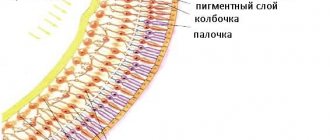
Retinal pathology can occur with various general and systemic diseases - hypertension, diabetes mellitus, kidney and adrenal gland diseases, as well as with eye injuries and traumatic brain injuries. Some infectious diseases can be complicated by retinal diseases.
The Rascheskov Eye Surgery Clinic provides treatment for the following retinal diseases:
- Retinal disinsertion
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Epiretinal fibrosis
- Vitreofoveal traction syndrome
- Macular hole (macular hole)
- Age-related macular degeneration AMD (macular degeneration)
- Central serous retinopathy
- Retinal vein occlusion (thrombosis)
- Peripheral retinal dystrophy
- Hemophthalmos
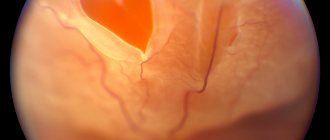
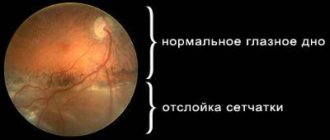
Retinal disinsertion
This is the separation of the retina from the underlying tissues. In most cases, retinal detachment occurs as a result of retinal tear, perforation or destruction. Retinal detachment is a disease that requires urgent treatment. A prerequisite for the success of operations for retinal detachment is their timeliness, since the long-term existence of a detachment leads to irreversible changes in the retina and loss of vision.
Treatment of retinal detachment
At the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic, treatment of retinal detachment (depending on the type) is carried out using the following methods:
- Microinvasive vitrectomy
- Extrascleral filling
- Restrictive peripheral laser coagulation of the retina (for local retinal detachment)
Surgical treatment of retinal detachment
Currently, there is only surgical treatment for retinal detachment, the goal of which is to evacuate subretinal fluid from under the detached retina, straighten the retina and attach it to the underlying choroid.
Depending on the condition of the vitreous body and retina, the type of retinal detachment, its area and duration, the presence of a single retinal break or multiple breaks, surgical treatment can be carried out using extrascleral methods or using the techniques and techniques of vitreoretinal surgery. In clinical practice, tractional, rhegmatogenous and exudative retinal detachment are distinguished. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (“rhegma” in Greek - hole, opening) is the most common form of retinal detachment. The essence of surgical treatment of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is to detect a retinal break and close it. To do this, the underlying membranes are brought closer to the detached retina, and around the break, inflammation is caused by thermal action (cryopexy or laser coagulation of the retina) and subsequent scarring in the area of the retinal break. All this restores the tightness (integrity) of the retina of the eye.
Diabetic retinopathy
One of the most severe complications of diabetes mellitus, in which changes occur in the blood vessels of the retina, which leads to a disruption in their oxygen supply. Diabetic retinopathy develops gradually, and even its pronounced stages may be imperceptible to the patient.
Depending on the stage, diabetic retinopathy causes various hemorrhages in the vitreous body, retinal detachment, glaucoma, and in the absence of timely detection and necessary treatment leads to blindness.”
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
The most effective and reliable method of preventing the progression of diabetic retinopathy is laser coagulation of the retina.
In this case, the main attention should be paid to the treatment of diabetes mellitus, constantly regulating the level of sugar and glycated hemoglobin in the blood
Depending on the stage of diabetic retinopathy, the following treatments may also be used:
- anti-VEGF therapy (intravitreal administration of the drug Aflibercept (Eylea)
- panretinal laser coagulation of the retina
- microinvasive vitrectomy
Classification of the disease
Depending on the provoking factors, the following types of retinal detachment are distinguished:
- Rhegmatogenous (primary). Appears when thinning and vascular insufficiency of the retina continues for a long time. Gaps form, after which the fluid filling the vitreous body flows under the retina, causing a disruption in its nutrition. This can occur after injury, unsuccessful surgery, injections into the eyeballs, scleral filling, etc.
- Exudative (secondary, serous) often occurs at the same time as rejection of the pigment epithelium. It usually results from intraocular infections, retinal tumors, and inflammation of the fundus, in which fluid accumulates in the eye.
- Traumatic. A consequence of eye injury, which can manifest itself either immediately after it or after a long period of time.
- Tractional detachment often results from retinal tears caused by vitreous pressure (traction).
Based on reversibility, the detachment of the mesh layer is divided into:
- Movable. After two to three days of pastel mode, the retina is reattached to the underlying tissues
- Rigid. Bed rest does not give results.
By scale of damage:
- Local. The lesion occupies 25% of the retinal area;
- Common. The lesion occupies 50% of the retina;
- Subtotal. Distribution to 75% of the retina.
- Total. Detachment over the entire surface of the retina.
Epiretinal fibrosis
This is a thin film that forms in the vitreous cavity in close proximity to the macula. It is usually a slowly progressive disease that impairs central vision, causing blurred and distorted images. As it progresses, the membrane begins to pull the macula towards itself, which causes its swelling, the formation of a hole in it and detachment. Epiretinal fibrosis can lead to the development of vitreomacular traction syndrome
Treatment of epiretinal fibrosis
Microinvasive vitrectomy.
Vitreofoveal traction syndrome
Vitreofoveal traction syndrome
Vitreofoveal traction syndrome (VFTS) develops as a consequence of epiretinal fibrosis. In this case, traction of the retina occurs in the macular zone, which can lead to its rupture.
Symptoms: visual distortion, metamorphopsia. HFTS can lead to decreased or loss of central vision.
Treatment of VFTS
Microinvasive vitrectomy.
Macular hole (macular hole)
This is a condition in which there is a tear in the layers of the retina in the central zone, which consists of a large number of densely located photoreceptors, which provides good object vision.
It occurs as a result of eye injury and some of its diseases. But most often, the formation of a hole in the macula occurs as a result of aging. A macular hole in the retina leads to a significant decrease in central vision, image distortion, and difficulty working at close range and reading.
Treatment of macular hole
Microinvasive vitrectomy
Restrictions after surgery
In addition to protecting the eyes from mechanical particles and excessive light load, after surgery it is important to pay attention to the proper blood supply to the operated organ of vision. To avoid quick and long-term negative consequences, after the intervention, patients should not provoke blood flow to the head. To do this you need to avoid:
- hot and stuffy rooms, refrain from visiting baths and saunas;
- physical and emotional stress;
- bending forward, lying in a lying position with your head thrown back and sleeping on the side where the eye was operated on;
- airplane flights;
- diving underwater.
You should also avoid eye strain, which occurs when watching TV for a long time, working at a computer, or being under the bright sun. If circumstances require working with monitors and reading small print, you should look into the distance every 30 minutes or rest with your eyes closed. On clear days you should wear sunglasses.
Age-related macular degeneration AMD (macular degeneration)
This is a degenerative disease of the central part of the retina - the macula, which is responsible for central, clear vision. Therefore, in AMD there is loss of central vision. In the initial stages, the disease occurs unnoticed by the patient and can only be detected during an appointment with an ophthalmologist. As AMD progresses and passes into the so-called neovascular (wet) form, the patient may notice decreased vision, a sensation of curved lines, blurred and disappearing areas.
In the wet form of AMD, due to a lack of oxygen in the retina, the growth of new defective blood vessels (neovascularization) occurs. The walls of these new vessels are much thinner than the walls of ordinary vessels, so they can rupture very easily, leading to hemorrhage and the formation of retinal edema.
Treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Currently, the most effective treatment for AMD (wet form) is anti-VEGF therapy - this is a therapy aimed at blocking angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) in the eye. It is carried out by intravitreal administration of drugs. The clinic "Eye Surgery Combs" uses
Intravitreal administration of the drug Aflibercept (Eylea).
Prices for examination and treatment
At the Moscow Eye Clinic you can undergo a full diagnostic examination and receive recommendations on the most effective treatment methods. A comprehensive examination of the patient (including methods such as testing visual acuity, biomicroscopy, autorefractometry, small-pupil ophthalmoscopy, pneumotonometry) costs 3,500 rubles.
The cost of episcleral cerclage surgery according to Arruga at the Clinic starts from 90,000 rubles. The final cost of treatment is determined individually in each case and depends on the specific diagnosis, stage of the disease, medical procedures performed, tests available, etc.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by calling or online, using the appropriate form on the website; you can also check out the “Prices” section.
Go to the "Prices" section
Central serous retinopathy
This is a disease of a toxic-infectious nature, characterized by vasospasm of the choriocapillary plate of the choroid and manifested by a sudden deterioration of vision (decreased acuity and narrowing of visual fields) with the development of a central scotoma, opacification and swelling of the retina in the macula area. May lead to retinal detachment.
Treatment of central serous retinopathy
Laser coagulation of the retina
Possible risks of surgery
All possible complications after episcleral filling can be divided into several groups. Immediately after the operation, there is a risk of symptoms associated with a violation of the technique of its implementation (drooping of the upper eyelid, slight strabismus as a result of damage to the extraocular muscles), infection, secondary retinal detachment or an increase in intraocular pressure. In the later postoperative period, changes in the fundus may be detected with the formation of cysts, foci of degeneration or membranes in the macula, decreased transparency of the lens, or symptoms of myopia. In some cases, exposure of the implant is detected as a result of a violation of the suturing technique, with subsequent infection of the filling. In addition, if the retina does not fit completely in the area of the break, the extrascleral filling operation may not be effective and may be complicated by recurrent retinal detachment.
The success of surgical treatment for retinal detachment largely depends on the skill of the surgeon and the equipment of the clinic in which the operation is performed. Doctors at the Retina Center masterfully master all modern methods of surgical treatment for patients with retinal pathology, including retinal detachment and ruptures. Our clinic is equipped with the best samples of ophthalmological equipment. By contacting our ophthalmology center, you choose comfortable conditions and the best treatment result.
Retinal vein occlusion (thrombosis)
Poor circulation in the central retinal vein or its branches. May lead to complete, irreversible loss of vision.
It occurs when this blood vessel or its branches is blocked, which leads to reverse flow of venous blood into the capillaries of the retina, an increase in pressure in them, hemorrhages in the retina, its edema and ischemia (lack of oxygen).
Over time, due to the consequences of venous obstruction, pressure in the eye may increase and glaucoma may develop.
Treatment of retinal vein occlusion (thrombosis)
As a rule, combination treatment is used:
- intravitreal administration of the drug Aflibercept
- intravitreal administration of the drug Ozurdex
- laser coagulation of the retina
Peripheral retinal dystrophy
Retinal dystrophy is usually caused by disorders in the vascular system of the eye. It mainly affects older people, whose vision gradually deteriorates. With retinal dystrophy, the photoreceptor cells responsible for distance vision and color perception are affected. At first, retinal dystrophy can be asymptomatic and often a person does not even suspect that he has such an insidious disease.
Retinal dystrophies can be divided into: central and peripheral. Peripheral retinal dystrophy is most often present in myopic people, since with myopia the length of the eye increases, resulting in stretching of its membranes and thinning of the retina at the periphery. The essence of this pathological process is the deterioration of blood flow in local areas of the periphery of the eye, which leads to metabolic disorders and the appearance of dystrophic foci.
Treatment of peripheral retinal dystrophy
Peripheral laser coagulation - the main goal of treatment is the prevention of retinal detachment.
Prevention of retinal detachment
The main medical method for preventing retinal detachment today is PPLC, a procedure of peripheral preventive laser coagulation. The essence of the method is to strengthen the retina by creating point fusions between the retina and choroid of the eye. PPLC is performed using a laser, non-contact and bloodless .
As a general prevention of retinal diseases, experts recommend:
- stop smoking and excessive drinking of alcohol;
- diversify the menu with products that have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the visual system - nuts, fish, egg yolk, vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, etc.;
- maintain a sleep-wake schedule;
- pay attention to harmonious physical development, avoid traumatic sports;
- observe the rules of visual hygiene.
It is necessary to regularly monitor blood sugar levels and blood pressure, and for people at risk, make routine visits to the ophthalmologist more frequent.
As a medicinal prevention of problems with the retina, the doctor may recommend various vitamin complexes, as well as courses of special medications for the eyes. For vascular diseases, these can be Quinax, Emoxy-Optic, Emoxipin drops. As part of the complex treatment of retinal dystrophy - Taufon, Aisotin and other drugs, which are used only after examination of the visual system and as prescribed by a doctor.
Hemophthalmos
This is a hemorrhage into the vitreous body of the eye, the causes of which are eye trauma, inflammatory processes in the vascular tract and retina, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, retinal rupture (retinal tears).
Hemorrhage into the vitreous body of the eye can also occur against the background of common diseases - atherosclerosis, hypertension, blood diseases, endocrine disorders. As a result of hemophthalmia, visual acuity sharply decreases, ranging from dots or threads floating in front of the eye, and up to complete blindness.
Treatment of hemophthalmos
In cases where the hemorrhage into the vitreous body is massive, or hemophthalmos is recurrent in nature, surgical treatment is performed - microinvasive vitrectomy
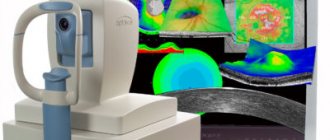
Diagnostics
In the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic, a diagnostic complex is used to identify pathologies of the retina and fundus of the eye, including the following studies:
- optical coherence tomography (OCT);
- slit lamp examination of the anterior part of the eye;
- autorefractometry;
- visometry;
- examination of the fundus with pupil dilation;
- tonometry;
- Ultrasound (B-scan);
- fluorescein angiography of the retina;
- optical coherence tomography of the macular zone in angio mode.
The most informative research method for retinal diseases is optical coherence tomography, which allows you to obtain ultra-thin images of the layers of the retina with a resolution of 8-10 microns
The cost of a diagnostic complex for retinal diseases is 2500 rubles.
To study the vessels of the retina, optic nerve and choroid, the clinic uses one of the most effective diagnostic methods - fundus fluorescein angiography (FAG), which is carried out using the latest equipment - the FF 450 Visupac Zeiss fundus camera.
FA makes it possible to diagnose a number of diseases that are characterized by pathological changes in the blood flow of retinal vessels and which cannot be detected using traditional diagnostic methods.
Early diagnosis of a number of retinal diseases and timely treatment are the main principles that will prevent vision loss, minimize damage to the eyes and significantly increase the chance of cure, as well as avoid blindness!
Each case of the disease is individual; only a specialist can decide which method or combination of treatment methods is most preferable for each individual patient.
The specialists of the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic have extensive experience in managing patients with pathologies of the retina and fundus of the eye. For each patient who comes to the clinic, after a thorough diagnosis, an optimal individual treatment program is selected using all possible modern techniques to achieve maximum effect in the treatment of complex retinal diseases.
Diagnosis of retinal detachment
In order to confirm or refute the diagnosis of retinal detachment, it is necessary to undergo a thorough ophthalmological examination. At the Excimer clinic, diagnostics are performed using a complex of modern computerized equipment; the level and quality of such studies allow our specialists to create the most complete and objective picture of the condition of the patient’s retina.
Evaluation of patients with suspected retinal detachment may include:
- examination of the fundus (ophthalmoscopy);
- optical coherence tomography of the posterior segment of the eye;
- study of visual fields (perimetry) in order to assess the condition of the retina in its periphery;
- electrophysiological study - determination of the viability of nerve cells of the retina and optic nerve;
- ultrasound examination of the internal structures of the eye and other diagnostic procedures.
Retinal detachment can only be diagnosed by an ophthalmologist. If a pathological process develops, treatment must be started as early as possible, this significantly increases the chances of a successful outcome.
Vitreoretinal surgery
Vitreoretinal surgery is the most complex area of surgical ophthalmology, which is a combined surgical intervention performed on the retina and vitreous body. Methods of vitreoretinal surgery include microinvasive vitrectomy.
Microinvasive vitrectomy
Vitrectomy (“vitreum” - vitreous; “ectomy” - removal) is a surgical operation, the purpose of which is partial or complete removal of the vitreous. Depending on the area of the vitreous body to be removed, the operation may be:
- total, which involves the removal of the entire vitreous.
- subtotal (partial) vitrectomy, which includes such varieties as anterior and posterior vitrectomy.
Currently, vitrectomy makes it possible to treat many diseases of the retina and vitreous body, which were previously considered incurable; moreover, the latest equipment and technologies allow vitrectomy to be performed on an outpatient basis without hospitalization.
At the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic, vitreoretinal surgeries are performed using the latest multifunctional surgical combine Constellation (Alcon, USA).
Indications for vitrectomy surgery:
- proliferative diabetic retinopathy, complicated by vitreous hemorrhage, traction retinal detachment, traction macular edema;
- macular hole;
- epiretinal fibrosis, vitreoretinal traction syndrome;
- retinal detachment
- intraocular infection (endophthalmitis, severe uveitis);
- severe eye injury, accompanied by vitreous hemorrhage, retinal detachment, intraocular foreign bodies;
- recurrent hemophthalmos (vitreous hemorrhage);
- dislocation of the lens into the vitreous body, luxation of the intraocular lens into the vitreous body after cataract removal.
How is the operation performed?
The vitrectomy operation is performed through three very thin punctures, which are positioned in such a way that the insertion of special instruments does not damage the healthy tissue of the retina and lens.
During the operation, blood or pathologically altered tissues that cause traction (tension) of the retina are removed from the vitreous body of the eye. After complete removal of the altered vitreous, vitrectomy is completed by introducing into the eye one of the vitreous substitutes, which include balanced saline solution, sterile air or a gas-air mixture, perfluoroorganic liquids (PFOS) or silicone oil.
Such artificial substances, expanding, press the detached retina from the inside to the walls of the eye. Thus, keeping the retina in its normal position, repeated intraocular hemorrhages and the growth of newly formed pathological vessels are prevented.
The operations are performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The operation time is up to 1.5 - 2 hours, depending on the complexity and the presence of aggravating factors.
Treatment results
Vitrectomy has proven itself to be an effective means of improving vision in cases with long-term non-absorbing hemorrhages in the vitreous area. Microinvasive vitrectomy can reduce the risk of severe bleeding in cases with incipient hemorrhage, as well as in cases of proliferation of pathological blood vessels.
How to prepare for surgery
If you are scheduled for microinvasive vitrectomy, you need to obtain the opinion of the following specialists that there are no contraindications to the operation:
- Endocrinologist (if you have diabetes)
And also undergo a number of tests and studies:
- blood for general analysis (expiration date 10 days);
- blood sugar test (expiration date 10 days);
- urine for general analysis (expiration date 10 days);
- Wasserman reaction (RW) (shelf life 10 days);
- blood for antibodies to HIV (regardless of age), HBs antigen, hepatitis C (expiration date 1 month).
- fluorographic examination (expiration date 1 year);
- ECG (expiration date 1 month)
After receiving the results of all studies and undergoing examinations from specialists, it is necessary to obtain a physician’s opinion about the absence of contraindications to the operation.
The day before the operation, the medical receptionist will call you and inform you of the time at which you need to come to the clinic. Taking into account the preparation for the operation, the operation itself and the post-operative examination, you will spend about 3 hours in the clinic. Depending on the complexity of the pathology, the duration of the operation may be longer.
It is not recommended to come to surgery wearing woolen clothing.
What to do after surgery
The postoperative period after vitrectomy varies from several days to weeks depending on the condition of the patient's retina, as well as the extent of the affected area and the type of replacement vitreous component. In the presence of severe severe changes in the retina, even after vitrectomy, complete restoration of vision is impossible, since in this case irreversible changes in the retina and optic nerve occur.
Depending on the substance administered, the doctor will give individual recommendations regarding behavior in the postoperative period. This may be a certain position of the head, or bed rest.
To protect against possible infection and speed up recovery, eye drops must be instilled into the operated eye. Your doctor will give you a regimen for instilling drops.
After surgery it is not recommended:
- visiting a sauna, hot bath - within 4 weeks after surgery
- lift weights up to 10-15 kg.
Contraindications
- pronounced opacities of the cornea, as well as gross changes in the optic nerve and retina.
Cost of the operation
Microinvasive vitrectomy – from RUB 65,000. Combined operation microinvasive vitrectomy + phacoemulsification – from 101,000 rubles.
Treatment of retinal detachment
This disorder is not amenable to drug therapy; it is considered as an auxiliary measure. With the help of drugs you can only stop intraocular bleeding. Vitamins are used to support the performance of the retina.
During the operation, the surgeon presses the retina against the vascular layer.
This allows you to restore its trophism and, as a result, its performance. Retinal compression can be done in different ways. On the outside of the eye these are the following operations:
- Sclera filling - indentation using silicone sponges
- Circlage - indentation over the entire surface of the eye with a large number of ruptures
- Ballooning is the introduction of a special balloon at the site of the lesion, followed by inflating it to press and tightly fit the retina (it is removed after restoration of the retina).
Operations on areas under the eye shell
- Vitrectomy - removal of the vitreous body and filling the resulting cavity with silicone oil to press and fuse the detached retina with adjacent healthy areas
- Pneumoretinopexy is an increase in the volume of the vitreous body by introducing air into it. This allows you to press the retina and return its shape to its original position
- Laser coagulation – fixation of the retina on the choroid under the influence of high temperatures.
Most often performed on an outpatient basis. At the same time, it is possible to glue the torn areas.
Extrascleral retinal filling
Extrascleral filling is a surgical method for treating retinal detachment by intervening on the surface of the sclera. The purpose of such an operation, like any other operation for retinal detachment, is to bring the detached area of the retina closer to the pigment epithelium.
How the operation goes.
Before the operation, the exact location of the detachment is determined and a filling of the required size is made. Currently, the main material for cutting fillings is a soft silicone sponge, an elastic and easy-to-use material. After this, the conjunctiva is cut and a seal is placed on the sclera, fixed with sutures. Depending on the type of detachment, location and many other factors, radial, sectoral and circular retinal fillings are distinguished. If necessary, the accumulated liquid is also drained and removed through a special hole. In some cases, it is necessary to introduce a special expanding gas or air into the eye cavity. The operation ends with suturing along the conjunctival incision.
Treatment results
Improvement in vision after applying a filling occurs gradually over several days, in some cases the process can take up to six months. In older people and people with myopia, recovery may take longer.
After extrascleral filling, in most cases, vision is not completely restored. The maximum level of vision depends on the “age” of the retinal detachment and the degree of involvement of the central parts of the retina in the process of detachment.
How to prepare for surgery
If you are scheduled for extrascleral filling surgery, you need to obtain the opinion of the following specialists about the absence of contraindications to the operation:
- Endocrinologist (if you have diabetes)
And also undergo a number of tests and studies:
- blood for general analysis (expiration date 10 days);
- blood sugar test (expiration date 10 days);
- urine for general analysis (expiration date 10 days);
- Wasserman reaction (RW) (shelf life 10 days);
- blood for antibodies to HIV (regardless of age), HBs antigen, hepatitis C (expiration date 1 month).
- fluorographic examination (expiration date 1 year);
- ECG (expiration date 1 month)
After receiving the results of all studies and undergoing examinations from specialists, it is necessary to obtain a physician’s opinion about the absence of contraindications to the operation.
The day before the operation, the medical receptionist will call you and inform you of the time at which you need to come to the clinic. Taking into account the preparation for the operation, the operation itself and the post-operative examination, you will spend about 3 hours in the clinic. Depending on the complexity, the duration of the operation may be longer.
It is not recommended to come to surgery wearing woolen clothing.
What to do after surgery
The doctor will give universal recommendations for the postoperative period. This may be a certain position of the head, or bed rest.
To protect against possible infection and speed up recovery, eye drops must be instilled into the operated eye. Your doctor will give you a regimen for instilling drops.
After surgery it is not recommended:
- visiting a sauna, hot bath - within 4 weeks after surgery
- lift weights up to 10-15 kg.
Cost of the operation
Extrascleral filling – 65,000 rubles.
Combined methods of surgical treatment
Depending on the specific type of retinal detachment, our specialists will choose one of certain surgical methods or a combination of them. The combination of these interventions is selected individually for each patient, which depends on the condition of the vitreous body and retina, the number and location of retinal breaks, the prevalence and duration of retinal detachment. Depending on each specific case, treatment can be carried out in one or several stages, using short-term tamponade of the vitreous cavity with gaseous or liquid perfluoroorganic compounds or long-term tamponade with silicone.
Our successes in the field of retinal and vitreous surgery, thanks to which we are able to restore and preserve vision, restore social adaptation to patients previously considered inoperable, would have been impossible without the introduction into practice of the latest advances in vitreoretinal surgery, the basis of which is vitrectomy.
Modern surgical systems, high-speed vitreotomes, xenon endo-illuminators, perfluoroorganic compounds, endolasers, advanced micro-instruments, combined with our vast clinical experience, allow us to provide treatment for retinal detachment at a completely new quality level.
A comprehensive and individual approach to choosing a treatment method for retinal detachments, offered in our clinic, allows patients suffering from this terrible disease to preserve their vision.
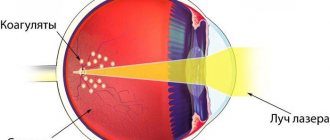
Laser coagulation of the retina
Laser strengthening (coagulation) of the retina is today one of the most effective procedures used to treat degenerative pathologies of the retina and prevent the development of severe complications, including complete loss of vision. The procedure is also used in the complex treatment of vascular lesions of the retina (in patients with diabetes mellitus or arterial hypertension) and for certain types of tumors.
Degenerative processes in the retina are most often detected in patients with moderate and high myopia. With the help of laser coagulation, it is possible to avoid further progression of pathological changes and the development of retinal detachment. Strengthening the retina can be performed on pregnant women who, against the background of myopia, have pronounced degenerative changes in the retina, and there is a high risk of retinal detachment during natural childbirth (peripheral preventive laser coagulation).
Indications for laser coagulation
- retinal dystrophy;
- age-related macular degeneration AMD;
- thrombosis of the central vein in the retina;
- local retinal detachment;
- diabetic retinopathy.
Laser coagulation of the retina is practically the only effective treatment method for diabetic retinopathy, angiomatosis, thrombosis of the central retinal vein, age-related macular degeneration and some other retinal diseases.
How is laser coagulation of the retina performed?
At the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic, the laser coagulation procedure of the retina is performed using the latest ophthalmic laser - Diode laser VISULAS 532 (Zeiss, Germany).
No special preparation or tests are required before the laser coagulation procedure. It can be carried out on the day of diagnosis.
The technique of laser coagulation of the retina is based on the properties of argon laser beams, under the influence of which a local increase in temperature develops in a limited area of the retina, accompanied by the process of tissue coagulation (clotting). Thus, the treated areas of the retina are literally “soldered” to the choroid.
One session of laser coagulation lasts 10 - 20 minutes. Laser coagulation is performed on an outpatient basis under local drip anesthesia. The patient is instilled with drops that dilate the pupil, which provides sufficient access even to hard-to-reach areas of the retina. After this, a special lens with an anti-reflective coating is installed on the patient’s eye, which allows laser radiation to completely penetrate inside the eyeball. The surgeon monitors the progress of the manipulation through a stereomicroscope. Depending on the indications, laser coagulation can be performed on limited areas of the retina or circularly, along the periphery of the retina.
There are the following types of laser coagulation of the retina:
1. Restrictive preventive laser coagulation of the retina (RPLKS)
Therapeutic and prophylactic outpatient laser surgery, in which dosed burns are applied to the retina using a laser coagulator in order to create a barrier (barricade) around pathological foci. It is believed that this prevents the spread of the pathological process and helps prevent complications - retinal detachment.
2. Peripheral preventive laser coagulation of the retina (PPLC)
This is a procedure to strengthen the peripheral zone of the retina, aimed at preventing the occurrence of retinal detachment. The PPLKS method is based on laser treatment of thinned areas of the retina. Using laser radiation, the so-called “soldering” of the retina is performed in weak areas and adhesions of the retina with the underlying tissues are formed around the breaks.
3. Panretinal retinal laser coagulation (PRLC)
The panretinal laser coagulation method involves causing micro-burns using a laser beam. This treatment involves laser treatment of all areas of the retina with the exception of the central part. The procedure is carried out in several stages. The number of stages depends on the stage of the disease and ranges from 3 to 5. In each session, from 500 to 800 point burns are performed. The duration of the session is about 60 minutes, the interval between sessions is 2-4 months.
Advantages
- The procedure is carried out contactlessly using a laser, without making an incision in the eyeball, which completely eliminates the risk of infection
- Possibility of repeating if necessary;
- After strengthening the retina, the patient can return to his normal lifestyle on the same day.
Treatment results
After laser coagulation of the retina, blood flow is restored, vision improves, and further detachment and fluid leakage under the retina are prevented. You should be examined annually by an ophthalmologist to promptly detect changes in the retina and, if necessary, undergo another course of treatment.
Contraindications
- Insufficient transparency of the optical media of the eye,
- in patients with severe rubeosis of the retina and pronounced changes in the fundus,
- With epiretinal gliosis accompanied by traction syndrome.
- On the recommendation of a doctor for low visual acuity (less than 0.1 diopter).
Price
Panretinal laser coagulation of the retina – 6500 rub. (1 session)
Focal laser coagulation of the retina (restrictive peripheral laser coagulation of the retina) - RUB 10,000. (1 session).
Scleral filling for retinal detachment
Episcleral filling has become widespread due to its simplicity, safety and effectiveness. With this method, a fine-mesh silicone sponge is used as a filling material, which is sutured from the outside to the eyeball, pressing the wall of the eye and bringing the choroid closer to the detached retina, thereby blocking the retinal tear at the depression shaft. In the future, the retinal tear can be further delimited using cryopexy or laser photocoagulation of the retina.
Depending on the volume of indentation and the location of the fillings, episcleral filling can be local (radial or sectoral filling of the sclera) and circular. Episcleral surgery for retinal detachment can be performed as an independent method of surgical treatment of retinal detachment, or in combination with endovitreal intervention.
| Radial scleral buckling is performed in cases where there is a single retinal tear with perifocal fresh local retinal detachment. Sectoral filling of the sclera is indicated for several adjacent retinal breaks, for giant breaks and separations from the dentate line, that is, in cases where the depression shaft should be more pronounced and extended. Circular filling of the sclera (cerclage) is used in more severe cases, when there is a single retinal break with extensive areas of peripheral retinal degeneration, multiple retinal breaks in several quadrants. Circlage with silicone tape or circular filling of the sclera with a silicone porous tourniquet is also carried out in cases of retinal detachment with pronounced traction of the vitreous body onto the retina in large areas of peripheral retinal dystrophy and undiagnosed retinal tears. |
Intravitreal administration of Aflibercept (Eylea)
Aflibercept (“Eylea”) is a drug jointly developed by Regeneron Pharmaceutical Inc (USA) and Bayer HealthCare (Germany). The drug helps maintain and improve visual acuity and, as a result, improve the quality of life of patients with serious visual impairments.
Indications for treatment by intravitreal administration of Aflibercept:
- age-related macular degeneration (wet form),
- diabetic macular edema,
- visual impairment caused by macular edema due to occlusion of the central retinal vein or its branches
- visual impairment due to myopic choroidal neovascularization (myopic CNV)
How is intravitreal administration of Aflibercept performed?
The drug is administered intravitreally (i.e., into the vitreous body) at a dose of 2 mg in a sterile operating room by an ophthalmologist with experience in administering intravitreal injections.
First, 3 consecutive monthly injections are performed (the “stabilization” phase), then the number of injections is recommended by the doctor depending on the state of visual functions and the degree of the disease (the “maintenance” phase). The interval between doses is at least 1 month.
The injection is performed on an outpatient basis using drip anesthesia; a hospital stay is not required.
Treatment results
According to the results of international multicenter, double-masked, randomized, active-controlled phase III studies VIVID, VISTA and VIVID East, the effect of Aflibercept (Eylea®) in patients with DME develops after the first injection and does not weaken over time. The majority of patients with Aflibercept (Eylea®) experienced a significant improvement of two lines of vision.
The drug has already been approved in more than 96 countries for the treatment of patients with (“wet” AMD) and in more than 84 countries with DME. Also in 90 countries, Aflibercept (Eylea®) is approved for the treatment of visual impairment caused by macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO), and in 59 countries for the treatment of visual impairment caused by macular edema secondary to central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO). OCVS).
Aflibercept not only slows down the progressive decline in vision, but also restores visual acuity in many patients. It should be remembered that intravitreal administration of Aflibercept does not always restore previously lost vision. This procedure should primarily be considered as a way to stop the progressive decline of vision and prevent its complete loss.
Therefore, before starting treatment, a mandatory diagnostic vision examination is necessary, based on the results of which the doctor can get a complete picture of the state of the visual system of a particular patient, verify the need for treatment with the drug Aflibercept, develop an individual injection schedule and make a forecast of what the vision state will be after course of procedures.
How to prepare for the procedure
The following tests are required:
- Wasserman reaction (RW) (shelf life 10 days);
- blood for antibodies to HIV (regardless of age), HBs antigen, hepatitis C (expiration date 1 month).
The day before the procedure, the medical receptionist will call you and inform you of the time at which you need to come to the clinic. It is not recommended to come to surgery wearing woolen clothing.
What to do after the procedure
After the procedure, antibacterial eye drops should be used for 1-2 weeks. Your doctor will give you a regimen for instilling drops. Repeat injections are usually given at intervals of 4-6 weeks.
Contraindications to intravitreal administration of Aflibercept:
- individual intolerance to the drug,
- pregnancy, lactation (breastfeeding),
- age under 18 years (relative contraindication)
- viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva.
Price
Intravitreal administration of the drug Aflibercept (Eylea®) RUB 55,000. (1 injection) taking into account the cost of the drug
Diagnosis of retinal detachment
In order to confirm or refute the diagnosis of retinal detachment, it is necessary to undergo a thorough ophthalmological examination. At the Excimer clinic, diagnostics are performed using a complex of modern computerized equipment; the level and quality of such studies allow our specialists to create the most complete and objective picture of the condition of the patient’s retina.
Evaluation of patients with suspected retinal detachment may include:
- examination of the fundus (ophthalmoscopy);
- optical coherence tomography of the posterior segment of the eye;
- study of visual fields (perimetry) in order to assess the condition of the retina in its periphery;
- electrophysiological study - determination of the viability of nerve cells of the retina and optic nerve;
- ultrasound examination of the internal structures of the eye and other diagnostic procedures.
Retinal detachment can only be diagnosed by an ophthalmologist. If a pathological process develops, treatment must be started as early as possible, this significantly increases the chances of a successful outcome.
Intravitreal administration of the drug Ozurdex
Ozurdex is an intraocular implant placed inside the vitreous. At the same time, its main active ingredient, the glucocorticosteroid dexamethasonum, begins to be released continuously in small doses, providing a multicomponent long-term effect. Thanks to this innovative technology of drug administration, the duration of the therapeutic effect is significantly increased.
Indications for treatment by intravitreal administration of Ozurdex:
- macular edema due to occlusion of the central retinal vein or its branches;
- visual impairment due to diabetic macular edema in patients with aphakia; patients who have an insufficient response to therapy, or those who are not suitable for therapy with drugs other than glucocorticosteroids;
- inflammation of the choroid of the posterior part of the eye, which is non-infectious uveitis.
Ozurdex has a multifaceted effect.
The drug not only eliminates macular edema, but also fights the main cause of its occurrence - retinal vein occlusion. Ozurdex has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. As a result of its action:
- the triggering factors of inflammation (mediators) that cause macular edema are blocked - protoglandins;
- blood clots resolve (fibrin deposition stops) and blood flow through the veins and capillaries is restored;
- the walls of pathological vessels and capillaries are strengthened;
- the formation of new vessels with high permeability of the walls stops.
How is intravitreal administration of Ozurdex performed?
The injection is performed intravitreally (i.e., into the vitreous body) in a sterile operating room by an ophthalmologist experienced in administering intravitreal injections.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis using drip anesthesia; a hospital stay is not required.
Treatment results
The therapeutic effect of Ozurdex lasts for 90 days from the date of administration . Just one injection is enough for therapy lasting up to 6 months.
Clinical studies of the use of the Ozurdex implant have shown its effectiveness in the following indicators:
- in patients who received one implant, on the 90th day the thickness of the retina decreased almost 3 times - from 600 microns to 240 (with the norm being 220 microns);
- after 90 days, a significant number of patients had visual acuity improved from 5% to 65%;
- The implant prevents vision loss due to macular edema.
How to prepare for the procedure intravitreal administration of the drug Ozurdex
If you are prescribed intravitreal administration of the drug Ozurdex, you must undergo the following tests:
- Wasserman reaction (RW) (shelf life 10 days);
- blood for antibodies to HIV (regardless of age), HBs antigen, hepatitis C (expiration date 1 month).
The day before the procedure, the medical receptionist will call you and inform you of the time at which you need to come to the clinic. It is not recommended to come to surgery wearing woolen clothing.
What to do after the intravitreal administration of Ozurdex
After the procedure, antibacterial eye drops should be used for 1-2 weeks. Your doctor will give you a regimen for instilling drops. Repeat injections are usually given at intervals of 4-6 weeks.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to the active or excipients of the drug;
- active or suspected ocular or periocular infection;
- viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva;
- fungal diseases;
- advanced stage of glaucoma;
- age up to 18 years.
The drug should be used with caution:
- for herpetic eye infections;
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- with aphakia (absence of a lens in the eye);
- patients taking anticoagulants (medicines that prevent the formation of a blood clot) or antiplatelet agents (reduce blood clotting).
Price
Intravitreal administration of the drug Ozurdex RUB 75,000. (1 injection) taking into account the cost of the drug
Types of operations
In ophthalmological practice, the following types of surgical intervention are used to eliminate retinal detachment:
Laser treatment
Laser treatment of retinal detachment
Eye surgery with a laser can be indicated not only in the presence of a detached area, but also in cases of thrombosis of the main vein, retinopathy, age-related degeneration and partial detachment. Cauterization of the retina with a laser is performed painlessly on an outpatient basis and takes about 20 minutes. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia, so this treatment can be used even for older people.
Laser treatment produces a minimal number of complications and is not a contraindication for use during pregnancy. Anesthetic drops are instilled into the patient's eye and then the head is fixed to the device. A targeted laser is directed to a specific point and cauterizes (glues) fragments of the inner membrane of the eye.
The advantages of this technique include the absence of severe discomfort or pain during all actions. Complete healing occurs within two weeks after surgery. During this period, it is recommended to observe restrictions and not put stress on the operated eye: watching TV for too long, working at the computer, driving. Before going outside, you should wear sunglasses to avoid getting sunlight or dust in your eyes.
Complications from laser treatment are extremely rare, but sometimes cataracts, corneal edema or increased intraocular pressure may occur after treatment. Contraindications to surgery: vitreous opacification, hemorrhage and proliferation of iris vessels.
Advice: In order to avoid any complications after laser surgery, you must regularly visit your doctor, undergo ophthalmological examinations and follow the prescribed restrictions.
Scleral filling
Scleral filling
An operation called scleral buckling is a procedure during which a silicone filling is placed on the outside of the affected eye. The filling is quite flexible and soft, so it cannot damage the eye in any way. It is attached to the site of the retinal tear and secured with sutures. This treatment promotes the formation of a protective shaft against retinal tears and helps eliminate the resulting fluid.
Extrascleral filling is performed by cutting the conjunctiva and placing the filling in a predetermined area. The accumulated fluid is drained using special instruments and then removed outside. At the end of the operation, a suture is placed on the eye in the place where the conjunctival incision was made.
Improvement in vision after such surgery is observed gradually over six months. It is not possible to achieve complete restoration of vision by filling the sclera. Complications that may occur after extrascleral filling include wound infection, exposure of the filling, increased intraocular pressure, and cataracts.
During rehabilitation, it is forbidden to lift heavy weights or engage in physical exercise, so as not to cause suture dehiscence. It is necessary to ensure that no water or dust gets into the operated eye, and also be sure to wear a protective bandage. Eye drops prescribed by your doctor will help prevent infection from getting into the wound.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy
This surgical treatment is a procedure during which the changed vitreous body is removed and replaced with artificial silicone or other material. Vitrectomy effectively presses the retina onto the sclera and restores vision.
During the procedure, micro-incisions are made through which an instrument is inserted and the vitreous body is removed. The operation takes up to 90 minutes, and pain is practically eliminated due to local anesthesia.
After such treatment, visual stress on the eye, physical activity and the use of cosmetics are temporarily eliminated. The eye patch must be changed frequently to avoid the development of inflammation and infection.
Possible complications of vitrectomy include inflammation, bleeding, and increased intraocular pressure. Contraindications to surgery: allergic reaction, significant clouding of the cornea, bleeding disorders.
Price
Microinvasive vitrectomy from RUB 65,000.
Combined operation: Mircoinvasive vitrectomy + Phacoemulsification from RUB 101,000.
Extrascleral filling from RUB 65,000.
Laser coagulation of the retina 6500 rub. (1 session)
Intravitreal administration of the drug Aflibercept (including the cost of the drug) RUB 55,000. (1 injection)
Intravitreal administration of the drug Ozurdex (including the cost of the drug) RUB 75,000. (1 injection)