Causes
A tear develops against the background of age-related destructive processes and thinning of the membranes of the visual apparatus. The causes of the tear are concomitant diseases of the visual organs, such as myopia or farsightedness. The mechanism of tearing on the surface is based on a decrease in the volume of the vitreous body or its increase.
Additional reasons that provoke the development of the disease are:
- dystrophic changes;
- fusion of the retina with the vitreous body;
- thermal damage to the visual apparatus;
- eye injuries;
- complicated myopia;
- jumps in blood pressure levels;
- chemical damage;
- rehabilitation period due to surgical intervention;
- inflammatory processes;
- complications of myopia;
- active physical activity;
- emotional stress;
- diabetes.
Also, the occurrence of tearing of the ocular surface is influenced by the patient’s individual predisposition to thinning of the membranes of the visual apparatus.
Causes of the disease
Retinal tears often occur in older people and in patients with chronic diseases associated with impaired blood circulation in the eye. This disease is also provoked by traumatic brain injuries, concussions and poor heredity.
A retinal tear can result in complete loss of vision, so at the slightest sign of this pathology you should immediately consult a doctor. The specific causes of ruptures can be different and ophthalmologists divide them into 4 types:
- Macular retinal hole, the treatment of which is the most labor-intensive and requires a highly qualified surgeon. The most dangerous, often leads to loss of vision. The retina fuses with the vitreous body, excessive tension occurs, which leads to rupture. Typically occurs in the central part of the eye
- Valvular retinal tear. It occurs due to the penetration of the contents of the vitreous body under the retina, and torn tears of various configurations appear.
- Serrated line separation. Often observed with various injuries. The main site of localization is the place of attachment of the retina to the choroid.
- Perforate retinal tear. The main reason is thinning of the retina due to poor circulation. Gaps appear in the thinnest places, forming so-called “lattice dystrophies”.
Often the first signs of the disease go unnoticed by the patient. The fact is that at the initial stage this pathology may not manifest itself in any way and the patient will pay attention to it only when precious time has already been lost.
That is why, at the slightest disturbance in the functioning of the organ of vision, it is necessary to urgently consult an ophthalmologist. The main symptoms of a retinal tear are as follows:
- Sensation of some kind of cloudy veil from one corner of the eye
- Floaters in the eyes. Indicate a violation of the blood circulation of the eyeball and, possibly, the onset of retinal detachment
- In the dark there are flashes in the eyes. Sometimes they feel like bright sparks
- Visual impairment – distortion of objects, blurred images, narrowing of the field of vision
All of the above symptoms often disappear after a night's sleep, since the retina fits tightly to the eye during rest. But if you ever notice these symptoms, be sure to see an ophthalmologist. Treatment methods for this disease may vary and are determined by the attending physician.
They mainly depend on the location of the rupture, the age of the patient, and the neglect of the process. Laser coagulation of the retina, cryotherapy and surgery are used. If the detachment has not yet begun, you can “weld” the retina.
Often, when a retinal tear is diagnosed, laser treatment is the best option. Using a laser beam, you can weld the eye tissues together and thus prevent the severe course of this disease. The procedure lasts less than an hour and is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia.
With a macular hole or an advanced stage of the disease, surgery to rupture the retina is inevitable. It must be performed by an experienced surgeon, since it often happens that the first time it is not possible to achieve a positive result.
To prevent relapses, the patient needs to take medications to improve blood circulation, lead a healthy lifestyle and monitor blood pressure.
Types of retinal tears
Depending on the degree of damage to the organs of vision, several forms of ruptures are distinguished:
- Full. In this pathological condition, almost all the membranes of the visual organ are involved. The disease is characterized by the appearance of flashes of light in front of the gaze and a sharp decrease in the level of vision.
- Lamellar. The tear is observed only in the upper layers of the eye. The pathology is asymptomatic. It begins to appear during periods of increased visual stress or physical activity. If there is damage to 1 eye, symptoms are noticeable when the healthy organ closes.
- Valve ruptures. Pathology is observed when the membrane of the eye and the vitreous body grow together. Elderly patients may experience additional detachment or destructive processes.
- Perforated. Appear against the background of thinning of the retinal surface. Peripheral ruptures provoke areas of dystrophic changes in the membrane of the eye, which are located at the edges of the organ of vision. The condition is characterized by the appearance of visual defects in some fields.
- Pre-tears of the retina from the dentate line. Appear due to trauma or severe shock to the visual apparatus.
- Macular tear. The disease causes a hole to form in the center of the retina. The tear also appears due to stretching of the retina.
- Valve. Accompanied by the presence of vitreous detachment.
The appearance of a certain type of disease depends on the provoking factors and predisposition of the patient.
Symptoms
Clinically, a retinal tear is manifested by loss of visual acuity. The nature of such changes and their intensity depend on the location of the damage and accompanying phenomena. General symptoms of pathology:
- the appearance of bright flashes reminiscent of lightning or the flickering of a lantern located in the distance;
- the appearance of dark flies in the field of view;
- inability to focus your gaze;
- deterioration of twilight vision.
Specific visual impairments are symptoms of certain types of pathology:
- macular holes are accompanied by a sharp decrease in the field of vision, the appearance of white or gray fog, and distortion of the picture;
- damage to the retina in the fovea leads to a change in color perception, loss of images in the center of the visual field;
- damage to the peripheral areas of the retina provokes the appearance of impenetrable colored or black spots throughout the entire field of vision.
Macular, valvular and peripheral ruptures can be accompanied by retinal detachment. It appears as a thick gray curtain before the eyes. It is characterized by serious consequences in the form of irreversible blindness.
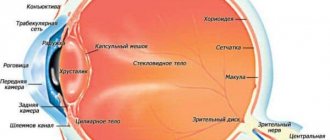
It is important to understand that the retina does not have many nerve receptors that can signal damage, such as the cornea. Even if the eye is injured, resulting in damage to the retina, it may not hurt at all. Therefore, you should not wait for physical discomfort to appear, but consult a doctor immediately after signs of pathology appear.
Symptoms of retinal damage
The severity of symptoms depends on the degree of tear and severity of the disease:
- the formation of a white veil before the gaze;
- the appearance of flies;
- intense light flashes;
- decreased quality of vision;
- flickering of dark flies;
- blurry picture;
- an increase in the black area in front of the eyes.
There are no obvious signs indicating the presence of tears on the surface of the eye. The listed symptoms indicate the onset of the disease.
Photo
Causes and nature of damage
Damage may look like this:
- L-, U-shaped.
- Arrow-shaped.
- Giant.
The causes of damage are:
- temporary changes in the retina (dystrophic);
- stress;
- concussions;
- heavy loads;
- eye injuries;
- hypertension;
- myopia that progresses;
- ophthalmological operations.
Eye injury
Treatment
Detachment of the membrane cannot be cured with medication. Regardless of the degree of detachment, surgical manipulations are necessary to stop the pathological process. The operations are aimed at attaching the retina using various adhesion methods:
- local attachment;
- circular commissure;
- vitrectomy;
- cryopexy;
- laser coagulation;
- retinopexy.
Treatment depends on the location of the tear, the severity of the process and the depth. To eliminate the pathological condition, several methods are used:
- Laser coagulation. It is used to eliminate retinal rupture or postequatorial retinal dystrophy. With the help of burn therapy, the vascular network of the ocular surface is connected. The duration of the manipulation does not exceed 30 minutes. Due to the procedure, there is no need for additional rehabilitation techniques. On average, the cost of intervention ranges from 8,000 to 17,200 rubles.
- Cryotherapy. Low temperatures are used to fuse the membranes of the visual apparatus. The cost of the procedure is about 15,000 rubles. Cryotherapy is a short procedure and does not require additional rehabilitation.
- Pneumatic retinopexy. A small amount of air is introduced into the organ of vision, which presses the retina against the vascular network. Pressing promotes more active healing. About 60,000 rubles.
- Vitrectomy. To fill the cavity of the visual apparatus, liquid silicone or a special eye is introduced, which is placed instead of the vitreous body. This manipulation ensures that the retina is pressed against the vascular network, which promotes more active healing. The operation is prescribed for complicated cases of detachment of the superficial membrane in the macular zone. Anterior vitrectomy costs about 88,800 rubles. The cost of performing a posterior vitrectomy ranges around 97,000 rubles.
After the procedure, regular visits to the ophthalmologist are necessary to prevent the development of complications.
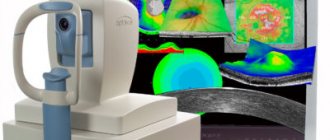
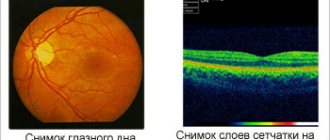
Diagnosis of retinal rupture and detachment
Timely diagnosis and treatment of the tear increases the chances of retinal restoration and vision preservation. Old defects are difficult to treat, and even operations are often ineffective.
A retinal tear can be confirmed using ophthalmoscopy, biomicroscopy (examination of the fundus with a slit lamp), sonography and ultrasound of the eyes. After making a diagnosis, the doctor specifies the location of the defect, as well as its size and age. These indicators will determine the treatment method.
Early diagnosis of retinal tears is difficult but is of utmost importance. In the process of examining a patient, the following methods are usually used:
- visometry (measurement of visual acuity);
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye);
- perimetry (study of visual fields);
- biomicroscopy (assessment of the anterior segment of the eyeball);
- tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure);
- definition of entoptic phenomena.
If necessary, also prescribe:
- ultrasound scanning in B-mode;
- laboratory tests.
Ophthalmoscopy should be given importance when diagnosing a rupture. It will show the detachment if it is present and will allow you to assess the extent of the defect, assess the condition of the macula and find the location of the rupture. It is recommended to combine fundus examination techniques to obtain all the information about the condition of the retina. Repeated fundus examinations allow you to detect a retinal tear and choose a treatment technique.
It is also worth conducting research into entoptic phenomena. They help determine the presence of detachment due to clouding of the lens or vitreous hemorrhage (conditions in which it is impossible to examine the fundus). In these cases, ultrasound in B-mode is also prescribed.
If a detachment is suspected, electrophysiological tests are sometimes prescribed to evaluate the functionality of the retina. Laboratory tests are needed before surgery (blood and urine tests, testing for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis, x-ray of the chest and nose). Before the operation, you must also obtain permission from your physician, dentist, and otolaryngologist.
In case of rapid progression of detachment, emergency hospitalization of the patient is necessary due to the risk of damage to the macular area. Hospitalization does not require all tests, a blood test is sufficient. This increases the risk of complications, but will speed up the operation.
Useful video
Retinal rupture is characterized by spontaneity. At the initial stages of development, there may be a complete absence of signs of a pathological condition. At the first symptomatic manifestations, timely consultation with a doctor is necessary, since delaying therapy leads to a complicated course of the disease. The pathology can only be eliminated surgically. Medications and traditional methods are powerless against the disease.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Distinctive signs of retinal damage
A retinal tear can take various forms and be located anywhere. The most common type is considered to be a macular hole, that is, a central hole. It is also commonly called valve. This disease also has a second name - macular hole. It occurs most often in older people, usually women.
- Oftalmovit-f capsules for eye health help with dacryocystitis and problems with the retina;
- Increases sharpness, vigilance and clarity of vision;
- Improves blood movement through the vessels, activates visual functions, has a positive effect on chorioretinopathy;
- Certification: Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP).
One type of mesh tear is lamellar damage. It looks like a scale or a small detachment. This sign of damage comes in two forms - U and L, ruptures in the shape of a valve or a small tooth. Each of them can be located in any eye area, while having similar signs of damage:
- visual acuity is lost;
- there is a feeling of blind spots;
- floaters and dark round spots appear before the eyes;
- visibility is like through a fog, as if some kind of veil appears before the eyes.
Lamellar damage to the retina is a defect that preserves the layer of photographic receptor properties. At the same time, visual accuracy may well be maintained, sometimes reaching a value of 0.9. Upon examination, a large lamellar lesion may appear as a round, red spot located in the central area of the macula. The thin beam emitted by a special slit lamp bends at the site of the break and seems to be lost. But a small-diameter rupture cannot always be seen and diagnosed. Quite often it is mistaken for a pre-rupture state.
Doctors specializing in vision believe that lamellar rupture does not occur immediately; the phenomenon occurs in two stages.
At the first stage, the formation of a so-called gap or cyst occurs. Then the inner wall of this cyst is opened, forming non-through ruptures. Specially conducted studies fully confirm this theory. In the process of posterior hyaloid detachment, a detachment of the internal sections of the retina is formed. In this case, the photoreceptor layer remains in the same place, representing the bottom of this lamellar damage. This process can take up to several months. But sooner or later the rupture will transform into through damage. And here urgent surgical intervention is already necessary.
Traditional treatment
Many people do not trust doctors and therefore try to cure a retinal tear on their own, using improvised means. One of the most common methods is to eat more berries such as blueberries and blueberries. Doctors agree that these berries are really good for the eyes and also recommend eating them for diseases such as cataracts and glaucoma. Of course, they cannot claim that such treatment will definitely produce results, but they also do not deny that there is still a positive effect on the condition and health of the eyes. Blueberries and blueberries can be eaten either raw or in the form of nutritional supplements, which can be purchased at any pharmacy. If you regularly eat these berries for several weeks, the retinal tear may decrease or even disappear completely. After such treatment, surgical intervention will not be necessary, and the condition of the eyes and vision will improve several times.
Diagnostics
The problem is that with a retinal rupture, all symptoms may be completely absent; ophthalmologists know this, who not only carry out a detailed external examination, but also conduct a very thorough diagnosis with lenses or a special slit lamp. To obtain the most accurate diagnosis, the ophthalmologist very often uses special drops that are instilled into the patient’s eyes, and with the help of such a medicine that dilates the pupil, the doctor can examine the fundus of the eye in more detail. Using diagnostics using drops, the ophthalmologist determines the size, as well as the number of areas in which damage has occurred, only after that he selects the most suitable option for eliminating this problem.
If there were any symptoms during a retinal tear, the doctor does not focus too much on them, since they may be very similar to the symptoms of some other diseases. To obtain the most accurate results, the ophthalmologist will also prescribe an ophthalmoscopy, which is carried out using special modern devices for additional examination of the fundus.
A person who has suffered a rupture for some reason should not waste time, since the danger of such damage lies in further deterioration of vision up to its complete loss. In case of a macular hole in the retina, the doctor often sends the patient for an ultrasound, since it can be used to find out exactly where the perforation has formed.
Diagnostic methods
Any disease requires special therapy; in order to choose it correctly, you need to make the correct diagnosis. Before sending a patient for examination, the doctor collects anamnesis by asking the patient about symptoms.
But since pain and visual disturbances occur extremely rarely during a rupture, in addition to a visual examination, a number of diagnostic measures are required to help accurately determine the pathology:
- Ophthalmoscopy. Helps analyze the condition of the fundus and identify existing damage;
- Examination of the visual apparatus using a slit lamp;
- Ultrasonography.
Ultrasound is an additional procedure; with its help, the doctor determines in detail the type of damage, the size of the tear and its location.