In ophthalmology, the most dangerous disease is ocular retinoblastoma (RB), a malignant tumor that affects the inner lining of the eye. This disease was discovered in 1926. Scientist Verlhof discovered that the neoplasm is formed from retinoblasts - cells that form the retina in the prenatal period. However, if a malfunction occurs in the process, the cells begin to rapidly divide and give rise to a tumor.
The diagnosis of retinoblastoma is made mainly in childhood. The main danger of the disease is that the initial stage is practically asymptomatic. This leads to serious consequences, including loss of vision and removal of the affected eyeball.
To avoid this, you should know how the disease manifests itself at the very beginning, what its causes are, and how it can be diagnosed. After all, a timely diagnosis in 95% of cases helps to completely cure the child, preserving his vision.
Causes of pathology
The development of retinal cancer is in most cases hereditary. It is based on a mutation at the gene level. The RB1 protein prevents cells from dividing excessively, but at some point it becomes inactive. Subsequently, the defective gene is passed on from generation to generation, which is the cause of the development of retinoblastoma.
Most cases of bilateral eye cancer are hereditary. The diagnosis is made before the age of 2.5 years, and the presence of the mutated gene is confirmed in 90% of cases. The first symptoms of the disease can be noticed already in the first year of a child’s life. A congenital tumor can lead to the development of glaucoma.
There is a sporadic (non-hereditary) form of retinoblastoma, which occurs due to random glitches in the gene program and mutations. It is detected in adolescence. Provoking factors are the late age of parents, their employment in hazardous industries, and unfavorable ecology. This pathology of the retina is unilateral and develops locally.
In adults, cancer of this form is extremely rare, and its causes remain unidentified.
Treatment
To cure retinoblastoma, an integrated approach should be taken. To determine the optimal tactics, it is necessary to take into account the general condition of the child, the stage of the tumor, the risk of developing secondary neoplasms, and commitment to organ preservation. With a small size of retinoblastoma, local destruction can be used, which is effective in 83% of cases (when combined with polychemotherapy, the effectiveness increases to 90%).
If the tumor is large, then enucleation is performed and polychemotherapy is prescribed. The four-year survival rate is 90%.
Classification of the disease
In ophthalmology, there are several broad classifications of this pathology.
According to the prevalence of the oncological process, the following are distinguished:
- Monocular, which affects only one eye.
- Bilateral (bilateral) is detected on the membranes of both eyes.
By type of growth:
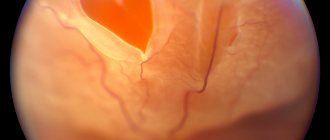
- Endophytic. It spreads to the central part, affecting the orbit of the eye, nerves, and also the macula (the yellow spot in the very center of the retina). The surface of the tumor is lumpy.
- Exophytic. The tumor grows towards the retina. Its further spread leads to an increase in the amount of intraocular fluid, increased intraocular pressure and retinal detachment. In this case, blood vessels can be damaged, hemorrhages occur, which is why the tumor acquires a pinkish tint.
Depending on the size and location of the pathological process, the following stages of retinoblastoma are distinguished:
- the most unfavorable, in which there is a widespread spread of metastases. The disease affects all tissues, nerves, orbit and retina.
- Unfavorable - the process has affected more than 50% of the retina of the eye, and multiple pathological foci are diagnosed on the vitreous body.
- Doubtful - the size of the tumor does not exceed 10 mm (disc diameters), it is located anterior to the ocular equator. Another option is that the diameter of the neoplasm is more than 10 mm, but it is localized posterior to the equator. Here various degrees of protrusion of the eyeball occur.
- Favorable - a lesion measuring 4-10 mm, located behind the equator of the eye.
- The most favorable. The size of the tumor does not exceed 4 mm. Lesions are single or multiple, located behind the equator line of the eye or directly on this line.
Retinoblastoma of the eye in children of stages 1 and 2 of development can extend beyond the eye orbit. Metastases of neuroblastoma first affect regional lymph nodes, then penetrate the brain and spinal cord. It is important to detect an insidious disease in time in the first stages.
Classification
According to statistical data, secondary tumors occur more often than primary ones. The following types of cancer of the optical system are distinguished:
- Benign tumors of the eyelids. Hyperkeratosis - the keratin layer of the eyelid skin grows excessively. Xanthelasmas are fatty deposits on the eyelids.
- Malignant tumors also form in the eyelids. Most often basal cell carcinoma. This is a basal cell skin cancer that develops in the corners of the eye and on the eyelids. Spinal cell carcinoma or malignant melanoma are found much less frequently. Experts believe fair-skinned people who are exposed to sunlight for many years are more likely to develop skin cancer.
- Melanoma. It is an extremely dangerous pathological process. Develops on the conjunctiva, eyelids, and affects the choroid. Melanoma tends to metastasize early and the prognosis is poor.
- Retinoblastoma is the most common malignant neoplasm in childhood. Affects the retina and develops for genetic reasons. Parents already carry the gene mutation and pass it on to their child. However, this hereditary form of retinoblastoma occurs in only 10% of cases. In 90% of cases, the gene defect occurs spontaneously.
Other types of tumors: squamous cell carcinoma and sarcoma. The latter type of cancer progresses rapidly. Sarcoma makes it difficult for the eyeball to move, causing the patient's optic nerve to atrophy.
Based on the location of formations, there are two types:
- Extraocular. Localized on the eyelids, third eyelid, conjunctiva, orbit and optic nerve. Extraocular types include lymphoma, melanoma, adenoma, SCC, basal cell carcinoma, mastocytoma, viral papillomatosis, meningioma, osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma.
- Ocular. Cancer is localized on the cornea and sclera, iris and ciliary body, retina and choroid. The ocular type includes corneal SCC, lymphoma, ciliary body adenoma, retinoblastoma, melanoma and medulloepithelioma.
Symptoms of the disease
The initial stage occurs quite early - up to 12 months. At this age, the child cannot complain of decreased visual acuity or blindness. In this case, parental attentiveness is extremely important.
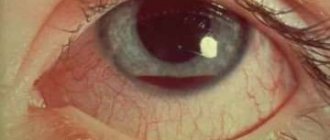
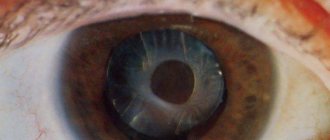
The most noticeable external sign is strabismus. This defect should not be ignored; it is better to consult an ophthalmologist. As the tumor enlarges and when bright light hits it, a white pupillary reflex appears (the tumor is visible through the pupil). In medicine, this symptom is called “cat's eye”. The effect is clearly visible in flash photographs.
When inflammation and/or swelling occurs, pain, photophobia appear, and glaucoma develops. As a result of damage to the retina, the eye may stop responding to light, vision becomes cloudy, and blindness may occur.
Next, retinoblastoma destroys the walls of the orbit and extends beyond the eye. Exophthalmos (“bulging” of the eye) of varying severity appears.
In the later stages of eye cancer, when metastases have affected the optic nerve and spread to the brain, migraine attacks, vomiting, nausea appear, and general intoxication develops.
Diagnosis of eye tumor
An ophthalmologist can detect single small tumors during a preventive appointment. However, diagnostics in ophthalmology also includes hardware techniques.
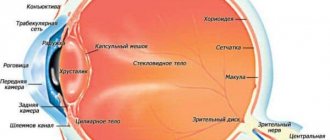
A detailed examination of the structures of the eye in ophthalmology is carried out using:
- Retinal camera (fundus camera). It can be used to photograph the fundus of the eye to identify pathological changes.
- Ultrasound.
- Biomicroscopy of the eye - examination of the tissues of the eyeball using a slit lamp. For young children, it is performed under general anesthesia.
- X-ray of the orbit - allows you to assess the extent of the tumor.
- CT allows you to see the exact contours of the tumor and determine the spread of metastases.
- An additional research method is MRI.
If retinoblastoma is suspected, cerebrospinal fluid sampling and examination is prescribed. In all cases of eye cancer detection, genetic diagnosis is carried out, and the medical history of all family members is collected.
Only after a full course of diagnostic measures can the stage of the disease be accurately determined and a method for combating the disease determined.
Diagnostics
To identify a neoplasm, you need to perform an ophthalmoscopy after maximum mydriasis. In young children, medicated sleep may be necessary. When examining the peripheral zone of the retina, sclerocompression should be used. This allows for better visualization of hard-to-reach areas of the fundus. It is necessary to study the fundus of the eye during ophthalmoscopy along all meridians. If the tumor is located in the preequatorial region or in the presence of a pseudohypopyon, a fine-needle biopsy of the suspicious node is performed. Ultrasound can assess the size of retinoblastoma and determine the presence of calcifications.
Methods of organ-preserving treatment:
- Local chemotherapy for retinal cancer is designed to reduce the pathological focus. In this case, the drug can be injected both into the vitreous body and into the artery of the eye.
- Laser coagulation is used only for tumor sizes up to 1.5 mm.
- External radiation therapy. Children are undergoing anesthesia with mandatory head fixation. Typically, this method is used for tumors that are located far from the center of the eye. Radiation therapy with chemotherapy gives a positive result in 75% of cases.
- Cryodestruction, or cauterization of the tumor with liquid nitrogen.
In case of significant tumor growth, the presence of metastases, glaucoma, or loss of vision, surgical removal of the eyeball (enucleation) is performed. To avoid the development of complications, such as macular edema of the retina, treatment is combined with subsequent chemotherapy. This also helps reduce the risk of recurring tumors. The operation is performed as a last resort if there is a risk to the patient's life. More often this method is prescribed up to 3 years. Subsequently, eye prosthetics are performed.
Retinal tumor
A malignant tumor of the retina must be treated immediately, and for these purposes doctors use surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
The intensive care regimen can be determined solely on an individual basis, and the patient’s health status and the stage of the predominant disease play an important role in decision-making.
If a retinal tumor is recognized in a timely manner, the clinical outcome is very favorable, and vision can be fully restored.
The surgical method is represented by enucleation, the indications for which are the extensive nature of the intraocular lesion, lack of vision and glaucoma. The essence of the operation is cutting off the optic nerve over long distances with further prosthetics (after 6 weeks).
Among the advantages of such surgical procedures, it is worth highlighting the following:
- the list of contraindications is kept to a minimum;
- minimal number of side effects;
- minimal health risk;
- no lethal outcome and unlimited age audience.
But the disadvantages are cosmetic defects, which are appropriate in those clinical pictures when the operation was performed before three years. In addition, a long rehabilitation course is required.
Radiation therapy aims to cure the disease while preserving vision. Patients of this procedure are children under three years of age, and it can be performed exclusively under anesthesia and with preliminary fixation of the patient on a rigid basis. The clinical outcome is quite favorable, and the disease is cured in 75% of clinical cases.
Chemotherapy is appropriate for invasion of the optic nerve, as well as in the case of orbital damage and regional metastases. The main medications are cytostatics, represented in modern pharmacology by combinations of Carboplatin, Vincristine, Vepesid, or Vincristine, Doxorubicin and Cyclophosphamide. The therapeutic effect is also noticeable, but a one-time procedure may not be enough.
In modern oncology, doctors choose a conservative method of treating retinoblastoma, represented by cryotherapy and photocoagulation, where the first procedure is indicated for extensive damage to the anterior retina, and the second - in case of damage to the posterior retina. These methods are highly effective and gentle, and in case of recurrence of the disease, repeated therapy is appropriate. With the right treatment approach, complete recovery can be achieved.
Retinal cancer in a child: the main subtleties
This diagnosis, according to statistics, occurs in only one newborn out of 15-22 thousand worldwide. In 80-90% of cases, the diagnosis is established before the child reaches 3 years of age. Hereditary retinoblastoma always affects both eyes, and its first signs appear already in the first year of a baby’s life.
Children who have had retinal cancer should undergo examinations every six months after treatment. They are registered with the dispensary for life. If they want to start a family, such patients are required to visit a geneticist and get advice, since most often the pathology is inherited.
Children with this diagnosis are at high risk of developing other types of cancer.
Prevention and prognosis of retinoblastoma
The best way to prevent the disease is to conduct DNA diagnostics at the stage of pregnancy planning. If a mutation in the RB1 gene is detected, IVF should be used.
Preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist in the first years of a child’s life will help identify the disease at an early stage. A child's eyes should be monitored more closely if a family member is known to have the mutated gene.
If the disease is detected early, the prognosis is favorable. Even when cancer is detected in late stages, remission is achieved in 47% of patients. Modern methods practically eliminate death that occurs due to extensive metastases. In most cases, it is possible to save the eye and vision of a small patient, which contributes to his further harmonious and versatile development.