Just a few decades ago, problems of the eye organs in the form of: severe injuries to the visual analyzer, hemorrhages in the vitreous body of the organ, or the process of retinal detachment, were considered serious diseases. There was no way to cure them and as a result the person completely lost his sight. Today, these diseases are effectively cured through a special operation - vitrectomy. The rescued eye organ is completely restored and continues to perform its anatomical functions.
Vitrectomy of the eye is successfully performed by both foreign and domestic ophthalmologists. Modern methods and special equipment make it possible to restore the eye organ even on an outpatient basis. This article will help you understand the features of this surgical procedure, and will also tell you about possible complications and measures that will help you avoid them.
Vitrectomy of the eye
Vitrectomy of the eye is a surgical procedure during which the vitreous body, which occupies most of the organ, is removed from the eye organ. Depending on the affected area, the body may be partially or completely removed. Partial removal is called subtotal vitrectomy. Complete removal of the vitreous body - total vitrectomy.
Removal of the vitreous body allows the ophthalmologist to gain access to the retinal tissue and perform:
- photocoagulation (a kind of soldering of the retina);
- reproduce the restoration of the integrity of the shell, which could be damaged when receiving a serious injury;
- move the formed scar tissue from the surface of the retina that interferes with the eye organ.
Simultaneously with these procedures, additional ones can be carried out (we will consider further).
The removed vitreous body is replaced with silicone oil or a gas mixture - special means that ensure close contact between the retina and the choroid, and also minimize the risk of postoperative complications.
Important: Today, vitrectomy is the only way to solve problems associated with eye disease. These are various hemorrhages, retinal detachment or injury to the visual analyzer.
Such an operation requires not only the use of high-tech equipment, but also highly qualified doctors.
Performing eye vitrectomy, indications and rehabilitation
What is eye vitrectomy?
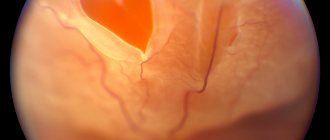
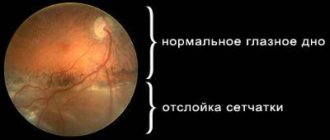
Surgery to remove the vitreous humor of the eye is called vitrectomy. Moreover, during surgery, it is most often performed to remove blood clots, cords, protein structures and scars formed in it. Often the main reason for performing such an operation is the need to access the central part of the retina - the macula. Removing the vitreous allows you to block retinal breaks and remove retinal detachments.
The vitreous body is a liquid that fills the central part of the eye; 99% of it consists of water; after removing the affected part, a special saline solution, gases, perfluoroorganic compounds, silicone oil or artificial polymers are pumped into its place.
Over time, the eye after vitrectomy fills with its own fluid, and saline solutions or gases are absorbed, artificial polymers can remain in the eye for no longer than 10 days, and silicone oil for several years, and then it needs to be replaced.
Despite the complexity of the operation, it is often performed under local anesthesia, during which the patient does not feel pain, but may experience some discomfort.
Indications for eye vitrectomy
Eye vitrectomy surgery is performed to eliminate pathological conditions; it is prescribed if the following is required.
- Restoring integrity in retinal tears. This is the most common reason for surgery.
- Removal of the consequences of hemorrhage into the vitreous body (total or subtotal hemophthalmos), in the absence of improvement from drug treatment.
- Prevention of the formation of strands leading to retinal detachment in the presence of proliferation (inflammation, increased permeability, growth into the vitreous body) of pathological vessels.
- Removal of scar tissue formed as a result of diabetic retinopathy, treatment of pathology.
- Restoring the quality of vision in cases of injury with the introduction of a foreign object into the vitreous body.
Vitrectomy is also performed when the artificial lens is displaced after implantation.
When surgery is prohibited
Although microinvasive vitrectomy is an operation with minimal traumatic intervention and is often performed as an emergency, it has several contraindications, the operation is not performed this way:
- with a reliably established lack of light perception;
- if it is impossible to restore vision;
- in tumor processes (retinoblastoma, choriodal melanoma);
- during pregnancy;
- with severe clouding of the cornea.
If during vitrectomy treatment of macular holes or removal of the epiretinal membrane is performed, then the use of drugs such as antiplatelet agents and systemic anticoagulants is taken into account.
This operation is prescribed with caution in the presence of severe systemic coagulopathies.
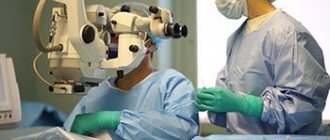
How is eye vitrectomy performed?
With microinvasive vitrectomy, trauma to the ocular structures is minimal.
The operation can last from half an hour to three hours. The duration depends on the complexity of the disease and the extent of surgical intervention. In the most difficult cases, the operation is performed in 2 stages. Repeated surgery is performed 7-10 days after the first, but the surgeon warns the patient about its necessity before the first operation. Vitrectomy is performed in 25G format. At the initial stage, the eyelid is fixed and 3 ports in 25G format are installed in the vitreous cavity between the iris and retina. At the end of the operation, after their removal, self-tamponade of the operating holes occurs and no sutures are required.
There are two types of operations.
- Total vitrectomy. The vitreous body is completely removed and its volume is filled with substitutes.
- Subtotal. During its implementation, only part of the changed or affected liquid is removed, and gas, saline solution or silicone oil is pumped in its place. This type of surgical intervention is divided into two more subtypes.
- Anterior vitrectomy. Used to remove vitreous particles from the anterior part of the eye.
- Posterior vitrectomy. The most commonly used operation is used to treat retinal pathologies (detachments, tears, strands).
Depending on the type of intervention, further actions of the surgeon will be carried out. A light guide (endo-illuminator) is inserted into one of the ports (conductors), the other is used for the infusion line (a special solution necessary for the operation is injected through it). First, the affected area of the vitreous body is removed to the extent necessary. Then, according to indications, other actions are carried out (scars are removed, ruptures are coagulated, etc.).
The operation is carried out under a strong special microscope; during the operation, blood pressure and blood clotting are monitored, and a cardiogram is taken.
After the necessary surgical intervention, one of the substitutes is pumped into the site of the removed vitreous:
- Air-gas mixture or sterile air. They are intended for tamponade; with their help, the detached retina is held in its natural position and retinal tears are blocked. Tamponade requires compliance with a certain position of the head after surgery, but its advantage is the spontaneous resorption of the mixture (within 10-20 days) and its replacement with intraocular fluid.
- PFOS (perfluoroorganic compounds) or heavy water. It holds the press better, and is suitable for rougher methods of holding the retina, but it must be removed after 10-14 days. A longer period is undesirable.
- Silicone oil. It is highly inert and does not interact with the tissues of the eye, and its transparency is almost equal to the media of the eye, silicone oil allows the detached retina to fit more tightly, and the scars from laser coagulation become very durable. The oil is removed on average after 2-4 months, but according to the doctor’s decision, it can be removed a month after the operation or remain in the eye for up to one year.
Rehabilitation period after surgery
After vitrectomy surgery, which is often performed on an outpatient basis, the patient requires a period of rehabilitation. The patient remains in outpatient treatment for 7 to 10 days. Throughout this period, it is observed by the ophthalmic surgeon who performed the operation. And then he can lead a normal life.
The patient leaves the hospital after the operation with a special bandage, which is removed on the second or third day. Your doctor may recommend using ophthalmic drops.
During posterior vitrectomy with blockade with an air-gas mixture, you will need to follow a special “head down” regime for the first few days. With it, every hour you need to spend 45 minutes lying on your stomach and use 15 for rest.
In uncomplicated cases, vision is restored within 10-14 days. In the presence of retinal detachments or tears (posterior vitrectomy), this period is prolonged while it is in place (1.5-2 months).
In some cases (not often), even with complete restoration of the anatomically correct location of the retina, vision is not restored.
Possible complications after surgery
Among the possible complications in the postoperative period, ophthalmologists name the following.
- Increased intraocular pressure.
- Secondary glaucoma (angle-closure form).
- Cataract formation.
- Hemorrhages into the vitreous body.
- Recurrent retinal detachment.
- Clouding of the cornea (ribbon form of dystrophy).
- Infectious lesions of the vitreous body (endophthalmitis).
The cost of surgery in different regions of Russia varies significantly and depends not only on the level of the clinic, the qualifications of the ophthalmic surgeon and the quality of the equipment, but also on the complexity of the disease, the size of the required surgical intervention, and the quality of the substitute used. On average, it ranges from 34 thousand rubles. up to 160 thousand rubles.
What is the indication for vitrectomy?
Vitrectomy has opened up new opportunities in ophthalmology for the treatment of many diseases that were considered complex and previously untreatable. A person had to go blind with no hope of recovery. Among these diseases:
- the presence of an eye infection, which manifests itself in severe form;
- cases of retinal detachment due to: penetrating injury to the eye organ, as a result of diabetes mellitus, with a high degree of myopia (myopia), in the presence of sickle cell anemia, as well as due to physiological aging of the vitreous body in the eyeball;
- penetration of an otherworldly object into the eye organ;
- a hole or tear in the macula (macula);
- large retinal tear;
- there has been significant clouding in the structure of the vitreous body;
- hemophthalmos - the vitreous body is partially or completely saturated with blood;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus often causes the formation of retinopathy - damage to the blood vessels of the eye organ, which disrupts the blood supply to the retina;
- in cases of dislocation of the lens or intraocular lens, which was replaced during cataract surgery.
Repeated hemorrhages and gross opacities lead to scarring of the retinal tissue. These scars prevent a person from seeing clearly. The purpose of surgery is to remove them.
What can be a contraindication to vitrectomy?
Vitrectomy is a modern and unique method of surgical intervention, but not all patients can use it. Among the contraindications are: significant opacities of the cornea, allergic reactions to medications, the general serious condition of the patient, as well as problems with blood clotting, which can cause serious complications at the time of surgery and the postoperative period.
How is the operation performed?
First, the specialist decides whether vitrectomy will be performed under local or general anesthesia. Preliminary analyzes can play a big role in this decision. If the surgical intervention involves a large volume of various manipulations, the patient has concomitant diseases, and if local anesthesia cannot be performed due to the patient’s special condition, the operation will be performed under general anesthesia. For small volumes of surgery, local anesthesia with anesthetic drops is most often used.
The patient is positioned on the operating table. After the anesthesia takes effect, the specialist spreads the eyelids using a special device and fixes them in this position.
Vitreous replacement compounds
In ophthalmology, the following are used to replace the vitreous body: liquid perfluoroorganic compounds, silicone oils, and gas mixtures. Each of these compositions differs in its structure and requires compliance with certain rules in the postoperative period, but all of them are designed for close contact and fixation of the retina to the choroid, as well as to prevent possible complications. Read more about these compounds.
- Using silicone oil. This substance has a unique structure, characterized by chemical and biological inertness, which makes the oil easily tolerated by the body. The substance promotes the correct anatomical position of the retina and the rapid restoration of all its functions. The risk of an allergic reaction is minimal. If we consider the refractive index of light using this filler, then it is 90% identical to the natural refraction, which is reproduced by the eye organ. Unlike other types of vitreous substitutes, silicone oils have the longest service life (about a year).
- Application of perfluoroorganic liquid compounds. The second name for these fillers is “heavy water”. This name was obtained due to the molecular weight of these compounds, which weighs 2 times more than ordinary water. After filling the resulting cavity due to removal of the vitreous body, the patient does not need to follow any special regimens in the postoperative period. The filler holds the retina in the desired position for 3–4 months, after which it is removed by a specialist.
- Application of gas mixtures. The resulting cavity is filled with a gas bubble. Of the main advantages of such a filler, I would like to note that the gas bubble completely resolves on its own in 2–3 weeks. Its composition is gradually replaced by anatomical intraocular fluid. Of course, there are also significant disadvantages. The patient has to follow certain rules in the postoperative period. One of them is that the head must be in a certain position for a long time.
Important: With the use of gas mixtures, the patient is prohibited from air travel during the postoperative period. Changes in atmospheric pressure cause gas to expand, leading to an uncontrolled increase in intraocular pressure.
Basic rules after vitrectomy that will shorten rehabilitation time
If the surgical intervention was not associated with the patient’s extremely serious condition, he is sent home on the same day. In advance, the specialist gives recommendations necessary for a speedy recovery, which will also help to avoid postoperative complications.
- do not overwork your visual apparatus (reading, writing, sitting at the monitor, etc. for more than half an hour);
- During the first 2 weeks, it is prohibited to lift weights exceeding 3 kg.
- physical activity with sudden movements to the side and bending forward is contraindicated;
- mandatory use of eye drops that were prescribed by an ophthalmologist to heal the eye organ and prevent increased intraocular pressure;
- in the first month after vitrectomy, visiting saunas or steam baths is excluded;
- you cannot lean over the fire (it can be an oven, a gas stove or just an open fire).
Particularly severe cases may require the patient to remain in bed for several weeks. Also, special behavior will be required from the patient if a gas bubble was used to hold the retina during surgery. The specialist’s recommendations in this case will also concern the special position of the head during the rehabilitation period, which is about three weeks. For example, when sleeping, a person will need to sleep on one specific side or face down. In some cases, it is recommended that the patient rent a special system that is designed to keep the head in a face-down position at all times. It was specially developed for the rehabilitation period after vitrectomy and is designed for use from 5 days to 3 weeks.
Failure to follow the recommendations often leads to bleeding, return to the original state of the eye organ, postoperative infection and much more. This is, at best, additional treatment, and at worst, irreversible processes of vision loss.
Compliance with all the rules will affect the timing of vision restoration in the postoperative period.
Reviews about vitrectomy and the postoperative period
We are always glad when site visitors leave their feedback after undergoing operations. Thus, you help countless patients decide to take an important step and regain their health.
You can leave your feedback after undergoing vitrectomy, as well as tell your feelings in the postoperative period in the comments to this article.
- Love 08/30/2016 22:13 Reply
After an eye injury, a loved one’s vision began to deteriorate, they went to their clinic where they advised him to undergo examination at a specialized clinic. The diagnosis was not very happy: retinal detachment with hemorrhage, clouding of the vitreous body and macular edema began. They recommended vitrectomy surgery to save the eye. Now everything is behind us, the postoperative period is passing, the operation itself was successful thanks to high-tech equipment and the professionalism of the surgeon, chosen specifically for a specific person using a step-by-step technological method.
First of all, thanks to such good clinics that identify such complex eye diseases and treat people, thanks to specialists, doctors, surgeons, and rehabilitators. Dr Vizion is the best of the best companies.
I decided to correct the retina of the eye, as my vision deteriorated, clouding of the vitreous appeared, the Vitrectomy operation was professional treatment, I was able to gain absolutely perfect vision and remove visual defects, the treatment is by far the best.
Six months ago I had a vitrectomy. Everything went well (so the doctor said). The air came out after about 8-9 days. They did it under local anesthesia, I didn’t feel any pain. After two days there was a feeling of foreignness. I won’t say that it hurt, it was rather unpleasant. 4 months have passed. I see much better. The doctor said that my vision had improved by half. Before deciding, I read a lot of reviews and recommendations. I think I was lucky - I found a great doctor.
How long does it take for vision to be restored after surgery?
The terms of rehabilitation and restoration of visual functions of the eye organ depend on:
- from the filler used, which was used instead of the vitreous;
- number of additional surgical stages;
- on the volume of the operation;
- on the degree of transparency of the optical environment of the eye organ;
- initial and postoperative condition of the retina and optic nerve.
For example, if an anterior vitrectomy was performed, during which a small amount of the vitreous was removed, positive results with the return of vision are observed within the first week. Advanced stages are often accompanied by irreversible changes in the tissues of the visual organ. The purpose of the operation is to prevent complications, and in this case, noticeable improvements in visual acuity may not be observed.
Features of rehabilitation associated with vitreous substitutes are as follows. Substitutes based on saline solutions have a low viscosity, and the cavity of the eye organ contains blood and cellular elements that need several weeks to be absorbed. In this case, vision restoration does not occur immediately.
Patients who had the resulting cavity filled with silicone oils during surgery are often prescribed to wear plus glasses for correction.
The use of gas mixtures is manifested by the presence of a black veil before the eyes, but this negative rehabilitation aspect is corrected during the first week - the veil goes away.
When the retina is detached, its function is impaired. If the patient seeks help in a timely manner and the operation proceeds without complications, these functions will be restored quickly. But as the problem drags on, these changes become irreversible. There are disturbances in the optic nerve and in the functioning of the retina. Rehabilitation is greatly complicated, even if during the operation the most positive result in terms of retinal reattachment was achieved.
Any postoperative results are recorded by an ophthalmologist for a long time, so the patient is registered.
Reviews after surgery
2 months after vitrectomy, an unpleasant sensation appeared in the eye, it intensified with movement of the eyeball. I again turned to my doctor, and he removed the suture that caused the inflammation. My expectations don't quite match the result. The doctor said I came too late for help. Perhaps the operation itself and its consequences could have been avoided if I had consulted a specialist earlier.
Already 10 days after it, I began to see perfectly. If earlier I could not read and looked as if through water, now nothing prevents me from clearly seeing the surrounding objects. In addition, my headaches went away and I was able to return to work. The main thing is to turn to a true professional, because only an experienced and qualified doctor can help in such a situation.
The son was discharged home on the 5th day; he spent about 2 months in bed with his head down so that the gas escaped. The son says that his vision has improved, but not much. We'll be visiting again soon to get examined. I hope there will be no complications after the operation.
Video review:
Consultation
Hello! I am 37 years old, 32 weeks pregnant. Until the age of 18, I had absolute vision - no correction was required. Then my vision began to decline. By the age of 36, the left eye became 5.25, the right - 6.0 with astigmatism - 1.25. Around the end of 2020 (first trimester of pregnancy + severe stress over the last 2 years), I began to notice short-term flashes in my right eye (upper left quadrant of vision), mostly with my eyes closed at a certain eye movement. Didn't pay attention. At the beginning of March 2018, after an episode of physical. activity in the upper left quadrant of vision, a semicircular “shadow” appeared in the right eye. I went to the doctor. Retinal detachment was diagnosed. On March 7, she underwent surgery - vitrectomy. I am attaching a description of the operation (I live in Holland). The eye was filled with medical gas.
Additional stages of surgery
During a vitrectomy, a specialist may perform additional surgical steps, which include:
- Air injection. It is performed to extract intraocular fluid located in the posterior segment of the eyeball. This procedure maintains intraocular pressure, which is necessary to seal existing holes in the retina and keep it in place. The pressure generated by the air soon disappears, and the back part begins to fill with liquid again.
- Scleral screed procedure. A kind of support “belt” is installed around the eyeball, which, after fixing the retina, supports it in the proper position.
- Removal of the lens - lensectomy. Often such intervention is required when there is a cataract on it, as well as when it is attached to the tissues of an existing scar.
- Laser treatment – photocoagulation. Performed when blood vessels are damaged to close them. Often such damage occurs due to diabetes in the patient. The procedure also does an excellent job of sealing the resulting hole in the retina.
These additional stages of surgical interventions can significantly extend the rehabilitation period.
What postoperative complications may occur?
Among the complications of vitrectomy noted:
- The presence of cataracts in a patient at the time of surgery often results in its progression in the first year after surgery. This is especially true in cases where the vitreous was replaced with silicone oil.
- If during surgery an excessive amount of substitutes is introduced into the eye cavity, the patient's intraocular pressure increases. To eliminate this side effect, the specialist must prescribe special drugs against glaucoma.
- Recurrences with retinal detachment are possible.
- Complications in the form of endophthalmitis are an infectious and inflammatory process.
Important: The toxic effects of substitutes can contribute to corneal clouding.
Microinvasive vitrectomy is considered less traumatic
What it is
The vitreous body occupies more than half the volume in the eye cavity. Victrectomy involves complete or partial removal of it.
It is performed under anesthesia and has the following indications:
There are 2 types of operation:
- Total.
- Subtotal (the contents of the eyeball are not completely removed).
The latter species is divided into two more subspecies. Vitrectomy happens:
- Rear. Performed for pathology of the posterior segment.
- Front. In this case, the vitreous fluid leaks into the anterior chamber of the eye as a result of problems with the lens, trauma, glaucoma, or cataracts.
A type of surgical intervention is microinvasive vitrectomy . It is carried out using small instruments that are inserted into micro-punctures.
This operation has many advantages, including:
- short rehabilitation period;
- low level of trauma;
- reduced risk of bleeding;
- unnecessary hospitalization.
The success of the procedure depends on the qualifications of the surgeon and the availability of special instruments.
Video:
You will have to pay a lot for the operation. This manipulation is carried out only in large eye centers that have all the necessary equipment. There are not very many such clinics in Russia.
Only experienced vitreoretinal surgeons perform vitrectomy.
The cost of the operation starts from 20 thousand rubles and reaches 100 thousand rubles.
It depends on several parameters:
- type of surgical intervention;
- category of difficulty;
- type of anesthesia;
- surgeon's qualifications;
- region.
In each specific case the price will be different. Only a doctor and an anesthesiologist after an examination can fully determine it.
Features of microinvasive vitrectomy
The essence of the operation remains the same - partial or complete replacement of the vitreous body with fixation of the retina, but the intervention itself is carried out through three punctures with a hole diameter of 0.3–0.5 mm. These microscopic punctures require the use of a small instrument. This allows:
- achieve less trauma to healthy tissues;
- reduce the risk of possible bleeding, which often occurs due to pathological proliferation of blood vessels;
- the rehabilitation period is significantly reduced;
- This operation is often performed on an outpatient basis.
Microinvasive vitrectomy requires special equipment and highly qualified specialists, so the method is not used in all vision restoration clinics.
Patient reviews of vitrectomy are mostly positive. Everyone talks about different times for vision restoration, but it still happens. And this is already a big plus in favor of vitrectomy.
Sources used:
- Rosenblum, Yu. Z. Optometry / Yu.Z. Rosenblum. - Moscow: Lights, 1991.
- Stepanov, A.V. Modern ophthalmotraumatology / A.V. Stepanov. - M.: Medicine, 2007.
- D. Hubel. Eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- Wikipedia article
Postoperative period
Typically, after surgery, the patient stays in the hospital for no more than 3 days.
After the procedure, the doctor covers the eye with a bandage to protect it from dirt. It should be removed the next morning and the eyelids should be carefully treated with a sterile swab, which is pre-moistened in an aqueous solution of an antibacterial drug.
The speed of recovery depends on several factors:
- presence of severe retinal diseases;
- condition of the cranial nerves;
- the ability to perceive objects.
If the vitreous is replaced with a saline solution, the cloudiness of the eye persists for several weeks. In the presence of a gas mixture, a black film appears, which disappears after a week.
After the operation, for six months it is prohibited:
- read for more than half an hour;
- lift objects over 2 kg;
- stand bending over the fire;
- engage in active sports;
- drive;
- rubbing or pressing on the eye;
- look at UV rays;
- skip a doctor's appointment;
- ignore the doctor's recommendations.