Classification of retinal dystrophy
Retinal dystrophy is divided into two large types. These are hereditary and acquired forms of the disease. If we talk about hereditary dystrophies, then destruction occurs at the level of receptors that allow vision in the twilight. The following types of hereditary lesions are distinguished:
- Generalized - degeneration of the pigment type, congenital blindness or lack of night vision, impaired or absent color perception.
- Peripheral - retinal separation due to the characteristics of chromosomes, damage to connective tissue, dysfunction of the rod and cone systems.
- Central - hereditary macular degeneration with the appearance of spots or yellow lesions, dystrophy against the background of age-related changes.
If we talk about the secondary (acquired) form of retinal dystrophy, it is also divided into peripheral and central. The disease of the central type is in turn divided into wet and dry manifestations of dystrophy. In the first case, the formation of new vessels is observed in the affected area. They are very fragile, so elements contained in the blood leak through them. As a result, edema forms and the light-sensitive elements of the visual organs are damaged. This disease is severe, so increased attention is paid to its treatment.
Dry central retinal dystrophy occurs in 90% of cases. It becomes the result of a metabolic disorder. In this case, accumulations of products involved in metabolism form between the retina and the vessels.
Peripheral dystrophy
This manifestation is typical for myopic people and very often leads to retinal detachment. There are two types of peripheral dystrophy: chorioretinal and vitreoretinal. Peripheral chorioretinal dystrophy (PCRD) affects the membranes of blood vessels. Peripheral vitreochorioretinal dystrophy (PVCRD) affects the condition of the cornea. In addition, peripheral dystrophy can be cystic, frost-like and lattice.
People's Councils
Retinal dystrophy, like many other eye diseases, involves a process that disrupts the functioning of the entire visual apparatus. The disease is extremely dangerous, since during the development of the pathology a significant part of vision is lost. To combat the disease, it is necessary to use all possible means and techniques.
In order to maintain visual acuity at a high level, it is necessary to normalize nutrient metabolism. Nutrients and minerals have a positive effect on the eye environment and contribute to the normalization of all processes occurring in the body.
An incorrectly composed diet consisting of fatty foods has an adverse effect on the vascular system and can cause increased pressure inside the eyes. Fresh fruits and vegetables are foods rich in vitamins and nutrients. Vitamins A and C, contained in most leafy vegetables, have a beneficial effect on the condition of the body. People suffering from disorders in the retina of the eyeball are recommended to consume such products daily.
Pathology of the retina can occur due to eye injuries, hypertension, diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands, thyroid gland, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, etc.
Folk remedies containing the following herbs and berries are recommended for all patients with diseases of the visual system:
- eyebright;
- mallow;
- pine needles;
- blackberry;
- rose hip;
- grape.
The presence of fresh vegetables in the daily diet has a positive effect on the retina of the eyeballs. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to consume as many lemons and oranges as possible, as they contain a large amount of vitamin C.
Retinal detachment - what is it?
Retinal detachment is a dangerous condition in which, under the influence of many factors, its pigment layer is separated from the neuroepithelium (rods and cones). This process can be painless. Therefore, sometimes the patient does not suspect eye pathology for a long time. This is what leads to irreversible loss of vision.
Causes of retinal dystrophy
The causes of dystrophic changes in the retina can be the following factors:
- Scar formation as a result of disruption of the vascular system or decreased local immunity.
- Non-compliance with diet and consumption of unhealthy or low-quality food.
- Bad habits, in particular smoking and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Negligence in the treatment of infectious diseases.
- Presence of chronic diseases. This could be diabetes, blood pressure surges, diseases of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
- Eye surgeries.
- Obesity as a result of metabolic disorders.
These manifestations worsen the condition of the circulatory system and slow down metabolic processes. Because of this, the retina is affected. Here's what they say about the causes of retinal dystrophy on the Internet:
Types of retinal detachment
There are central and peripheral retinal detachments.
- With peripheral or marginal vision, deterioration and loss of vision begins around the circumference, that is, from the edges. In the morning the symptom is usually mild and intensifies in the evening.
- Central is characterized by the loss of words, letters, and entire parts from the text being read.
It can also be mobile and rigid.
- Mobile – a milder condition in which, with bed rest for several days, the detached part fits into place.
- Rigid is an unfavorable form of the disease in which such adhesion is absent.
Symptoms of retinal dystrophy
Common signs for all types of retinal dystrophy are the following manifestations:
- Absence or decreased color perception.
- The appearance of image defects (floaters, lightning, flashes, fog).
- Loss of central vision.
- Perception of objects located to the side as a fuzzy picture.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Loss of sense of movement. An object at rest is difficult to distinguish from one that is moving.
- Need for excessive light while writing or reading.
If we talk about individual forms of the disease, peripheral dystrophy is expressed by the appearance of flashes and dots before the eyes. Damage to the macula is accompanied by curvature of the visible lines. Dry retinal dystrophy distorts visual images. The patient cannot work with small objects and fonts. He has difficulty seeing in the dark and distinguishing faces.
Here is one example of the development of retinal dystrophy and its treatment:
In most cases, the manifestation of symptoms is characteristic of one eye. In addition, the initial stages of retinal dystrophy occur unnoticed. Having discovered the first signs indicating the onset of the disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Retinal dystrophy during pregnancy
During pregnancy, retinal dystrophy occurs due to decreased blood flow to the eyes as a result of low blood pressure. If the development of the disease is not stopped in time, it can lead to retinal rupture or detachment. To avoid such consequences, a planned caesarean section or laser coagulation procedure is performed. Laser coagulation is prescribed before the 35th week of pregnancy. The procedure involves creating a reliable connection between the choroid and the retina. The result of such an intervention is to reduce the risk of complications on the visual organs during natural childbirth.
Symptoms of edema
The retina is located on the periphery of the visual center and is a thin membrane of the fundus of the eye in close proximity to the network of blood vessels. Any pathology of the fundus vessels immediately has a negative impact on the health of the retina. The quality of human vision depends on the retina, since the maximum acuity of perception of visual images is focused in the macula (its central part).
Edema is formed due to the accumulation of excess moisture and protein mass inside the orbit. This occurs due to damage to the vessels of the fundus, the walls of which lose their elasticity and become inflamed. Liquid fills the eye socket, the white membrane of the eye is deformed. A person loses full vision, the outlines of objects become blurred and are seen in pink tones.
Note! Retinal edema is not an independent disease, but a consequence of the development of another pathology in the body.
Symptoms of edema:
- fog before the eyes;
- pink haze around objects;
- decreased visual acuity in the morning;
- high photosensitivity.
A defect in visual perception distorts the correct shapes of objects: a straight line appears curved or wavy.
With swelling of the nerve disc, symptoms are not expressed for a long time. The pathology manifests itself as sudden short-term loss of vision. It happens instantly and unexpectedly. Attacks of sudden blindness may occur several times a day. A characteristic feature of papilledema is that it affects one eye rather than both. The pathology is accompanied by a failure of pupillary reflexes.
How is retinal detachment diagnosed?
Only an ophthalmologist can determine retinal detachment. One of the most important methods for diagnosing retinal detachment is the following:
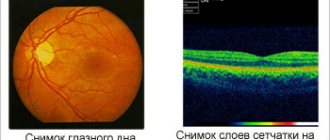
In the photo (top left, clockwise) are examples of diagnosing retinal detachment: computer perimetry, tonometry, electrophysiological study (EPI), ophthalmoscopy
- Determination of visual acuity - to determine the center of the retina.
- Using computer perimetry, we examine visual fields and determine peripheral vision.
- We perform tonometry - we measure the patient's intraocular pressure.
- Electrophysiological study - to determine the viability of retinal and optic nerve cells.
- Direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy - an ophthalmologist examines the fundus of the eye, which allows you to determine the location of the ruptures, their number, and detect thinned areas in order to avoid further retinal ruptures.
After carrying out all diagnostic methods, the ophthalmologist can make a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Identifying dystrophy and making a correct diagnosis involves conducting the following studies:
- Checking visual acuity (visometry).
- Identification of the visual field (perimetry).
- Check for distortion of visible lines - Amsler test.
- Detection of abnormal deviations in the refraction of light rays (refractometry).
- Biomicroscopy.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Determination of the degree of color perception.
- Electroretinography.
- Determination of the degree of adaptation of visual functions in the dark (adaptometry).
- Finding affected areas.
- Retino- and coherent tomography.
- Ultrasonography.
- Collection of analyses.
Depending on the clinical picture, the patient is prescribed a consultation with doctors of other specialties.
Operative methods
For rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, the following methods are used:
- Extrascleral. These include ballooning and filling.
- Endovitreal - vitrectomy.
- Cryocoagulation of ruptures.
- Laser treatment.
Extrascleral methods are effective only if the rupture, which resulted in a detachment, occurred recently (up to 1 month).
Ballooning is an operation that is performed on the surface of the tunica albuginea (sclera). The essence of the method is as follows: the surgeon identifies the location of the rupture and, accordingly, the detachment. After this, he sews a balloon made of elastic material to the tunica albuginea. This small container is then filled with gas or liquid. Gradually, an indentation area forms on the eyeball. Thanks to this, the membranes come together, resulting in the elimination of rhegmatogenous detachment. The operation is effective if no more than 1 of the 4 quadrants of the retina is affected.
Filling is a type of surgical intervention that is also performed on the surface of the tunica albuginea. At the diagnostic stage, the doctor determines the location, shape and size of the exfoliated area. Based on this information, a filling is made, consisting of a biocompatible material. As a rule, sponge silicone is used in ophthalmology clinics.
In case of retinal detachment, the operation is performed as follows: the surgeon makes an incision in the conjunctiva, through which a seal is applied to the site of the tear. After this, it is fixed with sutures. If the pathology is accompanied by severe swelling, drainage is performed. The final stage is suturing the conjunctival incision.
Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure during which the vitreous body is partially or completely removed. Instead, a substance with similar properties is introduced. This method is considered minimally invasive, since a minimum of perforations are made during the operation.
Cryocoagulation of fractures involves the use of low temperatures. The operation algorithm is as follows: the doctor drops an anesthetic drug into the patient’s eyes, while it begins to act, the surgeon lowers the cryoapplicator into liquid nitrogen. The latter is then placed on the eyeball. Through the use of ultra-low temperatures, a high penetration rate is achieved, while there is no effect on the tunica albuginea and muscle tissue. Cryocoagulation can be considered both as an independent and as an auxiliary method of treating rhegmatogenous detachment.
Laser treatment is also carried out under local anesthesia. This is a modern method, which is considered the safest due to the minimal risk of complications. In case of retinal detachment, the operation is carried out according to the following algorithm: the doctor directs a high-precision laser beam to the lesion, which promotes the fusion of the vascular and nerve membranes. The doctor monitors the progress of the operation using a microscope. Its duration is about 20 minutes, after it the patient can immediately begin his daily activities.
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies for retinal detachment helps in the initial stages of the disease. The following recipes are the most effective:
- Collection of herbs. To prepare the product, you need to mix St. John's wort, violet, bearberry and knotweed. Recommended proportions for collection are 1:1:2:3. To prepare the medicine, you need to take a tablespoon of the herbal mixture and pour 220 ml of boiling water over it. The product should sit for 30 minutes. The medicine is filtered and taken 70 ml three times a day. The recommended course of treatment is 10 days.
- Pine decoction. To prepare the medicine, you need to prepare needles collected from a young tree. Plant materials are thoroughly crushed. Six tablespoons of needles are poured into 510 ml of boiling water, then boiled for 15 minutes and left overnight. The resulting medicine is divided into equal five parts, which must be drunk throughout the day.
- Oatmeal broth. To prepare an effective folk remedy, take 500 g of grain, well washed and free of contaminants. The oats are poured with cold water, and after 4 hours they are filtered. The grain is transferred to a saucepan, 3 liters of boiling water is added, and then boiled for 30 minutes. The cooled broth is taken in a glass four times a day for 2 weeks.
- Mistletoe infusion. The product significantly reduces the pressure inside the eyeball. To prepare it, pour a teaspoon of mistletoe into 210 ml of boiling water. After cooling and straining, the medicine is taken three times a day at the rate of one glass at a time.
- Rinsing the eyes with elderberry infusion. You need to take two tablespoons of flowers and pour a liter of boiling water. When the medicine has cooled, it is used to wash the eyes or as a lotion.
- Infusion of medicinal eyebright. To prepare, you need to take two tablespoons of the plant and pour 500 ml of boiling water. The resulting infusion is used for lotions that effectively fight inflammatory eye diseases.
- Alcoholic extract of hawthorn. It helps cope with high eye pressure and improve blood supply to the retina. For effective treatment, it is recommended to take a teaspoon of pharmaceutical tincture twice a day.
Treatment of retinal dystrophy
The standard treatment regimen for dystrophy using medication looks like this:
- Drugs that strengthen and dilate blood vessels. The dosage of Complamin, Noshpa, Papaverine or Ascorutin is selected individually for each patient.
- Medicines to prevent blood clots. This may be Aspirin, Ticlodipine or Clopidogrel.
- Vitamin B, administered intramuscularly, and a complex of other vitamins in tablet form.
- Medicines that prevent the formation of new painful blood vessels (Lucentis).
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs.
- Means for improving metabolism inside the eye. Injected intravenously or directly into the structure of the visual organs.
- Retinalamin, injected into the lower eyelid or eye shell for 10 days.
- Eye drops that speed up the healing process and metabolism.
Conservative treatment is complemented by physiotherapy. The patient is prescribed procedures such as photo- and electrical stimulation, electrophoresis, and magnetic therapy. If we talk about the use of small doses of laser radiation, they are used to influence the retina and blood.
Laser treatment
The laser beam extends its effect directly to the affected areas of the visual organs. They are exposed to irradiation in order to stimulate and start the metabolic process. The laser is able to strengthen blood vessels through their coagulation and separate affected areas from healthy ones, thereby stopping the spread of the disease. This process involves soldering defective tissues.
Surgery
If conservative and laser treatment methods do not help to cope with retinal dystrophy, the doctor decides to prescribe surgery. Depending on the complexity of each case, the following surgical interventions are performed:
- Revascularization – restoration of blood vessels.
- Vasoconstruction is a narrowing of the spaces between blood vessels.
- Vitretomy is complete or partial removal of the vitreous.
After surgery, it is necessary to take measures to help quickly restore visual functions. You need to make sure that your eyes are not overstrained, wear sunglasses outside, and take vitamins. In addition, it is necessary to stop smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Traditional methods of treating retinal dystrophy
Traditional medicine recipes for dystrophy should be used in conjunction with the main treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor. The following remedies have a good effect:
- Goat milk diluted with boiled water in equal proportions. Within a week, the resulting solution is dripped into the eyes, then covering them with a dark cloth. As a result, the process of retinal detachment will stop.
- For a month, drink half a liter of decoction per day. To prepare it, take 5 parts of pine needles, 2 parts of rose hips and onion peels. They are poured with boiling water and cooked for 10 minutes.
- A decoction of cumin and cornflower flowers is instilled into the eyes 2 times a day.
- For a month, a decoction of celandine is instilled into the eyes 3 times a day.
- Tinctures of birch, horsetail, lingonberry, and mustard are taken orally.
- Wheat grains are left to germinate in a warm place. The embryos grind and eat the resulting mixture.
- For 9 days, a decoction of mumiyo and aloe juice, boiled in proportions of 5:1, is dripped into the eyes.
Before using folk remedies, you need to consult a doctor and make sure that the components of the decoctions do not cause allergic reactions.
Please note: If, when a disease is detected, you refuse the help of a doctor and self-medicate, the disease may develop to a severe stage. It can lead to complete loss of vision, which is characterized by the irreversibility of the process.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of pathology change quickly. The manifestations of symptoms are conventionally divided into several stages:
- Elementary. Patients note flashes, sparks in the eyes - photopsia . The latter are provoked by direct sunlight or external exposure to the eye. Both causes act as an irritant to nervous tissue. The thin nerve layer is stretched and a false sensation of flashes, spots and rings appears. At the initial stage of the disease, the shapes of objects blur and their clarity is lost. Coordination of movements is impaired .
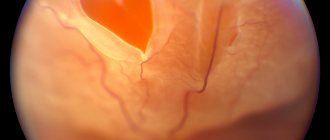
Photo 1. An example of photopsia that occurs in front of the eyes when the retina is detached (flashes are indicated by arrows).
- Floating. The patient at this stage begins to see points, threads, and spots in the eyes slowly changing position. They do not always indicate the onset of retinal detachment. Such symptoms may correspond to destruction of the vitreous. But the appearance of floating flies is definitely a serious reason for examination by a doctor.
- Final. A symptom of the last stage of the disease is an oval-shaped clouding called “Bates’ ring” . This manifestation suggests that, in addition to the detachment of the nervous tissue, the posterior hyaloid membrane was damaged. In this case, surgical intervention is not only necessary, but also vital. In addition to clouding, at the final stage there is a loss of clarity of vision and photopsia. If the patient is not provided with medical assistance at the last stage, he or she faces the risk of blindness .
What causes farsightedness in children
Children's farsightedness, along with strabismus and amblyopia, is one of the most common vision disorders. Children are born farsighted, but this problem usually corrects over time.
How is hypermetropia treated in children, does it create any restrictions?
Characteristics of farsightedness
According to ICD-10, each disease and disorder has its own code. Hyperopia – code according to the international classification system ICD-10 – H52.0.
Farsightedness - what is it? First of all, it is important to know that hypermetropia is not a disease. This is a disorder characterized by changes in the shape and size of the eyeball. The most common is axial childhood farsightedness, which is characterized by a deviation in the anteroposterior axis of the eye. We can say that farsighted visual organs are considered as not fully developed and are characterized by a delay in their growth.
At birth, almost every person is equally farsighted, and as the entire body grows, the sagittal length of the organ of vision increases. In newborns, the average eye length is about 18 mm, at two or three years old it is already 23 mm. From 4 years to 14 years of age, a child's growth slows down by about 0.1 mm per year. The length of the eyeball in older age is about 24 mm, which does not apply to hypermetropia of both eyes - in this case the length is shorter. The deviation value determines the degree of disorder. Degrees in children and adults are classified as follows:
- low degree hyperopia (plus 2 diopters, +2D);
- moderate hyperopia (plus 5 diopters, +5D);
- high degree hypermetropia (plus 5 diopters and above).
The treatment of farsightedness in children and the choice of correction method depend on the degree of the disorder (the first degree, as a rule, does not require correction; special exercises are used).
The shortening of the anteroposterior axis of the eye rarely exceeds 2 mm. A decrease in length of one millimeter represents a change in refraction of about plus 3 diopters.
Important! Improvement in vision (in most cases) during childhood distinguishes hyperopia in children from age-related farsightedness, called presbyopia.
Farsighted newborns and vision development
Natural farsightedness in children is associated with the shape of the eyeball. Newborns have imperfect vision at birth. Their eyes are immature and they do not perceive the outside world clearly. Therefore, there is no point in talking to them at a distance greater than 25 cm - they will see you blurry. Gradually, slowly, the baby builds eye contact with the people around him. Soon he can look at the offered toy, and at about 2 months he will begin to follow it with his eyes. Sometimes it happens that one eye squints, but for 6 months there is no need to worry - during this time, children's eyes develop, the interaction of both eyes and the visual centers in the brain. Thus, farsightedness in children under one year of age does not require correction. If a one-year-old child continues to have some degree of impairment, some restrictions on eye strain are needed. Doctor E.O warns about this. Komarovsky, who also recommends spending time with your baby outside more often - this will help speed up the improvement of vision.
At the age of six, a small person can see as well as an adult. Before this time, however, errors may occur that can disrupt the normal development of vision. During their stay in the maternity hospital, newborns are screened for cataracts as part of a general examination. The critical period for visual development is the first year of life, when binocular vision begins to form.
As mentioned, congenital farsightedness in children is normal. In only about 6% of young patients, hypermetropia values remain elevated, which can lead to strabismus and amblyopia in later life. These disorders are usually diagnosed before age 8. Vision development is completed during puberty, around 15 years of age.
Development of the disorder
In the case of farsightedness in children, the eye is unable to focus vision at close range. In general, this disorder manifests itself in such a way that a person has no problems contemplating distant objects, but cannot focus his vision on close objects. Farsighted people may have problems with reading and writing, cutting, gluing...
Farsightedness in children 1 year of age is most often caused by congenital shortness of the anteroposterior axis of the eyeball. Light rays are refracted behind the retina, not on it.
Important! Since the eyes are able to partially compensate for this problem by increasing accommodation, farsightedness may not be obvious in children under 3 years of age.
The disorder causes increased fatigue and headaches from excessive accommodation. Defective vision, like any ophthalmological disorder, can cause slow psychomotor development. Therefore, parents with farsighted children should consult an ophthalmologist. If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe a correction.
What causes hypermetropia
Genetic predisposition is responsible for many cases of refractive disorders, which include hypermetropia. But people also suffer from farsightedness of any degree, without having a genetic predisposition to this disorder.
In addition, environmental factors play a certain role in the development of farsightedness and its degree. However, heredity remains the best known cause, especially for the higher forms of this disorder (as well as other ophthalmic diseases).
The following factors involved in the formation of farsightedness are:
- flat cornea;
- insufficient refractive value;
- small lens thickness;
- congenital small visual organ (microphthalmos);
- short length of the sagittal axis of the eye;
- exposure to certain medications;
- injuries.
Farsightedness can also be caused by certain diseases (cancer, retinal detachment, etc.). In older people, provoking factors are decreased lens refraction and diabetes. Backward displacement of the lens due to illness or injury, aphakia (lack of an intraocular lens - lens) can also cause hypermetropia.
How to determine farsightedness in a baby
All parents should be attentive, especially in families where there is a history of visual impairment. There is a high probability of inheriting an ophthalmic disorder. Many parents, however, focus on the disorder when children start school, and problems with schoolwork may arise.
Farsightedness in a 2 year old child can be expressed as follows:
- while playing, he brings objects closer to his eyes, changes the viewing distance;
- when drawing, tilts his head over the table;
- the baby has an unnatural head tilt - in this way he can compensate for strabismus;
- periodically closes one eye;
- farsighted children quickly get tired when performing activities at close distances;
- they do not focus on details (pictures, toys);
- sit as close to the TV as possible;
- mistakenly determine the location of objects.
Important! If in any doubt, consult your pediatrician or ophthalmologist. He will assess the presence and extent of the disorder at an early age, and recommend opportunities for improvement.
How to help your baby
Below are some tips that you can follow to help maintain your eye health and vision.
- Daily Exposure to Natural Daylight – Scientific research indicates that everyone should spend at least 30-60 minutes a day outdoors in natural daylight. This rule does not mean direct exposure to sunlight!
- Limit watching TV and playing on the computer. They are sources of artificial light, which directly affects the quality of impaired vision. The maximum period for TV/computer is 30 minutes/day in total.
- Include physical activity in your daily routine. The type of activity does not matter - oxygenation of the body is important, preferably in the open air.
- If your child already wears glasses for farsightedness, let him take them off whenever possible.
- Provide a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals. Include as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible (especially leafy green vegetables - spinach, cabbage, lettuce, etc.). Avoid white sugar (sweets, carbonated drinks) - it can be replaced with cane sugar. Make sure you stay hydrated.
Contact lenses and glasses
At what age can you wear contact lenses? Age is not a limiting factor in the use of contact lenses, it is a personal matter, depending on the particular child, his motivation, responsibility and ability to use contact lenses. Treatment of farsightedness in young children involves wearing glasses; children in the older age group can use lenses.
Lenses are usually worn throughout the day. The mode of wearing glasses is determined by the doctor depending on the specific condition. Usually, with low degrees of farsightedness, you can wear glasses only at school; in cases of moderate or severe impairment, you may have to wear them constantly. An important role is played by the presence of associated strabismus, amblyopia or astigmatism - for these disorders, correction is mainly permanent.
Causes and treatment of macular degeneration
Macular degeneration of the retina is a disease that affects the macula (the central part of the retina), causing it to become depleted.
Hide content
This disease develops as a result of the decrease in the lumen of the membrane vessels that nourish the retina, which causes oxygen starvation of the retina.
Due to disruption of the macula, central vision deteriorates.
Kinds
Macular degeneration can be of two types: dry and wet. Both types of disease do not appear immediately.
Dry macular degeneration usually develops first in one eye, which does not greatly affect overall visual acuity in the early stages of development. It becomes difficult for a person to do any small work and read; he needs brighter light.
Those who suffer from wet dystrophy notice that straight lines begin to appear wavy, and their vision has become sharply worse. Patients with wet macular degeneration often complain of the appearance of a dark spot in the middle of their field of vision.
Both forms of the disease are characterized by low-contrast images, impaired color vision, and blurred vision. Patients do not experience any pain. With macular degeneration, complete loss of vision rarely occurs.
Causes of the disease
The causes of macular degeneration are not fully known; this disease is multifactorial.
There are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing the disease:
- Age is the main factor in the appearance of macular degeneration; it is the most common reason why vision declines in people over 50 years of age;
- Gender – this disease is more common in women;
- Heredity - people whose relatives suffered from this disease may be diagnosed with congenital macular degeneration;
- Ultraviolet radiation – sunlight often damages the retina of the eye;
- Smoking;
- Cardiovascular diseases (myocardial infarction, angina, stroke, arterial hypertension);
- Overweight;
- Poor nutrition – food contains low amounts of substances that promote eye function (zinc, antioxidants, vitamins A, C, E).
Treatment
Macular degeneration of the retina is treated both conservatively and surgically.
The conservative method of treatment uses immunomodulators, antioxidants, vitamins A, B, E, as well as drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
If treatment does not produce the desired effect, vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors are used. The drug is injected into the eye. It can reduce swelling and prevent further loss of vision.
For dry macular degeneration of the retina, low-intensity laser therapy is often used. Drusen are removed using a laser, but it is worth noting that photoreceptors cannot be restored with this treatment.
If a person has wet macular degeneration, then laser coagulation is used, which prevents bleeding from newly formed vessels. This can stop vision deterioration.
There is also a method of treating wet macular degeneration, where the drug is activated using a laser. The drug itself is administered intravenously, and it spreads throughout the circulatory system of the entire human body. Then they shine a laser into the eye.
- In such a short period of time, laser exposure does not damage eye cells, but it can activate the drug - a highly active component is released from it, which damages newly formed unhealthy cells.
- This treatment does not restore vision, but makes it possible to stop its loss.
Traditional methods
You can also stop vision loss with the help of folk remedies. Treatment of macular degeneration of the retina is carried out by including sprouted legumes and grains in the diet.
It is worth noting that any use of traditional methods should be discussed with your doctor in order to avoid any unpleasant consequences.
Wheat is a good remedy for macular degeneration. It must be washed, sorted, then laid in a thin layer and filled with water. After it sprouts, the wheat is washed and passed through a meat grinder.
Shredded wheat can be stored in a cold place for no more than 4 days. Every morning, 14 tablespoons of crushed wheat are poured with hot water and consumed after swelling.
To improve the taste, you can add berries or honey. If the product is used as a preventive measure, then 4-7 tablespoons will be enough.
Treatment of macular degeneration can be combined with the consumption of chickpeas (grain legumes). It should be added to salads, cooked cutlets or made into soup.
To slow down the disease, it is important to follow a diet . To do this, substances that can slow down age-related vision degeneration are added to the diet. For this purpose, fruits, tomatoes, green vegetables, strawberries and blueberries, as well as nettle leaves are consumed.
To restore vision, an infusion of mumiyo with aloe juice is often used. This infusion is used to instill eye drops. To prepare it, take 50 grams of purified mummy and dissolve it in 10 grams of fresh aloe juice. The prepared composition must be stored refrigerated.
Before use, the infusion is warmed to room temperature and one drop is instilled into the eyes twice a day. Shilajit infusion with aloe juice can also be taken orally: 10 ml in the morning on an empty stomach and in the evening before bed.
Treatment lasts 10 days, after which a break of 30 days is taken and the course is resumed.
It has been proven that people whose diet includes plenty of fruits and vegetables every day are less likely to suffer from macular degeneration of the retina.
- Such products contain a large amount of vitamins, antioxidants, microelements and nutrients that have a positive effect on the eyes.
- Products containing lutein and zeaxanthin are the most important in the treatment and prevention of the disease.
Source: https://medoptical.info/bolezni/makulodystrophiya
Prevention of retinal dystrophy
In order to reduce the risk of developing retinal dystrophy, you must follow these rules:
- Make sure your work area is properly lit.
- Any load on the visual organs should be accompanied by periodic rest.
- It is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist once a year.
- The diet should consist of foods containing vitamins and microelements necessary for normal metabolism.
- You need to give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking).
Massage and exercises strengthen the visual organs and normalize blood flow to them. Watch your health. Contact your doctor at the first signs of the disease to begin treatment on time.
Development mechanism
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is a multifactorial disease. This is a primary pathology resulting from rupture of nervous tissue.
There are two main mechanisms for the development of the disease:
- The occurrence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment against the background of thinning of this layer. As a rule, this condition appears during the natural aging process of the body. For many people, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, but at the same time it can pose a health hazard. Over time, end-to-end defects form on the retina, through which fluid from the vitreous body begins to penetrate under it, causing detachment. In addition, often zones of dystrophy appear after injury to the eye.
- The occurrence of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment due to tension. The vitreous body is a gel-like substance that is 99% water. It is very tightly connected to the retina at the base of the latter, most weakly in the areas of localization of large blood vessels. During the natural aging process of the body, the vitreous body liquefies and the retina stretches. As a result, detachment occurs, which is not always accompanied by tissue rupture.
Since the disease is multifactorial in nature, in most cases both mechanisms are detected in patients at once. The risk of rhegmatogenous eye detachment increases significantly under the influence of provoking factors.
Folk remedies for floating floaters before the eyes
Given the fact that most eye floaters eventually dissolve back into the fluid from which they originated, one way to combat them is to not treat them. However, you can try a number of home remedies to get rid of floaters in front of your eyes. Antioxidants, vitamins A, E and C are known to help treat floaters. Hemp oil contains a balanced amount of omega-3 fatty acids, making it one of the most effective folk remedies for treating eye floaters. Taurine is another antioxidant that helps dissolve any waste that accumulates in the eyes.
Possible complications
Without timely intervention in angiopathy, a reversible change in the retina, tissue hypoxia and hemorrhage can be expected. The retinal vessels themselves also undergo changes. In turn, they become severely deformed and lose blood conductivity. In some cases, complete loss of vision is possible.
Complications can be caused by various bad habits, high blood pressure, hereditary vascular diseases, obesity, and high cholesterol.
Risk factors
Risk factors include both external and internal causes. There is a high probability of ruptures in persons diagnosed with myopia, when an enlarged eyeball causes thinning and rupture of the membrane. In old age, pathology is provoked by structural dystrophic changes in the vitreous body, leading to overstretching of the retina.
Pathological changes in the fundus, straining during childbirth, hypertension, diabetes mellitus and vascular diseases increase the risk of OS. All of them are associated with excessive tension and thinning of the retina. Serious ruptures are observed under the influence of traumatic factors and surgical interventions. During inflammatory processes, excess fluid accumulates in the subretinal zone, putting pressure on the retinal layer.
IMPORTANT! Every fifth child born prematurely suffers from retinopathy. In premature babies, the underdeveloped retina tends to rupture.
Bottom line
To prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary to cure existing diseases - diabetes and hypertension. Regular visits to an ophthalmologist for preventive purposes will allow timely detection of the onset of the disease. An annual vision test is the key to healthy eyes.
Sources used:
- Charles, Steve Vitreous and retinal microsurgery / Steve Charles, Jorge Calzada, Byron Wood. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2012.
- Demirchoglyan, G. G. Physiology and pathology of the retina: Primary mechanisms of vision: monograph. / G.G. Demircioglyan. — M.: Medicine
- Zhukova, S.I. Pigmented abiotrophy of the retina / S.I. Zhukova, A.G. Shchuko, V.V. Malyshev. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2010.
- Wikipedia article