But it is diagnosed extremely rarely.
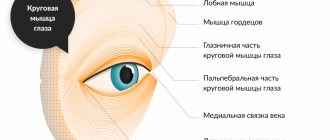
In this matter, the type of affected eye muscles is of decisive importance. So, if there is double vision in one eye horizontally, it means that the rectus muscles are damaged:
- Bottom.
- Upper.
- Lateral.
- Medial.
Items 1 and 2 are internal. Items 3 and 4 – external.
If there is double vision in one eye vertically, the pathology has affected the oblique muscles: lower or upper.
Both of them are internal.
Causes of the disease
Double vision in one eye can result from the following eye diseases:
1. Diseases of the cornea (keratitis, keratoconus, pterygium). In such cases, there is double vision in only one (sick) eye.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
2. Cataract. The lens becomes cloudy and this causes double vision. More often noticed when reading. Cataracts are treated surgically (the lens is replaced).
3. Astigmatism. Improve vision with corrective glasses.
4. Dry cornea. They save the situation with special drops.
5. Dislocation of the lens. He has been moved from his place, so he sees double. They resort to surgical intervention.
Causes of binocular diplopia (double vision in both eyes):
1. Strabismus is the main problem, and double vision is a concomitant one.
2. Diseases of the thyroid gland.
3. Hypertension, stroke. After a stroke, complete or partial loss of vision occurs. But this can often be avoided if you carry out medical therapy and be sure to do eye exercises. Eye massage and compresses are also indicated.
4. Diabetes mellitus. The nerves that move the eye are damaged. To be cured, you need to strictly adhere to the doctor’s prescriptions for the treatment of diabetes.
5. Multiple sclerosis.
6. Aneurysm. This disease is characterized by dissection of the blood arteries. If the blood vessels in the brain become stratified, double vision occurs.
7. Traumatic brain injuries, which damage the muscles of the eyes or the nerves that control their movements.
8. Myasthenia gravis. An autoimmune disease characterized by weakening of any muscles, including the eye muscles. The nerves that control muscle function are also damaged.
This is what myasthenia gravis looks like
9. Eye injuries when the lower wall of the orbit is affected or muscles are pinched. But how traumatic cataracts are treated and what the most effective means are are outlined here.
10. Tumors and hematomas in the head also sometimes “give” a double picture.
11. Head injuries with damage to the oculomotor nerve.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the following manipulations:
- study of pathological history;
- determination of hereditary predisposition;
- ophthalmological examination;
- vision level test;
- Coordimetry is carried out;
- Cover test;
- determination of visual acuity, refractive power of the eye;
- assessment of color perception.
Based on the data obtained, the type and root causes of diplopia are determined. Depending on the underlying causes of the disease, additional diagnostic measures are necessary:
- Determining the presence of additional symptoms: dizziness, vomiting, attacks of nausea.
- Neurological examination. The level of reflexes, the presence of ptosis, and the pupil's response to intense light are determined.
- Proserine test. The substance proresin is injected into the cavity of the eyeball, which helps determine myasthenia gravis.
- General analysis of biological material for blood cell and sugar levels. The manipulation allows you to exclude diabetic retinopathy from the causes of eye disease.
- Strabometry. Using the procedure, the presence of strabismus in the patient is determined and the level of displacement of the apple in the cavity of the organ of vision is measured.
- Computed tomography.
- Magnetic resonance examination. Allows you to obtain data on the functionality of the brain. Determines the presence of tumors, hemorrhages or injuries in a patient with diplopia.
- Consultation with a neurosurgeon.
How does binocular vision work?
Despite the fact that the eyes are a paired organ, they may have certain differences from each other. Otherwise, how can you explain the different optical powers, or even the color of the eyes? The image of objects on the retina of the eye is formed separately. Subsequently, this information is processed in parallel and transmitted to the brain. However, in order for this to happen, several conditions must be met, namely:
- symmetry of the generated pictures;
- finding images on the corresponding points of the retina;
- well-coordinated work of the eye muscles;
- location of the visual organs in one plane;
- the absence of any pathology of the retina, cornea or lens.
Combining two images into one is called fusion in ophthalmology. This process is carried out using a visual analyzer of the cerebral cortex. If a person has normally developed binocular vision, then he is able to see the world around him in a three-dimensional projection and can easily determine the distance between objects and their position in space.
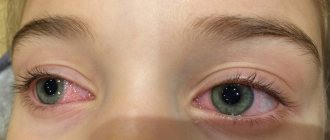
Symptoms of diplopia
The main complaint of patients with diplopia is double vision. In most cases, double vision of objects in the surrounding reality occurs when seeing with two eyes. This is how binocular diplopia manifests itself. Double vision can be partial and displayed only in a certain area of the visual field or complete.
Two images of the same object, resulting from diplopia, have different brightness and contrast. One of them is usually slightly offset vertically as well as horizontally and is located at a certain angle to the second image.
Due to progressive diplopia, the patient loses work skills. It may be difficult for him to do housework, drive, and sometimes just move around. To restore image clarity, a person with binocular diplopia has to close one of their eyes. For patients with another type of disease, monocular diplopia, this measure does not help.
The main symptom of diplopia is, of course, double vision. But it is also accompanied by dizziness, a mild form of disorientation and difficulty assessing the distance to objects. Moreover, if you close one eye, then, as a rule, these symptoms disappear.
Double vision - reasons
If the rectus muscles are affected, then the eyes see double in parallel. For problems with oblique muscles, a special effect is noted - one of the images appears to be higher than the other. Sometimes with diplopia, movement of the entire eye is difficult or impossible. A person can also hold their head in a special way, turning or tilting it towards the affected muscle. In this position, there is almost no double vision.
Symptoms of diplopia
If diplopia is a symptom of any other disease, then the main signs of these particular pathologies will be noted first. It is interesting that with botulism, double vision is observed almost immediately, but with diphtheria - only at the height of the disease.
The main signs of diplopia are double vision, accompanied by dizziness, as well as difficulty in assessing the location of objects. It should be noted that these phenomena disappear when one eye is closed.
The nature of diplopia is determined by the localization of the process. Thus, damage to the rectus muscles is accompanied by parallel double vision, and damage to the oblique muscles is characterized by the “location” of visible images one above the other. Deviation of the eye in the opposite direction from the affected muscle has varying degrees of severity.
In infectious diseases, vascular pathologies of the brain, meningitis, intracranial tumors and fractures of the base of the skull, the symptoms of diplopia are accompanied by clearly defined signs of the corresponding condition. With botulism, diplopia can be an early symptom of the disease, and with diphtheria, it develops at the height of the disease.
Manifestations of the disease appear almost immediately; there are no prerequisites for its development. The first sign will be double vision of objects when viewed close and far. This symptom is decisive; it is its severity and characteristics that help the specialist during diagnosis to determine the degree of neglect of the condition.
As the condition progresses, other manifestations appear. Dizziness and headache are the most common symptoms. They are associated with overstrain of the visual apparatus, when the patient tries to see the details of surrounding objects, but nothing works.
The headache may develop into a severe migraine, which is a sign that the condition is worsening. Additionally, the patient’s inability to navigate in space is noted, which also aggravates the condition. After some time, a person becomes helpless, because he is unable to perform ordinary household manipulations without outside intervention.
On the part of the organ of vision, there is increased fatigue, pain and burning in the eyes with prolonged strain. Visual acuity gradually decreases. If the disease affects a child, there is a decrease in academic performance, physical activity, and lack of interest in games and other entertainment. The long course of the disease provokes general disorders of the internal organs and systems.
The patient's performance decreases, he becomes irritable and lethargic. In addition, sleep disturbance may occur, manifested as drowsiness or insomnia. The patient's appetite worsens, he loses weight, and becomes weak. Against the background of such manifestations, the immune system is weakened, and other diseases may develop.
Double vision: reasons
If you see double, the reasons can be different - from completely harmless to those that can lead to death. Pathologies can be muscular or neurological, and a violation of the location of the eyeball (dislocation) can also affect it.
If double vision begins, the causes and treatment are interrelated. It is the reason that will influence the choice of subsequent therapy tactics.
- Cataract. The cause of this disease is problems with the lens. When the lens becomes cloudy, diplopia can also occur. It is especially visible when the patient is reading. This pathology is very common, especially among older people. Cataracts can be treated with surgery.
- Pathologies of the cornea. This may be infection (keratitis), scarring, pterygium, keratoconus. When a person closes the affected eye, double vision in such lesions disappears. You need to have surgery, possibly laser treatment.
- Astigmatism. It also causes double vision, which is clearly noticeable when a person looks at small print or numbers.
- Lens luxation. For various reasons, the lens can move from its usual place. This pathology is called a dislocation. Distortions of visual images and double vision appear. Only surgery will help correct the situation.
- Drying of the cornea. If it is definitely determined that the cause is a dry cornea, all treatment will consist of moisturizing it. There are special preparations for this, drops that are regularly dropped into the eyes.
- Strabismus. With this pathology, the visual axes cannot focus on a specific object, since the eyes look in different directions. Because of this, vision is seriously impaired, and double vision may occur. The pathology can most often be corrected through surgical intervention. In mild cases, special gymnastics will help.
- Vascular diseases, hypertension. With this disease, you often feel dizzy. This can also be a symptom of a stroke. This is the result of impaired blood circulation. Interruptions in blood flow also cause osteochondrosis. To improve the condition, it is necessary to undergo targeted treatment, and it is important to eliminate the underlying disease. If the case is severe, the patient may be admitted to a hospital.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland. They can provoke a weakening of the external motor muscles of the eye. In this case, drug treatment of the underlying cause will be required.
- Myasthenia. This disease is classified as autoimmune. It affects nerves and muscles, including the motor muscles of the eyes. They quickly become thinner and weaker. The eye muscles are directly involved in capturing visual images. If a certain part of them weakens, the eye may move unevenly. When a person looks in the direction from which the muscles have weakened, double vision may begin. With myasthenia gravis, the nerves that are located inside the skull stop stimulating muscles, including the eye muscles. Double vision and drooping of both eyelids are the main signs of myasthenia gravis.
- Graves' disease. It is also associated with disruption of the muscles that control the eyeball. With it, vertical diplopia is most often observed. A characteristic feature is that one image is located above the second.
- Pathologies of nerve fibers. The nerves that control the eye muscles can become damaged for a variety of reasons. This happens with multiple sclerosis, diabetes, cervical osteochondrosis, etc.
- Diabetes. In diabetes, not only the blood vessels are often damaged, but also the nerves that are responsible for controlling the movements of the eyeballs.
- Aneurysm. It appears as a result of arterial dissection. If the aneurysm is located in the area of the brain responsible for vision, diplopia may occur.
- Multiple sclerosis. This disease affects the central nervous system. The bottom line is that your own immunity begins to attack the cells of the spinal cord and brain.
- Neoplasms in the area of the brain, orbit. In general, problems with the brain often lead to vision problems. They are often accompanied by migraines.
- Injuries. TBI and bruises can cause damage to the muscles of the orbit (eye socket), as well as the nerves responsible for eye motility. Very often, diplopia appears precisely after a head injury. Strong impacts during an accident are especially dangerous.
- Intoxication (botulism, nitrate poisoning, alcohol poisoning). If a drunk person sees double, this means that his body is suffering from severe ethyl alcohol poisoning.
- General diseases (ARVI, influenza). Diplopia can occur with high temperature and fever. This is the result of poisoning the body with toxins. It is important to take the treatment of such diseases seriously. You should not rely only on folk remedies. They can be used, but only as an addition to the main treatment prescribed by the doctor.
- Intoxication from alcohol.
- Eye fatigue from prolonged reading, general fatigue.
- Strong blow and concussion.
- Taking certain medications (anticonvulsants, antiepileptics).
Not every disease manifests itself with a number of symptoms that are unique to it. Therefore, it is often necessary to reduce the entire symptom complex one to one in order to make the correct diagnosis.
For example, watery eyes, dizziness, pain, or double vision can occur in a number of conditions. The doctor's task is to correctly separate one from the other.
Manifestation of double vision
Despite the fact that the name of the symptom sounds unambiguous at first glance, in fact, double vision can manifest itself in two directions. On the one hand, this is a fuzzy vision of the object, and on the other, a double image.
Double vision can occur for a variety of reasons. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment after examination and a full examination. Therefore, when diplopia appears, you should immediately contact a specialist without self-medicating.
Monocular double vision most often indicates unilateral damage to the cornea, iris, lens or retina. With such double vision, you need to see an ophthalmologist.
If signs of damage to the nervous system appear, it is better to consult a neurologist. For nausea, vomiting and other symptoms of intoxication, the help of an infectious disease specialist is required.
Persons with various tumors of the orbit or eyeball often need consultation with an oncologist.
Examination of a patient with diplopia may include the following methods:
- determination of visual acuity and fields;
- slit lamp eye examination;
- performing direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy;
- electromyography, cordimetry;
- four-point color test;
- endophony test;
- CT, MRI, lumbar puncture, laboratory tests.
In children, diplopia most often indicates strabismus. This disease is very dangerous because it can lead to the development of amblyopia - the exclusion of one or both eyes from the visual act. This pathology is characterized by an uncorrectable decrease in visual acuity to tenths or hundredths. So, if double vision appears in a child, he should be immediately taken to an ophthalmologist.
Treatment
Therapy may contain measures necessary to eliminate the causes of pathology:
- taking medications that improve blood circulation in the brain;
- normalization of blood pressure levels inside the eye cavity;
- hormonal medications;
- plasmapheresis;
- in the presence of infectious lesions, antibiotic therapy is prescribed;
- surgery to eliminate tumors in the brain;
- medications whose effects are aimed at increasing neuromuscular conduction.
Treatment of diplopia is carried out depending on the form and level of the disease. Targeted therapy against the disease is based on several methods.
Prismatic correction
The method is based on wearing a special correction device. The product is manufactured taking into account individual characteristics, depending on the need to shift the picture. Glasses will activate the restoration of the quality of vision, and the double vision will disappear.
Occlusion
The method involves using a special bandage to eliminate one eye from work. Workers are left with an organ that has problems with functionality. With double the load, the restoration processes of the organ of vision are activated, which leads to recovery. The bandage must be worn for at least 2 hours daily.
Eye surgery
The most effective method of treating bifurcation. Especially if the pathology is triggered by injury, and the body cannot restore its functions on its own. During the intervention, the muscles are pulled to the back of the eye or the tendons are sutured to the sclera.
Eye exercises
In the initial stages of diplopia, the pathology can be eliminated with the help of special gymnastics. Exercise is an effective prevention of disease in healthy people. It is better to do gymnastics before meals or after a high load on the visual organs.
The frequency of exercises is up to 5 times. The best period for charging is when the first signs of eye fatigue occur.
The exercises are carried out in stages:
- Sit on a chair and close your eyes with your palms.
- Free your eyes in advance from means of contact correction of vision quality.
- Before charging, you need to close your eyes with your palms for a minute.
- Open your eyes and look along the vertical axis. In this case, it is necessary to hold your gaze for several seconds at the extreme point.
- A similar exercise, but only on the horizontal axis.
- Rest for a few minutes.
- Draw a circle with your gaze clockwise and vice versa.
- Using continuous movements, draw a square or triangle.
When performing exercises, the eyes can be either closed or open.
Traditional methods
Among the folk recipes, the most effective are:
- Take flower pollen 2 times a day, which can be purchased at a pharmacy. Dosage - 1 teaspoon. Before taking the course, you must make sure that there are no allergic reactions to pollen components.
- Grind valerian root and mix with lavender leaves. The ratios of the components must be equal. Sprinkle a tablespoon of the mixture with white wine (200 ml) and leave for 3 days. The place for infusion should be dark. The container must be shaken once a day. Take a tablespoon of the tincture before meals.
- Mix rose hips and viburnum in equal proportions. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture with boiling water (0.5 l) and boil for 10 minutes. Allow the mixture to cool, remove small particles by straining. Take the decoction orally, 1 spoon, 2 times a day.
Surgery
If conservative treatment of binocular duality does not produce tangible results, then surgical correction is prescribed. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Indications for surgical intervention are:
- significant degree of deviation;
- high risk of complications of diplopia;
- irreversible eye pathologies.
Treatment consists of tightening or weakening the muscles. Surgery for strabismus is performed in a similar manner. If both phenomena are present, then surgical correction will relieve both strabismus and diplopia. Restoration of the anatomical position of the eyes in case of injury is carried out no earlier than six months after the incident. In the future, functional treatment and prismatic correction are prescribed. Eye drops prescribed by a doctor, moderate exercise, and correction of visual stress can help shorten the rehabilitation period.
Surgical treatment is the main treatment for paralysis of the extraocular muscles. Plastic surgery of the external rectus muscle is combined with resection and recession of adjacent muscles. If diplopia is a consequence of a previously performed operation to eliminate strabismus, then surgical correction is not performed. The emphasis in therapy is on prismatic treatment and hardware influence.
Special mention should be made of occlusion. It is not a treatment method, but it allows you to remove annoying symptoms. One eye is closed, which returns the clarity of the observed picture. Three-dimensional perception disappears, and the “switched off” eye loses functionality over time. Therefore, the eyes alternate during occlusion.
Stages and degrees
Diplopia, the causes of which can be different, always develops in several stages, regardless of the type of disease. At the initial stage, symptoms are present, but not constantly. When overworked, the patient notes worsening vision and an inability to focus on an object. However, symptoms may disappear after rest.
The progressive stage is accompanied by severe double vision, a significant decrease in visual function, and rapid fatigue. Even after a long rest, the patient notes that vision does not improve. The advanced stage is characterized by the appearance of accompanying symptoms, the patient sees quite poorly, which affects the quality of life.
Most of the time he tries to stay at home, where all objects are familiar to him and unpleasant situations arise less often.
Symptoms appear with varying degrees of intensity. Sometimes the patient does not notice the rapid progression of the disease, but in most cases problems appear at the initial stage.
Varieties
The parallelism of the visual axes is disrupted for various reasons. But what all forms of the disease have in common is double vision. It is possible to “adjust” vision at first, but as the pathology develops, visual stress becomes increasingly difficult. A person not only cannot focus, he gets lost in space.
With binocular diplopia, disturbances can be temporary or permanent. In the first case, we are talking about symptomatic double vision. As soon as the main cause of visual impairment disappears, parallelism of the visual axes is restored. With persistent diplopia, specific treatment cannot be avoided. Often this disorder is congenital and can only be corrected surgically.
Binocular disorders are divided into:
- motor is the most common type. Caused by dysfunction of the extraocular muscles, often accompanied by strabismus;
- sensory – also associated with progressive strabismus, observed more often in childhood, due to a violation of the bifixation mechanism;
- mixed - a rare form that occurs due to unsuccessful surgical treatment and other effects on the eyes.
Based on the nature of double vision, binocular diplopia is divided into vertical, horizontal, homogeneous and cross. There are other criteria to characterize diplopia. Thus, complete and partial double vision, paradoxical and non-paradoxical, are identified. The last two types are classified as sensory diplopia.
According to etiology, the disease is classified as follows:
- strabogenic diplopia - appears against the background of strabismus;
- neuroparalytic – occurs when the nuclei are damaged and as a result of neuromuscular diseases;
- orbital – it is caused by injuries and tumor diseases of the orbit;
- oculogenic – develops due to bilateral aphakia and macular pathologies.
Prevention
To prevent diplopia, certain rules must be followed:
- adhere to a healthy lifestyle;
- minimize smoking;
- conduct daily walks of 1.5 km in the fresh air;
- use glasses on sunny days;
- control blood sugar levels;
- diseases of the visual apparatus are treated in a timely manner;
- monitor changes in pressure levels inside the eye cavity;
- undergo treatment in the presence of neurological pathologies;
- monitor thyroid hormone levels.
With the help of preventive manipulations, it is impossible to completely stop diplopia, but it is quite possible to significantly reduce the rate of its development.