Causes and methods of spread of the disease. Diagnostics
https://youtube.com/watch?v=tNZPv8jmq54
How the virus spreads:
- upon contact with a patient;
- by airborne droplets;
- close contact, or through hands.
Factors that can provoke the occurrence of the disease:
- vitamin deficiency - lack of vitamins in the body;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- weak immune system;
- metabolic disease;
- chronic fatigue.
The whole family can become infected and get sick with viral conjunctivitis, the virus spreads quickly, parents should know how to help the patient in a timely manner.
Manifestations
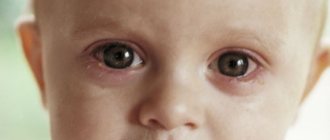
The incubation period of the disease is from four to ten days. Inflammation of the transparent membrane of the eye, combined with catarrh of the upper respiratory tract, is widespread in children and is common.
The symptoms are quite harmless at first glance:
- feeling that there is a speck in the eye;
- tearfulness;
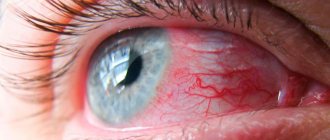
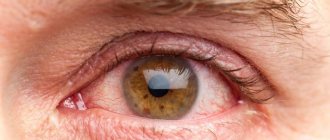
- redness of the eyes;
- First one eye leaks, then the other joins;
- the appearance of follicles on the conjunctiva of the eye;
- severe itching, the patient continuously scratches his eyes;
- the eyes swell very much, when looking at the light they hurt;
- the lymph nodes located near the auricle enlarge;
Appetite worsens, sleep is disturbed, the child becomes lethargic.
Self-diagnosis and self-medication are extremely dangerous! At the first symptoms of conjunctivitis, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Characteristic signs of inflammation appear very quickly. Against the background of colds, the patient’s general health suffers, the temperature often rises, weakness, and headache are observed. Viral conjunctivitis lasts a long time, as it is accompanied by a general reaction of the body. In order to avoid serious complications, inflammation of the cornea, it is necessary to closely monitor the child so that he does not scratch his eyes to prevent infection from entering and spreading into them.
How to prevent eye infections?
According to the form of its course, this disease is divided into acute, chronic, purulent, catarrhal, follicular, membranous. The nature of the development of the disease is determined by the number and intensity of symptoms. Acute conjunctivitis is characterized by pronounced symptoms.
The first signs appear within a day or two after a person is infected with bacteria, which most often cause this form of inflammation. Acute bacterial conjunctivitis is almost always purulent, that is, accompanied by the release of pus in a large volume. The chronic type of inflammatory process manifests itself moderately. The patient's eyes quickly become tired, the conjunctiva becomes noticeably red, and lacrimation is bothersome.
Catarrhal, follicular and membranous forms of conjunctivitis are observed in viral infections - adenoviral and herpetic. Inflammation of the catarrhal type passes without complications; within a few days after taking antiviral drops, the symptoms of the disease disappear. Follicular and membranous forms of conjunctivitis can be considered complicated.
These are the main forms of conjunctivitis. In some cases they are also stages. The longer a visit to the doctor is delayed, the more severe the illness becomes. The risk of complications increases. Treatment methods for conjunctivitis are determined not only by the nature of its development, but also by the type of inflammation. The most common of them are bacterial, viral, fungal, and allergic. We list their main symptoms and methods of treatment.
First of all, you need to adhere to preventive measures. To prevent infection if there is a sick person in the family, you should not use his personal belongings and personal hygiene items, especially his towel, soap, cosmetics, glasses, contact lenses.
Contact with the patient should be minimal. Since adenovirus is transmitted through airborne droplets, the patient should wear a gauze bandage to protect all family members.
You cannot use the patient’s medications (ointments, eye or nasal drops, pipettes). Even if you wipe the pipette with alcohol, the virus will not die. It dies only after boiling for 15 minutes.
If infection cannot be avoided, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. When treating ARVI, one should not forget about antiviral drugs for the eyes.
Temperature with conjunctivitis in an adult
When a person observes sour eyes and a hot forehead in himself or his child, does he worry about whether there is a fever with conjunctivitis, or are these signs of a more serious pathology? Inflammation of the conjunctiva often occurs as a result of infection. To successfully fight germs, the body raises its temperature. This is a completely normal reaction of the immune system to an irritant.
Causes of fever with conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis with fever can occur as an independent disease or develop against the background of infectious inflammation of the respiratory tract: ARVI, rhinitis, bronchitis and others. Depending on the pathogen, the following types of conjunctivitis occur:
- Bacterial - appears due to infection with staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus, gonococcus. Transmitted through shared household items and close contact. Bacteria are often brought into the eyes by dirty hands or from stale towels or pillowcases. The spread of infection is likely due to sinusitis.
- Viral is the most common type of conjunctivitis. It is transmitted by airborne droplets and can develop against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or a runny nose.
- Adenoviral - characterized by simultaneous inflammation of the throat and conjunctiva. Another name is adenopharyngoconjunctival fever (AFCL). Infection occurs from an infected person. The peak of the disease occurs in the spring.
Symptoms
A high temperature during conjunctivitis in adults and children indicates an acute course of the disease. When the conjunctiva is infected, the average incubation period lasts from 2 to 7 days. The following symptoms are observed:
- Severe redness of the eyes, swelling of the eyelids. The phenomenon is accompanied by itching and a feeling of sand.
- Tear production increases. Discharge appears. The eyes turn sour during sleep, the patient has difficulty opening his eyelids in the morning. A viral infection produces clear, thick mucus, a bacterial infection produces pus, and an adenoviral infection produces pus with mucus.
- Increased sensitivity to light and wind.
- General malaise, loss of strength, loss of appetite.
- AFCL always occurs together with pharyngitis. The throat turns red and hurts, the voice becomes hoarse, and a dry cough appears. Adenovirus infection also provokes the formation of films on the eyes.
- The lymph nodes, usually the ones in the air, become enlarged.
It is not difficult for an ophthalmologist to diagnose infectious conjunctivitis based on these signs. Sometimes, to select medications, it is necessary to do an analysis of pus and mucus from the eyes to accurately determine the pathogen. Additional consultation with a therapist or pediatrician is recommended to identify concomitant ailments.
Treatment of conjunctivitis with fever
For adults, concomitant infections should be treated to make a full recovery. The following drugs are prescribed locally:
- For a bacterial infection, apply ointments under the lower eyelid at night, and antibacterial drops during the day.
- At temperatures above 38.5, antipyretics based on paracetamol and ibufen are used. Adults can take Aspirin. It will not only reduce the temperature, but also improve tissue nutrition by thinning the blood.
- Anti-inflammatory drops are used to reduce hyperemia and relieve itching. When the mucous membrane is dry, artificial tears are recommended.
- Local and general vitamin therapy is prescribed, including calciferol, ascorbic acid and B vitamins.
It is useful to wipe pus from your eyes during the day with diluted aloe juice, chamomile and calendula decoctions.
If all the doctor’s recommendations are followed and the disease progresses well, treatment takes from 7 to 15 days.
Features of the disease in children
If a child has a fever and his eyes are purulent, he needs to be seen urgently by a doctor, especially when the baby is less than a year old. In children, the spread of infection occurs much faster and the likelihood of complications is higher.
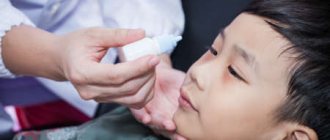
As first aid, the eyes are washed from pus with a swab of sterile gauze moistened with chamomile infusion or boiled water. If the temperature is above 38.5 degrees, it is brought down with Efferalgan, Paracetamol, Panadol. Albucid can be used topically. All other medications are used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Conjunctivitis and fever are common companions in children under 7 years of age. Often, every cold in a child occurs with inflammation of the conjunctiva, which goes away on its own after recovery. In this case, the eyes do not require separate treatment.
Prevention and treatment
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory lesion of the conjunctiva, which is also called the connective membrane of the eye.
Many eye diseases are reflected precisely in the state of this structure of the eyeball. It is an outer covering that protects the inner parts of the eye from external influences. In addition, the conjunctiva performs a secretory function, helping to moisturize the surface of the cornea. How is conjunctivitis treated, and how dangerous is this disease for the eyes? If treatment is prescribed in the first days of the illness, the patient is guided by all the doctor’s instructions and no unpredictable situations arise, then the inflammation goes away quite quickly, in a week or two. In some cases, the disease drags on.
This usually becomes a consequence of untimely prescribed therapy or a person’s irresponsible attitude towards their health. Many patients continue to go to work and stop taking medications, as a result of which conjunctivitis becomes chronic. Let's take a closer look at this pathology, find out its causes, symptoms, and types. Next, we will analyze the methods used to treat adult patients with conjunctivitis.
In children and adults, conjunctivitis occurs for the same reasons. Direct causative agents of inflammation of the eye mucosa are bacteria, viruses and fungi: staphylococci, gonococci, adenoviruses, herpes, etc.
It can also be caused by allergies. Sometimes the inflammatory process develops due to exposure to chemicals in the eye. These are the main factors that can cause connective membrane disease. There are also indirect reasons - a group of factors that increase the risk of developing conjunctivitis. These include:
- diseases and conditions that negatively affect the immune system;
- refractive defects - astigmatism, myopia, hypermetropia, presbyopia;
- ophthalmopathology of infectious or viral etiology - blepharitis, keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis;
- poor hygiene, including when using contact optics;
- mechanical injuries to the eyeballs, penetrating wounds;
- viral infections - influenza, measles, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, herpes;
- vitamin A deficiency, which makes the visual organs more vulnerable to environmental conditions;
- food and drug allergies;
- venereal diseases;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- frequent unsystematic use of eye drops.
During diagnosis, the doctor tries to determine the cause of the disease, its type and form. It depends on them how and with what they will have to treat conjunctivitis.
Inflammation of the ocular mucosa caused by bacteria is usually acute. The causative agents of the disease are staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, pneumococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other microbes.
Any acute conjunctivitis of bacterial origin is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- mucous and purulent discharge;
- severe itching and burning in the eyes;
- a feeling that a foreign body has entered under the eyelids;
- tearfulness;
- painful reaction to light;
- pain in the eyeballs when moving them;
- swelling and hyperemia of the conjunctiva and eyelids.
First, all these signs appear on one eye, and after a day or two - on the second. In rare cases, it is possible to avoid infection of a bilateral nature. Much depends on the patient's compliance with hygiene rules.
Other symptoms of the disease may also be observed. Some of them can help determine the cause of inflammation. With pneumococcal infection, red dots are observed on the conjunctiva, which indicate hemorrhages. With staphylococcal conjunctivitis, a lot of pus is released. The eyes have to be washed with special solutions several times a day. Mucous and purulent masses accumulate and flow over the eyelids.
Gonococcal inflammation of the eyes in adults is diagnosed extremely rarely. It usually occurs in newborns who become infected with gonococci from the mother while passing through the birth canal. Diphtheritic conjunctivitis is also usually detected in childhood, which develops against the background of diphtheria. Streptococcal infection also occurs in adults. Sometimes it occurs as a result of the spread of infection from the upper respiratory tract.
Acute bacterial conjunctivitis is highly contagious. It can be contracted through household contact. Bacteria live almost everywhere. You can accidentally get them into your eyes with dirty hands. For this reason, it mainly affects children who pay less attention to hygiene. Treating bacterial conjunctivitis in children and adults requires different medications. The former are less likely to be prescribed antibiotics. Otherwise, the principles of treatment are similar. What are they?
Treatment of conjunctivitis in adults, if it occurs in an acute form and is caused by bacteria, is necessary with the help of antibiotics and drugs with antibacterial action. Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, and Levomycetin are usually prescribed. All these products are prescribed in the form of ointments and eye drops. If the inflammation is caused by gonococci and meningococci, injections are given intramuscularly.
Treatment of adults with medications of this type, as a rule, does not cause complications. It is not always possible to predict the reaction of a child’s body to antibiotics, so they are prescribed to children only when the disease is severe.
If the patient consults a doctor a day or two after the first symptoms of conjunctivitis appear, he will not have to be treated for long. Depending on which bacterium caused the inflammation, treatment lasts 7-14 days.
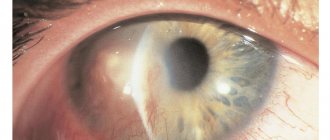
Often, the causative agents of viral conjunctivitis are herpes and adenoviruses. The first type of inflammation can be determined simply by such a characteristic sign as the formation of blisters on the eyelids. They cause itching, burning, lacrimation, blepharospasm, swelling, redness. Herpetic conjunctivitis can lead to blurred vision.
Most often this happens because the patient ignores the symptoms. When a viral herpetic infection develops, he continues to go to work, does not go to doctors, and therefore does not use medications or uses drugs that are in the home medicine cabinet. The lack of proper treatment can lead to conjunctivitis being complicated by another eye disease, for example, bacterial inflammation, keratitis or blepharitis.
The fight against this type of disease is carried out with the help of anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs: “Riodoxol”, “Acyclovir”. Antiherpetic ointments are also prescribed: Florenal, Acyclovir, Virolex. The bubbles are treated with a brilliant green solution.
This type of inflammation occurs as a secondary disease that develops against the background of a viral infection. First, a person becomes infected, for example, with ARVI, and then accidentally introduces viruses into the eye, which leads to an inflammatory process. The first symptoms of the disease are characteristic of all viral infections:
- weakness and drowsiness;
- fever and chills;
- runny nose;
- cough;
- headache.
After a few days or a week, signs of conjunctivitis begin to appear: lacrimation, itching, burning, etc. Unlike bacterial inflammation, viral inflammation is not accompanied by purulent discharge. The formation of a mucous film on the surface of the eye is observed.
Viral conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral drops. Antibacterial agents are also prescribed. They are necessary to prevent a bacterial infection from joining the underlying disease.
Allergies are usually a chronic pathology. But allergic conjunctivitis always occurs in an acute form. Many people mistakenly believe that it is seasonal. However, it can occur at any time of the year; the risk of the disease simply increases in the spring and summer. In case of an allergic reaction, severe itching immediately appears in the eyes. This type of inflammation is also characterized by uncontrollable lacrimation, photophobia and burning.
When treating, the first step is to identify the allergen and eliminate contact with it. Antihistamines are prescribed to relieve inflammation. In severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are used. Immunotherapy is always performed. An allergy is a consequence of the immune system perceiving a substance as hostile. Strengthening the immune system helps eliminate symptoms of the disease and recovery.
For all forms and types of this disease, moisturizing drops based on natural tears are prescribed. Their advantage is that they have a gentle effect and do not cause side effects even for allergy sufferers. Such drugs (Systane, Artificial tear) are suitable for adults and children.
When treating conjunctivitis, it is necessary to carefully observe the rules of hygiene. Apart from allergies, all the other diseases listed are highly contagious. You can avoid re-infection, infection of both eyes at once and the spread of infection in the family using the following preventive measures:
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap, especially after interacting with a sick person or contacting his things;
- Boil pipettes and ointment sticks every evening;
- use disposable napkins and utensils;
- Do wet cleaning at home every day and ventilate the room more often;
- After recovery, do not use contact lenses that you wore before your illness.
If you consult a doctor on time and during treatment follow all the previously listed rules, conjunctivitis will go away quickly and will not cause complications.
Fever with conjunctivitis is a controversial issue that often makes parents worry about the health of their child.
Conjunctivitis is a disease of the horny part of the eye, and is manifested by inflammation of the conjunctiva, i.e. mucous membrane covering the surface of the organs of vision. This shell is necessary in order to protect the surface of the eye from negative environmental influences. It also provides the necessary hydration.
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antihistamines;
- chondroprotectors;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory.
How is the treatment carried out?
Drug therapy
Taking an antibiotic is advisable in the case of sinusitis as a causative factor for problems with the visual organs. All medications must be prescribed by a doctor; self-medication is prohibited. If the disease is accompanied by fever, antipyretics should be taken. Antiviral drugs are used to treat the underlying disease and inflammation of the conjunctiva. If a runny nose and conjunctivitis occur with sinusitis, antibiotics are prescribed. In general, therapy for eye disease includes the medications shown in the table:
| Medication group | Name |
| Antiviral drops | "Ophthalmoferon" (recommended for children under one year old) |
| "Poludan" | |
| "Ganciclovir" | |
| "Aktipol" | |
| "Oftan Idu" | |
| "Gludantan" | |
| Antibiotics for eyes | "Tobradex" |
| "Floxal" | |
| "Signitsef" | |
| "Tsipropharm" | |
| "Levofloxacin" | |
| Ocular liniments | "Florenal" |
| "Tebrofen" | |
| "Bonafton" |
Other methods
A patient can take Amizon to eliminate the main cause of his condition. Together with conjunctivitis therapy, the underlying disease should be treated in the following ways:
- Use antiviral agents - “Amizon”, “Amiksin”, “Novirin”, “Remantadine”, “Erebra”.
- When your throat hurts, do inhalations with essential oils of lavender, bergamot, and tea tree.
- If your temperature rises, take Nurofen or Paracetamol.
- Drink more to prevent dehydration and flush out toxins.
Classification and symptoms
Conjunctivitis happens:
Bacterial
The lion's share of the disease is conjunctivitis of bacterial origin. There are a lot of causative agents of this type of disease, but as practice shows, the main ones are pneumococci, gonococci, streptococci, and staphylococcus. Bacterial conjunctivitis is contagious and is transmitted through household objects
Therefore, it is very important to provide the patient with individual personal hygiene items. The development of the disease occurs in one to two days
Symptoms:
- temperature;
- redness of the sclera;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- purulent discharge from the eyes;
- itching;
- lethargy, lack of appetite.
A characteristic sign of bacterial conjunctivitis is redness of each part of the conjunctiva and purulent yellowish nitrous eyes after sleep. Body temperature can rise slightly to 37 degrees, or can reach 39 degrees. To prescribe effective therapy, the doctor prescribes a referral for bacterial culture of pus from the eyes to identify the pathogen, as well as sensitivity to the antibiotic. Therapy mainly involves using antibiotic ointments and eye drops for two weeks. Bacterial conjunctivitis is dangerous due to possible damage to the cornea of the eye and the development of bacterial keratitis.
Viral
Virology includes about one hundred and fifty pathogenic viruses, but the most interesting thing is that most of them affect the organs of vision. The causative agents of viral conjunctivitis are viruses, the most common of which are: enterovirus, herpes simplex, rubella, measles, and herpes zoster. This type of disease is contagious, transmitted by airborne droplets or through household objects by getting infected tears or contaminated nasal fluid from a sick person to a healthy person. Symptoms:
- temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- tearfulness;
- thick mucous discharge from the eyes.
A characteristic sign of viral infection is damage to both the right and left eyes. In the first hours of infection, body temperature rises slightly to 37-37.5 degrees, but after ten hours it rises to 39 degrees. For treatment, the doctor prescribes antipyretics and antiviral drugs.
Allergic
It is difficult to find a person who is not allergic. One of the ways allergies can manifest is conjunctivitis. The disease occurs seasonally or continuously, and is classified as acute, subacute and chronic conjunctivitis. Symptoms:
- redness of the sclera;
- itching;
- tearfulness;
- thick mucous discharge from the eyes;
- purulent discharge from the eyes.
This type of disease occurs without fever, since the cause of the disease is an allergy. Most often accompanied by rhinitis. In the advanced stage, photophobia is added to the symptoms. Treatment is complex (topical antihistamines, cromoglycic acid derivatives, artificial tears). Allergy is an individual disease. One of the radical methods of treatment is considered to be allergen-specific therapy (introduction of an allergen followed by an increase in dose until the body gets used to this allergen). Thanks to therapy, a person does not have to isolate himself from the allergen all his life, that is, it makes it possible to live the normal life of a healthy person.
Adenoviral or varingoconjunctival fever
It is transmitted by airborne droplets and affects the eyes and nasopharynx. Often occurs against the background of epidemics; children are at risk. The first signs of the disease are fever (lasts from four to ten days, rises to 39 degrees) and the manifestation of rhinovirus infection. First, one eye is affected, and after two or three days - the second. Symptoms:
- temperature;
- purulent discharge from the eyes;
- sore throat.
The doctor prescribes complex treatment (antiviral drugs, instillations, antibacterial drops, ointments, antihistamines), since a single drug to combat adenoviruses has not yet been created. Full recovery after drug therapy occurs within a month. There is a possibility of developing dry eyes, so artificial tears are additionally prescribed for prevention.
In newborns
A newborn baby who has not yet had contact with anyone may also experience conjunctivitis. In this case, all the blame falls on his mother, who did not treat the infection in a timely manner. The baby could become infected both in utero and during childbirth (while passing through the birth canal). In rare cases, infection occurs due to the fault of medical staff. The severe discomfort that the child experiences causes the baby to constantly cry, which causes the body temperature to rise even more.
Fortunately, this pathology is detected and treated directly in the maternity hospital, which means that the baby will be under the supervision of specialists. The child is prescribed eye rinsing (with saline solution, Furacilin solution, chamomile decoction), massage of the nasolacrimal duct (the technique must be shown by a nurse), instillation of drops or ointment. In case of hyperthermia, the baby may be prescribed antipyretics (in the form of intramuscular injections, or orally in the form of a powder dissolved in water).
Useful video
From this video you will learn about the symptoms and treatment of conjunctivitis:
It is very important to understand that such a seemingly harmless disease as conjunctivitis can cause quite serious complications - up to and including complete loss of vision. Experts know of cases where the disease provoked the development of meningitis and other dangerous pathologies in children.
Experts know of cases where the disease provoked the development of meningitis and other dangerous pathologies in children.
In adults, advanced stages of conjunctivitis can cause purulent inflammation of the eyeball, retinal detachment, and cataracts.
Therefore, at the first symptoms of conjunctivitis, it is necessary to consult a doctor and begin treatment, otherwise the disease may become chronic, occurring with periodic exacerbations, which are much more difficult to treat.
Author of the article
Ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist), 17 years of experience, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material and the author!
(1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Loading…
What diseases can manifestations signal?
Symptoms of a runny nose and inflammation of the conjunctiva can occur in many diseases. Typically these diseases have a bacterial, viral or allergic etiology:
- If you notice that your child has pus coming out of his eyes, this is most likely a bacterial pathology.
- Redness, irritation, but the absence of purulent secretion indicates the allergic nature of the pathology.
- The combination of conjunctivitis and pharyngitis indicates an adenoviral infection.
Measles
One of the most serious infections, which mainly manifests itself in children, is measles. Measles has a high degree of infection; at the first symptoms of the disease, the patient complains of fatigue, a slight cough, and his throat begins to turn red.
Further development of the disease entails a rise in body temperature, the child begins to feel body aches and severe headaches. Symptoms of rhinitis quickly begin to form with copious discharge of pus.
Gradually, the little patient begins to wheeze, and the cough becomes dry and frequent. To all of the listed symptoms, swelling and redness of the eyes, increased tearing and purulent discharge from the eyes are added. In some cases, photophobia occurs.
Reference. The appearance of the child also changes: a puffy face appears, the areas of the eyes, nose and lips swell.
ARVI
Viral pathologies of the upper respiratory system (ARVI) are most often associated with adenovirus. Typically, such diseases develop very quickly; the incubation period in children is no more than 7 days. The disease is acute and often affects not only the nasopharynx, but also the ocular conjunctiva.
There are three forms of adenoviral rhinitis and conjunctivitis:
- catarrhal (inflammation is minor);
- membranous (the mucous membranes of the child’s eyes twitch with a thin film);
- follicular (small blisters appear on the mucous membranes).
In addition to a runny nose and inflammation of the eyes, during the course of an acute respiratory viral infection, a child’s body temperature may rise (up to 37-38 degrees), the lymph nodes in the ear area may become inflamed, and a dry and frequent cough may appear.
Allergic rhinitis
The symptoms of allergic manifestations will depend on how quickly the body reacts to irritants, as well as on how high the concentration of these irritants is. The most common form of allergy is allergic rhinitis.
This form of rhinitis develops almost at lightning speed (a couple of minutes or a couple of days is enough - it depends on the type of allergen). Rhinitis, in turn, may be accompanied by symptoms of conjunctivitis.
Common symptoms:
- nasal congestion;
- mucous discharge from the nose (runny nose);
- repeated sneezing;
- profuse lacrimation;
- burning sensation under the eyelids;
- redness of the mucous membranes;
- itching in the eyes (sometimes unbearable).
Against the background of all the listed signs of allergy, symptoms of atopic dermatitis (redness and itching of the skin, small rashes, peeling) may also develop.
Diphtheria
This disease is characterized by a one-sided course. It is usually accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes (under the jaw and near the ear). The complicated course of the pathology is accompanied by an increase in body temperature (up to 39 degrees and sometimes higher), headache, and general weakness. To accurately establish diphtheria, you should examine other target organs that this disease affects (nasopharynx, larynx, skin).
Expert opinion Slonimsky Mikhail Germanovich Ophthalmologist of the highest qualification category. Has extensive experience in diagnosing and treating eye diseases in adults and children. More than 20 years of experience.
With the diphtheria type of conjunctivitis, the patient complains of swelling and hardening of the eyelids (sometimes they cannot even open their eyes). On days 3-5 of the disease, the eyelids become softer, and a purulent secretion with mucous impurities appears. When you open the palpebral fissure, you can notice gray films that form in the area of the cartilage and transitional folds. There is redness in the eyes, and there may be fluid coming out of the nose.
Gonorrhea
Gonococcal ophthalmia has recently been reported rarely in children. The disease occurs with copious purulent discharge and acute edema. It is especially hard for newborns, whose infection occurs through the birth canal of a sick mother.
The course of gonoblennorrhea occurs with bleeding of the conjunctiva, sometimes purulent discharge from the nose. The child may completely lose vision.
Treatment of pathology should be immediate and supplemented by repeated monitoring of the condition based on the results of bacteriological tests. Prevention of severe forms of the disease in newborns is carried out with drops containing a small concentration of erythromycin.
How does chlamydial conjunctivitis begin?
Chlamydial conjunctivitis has other names. Doctors may call this disease ocular chlamydia or ophthalmochlamydia. All this is the same disease, which occurs due to damage to the visual organs by chlamydia. It affects adults more often than children. Chlamydial conjunctivitis usually occurs against the background of chlamydia of the genitourinary tract.
The disease occurs due to the entry of an infectious agent into the conjunctival sac from the genitals. This can occur due to the use of hygiene items contaminated with sexual secretions, such as towels. Often, a carrier of genitourinary chlamydia can not only become infected with chlamydial conjunctivitis themselves, but also infect their partner with it.
- severe swelling;
- a burning sensation in the eyes;
- infiltration of the mucous membrane of the eyes and transitional folds;
- copious discharge of mucous or purulent exudate;
- increased lacrimation;
- photophobia.
In adults, symptoms of this pathology may appear when visiting public baths or swimming pools.
Often the disease is accompanied by lymphadenitis - damage to the lymph nodes. Or eustacheitis - an inflammatory lesion of the auditory tube. The main medications used to treat chlamydial conjunctivitis are antibiotics of different groups. It can be:
- macrolides;
- fluoroquinolones;
- tetracyclines.
Local therapy is also carried out at the same time. It involves the use of antibacterial eye drops, for example: Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin. Doctors often prescribe the use of ointment applications. For this purpose, tetracycline or erythromycin ointment is used.
Folk remedies
How to treat conjunctivitis in children using traditional home methods? Decoctions and infusions of herbs are used to treat sore eyes, but they do not replace medications. Typically used to wash the eyelids:
- dill water;
- chamomile infusion;
- cornflower flowers;
- cumin seeds;
- parsley casting;
- cucumber pulp;
- calendula flowers;
- infusion of birch leaves;
- a cup of tea;
- aloe juice
Chamomile and dill
Chamomile decoction is good at cleansing eye tissue from contamination, soothing irritated mucous membranes and destroying pathological microorganisms. A pinch of dry inflorescences is poured with boiling water in a ceramic cup, covered and allowed to stand for 25-27 minutes. Then the solution is carefully filtered through several layers of sterile gauze (or cotton wool) to prevent grass particles from entering. Wash the eyelids with this solution using cotton pads or sterile gauze.
Dill water is prepared from dry seeds (bought in gardening stores or pharmacies). Powdered seeds (1 tsp) are poured with boiling water (a cup) and left until cool. Eyes are washed with filtered water or lotions are made.
Aloe and cornflowers
Aloe juice disinfects eye tissue well and also helps eliminate purulent discharge. To prepare a solution with aloe for washing, you need to cut off a thick leaf of the plant and rinse well with boiled water. Next, the juice is squeezed out of the leaf, filtered and diluted with warm boiled water (take 10 parts of water for one part of the juice). This solution is instilled into the eyes twice a day. It is advisable not to squeeze the juice out of the entire leaf so that it does not spoil during storage. Divide the sheet into several parts and keep them in the refrigerator in the side compartment, wrapped in cling film.
An infusion of cornflower flowers is used in ophthalmology as an anti-inflammatory agent. Dried flowers (spoon) are poured with boiling water (cup) in an enamel or glass container and placed in a water bath. The infusion is simmered with the burner on low for about 15 minutes. Then leave it in the kitchen until it cools and filter well. You can simply steam the flowers with boiling water and let them sit for three hours under the lid. The eyes are washed with the decoction and applications are made. A decoction of cornflowers promotes rapid regeneration of affected tissues.
Cumin, parsley and cucumber
Cumin seeds have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. A spoonful of cumin is poured into a cup of boiled water and placed on the stove in an enamel or glass (fireproof) container, boiled for 10-11 minutes and cooled. The inflamed eyelids are washed with a filtered decoction and applications are made to the eyes.
Parsley leaves eliminate pain, destroy pathogens and stop the inflammatory process. You can use fresh and dried leaves. Boil the herb (a tablespoon) for 10-11 minutes (a glass of water), cool and rinse. You can also make applications on your eyelids.
Cucumber pulp helps eliminate discomfort in the eyelids, eliminates swelling and fights pathogenic microorganisms. Cucumber slices are applied to closed eyelids for several minutes (about ten). You can cover your eyes with a cloth to prevent the slices from rolling off.
Juice from cucumber pulp is used in the form of applications. To do this, the peeled fruit is crushed in a blender, the juice is squeezed out and cotton pads are soaked in it. The application lasts 10-18 minutes (depending on the child’s perseverance).
Calendula and birch
Calendula flowers have a pronounced antiseptic property, relieve pain and itching, and destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Take a pinch of inflorescences per cup of boiling water and leave for 20-22 minutes under the lid. Cotton pads are moistened in the filtered infusion, lightly squeezed and applied to the eyelids. 10 minutes are enough to complete the procedure.
Marigolds also work well against viral conjunctivitis; they can be used to wash the eyelids. Just before doing this, you should filter the infusion through sterile cotton wool so that particles of the herb do not get into your eyes.
A healing infusion is made from birch leaves to combat inflammation of the eye membrane. To do this, fresh leaves are thoroughly washed from dust, poured with a cup of boiling water and covered. After an hour, the strained infusion is heated to 30 degrees, cotton pads are moistened in it and applications are made.
Remember that independent use of herbal treatment without consultation with an ophthalmologist may result in an exacerbation of the disease. First, consult your doctor, and then use traditional medicine recipes. The danger of improper treatment is the spread of the infectious process to tissues adjacent to the conjunctiva and the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the blood.
Drugs
In some cases, when the infection has affected not only the organs of vision, tablet forms of drugs may be prescribed.
How to treat viral conjunctivitis in children with tablets:
- Acyclovir;
- Isoprinosine;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Tobrex.
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Note! The last 2 drugs are antibiotics. They are useless against viruses, but can be prescribed if there is a possibility of a bacterial infection
Ointments
How to treat viral conjunctivitis in a child using ointments:
- Florenal. Most often prescribed for the herpetic form of the disease. The product is applied 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
- Tebrofen ointment. Used for all types of viral conjunctivitis. Apply 2-4 times/day. The duration of therapy depends on the extent of the lesion.
- Bonafton. It is used for various lesions by adenoviruses, incl. and with conjunctivitis. Apply 1-4 times a day, the course of treatment is quite long, 2 weeks. Often this ointment is combined with hydrocortisone.
- Zovirax and Acyclovir. Most often prescribed for herpes infection. Apply every 2 hours. The duration of therapeutic measures depends on the degree of damage.
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Note! Effective ointments can only be selected by the attending physician. When applying them to the eyes, you must strictly follow all his recommendations, as well as the instructions for the drug
Effective drops prescribed taking into account the form of the disease and the age of the child
When deciding how to quickly cure viral conjunctivitis in a baby, the doctor must prescribe antiviral eye drops. Such drugs not only destroy pathogens, but also almost immediately remove unpleasant symptoms (pus, redness, swelling, pain, etc.).
Drops for children up to one year old
How to cure viral conjunctivitis in infants with drops:
- Oftalmoferon. The active substance in this drug is interferon. This substance destroys adenoviruses and herpes, stimulates the immune system to independently fight pathogens. As a rule, 1-2 drops are prescribed in each eye every 3 hours.
- Aktipol. The drug is based on para-aminobenzoic acid. Drops destroy various viruses. Typically, it is prescribed to use 3-7 times a day until the pathological process is completely eliminated.
- Florenal. They help well with diseases caused by herpes. Also prescribed for complications of the inflammatory process (keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis).
Expert opinion
Ermolaeva Tatyana Borisovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Note! It is best to choose drops for infants with a minimum concentration of the active substance (0.1%). This will help avoid overdose and corneal burns.
These drugs can also be used for older children. The most effective medication, dosage and duration of treatment must be selected by a pediatrician or ophthalmologist.
Viral conjunctivitis
With viral conjunctivitis in a child, both eyes are affected in frequent cases. Once the virus enters the body, its incubation period can last from several days to 2 weeks. The main symptoms of a viral disease are:
- in the early stages of the development of the disease, body temperature increases to 37 degrees, and after some time (from 7 to 10 hours) it already reaches 39 degrees;
- corneal clouding;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the appearance of serous discharge;
- formation of follicles on the conjunctiva;
- development of pain when trying to look at the light;
- cloudiness and darkening of the eyes.
It is prohibited to prescribe medications to treat a viral illness on your own. If a child’s temperature rises above 39 degrees, then it is imperative to bring it down with antipyretic drugs: Nurofen, Ibuprofen and others. For each patient, the doctor prescribes an individual treatment regimen. To relieve inflammatory symptoms, drugs such as Actipol, Albucid and Poludan are used
To stimulate the immune system, it is important to resort to the use of Polyoxidonium or Cycloferon. If you have viral conjunctivitis, you should not give your child antibiotics, as this will not help cure the disease, but will only complicate its form.
Features of the treatment of conjunctivitis with fever
Treatment of any disease should begin in the therapist’s office. If the doctor determines that the child has signs of conjunctivitis, he will refer him to an ophthalmologist. Depending on the form of the disease, the following treatment methods are used:
- eye drops;
- antibiotics to treat a bacterial type of disease;
- antiviral agents;
- antihistamines for allergic forms of the disease.
If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, you should resort to the use of medications to relieve fever. Be sure to strengthen your immune system and drink plenty of fluids. The liquid not only helps prevent the development of dehydration, but also accelerates the process of removing pathogenic viruses and bacteria from the body. In conclusion, it is important to note that temperature with conjunctivitis is a secondary symptom through which the presence of a serious illness can be assumed. Parents should monitor the temperature and not allow it to rise above 38 degrees.
How to prevent infection
If a person has been in contact with an infected person, one should resort to rules that will not allow pathogenic microorganisms to spread through organs and tissues:
- if conjunctivitis was caused by a virus, antiviral agents should be used prophylactically;
- if the disease is caused by a bacteria, antibiotics are not used, only antiseptics are used so that microorganisms do not develop resistance;
- the use of multivitamins, which activate the body’s defenses, accelerate metabolism and regeneration of damaged tissues;
- using bactericidal soap, gel, wipes after contact with an infected person to prevent the infection from spreading to other surfaces;
- upon arriving home, you should take a shower with bactericidal soap; the use of hot baths is not recommended, since bacteria and viruses spread faster in stagnant water;
- treatment of the nose and throat with a bactericidal agent (Furacilin, soda, Albucid), since these areas are the entrance gates for pathogenic microorganisms.
Applying the above rules does not always help. This is due to the fact that the patient may have reduced immune system function, so even a small penetration of a pathogenic microorganism causes infection and spread of infection to the eyes.
Basics of treatment for various types of diseases
For all types of conjunctivitis, it is necessary to carry out restorative treatment, which is aimed at improving the functioning of the nominal system. This includes:
- Vitamin therapy. The child is prescribed complexes of vitamins and microelements;
- Diet therapy. Nutrition should be varied, nutritious and easily digestible.
Etiological treatment, direction to eliminate the cause and pathological symptoms, depends on the type of conjunctivitis.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis
In this case, the use of antibacterial drugs, both local and systemic (in severe cases), is required. The drugs are prescribed by an ophthalmologist. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used more often.
To free your eyes from heavy discharge, you need to wash them with antibacterial and antiseptic solutions. The procedure is carried out 6 times a day.
Eye drops:
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ofloxacin.
Ointments:
- Tetrocycline;
- Gentamicin;
- Levomycetinic.
The medicine is administered into both eyes after rinsing. Ointments and eye drops are used 3 times a day.
For hyperthermia, the use of antipyretic drugs, for example, Nurofen, is indicated. This drug also has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis
In this case, symptomatic treatment is carried out:
- Rinsing the eyes with antiseptic solutions (for example, Furacilin);
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen);
- Albucid eye drops. They prevent the addition of a bacterial infection;
- Drink plenty of fluids.
The child needs to create comfortable conditions. Maintain a sleep and rest schedule.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis
First of all, the allergen should be excluded. Taking antihistamines is indicated.
Antihistamine eye drops:
- Cromohexal;
- Alomide;
- Lecrolin.
General antiallergic drugs for oral administration:
- Suprastin;
- Zodek;
- Zyrtec.
Symptoms depending on the type of conjunctivitis
Adenoviral infection is characterized by 1–2-day intoxication of the body. The temperature on the first day of infection rises to 38 degrees. It does not stay high for long and is quickly knocked down by antipyretic medications. With adenovirus infection, fever for more than 2 days is rarely observed.
Simultaneously with conjunctivitis, the child’s respiratory mucosa becomes inflamed and the lymph nodes of the abdomen become inflamed.
The first signs of viral conjunctivitis appear 5–12 days after infection. The pathology manifests itself as redness of the mucous membrane, watery discharge and a feeling of irritation in the eye, which quickly spreads to the second organ of vision.
If left untreated, the viral infection becomes severe. Patients complain of increased sensitivity to light, the sensation of a foreign body in the eye due to damage to the cornea. The doctor notes chemosis, fibrin pseudomembranes and finds inflammatory cells on the connective membrane.
The temperature with viral conjunctivitis lasts for several days. It gets knocked down quickly and rises just as quickly.
The bacterial form is highly contagious. There is profuse lacrimation, itching, and pain. After sleep, the child cannot open his eyes due to the appearance of crusts formed due to the appearance of purulent discharge. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- hyperemia;
- respiratory lesions;
- insomnia;
- pinpoint hemorrhages in the whites of the eyes.
The temperature stays within 37–38 C. An increase in temperature is accompanied by dehydration, leading to drying out of the mucous membrane and increased pain in the eyelids.