The optic nerve can be restored in glaucoma using medications or non-drug methods. It all depends on the degree of damage and the duration of the pathological process. If the disease is in the initial stages, a short therapeutic course is sufficient. When the return of adequate functionality of the visual organ becomes impossible, excavation of the nerve is recommended.
Optic nerve atrophy in glaucoma
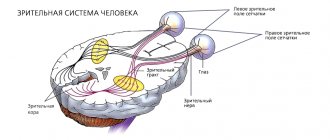
The optic nerve is a unique formation, the structure and functionality of which differs from all other nerves in the body.
In fact, these are nerve fibers intertwined with each other. In the center of this weave is the retinal arterial canal. Through it, the image is transmitted to the brain in the form of electronic impulses, which becomes impossible when these fibers are destroyed. More than twenty percent of the total number of cases of blindness and low vision occur due to atrophy. Atrophy is the depletion of organs and tissues in the body or their reduction that occurs during life. Optic nerve atrophy occurs when the fibers that make it up begin to die, and connective tissue forms in their place. There are many reasons for this, but in each specific case, only an ophthalmologist can determine them accurately and choose treatment.
How is optic nerve atrophy treated?
The key to successful treatment of this pathology is efficiency. The sooner therapy is started, the higher the patient’s chances of recovery.
Another component of success is eliminating the causes. They can become pathologies that cause swelling, inflammation and compression of nerve fibers. Atrophy is also possible after damage to the blood vessels supplying the optic nerves. Causes of damage: glaucoma, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, frequent vascular spasms, toxic damage from alcohol and nicotine products. Injuries and infectious diseases also play a role.
When diagnosed with optic nerve atrophy, treatment and prognosis depend on the stage. But in all cases, it should be remembered that restoration of nerve fibers does not occur in the human body. The impact should be aimed at stopping the pathological process and preserving the remaining healthy tissue.
Drug treatment
In most cases, vasodilators are required: No-Spa, Nicotinic acid, Papaverine and the like. Their use has a beneficial effect on blood circulation, which slows down when blood vessels narrow and their tissues degrade.
Those patients who experience blood thickening are prescribed Heparin and Tiklid. These are anticoagulant drugs that normalize blood consistency and eliminate the risk of blood clots.
To enhance metabolism in nerve tissues, biogenic stimulants are used. The preparations Peat and Aloe Extract are indicated. Heparin ointment is applied locally.
It is mandatory to support the body with B vitamins and ascorbic acid. Vitamins can be taken orally in the form of tablets; injections are prescribed for accelerated vitaminization.
To improve immunity, natural preparations based on eleutherococcus and ginseng are used. They enhance regeneration, suppress inflammation and improve general condition. Immunostimulants are especially necessary for infectious causes of atrophy.
If there are no contraindications to taking hormones, Prednisolone or Dexamethasone is prescribed. This allows you to quickly relieve inflammation. To improve the functioning of the central nervous system and saturate tissues with oxygen, you should take Cavinton, Phezam, Emoxipin.
All of these drugs can only be used under the supervision of a physician. Treatment can be carried out both at home with regular follow-up consultations with an ophthalmologist, and in a hospital. The regimen depends on the stage of the pathology and the complexity of its cause.
Physiotherapy for optic nerve atrophy
The list of physiotherapeutic effects includes several methods:
- Acupuncture;
- Electrophoresis;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Laser stimulation:
- Magnetotherapy
These procedures enhance the effect of the medications taken. However, they give a good effect only with incomplete loss of nerve cells.
Surgical treatment of optic nerve atrophy
If there is a threat of blindness that cannot be treated with drugs and physical therapy, surgical intervention is prescribed. One of four operations is prescribed;
- Vasoreconstructive;
- Extrascleral;
- Decompression;
- Choroidal revascularization.
During vasoreconstructive surgery, the doctor ligates the vessels of the temporal or parietal artery. As a result, blood flow is redistributed and blood supply to the ophthalmic artery is improved.
During extrascleral intervention, the surgeon artificially creates a focus of inflammation in the area surrounding the optic nerve. This occurs by transplanting the patient's own tissue. The result of the intervention is improved blood circulation and nerve nutrition.
The essence of decompression surgery is the dissection of the scleral or bone canal of the optic nerve. After tissue healing, the outflow of venous blood increases, the level of pressure inside the nerve decreases, and its performance increases.
Choroidal revascularization is the most complex operation. During the intervention, bundles of the rectus ocular muscle are transplanted. This causes the formation and development of new blood vessels. The result is increased nutrition of the optic nerve and the cessation of the loss of its cells.
Causes and symptoms
Heredity or congenital pathology are the root causes of optic nerve atrophy. In addition, it can occur as a result of diseases of the visual organs, namely pathologies in the optic nerve and retina. The cause of this illness may also be a disease of the nervous system or diseases not related to the organs of vision.
The main causes of optic nerve atrophy:
- Infectious diseases.
- Traumatic brain and eye injuries.
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Chemical or alcohol poisoning.
- Circulatory problems in the organs of vision.
- Physical impact on the organs of vision, as a result of which the optic nerve is affected.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
There are several classifications of atrophy:
- complete or complete and progressive, depends on the degree of death of the optic nerve: with the first, the patient has a chance to restore vision, if the atrophy is complete, then the consequences are irreversible;
- hereditary and acquired;
- partial or complete;
- one-sided and two-sided.
Signs of the disease
The very first sign of atrophy is impaired visual acuity. In this case, the eyeball may not have pathologies, but the electronic impulses from the transmission of images do not reach the brain.
- primary, in which central vision is impaired and often the appearance of scotomas, that is, dark spots before the eyes,
- and secondary, affecting peripheral vision and arising as a result of various pathologies.
The patient experiences difficulty reading, color vision may be impaired, and loss of space may begin. Signs of secondary optic nerve atrophy are determined by the causes of its occurrence.
In the late stage of syphilis or paralysis, the patient's vision decreases gradually. If, for example, he has sclerosis, then loss of the central field of vision is possible.
Hypertension affects lateral vision. Also, this disease can be a consequence of excessive blood loss, then the lower limits of visibility are affected. If the optic nerve is compressed, then the manifestations are likely to vary depending on the area on which the pressure is applied.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the reason for its formation. If you discover signs of optic nerve atrophy, such as amaurosis, that is, sudden loss of vision, scotoma, blurred vision and blindness, you must immediately be examined by an ophthalmologist to avoid disastrous consequences.
Definition of disease
Optic nerve atrophy (or optic neuropathy) is the process of death of nerve fibers, which occurs gradually and is most often the result of a malnutrition of the nervous tissue due to poor blood supply.
The transmission of images from the retina to the visual analyzer in the brain occurs through a kind of “cable”, consisting of many nerve fibers and packed in “insulation”. The thickness of the optic nerve is no more than 2 mm, but it contains more than a million fibers. Each section of the image corresponds to a certain part of them, and when some of them cease to function, “silent zones” (image disturbance) appear in the image perceived by the eye.
When nerve fiber cells die, they are gradually replaced by connective tissue or nerve auxiliary tissue (glia), which is normally designed to protect neurons.
Depending on the causative factors, two types of optic nerve atrophy are distinguished:
- Primary. The disease is caused by an affected X chromosome, so only men aged 15-25 years are affected. The pathology develops in a recessive manner and is inherited;
- Secondary. It occurs as a consequence of an ocular or systemic disease associated with impaired blood supply or congestion of the optic nerve. This pathological condition can appear at any age.
Classification is also carried out according to the location of the lesion:
- Ascending - characterized by damage to the nerve cells located on the retina of the eye. The progression of the process occurs in the direction of the brain. This type of lesion is observed in eye pathologies (myopia, glaucoma);
- Descending - the process occurs in the opposite direction from the visual center to the retina. Its development is typical in retrobulbar neuritis, pituitary tumors, and brain injuries affecting the area with the optic nerves.
The following types of atrophy are also distinguished: initial, partial, complete and incomplete; one-sided and two-sided; stationary and progressive; congenital and acquired.
Diagnosis and treatment
Before conducting a comprehensive ophthalmological examination, it is determined whether the patient has diseases leading to optic nerve atrophy, and information about lifestyle, contact with chemicals and alcohol is processed.
Next, a physical examination of the eyeballs is carried out, visual acuity is determined, perimetry and the degree of color perception are performed.
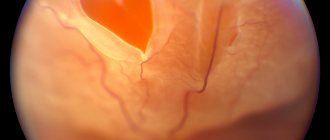
The main method for detecting atrophy is ophthalmoscopy, that is, the study of the internal structure of the eye. It is carried out using an ophthalmoscope; during the procedure, a beam of light is directed into the patient’s eye.
There are several types of this diagnosis:
- With the reverse method, the fundus is examined upside down.
- Direct ophthalmoscopy is possible if a special vasodilator solution is first dropped into the patient’s eye; the study takes place with an image magnification of fifteen times.
In addition to ophthalmoscopy, perimetry is used to diagnose atrophy. It identifies the visible space accessible to the eye and its boundaries, thereby revealing the degree of impairment of peripheral vision. The kinetic form of perimetry and statistical, that is, computer, are used.
The severity of atrophy can vary; a positive result in the treatment of this disease can only be achieved with partial tissue death. Adjusting the course of treatment for a patient with optic nerve atrophy is not an easy task for specialists, since the lost nerve fibers are practically not restored. There are chances with nerve tissue therapy, but provided that it is carried out on time.
As a rule, optic nerve atrophy does not occur on its own, but is a consequence of various eye pathologies. For this reason, treatment should begin with the elimination of these pathologies. If you have time to start treatment from the onset of the disease and within a couple of weeks, then your vision can be restored completely.
Treatment is carried out as follows: inflammation and swelling of the nerve fibers are eliminated, nutrition and blood circulation of the optic nerve are restored. This course of treatment takes quite a long time and often does not bring the expected effect if it is not started immediately after diagnosis. The main emphasis is on treating the disease causing optic nerve atrophy. At the same time, a course of therapy is being carried out to eliminate the consequences of this disease, which has caused complications on vision: drops, injections, as well as medications for oral administration. This course typically consists of a number of activities:
- Stimulating blood circulation with vasodilators.
- The use of biogenic stimulants that accelerate tissue metabolism.
- Slowing down inflammation with hormonal agents.
- Activation of the nervous system with emoxipine.
- In addition to physiotherapy, reflexology has been successfully used.
In which countries and how is optic atrophy treated?
Optic nerve atrophy can be congenital or acquired .
In the second case, the causes of atrophy are most often pathological processes in the retina or optic nerve.
The disease can develop after a syphilitic lesion, meningitis, with tumors and multiple sclerosis, with a brain abscess, with various intoxications or poisonings.
The cause of the pathology can also be vascular atherosclerosis, fasting, hypertension, vitamin deficiency, and profuse bleeding.
There are several forms of atrophy:
- Primary atrophy occurs after deterioration of nerve trophism and microcirculation disturbance. This includes descending atrophy of the optic nerve (a consequence of damage to the optic nerve fibers) and ascending atrophy (a consequence of damage to retinal cells).
- Secondary atrophy is the result of damage to the optic nerve head due to pathologies occurring in the retina and optic nerve.
- Not all forms of pathology cause vision loss. For example, with atrophy of peripheral fibers without involvement of the papillomacular bundle, vision is preserved.
- Hereditary Leber atrophy of the gender type is distinguished as a special form . The disease develops mainly in men of the same family aged 13 to 28. The clinical picture is characterized by a sharp decrease in vision in both eyes at once for two to three days.
- Glaucomatous atrophy occurs as a result of collapse of the lamina cribrosa as a result of increased intraocular pressure.
Atrophy can be complete or partial. With complete atrophy, the function of the optic nerve is completely lost. With partial atrophy, visual impairment occurs.
Picture: stages of optic nerve atrophy
During the course of the disease, the nutrition of nerve fibers deteriorates. Vision begins to gradually deteriorate until complete blindness. No vision correction is possible; sometimes, with the rapid development of the process, vision is lost irrevocably within three months.
With atrophy, the symptoms can be of a different nature: narrowing of the visual field, color vision disorder, or the appearance of black spots in the visual field (the most common symptom). In this case, you need to contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostics abroad
Abroad, the diagnosis of optic nerve atrophy is carried out using modern techniques:
- The examination begins with ophthalmoscopy.
- Spheroperimetry helps determine the boundaries of vision.
- Computer perimetry is used to identify atrophied areas of the nerve.
- Ophthalmography helps to identify the nature of the damage.
- Additional examinations, such as skull x-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help determine the presence or absence of a brain tumor, which may be one of the causes of the pathology.
- Fluorescein angiography and laser Dopplerography may also be prescribed as an examination.
As a rule, all procedures abroad are carried out in one clinic. The patient also undergoes a mandatory examination to identify hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes, etc.
Modern methods of treatment
The pathology is difficult to treat, since the nerve fibers are not restored. Therefore, treatment should begin as quickly as possible before complete destruction of the nerve fibers occurs.
First of all, during treatment the inflammatory process is eliminated, swelling in the optic nerve is removed, trophism and blood circulation are improved.
Ophthalmologists in many countries (Israel, Germany, etc.) have already gained extensive practical positive experience in treating the disease, thanks to close cooperation with research centers around the world.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0Xcf2kuvrxQ
At the beginning of treatment, it is necessary to provide the nerve with vitamins and nutrition. For this purpose, the most modern medicines are used abroad.
In some cases, a surgical method of delivering nutrients may be used. Physiotherapy allows you to achieve a positive effect. Magnetic stimulation, the effect on the nerve of magnetic alternating fields, helps to improve blood supply and normalize metabolism. Improvement may occur after the first 15 procedures.
In the photo: an eye examination by an ophthalmologist
Laser and electrical stimulation (impacting impulses on the nerve) are also used to treat atrophy. A good effect is observed after just a few sessions.
One of the newest methods of combating the disease is the use of tissue regenerative microsurgery.
Stem cells and the latest advances in nanotechnology are used for treatment, thanks to which nanoparticles are used to deliver nutrients to the optic nerve.
More often, not a single method is used for treatment, but the complex use of several techniques. Thanks to this approach, ophthalmology abroad has achieved outstanding results in the treatment of eye pathologies.
[adsp-pro-3]
Stem cell treatment
The newest treatment method abroad is stem cell treatment. Stem cells are injected into the optic nerve area. Administration is carried out every 2 hours up to 10 times a day.
A simpler method of introducing stem cells without surgery has been developed.
The method of introducing stem cells consists of injecting them into the patient, with an interval of 3 months to six months for three procedures. A simple lens is used as the basis for the stem cell carrier.
A positive effect is provided by cytokines, interleukins, and growth factors contained in stem cells, which activate restoration processes and support the vital activity of cells.
Where to go?
Treatment of the disease abroad is carried out in leading clinics in Germany, Israel, the USA, Austria, Finland, and Switzerland. Treatment is usually carried out in courses of up to 14 days, based on the diagnosis of the disease, identifying the causes of the pathology and their elimination.
Germany
In Germany, treatment is carried out:
- At the University Clinic of Cologne;
- At the L. Maximilian University Multidisciplinary Clinic in Munich;
- At the ophthalmology clinic of Dr. med. G. Palme in Düsseldorf;
- At the St. Martinus Clinic in Düsseldorf;
- At the ophthalmological medical center at the university clinic in Essen;
- At the University Center for Ophthalmology in Frankfurt am Main;
- At the Clinic for Refractive and Ophthalmic Surgery in Duisburg.
Treatment of optic atrophy in children is carried out at the Clinic for Psychomotor Disorders, Periocular Surgery and Pediatric Ophthalmology in Tübingen.
Israel
In Israel, pathology treatment is carried out:
- At Hadassah University Hospital in Jerusalem by Dr. Yitzhak Hemo;
- At the Ichilov Clinic by Dr. Shimon Kurtz;
- At the Assuta clinic;
- At the Herzliya Medical Center;
- At the medical center. Yitzhak Rabin;
- At the medical center. Souraski;
- At the Rambam medical center.
Austria
In Austria, treatment is carried out:
- At the University Eye Clinic of Vienna by Dr. E. Ergun;
- At the Clinic for Laser Eye Surgery in Vienna by Dr. Reinhard Schranz;
- At the Ophthalmology Center of the Confraternity-Private Clinic Josefstadt by Dr. Christian Lammerhuber.
Switzerland
In Switzerland, qualified and effective treatment can be obtained:
- At the Hirslanden im Park clinic in Zurich;
- At the Cécile Hirslanden clinic in Lausanne;
- At the Hirslanden Clinic in Zurich;
- At the Generale Beaulieu clinic in Geneva;
- At the clinic in Leukerbad.
China
Treatment of optic nerve atrophy in adults and children is successfully carried out in China:
- In Beijing - Beijing United Family Hospital and Clinics;
- at Tongren Hospital in Beijing;
- at Daqing People's Hospital.
Infographics: causes, symptoms and treatment of atrophy
Reviews
Natalya : “The child developed optic nerve atrophy due to hydrocephalus. The son was 8 months old, he did not see anything, he only reacted to sunlight. general treatment was carried out by a neuropathologist. After finishing the treatment we went to Ichilov in Israel. As a result of treatment, 70% of vision was restored."
Denis : “At the age of 27, he underwent surgery for basal arachnoiditis of the brain. A year later, a diagnosis of partial atrophy of the optic nerve was made. A year later he began to lose his sight and went with his brother to a Beijing clinic. After treatment, vision stabilized and gradually began to improve.”
Maria : “Atrophy of the optic nerve from birth. As a child, I had surgery to correct strabismus. At the age of 18, she went to the Ikhilov clinic, where she underwent a course of treatment. The eye began to see about a week after the start of treatment.“
Galimov : “I was engaged in karate from the age of 18, received a blow to the head, after which atrophy of the optic nerve began to develop. I went to a clinic in Germany, where after the treatment my vision improved to 90%.“
Source: https://medclinic-tour.com/oftalmologiya/atrofiya-zritelnogo-nerva
Researchers have proven the possibility of restoring the optic nerve
According to researchers from the USA, it is possible to preserve or even restore vision in patients of any age with a damaged optic nerve, hereditary or metabolic problems, neuritis, glaucoma, ischemic optic neuropathy (impaired nerve function as a result of a decrease in the supply of oxygen and nutrients due to insufficient blood supply ), etc.
Programmed cell death, caused not by depletion of functionality, but by the “completion” of the genetic code, called apoptosis, plays a significant role in cell death after damage to the optic nerve.
That being said, there are a number of methods that can potentially stop this process. Among them is the use of drugs that suppress the formation of glutamate and nitric oxide, preventing their toxic effect after release from damaged ganglia (a collection of nerve cells) located in the retina.
Substances that activate alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, such as brimonide, nerve growth factor and so-called temperature shock proteins, as well as vaccination with non-encephalitogenic protein molecules, can protect the organ of vision from the risk of developing disorders of the structure and function of the optic nerve.
If a nerve is crossed, then in the presence of a special cellular microenvironment it can grow anew, to the entire previously existing length.
One method of creating such a microenvironment is to remove myelin and its breakdown products while simultaneously introducing external growth factors into the outer part of the axon (the nerve cell processes that form the nerve), such as fibroblast growth factor and neurotropin.
Myelin is a special sheath around the nerve trunk that provides nutritional function and increases the speed of electrical impulses along nerve fibers.
In addition, it has been discovered that stem cells can replace dead or damaged nerve cells, providing an alternative enzymatic mechanism to correct an inherited or metabolic defect and create trophic support for neurons.
The study authors expect progress in clinical research in this area over the next decade.
There is a method for treating optic nerve atrophy using Alloplant biomaterial
There is a method for treating optic nerve atrophy using the Alloplant biomaterial, which can stimulate capillary regeneration. An alloplant is a plate of donor preserved tissue with a deep recess at one end for the optic nerve (Alloplant for revascularization of the optic nerve). The alloplant plate is introduced into the suprachoroidal space of the eye, carefully brought to the posterior pole of the eye, where the optic nerve enters the eye membranes, and is “seated” by the notch on the optic nerve, and the two “legs” at the edges of the notch are straightened so as to ensure good contact of the Alloplant with the optic nerve. nerve. This biomaterial stimulates neoangiogenesis, through which vessels grow from the surface of the sclera into the optic nerve and normalize its capillary circulation, eliminating optic nerve atrophy (Karushin O.I. Surgical treatment of optic nerve atrophy in primary glaucoma using the “alloplant” biomaterial, abstract of thesis. Candidate of Medical Sciences, Krasnoyarsk, 1998, p. 19. RU 2071302 C1, 01/10/1997, RU 2141809 C1, 11/27/1999. RU 2049452 C1, 12/10/1995; Muldashev ER, Muslimov SA, Nigmatullin R.T., Kiiko YI, Galimova VU, Salikhov AY, Selsky NE, Bulatov R.T., Musina LA Basic research conducted on Alloplant biomaterials. European Journal of Ophthalmology. - 1999.- Vol.9, No. 1. - P.8-13) . The disadvantages of this method are: the operation is traumatic, the risk of adverse reactions to allogeneic material. The effect of revascularization is mediated through the provocation of an aseptic inflammatory reaction, which carries the risk of progression and transition to chronic inflammation, possibly with the addition of an autoimmune component. The immunoprivilege of the eye and the ophthalmohematological barrier may be disrupted. There are risks of excess scarring that destroys the retina or the scar compressing the optic nerve. The technical result of the invention is the reduction of blindness and low vision in optic nerve atrophy while restoring the structure and function of the optic nerve due to the induction of organotypic tissue regeneration, including the vascular network of the optic nerve, its disc and the peripapillary choroid with autologous bone marrow stem cells. The technical result is achieved by the fact that autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells containing several populations of stem cells, including proangiogenic, endothelial progenitor, hematopoietic and mesenchymal, in the form of a suspension on a carrier solution are injected parabulbarly and through microdrainage fractionally into the subtenon (Nesterov A. P., Basinsky S.N. A new method of administering drugs into the posterior part of the sub-Tenon’s space. // Bulletin of Ophthalmology, 1991, N 5, p. 49-51) and suprachoroidal space (TWOlsen Treatment of exudative age-related macular degeneration : many factors to consider. Ocular Surgery News 2007. - Vol.25.- No. 2. - P.14) the patient’s eyes. The method is carried out in two stages. First stage. From the patient's wing of the ilium under local anesthesia, bone marrow is collected in an amount of 10-60 ml on an outpatient basis under aseptic conditions. The bone marrow aspirate with anticoagulant is sent to the cell technology laboratory. In the laboratory, under aseptic conditions, cellular graft material is prepared from the bone marrow in the form of a suspension of mononuclear cells in an aqueous isotonic solution. Not only autologous mononuclear cells, but also cultured multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells of bone marrow and adipose tissue can be used as cellular material. Some of the cells are frozen in liquid nitrogen and transferred to a cryobank for possible subsequent use. Second phase. 1-1.5 hours after bone marrow collection, autologous mononuclear cells isolated from it in the form of a suspension on a carrier solution are injected parabulbarly and through two pre-installed microdrainages fractionally into the sub-Tenon (1-4 ml per injection) and suprachoroidal (by 0.1-0.3 ml per injection) of the patient's eye space. The operation takes minimal time and is minimally traumatic. Micro-drainages are left for a day. After 1-2 hours, mononuclear cells are reintroduced in an amount of 100,000 to 1,000,000 cells per ml, no more than 10 times per day. Depending on the results of treatment, after 1-2 months it is possible to carry out repeated similar cell transplantations in order to improve and consolidate the results of treatment. Bone marrow stem cells with this method of transplantation exhibit known properties, namely: they activate neoangiogenesis, increasing blood circulation in the vessels of the retina and optic nerve of the eye, and improve the trophism of nerve cells and their processes. Conditions are created that stimulate organotypic tissue regeneration, in this case, the intraorbital part of the visual analyzer. This makes it possible to effectively restore impaired visual function. Organotypic regeneration of optic nerve tissue in this method of treating optic nerve atrophy can be associated not only with the plastic function of stem cells - the source of tissue regeneration - with subsequent differentiation and transformation into the desired population of specialized cells, but also with the well-known so-called trophic effect: stem cells produce bioactive factors that prevent apoptosis, suppress tissue fibrosis, scar formation, and have angiogenic properties, i.e. initiate the growth of new capillaries, enhance the division of local stem cells. An important ability of transplanted stem cells is the suppression of the autoimmune process in the pathologically altered organ of vision, which, given its immunoprivilege, is extremely important for the full restoration of visual function. Clinical examples. Example 1 Patient R., 68 years old. OD - open-angle glaucoma IIa OS - open-angle glaucoma IIIc. Visual acuity: OD=0.4s-1.0d=0.5 OS=0.02c+10.0d=0.1 OS - calm, deviated outward by 15-20 degrees. Aphakia. Remains of the posterior capsule along the edge of the pupil. The pupil is tightened at 12.30 o'clock. The optic disc is white, glaucomatous excavation. IOP=OD=20 mm Hg. OS=26 mmHg 13 days after the introduction of autologous stem cells: Visual acuity - OD=s-1.0d=0.7 OS=s+10.0d=0.4. IOP=OD=19 mmHg. OS=23 mmHg According to the patient, the field of vision expanded on the temporal side, and vision improved. Objectively: Doctor of Science. pink on the nasal side, with a pink rim visible along the edge of the disc. In 1 month. Vision: OD=s-1.0=0.7 OS=s10.0=0.6 IOP=OD=19 mm Hg. OS=21 mmHg The dynamics are positive. Process stabilization. Repeated injection of autologous stem cells parabulbarly. 3 months after the first injection: Visual acuity - OD=s-1.0d=0.7 OS=s+10.0d=0.6. IOP=OD=19 mmHg. OS=21 mmHg OS - calm. Deflected outward by 10 degrees. Aphakia, pink optic disc, slight decoloration on the temporal side. A contact lens for OS+9.0d was selected. Example 2. Patient K., 58 years old. From the anamnesis: 54 years ago, a benign brain tumor was removed in the chiasm area. After the operation, the patient lost his vision. Vision in both eyes; =0.01 n/k. The anterior segment of the eye is normal. Fundus: optic discs are white. Diagnosis: Descending atrophy of the optic nerves of both eyes. Parabulbar and suprachoroidal injection of autologous stem cells was performed. After 1 month - vision in both eyes = 0.05 n/k IOP - normal. Optic disc with a slight pink tint. Autologous stem cells were reintroduced.
Thus, these clinical examples clearly illustrate the high effectiveness of the proposed method of treatment. This method is easy to use and can be performed in a wide network of ophthalmology clinics. FORMULA OF THE INVENTION A method for treating optic nerve atrophy, including the delivery of biological material to the area of the optic nerve, characterized in that delivery is carried out by injection parabulbarly, as well as using two microdrainages through a through incision of the sclera into the sub-Tenon and suprachoroidal spaces of the eye and autologous is used as a biological material cellular material in the form of a suspension of bone marrow mononuclear cells containing the patient's stem cells on a carrier solution in a concentration of 100,000 to 1,000,000 cells per ml of suspension, administration is carried out fractionally every 1-2 hours up to 10 times a day for each individual route of administration, while 1 ml per injection is injected parabulbarly, 1-4 ml per injection is injected through microdrainages into the sub-Tenon's space, 0.1-0.3 ml per injection is injected into the suprachoroidal space.
Causes of pathology
The optic nerve consists of tiny cells - neurons and their fibers - dendrites and axons. All of them, through synaptic clefts and the mediator acetylcholine, which circulates in them, transmit information from the outside world and transform it into visual images. The latter enter the parietal cortex of the occipital areas of the brain, where a holistic picture of the world is formed.
Glaucoma is characterized by increased intraocular pressure, resulting in atrophy of the rods and cones, resulting in complete blindness.
Is it possible to restore?
Atrophy of rods and cones can be restored if the pathology is detected early; otherwise, regeneration is impossible.
Regeneration of the optic nerves with a persistent increase in intraocular pressure is possible only when the pathology is detected in the early stages. Neurocytes do not recover if prolonged hypoxia due to increased intraocular pressure affects them chronically. If the ophthalmologist promptly identified dangerous processes, prescribed effective diagnostics and provided adequate treatment, the regenerative abilities of rods and cones increase.
Symptoms of optic nerve damage
This disease is determined by the following clinical symptoms:
- The appearance of rainbow circles around light sources. They form in the form of a rainbow next to streetlights, car headlights, light bulbs or computer monitors.
- Periodic. lacrimation. It is a defensive reaction through which the eye tries to compensate for lost functions.
- Painful sensations and the illusion of the presence of a foreign body in the conjunctival sac. Such symptoms appear during the inflammatory process.
- Deterioration of visual function in one or both eyes. They can range from mild dysfunction to severe frostbite.
Return to contents
Methods of therapy
Restoration of the optic nerve is performed using medications, laser correction and physiotherapeutic techniques. If the process has gone too far, doctors recommend removing the optic nerve so that purulent processes that threaten meningitis and encephalitis do not occur in the area of the eye orbit.
Ophthalmic drugs
Medicines containing blueberry anthocyanins effectively help restore vision. It is also recommended to use injections and tablets with retinol and vitamin A. This biologically active substance effectively restores ophthalmological functions by being integrated into mediator substances, as well as forming visual pigment. Medicines containing components that optimize microcirculation of the retina and conjunctiva are also useful. When blood flow, red blood cells filled with oxygen, increases, regeneration becomes more effective.
Atrophy of the eye nerve in glaucoma
Optic nerve atrophy occurs in glaucoma due to increased intraocular pressure and changes in the blood supply to the visual organs due to compression of the choroid plexus. In this case, a person experiences severe pain in the eye, which spreads to the head, photophobia and lacrimation appear. If left untreated, this disease causes complete or partial loss of vision in both eyes.
Therapy for the pathology consists of normalizing the pressure inside the eyeball.
Symptoms of glaucoma
In the vast majority of cases, glaucoma does not manifest itself in any way at the initial stages and is completely asymptomatic!
Many people do not suspect that they suffer from glaucoma, and notice the first signs of its manifestation when a significant part of their vision has already been irretrievably lost. That's why it's nicknamed the "silent vision killer."
As already mentioned, with glaucoma, nerve fibers and retinal cells die, which leads to the formation of optic nerve atrophy. There is a gradual narrowing of the fields of vision from the periphery, and a person may feel “something is wrong” when only a small part of the entire field of vision remains. Ophthalmologists call this field of view “tubular” (to roughly imagine such vision, you can roll a dark sheet of paper into a tube and look through it like a telescope; the view presented to your gaze is the vision of a patient with advanced glaucoma). Visual acuity in the remaining “island” of the visual field can be quite high.
Since we look with both eyes at the same time, and visual acuity does not suffer at first, a person may not notice the gradual narrowing of his field of vision. This is why the disease is insidious. In rare cases, the glaucoma process can begin with an acute attack of glaucoma, which is characterized by sharp pain in the eye, in the head, a sharp deterioration in vision, the appearance of iridescent halos in front of the eyes, blurred images, and redness of the eye.
If these complaints occur, you must urgently contact an ophthalmologist! Failure to provide timely assistance can result in significant vision loss in a short time.
Causes of the pathological condition
In glaucoma, atrophy of the optic nerve is formed due to the influence of the following factors and pathological conditions on the human body:
- eye injuries and cuts;
- infection of a bacterial, viral or fungal nature;
- ingress of toxic or toxic substances;
- autoimmune processes;
- insufficient intake of vitamins;
- brain pathologies;
- fluctuations in intracranial pressure;
- impaired blood supply to the eye;
- atherosclerosis of the vessels supplying the organ of vision;
- increased blood pressure;
- neoplasm;
- diabetes;
- endocrinological disorders;
- changes in the functioning of the eyeball;
- burdened heredity;
- congenital structural anomalies.
The optic nerve serves as a “bridge” between the eye and the brain.
The eye nerve connects the organ of vision to the brain. This makes it possible to transfer information from analyzers and comprehend what is happening around a person. The death of neurons in this nerve trunk leads to disruption of connections and loss of vision for the patient. This process can be partial, while the person still has hope for restoration of visual functions due to the regeneration of neurons, or complete, when blindness is irreversible. If nerve atrophy occurs on one side, then the autoimmune process that triggered the death of cells provokes visual impairment in the second eye.
How does it manifest?
With optic nerve atrophy combined with glaucoma, the patient develops the following characteristic symptoms:
- decreased visual acuity;
- impaired clarity of vision of objects both near and far;
- eyelash loss;
- pressing pain in the eyeballs;
- tunnel vision with lack of visualization on the sides;
- redness of the sclera;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness.
During an acute attack of the disease, along with a sharp increase in IOP and ICP, nausea and vomiting are observed.
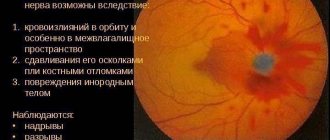
Glaucoma is characterized by a stable increase in intraocular pressure. Because of this, blood circulation and all trophic processes in the eyeball are disrupted with the death of the neurons that form the optic nerve. An acute attack of glaucoma is characterized by a strong increase in intraocular and intracranial pressure with nausea and vomiting as a result of irritation of the vomiting center of the medulla oblongata, severe photophobia and lacrimation. After an attack, the patient may notice a sharp deterioration in vision due to possible hemorrhages in the optic nerve.
Optic nerve atrophy - folk remedies and exercises for the eyes
In the development of optic nerve atrophy, swelling of the nervous tissue, compression, disruption of the blood supply and nutrition of the nervous tissue play an important role.
Often atrophy develops with damage to the central nervous system, skull injuries, tumors, multiple sclerosis, brain abscesses, encephalitis, syphilis, intoxication, alcohol poisoning with methyl alcohol, etc. There is complete and partial atrophy.
Auxiliary folk remedies for optic nerve atrophy
- Take 100 pieces of small unripe pine cones, 25 g of rue herb in bloom and 1 lemon (cut into 4 parts), pour 2.5 liters of water, add half a glass of sugar and cook for 30 minutes. Take 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 25-30 days.
- Take 3 tbsp. spoons of wild mallow roots and large burdock and cook in 1.6 liters of water for 30 minutes, then add 4 tbsp. spoons of the following composition: 80 g of sweet clover herb, 60 g of lemon balm leaves, 40 g of spring primrose flowers and cook for another 10 minutes, then strain. Take 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day before meals for 30-40 days. Repeat the course of treatment after 2 weeks.
In the treatment of retinal disease caused by arterial hypertension, hypotensive plants will provide significant assistance: the herb of Astragalus wooliflora, Vinca minor, the fruits and flowers of blood-red hawthorn, the fruits of chokeberry, the rhizome and root of skullcap Baikal, black cohosh, Daurian black cohosh, leaves of magnolia grandiflora, cudweed herb swampy.
Blueberries are also extremely beneficial for the eyes. It is rich in vitamins and contains anthocyanoside pigment, which has a positive effect on the function of the visual apparatus.
In order to take full advantage of the miraculous properties of blueberries, in the summer you should prepare blueberries for future use in a mixture with granulated sugar (1.2 kg of granulated sugar per 1 kg of freshly picked berries).
This mixture should be stored in the refrigerator, take 50 g daily for a month twice a year to improve visual acuity. Along with blueberries, you should take 1 teaspoon of pollen.
For degenerative processes in the retina, especially those that occur against the background of a hypotonic state, you should use a tincture of the fruits of Schisandra chinensis, rhizomes and roots of the plant, leuzea, aralia, ginseng, eleutherococcus, sea buckthorn fruits with pollen.
Plants that have an antisclerotic effect
In case of partial atrophy of the optic nerve, as well as in senile degenerative processes, it is advisable to use plants that have an anti-sclerotic effect - orange, cherries, fruits and flowers of blood-red hawthorn, rhizome of Diosco-rhea Caucasian, cabbage, corn, seaweed, dandelion, rowan aronia, onions, garlic, rose hips, wild strawberries, buckwheat, soybeans.
It is known that carrots are rich in carotene (provitamin A), B vitamins, vitamin D and contain a significant amount of microelements. It improves vision and increases the body's defenses.
It is better to take carrots in grated form, adding honey. The benefits of carrots will be significantly increased by adding honey and pollen (pollen) or taking carrot juice with honey and pollen (half a glass of juice with 0.5 teaspoons of honey and 0.5 teaspoons).
spoons of pollen) 1 time per day for a month.
Due to the content of a significant amount of zinc, garden beets help to improve not only the tone of the body in general, but also vision in particular.
The best option for taking beets is their juice, sweetened with honey with a small amount of pollen, which should be added to the juice first so that the pollen shell swells.
Beets can be taken on an empty stomach, raw or boiled, with a small amount of bee honey added to each piece.
In cases of congestion in the area of the optic discs and retinal edema, it is useful to use medicinal plants that have a diuretic effect.
Herbs that help with hemorrhage in the tissue of the eyeball
When hemorrhaging in the tissue of the eyeball, herbs that have a hemostatic effect help well: knotweed grass, knotweed, stinging nettle, horsetail, yarrow, viburnum bark. Taking royal jelly with honey (1:100 and 1:50) is also useful.
If you are prone to thrombosis, plants that reduce blood clotting will help, for example horse chestnut extract, an infusion of sweet clover herb in combination with pollen and propolis extract.
- You need to take several mustaches and young leaves of the golden mustache, place them in the refrigerator for 10 days, wrapped in a linen napkin. Then knead the raw material with your hands and mix the resulting pulp with an equal amount of natural honey. Place the mixture in a glass or porcelain container for 3 weeks. Then squeeze out through 2-3 layers of gauze and keep the resulting liquid in the refrigerator for 5 days. Take half a tablespoon (wooden) 2 times a day for a month. Then take a 10-day break and repeat the treatment. Such courses can be conducted 3-4 times a year.
- Take equal parts of mustache and golden mustache leaves, chop with a wooden knife, fill the bottle halfway, add half a glass of sugar, tie the neck with gauze. After 3 days, add vodka to the top of the bottle, after 3 days, strain and squeeze. Take 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day 30-40 minutes before meals.
- For age-related retinal degeneration, it is useful to take 3 times a day half a teaspoon of royal jelly with honey, prepared in a ratio of 1: 50 (keep in the mouth until completely absorbed), and 1 teaspoon of pollen. The course of treatment is 3-6 weeks. After a ten-day break, treatment can be repeated.
How to get rid of glasses before old age?
- Never read in poor lighting, especially if the text is in small print.
- Avoid straining your eyes when there is bright sunlight shining on a book, or when the sun is shining directly on your face.
- Do not watch TV without looking up from the screen, change focus more often, turning your eyes to foreign objects or looking at the foreground or background of the picture.
- When working at a computer, try to do other work during breaks that requires eye strain, change the focus of your eyes more often, turning your gaze to the ceiling, walls, window, etc.
- Cover your eyes with your palms several times during the day for a few seconds.
- Don't get carried away with dark glasses. Wear them only in very bright light (on a sunny winter day, on the beach, etc.).
- Don’t forget to do sunbathing for your eyes: close your eyes, turn your face to the sun for a few minutes, slowly rotate your head from side to side. Then turn away and blink quickly several times.
- If your eyes become inflamed or tired, wash them with a weak solution of boric acid or cold tea.
- Gymnastics to enhance visual acuity. Do it 1-2 times a day for 3-5 minutes.
- Focus your vision on close objects for a few seconds, then immediately on distant ones.
- Rotate your eyes in one direction or the other.
Among natural preparations, use an alcohol tincture of Schisandra fruits and seeds. Take it 20-30 drops.
You can also drink 0.5 g of dried lemongrass seed powder 15-20 minutes before meals 2-3 times a day. The course is not limited.
In case of eye fatigue and redness of the eyelids, vitamin A helps, the deficiency of which is compensated by eating carrots, cabbage, egg yolk, apples, dairy products, parsley, and radishes. It is useful to wash your eyes with infusions of chamomile or dill. It is best to make cool lotions from these infusions for 15-20 minutes. After the procedure, lubricate the skin of the eyelids with moisturizing cream.
Eye muscle training exercises
- Raise your eyes up, down. Repeat 3 times, pause and close your eyes. Then open and repeat the exercise 6-10 times.
- Look up, then straight down 3 times. Pause - close your eyes. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Look right, left 3 times. Pause - close your eyes. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Move your gaze diagonally: up-to-right, down-to-left. Pause - close your eyes. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Change the direction of gaze in the previous exercise: down-right, up-left, etc.
- Rotate the pupils in a circle, first in one direction, then in the other. Repeat 4-6 times.
- Change the focal length: look at the tip of the nose, then into the distance. Do 4-6 times.
- Look closely for a few seconds, without blinking, without tension in front of you.
- Close your eyelids tightly. Then blink them often. Close your eyes again and blink several times, etc. Perform for 12-30 seconds.
Super exercise for training the eye muscles
Hold the pencil at arm's length, focusing your gaze on it. Slowly move the pencil closer to your nose without looking away. Then, just as slowly, extend your arm again. With the help of such exercises, you can improve your ability to focus your vision so much that you will no longer need glasses. The value of this method is evidenced by the people it has helped.
published on chemicalvet.ru according to the materials naromed.ru
Source: https://cemicvet.mediasole.ru/atrofiya_zritelnogo_nerva__narodnye_sredstva_i_uprazhneniya_dlya_glaz
Diagnostic features
Optic nerve atrophy due to glaucoma can be suspected based on the characteristic clinical picture and complaints presented by the patient. To confirm the diagnosis and determine visual acuity, intraocular pressure is measured and direct ophthalmoscopy is performed. It is also important to determine the boundaries of the visible area accessible to the eye. Fluorescein angiography, which is performed by injecting a contrast agent into the vessel, will help detect foci of ischemia of the eyeball. In addition to this, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and eyes are performed.
You should take a general and biochemical blood test.
How to treat?
Treatment for optic atrophy due to glaucoma involves reducing intraocular pressure. For this purpose, drug treatment using agents that improve the outflow of intraocular fluid is indicated. These include sympathomimetics, prostaglandins and biomimetics. Drugs that reduce the production of eye substance are also used. These are beta-blockers Betaxolol, Betoptik and Timolol. They also use products that combine these 2 effects. If medication is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated to restore the outflow of fluid from the eye and normalize the pressure inside it. In complex therapy, drugs are used to eliminate swelling and inflammation of nerve tissue and improve metabolic processes inside the eye. Vitamin and mineral complexes are also used. This helps to partially or completely restore vision and accelerate the regeneration of optic nerve neurons.
How to restore visual field with glaucoma
Glaucoma is a common, serious disease of the visual organ. Glaucoma is caused by a disruption in the natural circulation of fluid inside the eye, causing an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP), which can damage the optic nerve, which transmits information from the eye to the brain.If glaucoma is not treated, the patient notices that he gradually loses the ability to see at the edges of the visual field (peripheral vision is lost). Progression of the disease leads to complete loss of vision.
A hereditary predisposition to glaucoma has been established. If either parent has glaucoma, the children are at increased risk.
Increased risk factors also include: myopia (myopia), age over 60-65 years, diabetes mellitus, hypotension, thyroid disease, etc.
Glaucoma is the second most common cause of blindness in the world.
Symptoms of glaucoma
Glaucoma is often called the “silent enemy of vision” because people with glaucoma usually do not feel pain or any other signs of the disease until they begin to lose their vision. Therefore, glaucoma often develops without being detected until the optic nerve is irreversibly damaged and irreversible partial vision loss occurs.
In the case of open-angle glaucoma (see below for a description of the types of glaucoma), the following symptoms may suddenly occur: blurred images, halos (circles of light) around light sources, sharp pain in the eye, nausea and vomiting. If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist to avoid irreversible vision loss.
Diagnosis of glaucoma
During a standard eye examination, intraocular pressure (IOP) is measured using a tonometer. Tonometers can be contact (the surface of the eye is gently touched by the measuring rod of the device) and non-contact (a stream of air is used for measurement).
Exceeding the normal IOP indicates too much intraocular fluid (aqueous humor) in the eye. Such an eye either produces too much tear fluid or has poor drainage.
Normal intraocular pressure is 21 mm. Hg Art. (millimeters of mercury).
If IOP is above 30 mm. Hg Art., then the risk of developing glaucoma is 40 times higher than the risk with an IOP of 15 mm. Hg Art. and below. This is why eye drops that lower IOP levels should be used.
More complex methods of diagnosing and monitoring glaucoma are also used using modern diagnostic equipment (optical coherence tomograph, laser scanning confocal ophthalmoscope, etc.), which make it possible to observe the optic nerve of the eye and its structures.
Assessing the visual field (called perimetry) allows the doctor to determine whether the patient has partially lost vision due to glaucoma. Visual field assessments in glaucoma should be performed regularly to detect the formation of blind spots due to optic nerve damage and to monitor their development in glaucoma.
To check whether the drainage pathways that allow the outflow of intraocular fluid (aqueous humor) are not blocked, gonioscopy is used. Using a special device, the doctor checks the angle of the anterior chamber, which is responsible for the outflow of aqueous humor. When the outflow of aqueous humor is obstructed, IOP increases. Ultrasound biomicroscopy is also used to assess the anterior chamber angle.
Types of glaucoma
The two main types of glaucoma are chronic, or primary open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma . The “angle” in these definitions refers to the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye, which controls the outflow of intraocular fluid. Other common types of glaucoma are normal pressure glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma, secondary glaucoma and congenital glaucoma .
Primary open angle glaucoma
Most patients are unaware that they have chronic glaucoma. Patients become aware of it only when they notice deterioration in peripheral vision. Chronic glaucoma has no other symptoms of the disease.
If the IOP remains high, the damage caused by this glaucoma will progress until a tunnel effect develops, in which only what is in front is visible. Intraocular pressure can increase for a number of reasons, including psychological stress, intoxication, diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
Angle-closure glaucoma
In this type of glaucoma, symptoms such as eye pain, headache, halos around light sources, dilated pupils, loss of vision, red eyes, nausea and vomiting suddenly appear.
These symptoms may last for several hours and then recur again after a while. With each repetition, part of the visual field is lost.
Glaucoma at normal pressure
This glaucoma is an open-angle type of glaucoma in which the visual field is damaged due to damage to the optic nerve. However, in this case, IOP does not exceed the norm.
There is usually no pain, and permanent damage to the optic nerve may only be noticed when symptoms such as tunnel vision appear. The causes of this type of glaucoma remain unknown.
However, many experts believe that it is associated with poor blood supply to the optic nerve.
Pigmentary glaucoma
This form of glaucoma is caused by pigment in the iris that clogs the angle of the anterior chamber, preventing the flow of aqueous humor. Over time, an inflammatory reaction develops, resulting in damage to the outflow system of intraocular fluid.
This type of glaucoma has few symptoms, although pain and blurred vision may occur. Pigmentary glaucoma is more common in men aged 35-45 years.
Secondary glaucoma
Symptoms of chronic glaucoma that occur after injury to the eye may indicate secondary glaucoma.
Congenital glaucoma
This form of glaucoma is inherited from parents and is present from birth. Diagnosed in 80% of cases under the age of 1 year. Children with this type of glaucoma are born with narrow anterior chamber angles or some defect in the drainage system of the eye.
It is very difficult to identify the symptoms of congenital glaucoma, because... At this age, children are too young to understand what is happening to them. More common in boys than girls.
Glaucoma treatment
The choice of the optimal treatment method (surgery, laser or medication) depends on the severity of the disease. Typically, in the early stages of the disease, eye drops are used to control glaucoma to lower IOP.
In the event of an attack of acute glaucoma, it is recommended to immediately seek specialized medical help.
Glaucoma Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to restore vision loss due to glaucoma?
It is no longer possible to restore vision lost as a result of the development of glaucoma, but further deterioration of vision can be avoided if appropriate treatment is used. The key factors to minimize vision loss due to glaucoma are:
– early diagnosis,
– appropriate treatment,
– constant monitoring.
Some types of secondary glaucoma, such as those that develop after the eye is damaged by a foreign object or, for example, in diabetes, can be avoided by wearing eye protection or taking diabetes treatment measures.
If eye drops are used for a long time, do they stop working over time?
Different drops “work” for different periods of time for different people. Some drops remain effective for 10-30 years. However, other drops may begin to “work” less effectively over time, although a decrease in their effectiveness may be a consequence of disease progression.
Therefore, it is important to regularly visit a doctor to monitor the condition of your eyes and promptly take the necessary measures if the condition worsens.
You may need to change the drops you usually take to other drops that are more effective, or use a combination of drops that can control intraocular pressure more effectively.
What to do if you have dry eyes?
Dry eyes and eye inflammation can be associated with hot, dry climates, airplane seating, too much screen time, and even the use of certain glaucoma medications. These conditions occur especially often in older people.
The main remedy to help get rid of these conditions are artificial tear preparations, produced in the form of drops for instillation into the eye. These drops replace natural tears and provide eye hydration and protection.
Artificial tear preparations are usually used after eye drops. Instill artificial tear preparations no earlier than 5 minutes after instilling glaucoma drops to prevent glaucoma drops from being washed out of the eye.
If drops do not help, use gels for dry eyes at night.
Are diabetics at higher risk of developing glaucoma?
Although the connection between diabetes and primary open-angle glaucoma has not been definitively established, some recent research suggests its existence.
One form of glaucoma, neovascular glaucoma, is known to be directly associated with diabetes.
People with diabetes should visit an ophthalmologist regularly for eye examinations to ensure early detection of glaucoma and other diabetes-related eye diseases.
Glaucoma control and aerobic exercise
A number of studies have shown that regular (3 times a week) aerobic exercise (hiking, jogging, cycling, swimming, gymnastics), which increases the heart rate and breathing for 20-30 minutes, helps to significantly reduce intraocular pressure.
Some exercises should, on the contrary, be avoided, because... they contribute to an increase in IOP. Such activities include exercises in which you stand on your head or shoulders with your legs raised up (some asanas), as well as diving and diving.
Some forms of glaucoma (eg, angle-closure) are not responsive to exercise; in other forms (pigmentary glaucoma), intense exercise may temporarily increase blood pressure.
Although regular moderate physical activity has beneficial effects on overall health, you should consult your eye doctor before starting exercise.
This article is for informational purposes only. The information contained herein should not be used to make a diagnosis or select a method of treatment for diseases. To make a diagnosis and choose a treatment method, consultation with an ophthalmologist or other specialist is necessary.
Restoration of the optic nerve in glaucoma
Retinal and optic nerve dystrophy and glaucoma
- AAA
Is it possible to use folk remedies to restore dying optic nerves in eye diseases such as glaucoma and retinal dystrophy? Now there is an advertisement for Pankov's glasses, where for 6,900 rubles they guarantee the regeneration of visual cells. I have little confidence in advertising; Official medicine does not solve the problem. I once read interesting articles by ophthalmologist Ya. V. Pronin about herbal treatment of glaucoma and retinal dystrophy. I would like to clarify: do these herbal teas simply delay the development of diseases or help the regeneration of visual cells? I am 70 years old and suffer from retinal dystrophy.
G Lyudmila Vasilievna,
Moscow region Elektrostal
I want to contact Dr. Ya.V. Pronin. I had surgery on December 16, 2008 for cataracts, and my torment began. Before the operation, I received a magazine where you described what a cataract is, what the operation to remove it involves, and gave advice on what to do after the operation. I made honey, raisins, nuts. How can you help the retina to work? What herbs are needed? Today I can't see anything with my right eye. I instilled the medications that were prescribed, but on March 5 the doctor canceled them.
On February 4th, I was still in the hospital (my retina was nailed with a laser), and I was informed that my husband had tragically died. I can’t describe how I endure everything. I am 57 years old.
S Galina Alexandrovna,
Dear readers, unfortunately, I have to repeat what I wrote about. There are no methods for complete restoration of the retinal neuroepithelium and the affected optic nerve in world medicine yet. All methods of official and traditional medicine are aimed at curbing degenerative processes. Sometimes it's possible to achieve
a sufficiently long remission. Therefore, Lyudmila Vasilievna, I recommend that you regularly take medicinal herbal teas in order to preserve your vision. The following collection is very useful:
we take equal parts of tansy flowers, horsetail, knotweed, birch leaves, plantain. Mix everything, grind. 2 tbsp. Place spoons of the mixture in a thermos, pour 3 cups of boiling water, leave for 6 hours.
Galina Alexandrovna’s question is much more complex and difficult. Judging by the extract, the condition of the right eye is extremely problematic. Patience and hope are needed here. Everything will be decided after the silicone is removed, which is carried out 5-6 months after the operation. It is extremely important to preserve vision in the left eye, and since you have been diagnosed with glaucoma of the left eye (OAG 1a), constant monitoring of IOP and regular instillation of antitlaucomatous drugs under the supervision of an ophthalmologist are necessary.
Traditional medicine recipes
1. Place 5 tbsp in a saucepan. l. pine or Christmas tree, 2 tbsp. l. chopped rose hips, pour 700 ml of water and boil for 10 minutes over low heat. This should be done in the evening, after which the pan should be wrapped in something warm and left to steep overnight until the morning.
In the morning, strain and drink the entire portion little by little throughout the day. Drink every day (at least 3-4 months). You can add honey.
In addition, apply eyebright tea compresses to your eyes 7-8 times a day. Eyebright is sold at the market by herbalists.
2. Apply 2-3 drops of fresh butter to your eyes 3 times a day.
3. Take 100 pieces of small unripe pine cones, lemon and 25 g of rue herb during the flowering period. Cut the lemon into several parts and mix everything. Pour 2.5 liters of water, add ½ cup of sugar and cook for 30 minutes.
Take 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day before meals. The course of treatment for optic nerve atrophy is 25-30 days.
4. Take 100 g of wheatgrass and calamus roots, 150 g of rose hips and mix. 3 tbsp. Put the mixture in a thermos in the evening, pour three glasses of boiling water, strain in the morning and take 150 g 4 times a day an hour before meals.
5. This folk remedy for treating optic nerve atrophy also helps: pour 50 g of lily of the valley flowers into 0.5 liters of vodka and leave it in a warm place to brew for 10 days.
Strain and take 7 drops 3 times a day.
6. Place 100 g of maple leaves in an enamel pan, pour in 1 liter of white grape wine and let it boil for 5 minutes under a closed lid. Remove from heat, let it brew for half an hour, strain and apply as a compress to your eyes.
These are the folk remedies for treating optic nerve atrophy at home.