Retinal abiotrophy refers to dystrophic pathologies caused by the gradual destruction of the retina with a decrease in the acuity of visual perception.
The disease leads to complete destruction of the retina and loss of basic functions. Sometimes it ends in complete blindness.
The disease occurs among patients 40–50 years old, and is less often detected in childhood and adolescence. Abiotrophy cannot be completely cured. You can only slow down the progression of the disease and weaken the clinical picture.
Causes of retinal abiotrophy
This condition is hereditary, that is, transmitted from parents. The transmission path of abiotrophy occurs according to the autosomal dominant and recessive type. The defective gene links to the X chromosome.
The cause of the pathological condition is more than 150 variants of mutations in several dozen genes. Almost ¼ of it is inherited due to mutations in the opsin protein gene.
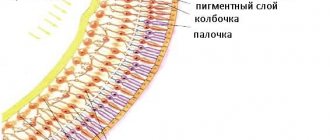
Due to damage to the material carrier of heredity, the pigment layer of the retina is destroyed. It contains cones and rods - these are photoreceptors, their largest concentration is located on the periphery of the visual organ.
Damage begins from the peripheral areas of the eye, gradually spreading to the center. The pathological process takes up to 10–20 years. Simultaneous damage occurs to both eyes equally.
Less commonly, pigmentary abiotrophy affects the right or left visual organ or affects a certain part of the retina.
The prevalence of the pathological condition ranges from 1–10 per 10,000 patients.
Treatment abroad
Patients often ask questions about the treatment of retinitis pigmentosa in Germany. This is one of the countries that uses the latest methods of treating this disease. At the initial stage, detailed gene diagnostics are carried out in German clinics. It is necessary to identify the type of mutation in each gene. Electroretinography is then used to determine the degree of damage to the rods and cones.
Depending on the diagnostic results, treatment is prescribed. If the disease is not associated with a mutation of the ABCA4 gene, then patients are prescribed high doses of vitamin A. Drug therapy is supplemented with sessions in a pressure chamber filled with oxygen.
Innovative methods for the treatment of retinal pigmentary abiotrophy are used. If the patient's eye damage reaches the stage of vision loss, then an artificial retina transplant surgery is performed. This graft is a prosthesis penetrated with many electrodes. They mimic the photoreceptors of the eye. The electrodes send impulses to the brain through the optic nerve.
Of course, such a prosthesis cannot completely replace a real retina. After all, it contains only thousands of electrodes, while the human eye is equipped with millions of photoreceptors. However, after implantation, a person can distinguish the outlines of objects, as well as bright white and dark tones.
Gene therapy is being carried out using retinal stem cells. This treatment method is still experimental. Scientists suggest that such therapy promotes the regeneration of photoreceptors. However, before treatment, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the patient and do a trial implantation, since stem cells are not indicated for all patients.
Classification of retinal abiotrophy
Ophthalmologists distinguish several classifications of abiotrophy. It is divided depending on the location of the disease and the type of inheritance.
Depending on the location of the disease, the following types of dystrophies are distinguished:
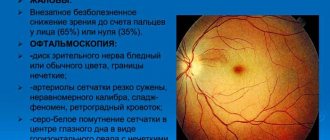
- Generalized. This form of the disease is characterized by a triad of symptoms. This is the deposition of pigment in the form of bone bodies, thinning of blood vessels, waxy pallor of the optic nerve head. Generalized dystrophy covers the entire retina. This includes Leber's amaurosis.
- Peripheral. This type of pathology is more common in myopic patients. The peripheral zone is not visible during normal examination, so diseases arise here, leading to further complications. The dystrophic process begins from the edges and affects the rods, resulting in impaired vision in the periphery. This type of dystrophy includes lattice, frost-like, and small cystic dystrophy, ruptures and retinoschisis.
- Central (macular degeneration) can be triggered by diseases of the cardiovascular system or endocrine system. This type of abiotrophy represents damage to the central part of the retina or macula. Examples are Best and Stargardt disease.
Depending on the type of inheritance, the disease is divided into the following autosomal recessive forms:
- early;
- late;
- dominant;
- adhered to the floor.
Doctors' recommendations
Persons who have been diagnosed with pathology need to make adjustments to their lifestyle. This not only increases the effectiveness of treatment of retinal pigmentary degeneration, but also serves to prevent the development of other ophthalmological diseases.
Doctors' recommendations:
Following these recommendations as quickly as possible helps stop the progression of the pathology.
Symptoms of retinal abiotrophy
Retina pigmentary dystrophy is manifested by various defects in visual perception. The clinical picture depends on the location of the degeneration.
General signs of abiotrophy:
- deterioration of daytime vision;
- decreased severity;
- scotomas;
- nyctalopia and hemeralopia.
The central form manifests itself as a disorder of color perception, a decrease in the acuity of visual perception. PVHRD is a sharp thinning of the retina. Often affects not only the retina, but also the adjacent vitreous body and the uveal tract. The generalized type of dystrophy is manifested by impaired visual acuity, refractive error, night blindness, decreased visual field and impaired color vision.
Clinical manifestations
Retinal pigmentary degeneration is one of the most dangerous diseases in ophthalmology. This is due to the fact that at the initial stage of development the disease is not accompanied by the appearance of severe symptoms. In most cases, patients consult a doctor only when they have all sorts of complications. The most common consequences of retinal pigmentary degeneration are glaucoma and cataracts.
The first warning sign is a condition characterized by difficulty navigating in low light conditions. It already indicates that a narrowing of the visual field has occurred.
Night blindness is the main alarming symptom. If it appears, you should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. Ignoring this sign leads to progression of the disease. Over time, peripheral vision disappears.
The advanced stage of the disease rarely proceeds without complications. At this stage, most patients develop glaucoma and cataracts. Central vision begins to slowly lose sharpness. The natural consequence is blindness.
Treatment of retinal abiotrophy
There is no specific therapy for abiotrophy. Doctors only take measures that can improve the patient’s condition and slow down degenerative processes in the eye.
Catheterization of the retrobulbar space
This treatment method involves inserting a conductor in the form of a metal tube with a tapered edge into the retrobulbar space.
Medicines are administered through an installed catheter. The quantity and frequency of administration are prescribed by doctors. This method of treatment is used for central pigmentary dystrophy, but is rarely used.
Long-term catheterization is performed on the operating table. The catheter is installed for up to 3 weeks.
Barrage of the macular region
The procedure is performed to treat certain forms of macular degeneration. Laser coagulants are applied in a circle near the central part of the retina.
The manipulation relieves swelling from the macula. Visual functions are restored partially or completely.
The procedure is performed for some wet forms of central retinal abiotrophy.
Photodynamic therapy
It is used to treat the central form of abiotrophy. The most effective treatment is for swelling in the macula.
Photodynamic therapy has shown positive results. After its implementation, the visual perception of many patients approaches normal. After a month of therapy, the thickness of the retina in the macular area may decrease by another 3%.
Proton irradiation
It is performed for tumors of the choroid. Radiation therapy shows good results. The physical properties of the proton beam allow you to achieve maximum comfort.
Cryotherapy
Involves cold treatment. Cryotherapy is contraindicated in acute infectious diseases, tuberculosis and mental disorders.
Dystrophy cannot be cured in one go. It is necessary to carry out 10–14 procedures, which are performed at intervals of 2–3 days.
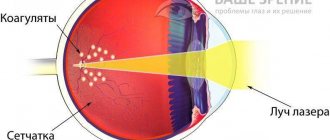
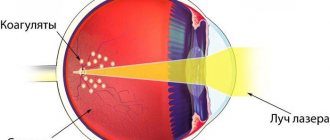
Peripheral preventive laser coagulation
The procedure is performed by a qualified specialist on an outpatient basis. Laser coagulation is well tolerated by patients. It involves influencing the retina along the edge of the dystrophic focus. Thanks to laser coagulation, retinal gluing is achieved at the points of exposure to laser radiation.
The procedure takes no more than 20 minutes. Its advantages:
- no recovery period;
- painless;
- the retina is strengthened;
- bloodless intervention.
More than 60% of patients undergo PPLC annually. This method has been used for more than 40 years and is considered effective. In ophthalmology it is impossible to do without laser coagulation for preventive or therapeutic purposes.
Drug treatment
Therapy with medications is based on the use of vitamin complexes, antioxidants, antiplatelet agents and drugs that improve the vascular wall.
Medication treatment is prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Drug therapy is carried out to improve nutrition and the condition of the retina.
Studies have shown that after a course of Retinalamin, visual acuity improved in 58% of patients. In most of these patients, peripheral vision expanded.
Treatment is recommended to be repeated 1–2 times a year. Retinalamin improves visual functions and reduces the total area of absolute scotomas after the first two courses.
Vasoconstrictors improve blood circulation in the retina. They also slow down degenerative processes.
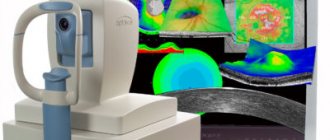
Diagnostics
If the first alarming signs occur, you should contact an ophthalmologist. The specialist will carry out primary diagnostic measures, consisting of interviewing the patient and collecting anamnesis.
In addition, the doctor’s task is to carry out an examination, including:
Based on the research results, the doctor indicates in the patient’s medical record the diagnosis of retinal pigmentary degeneration, code according to ICD-10, and also reflects the treatment regimen.
It is important to know that pathology is almost impossible to detect in children under six years of age. But in any case, the child should be shown to a doctor if he experiences difficulties while moving at dusk or in very dimly lit rooms.
Complications
The main complication in the absence of therapy is the degeneration of the pathological process into a malignant formation.
If the disease begins to develop after 30 years of age, there is a high risk of developing glaucoma, cataracts and edema of the central part of the retina.
The main danger with peripheral retinal abiotrophy is the occurrence of detachment. The dystrophy itself is not felt by the patient in any way, but when detachment occurs, serious surgical intervention will be required.
Prevention
It is impossible to prevent the development of dystrophy process, since the disease is hereditary. Scientists are now conducting multiple studies in the field of gene treatment. They are trying to find a way to restore damaged genes.
To identify the presence of a pathological condition at an early stage of development, you should visit an ophthalmologist annually. No doctor can prevent or completely cure the disease. There are ways to help only slow down the development of dystrophies.