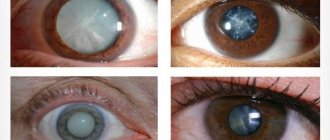
Symptoms of recurrent cataracts
After the intervention, patients experience a significant improvement in visual function. However, it happens that a short time after the implantation of an artificial eye lens, vision deteriorates again. Moreover, this symptom manifests itself both after a few months and after a few years. The symptoms of this complication are the same as with primary cataracts.
The main signs of secondary cataracts are as follows:
- a rapid decrease in visual acuity and the appearance of blurred images after a noticeable improvement in the ability to see after surgery;
- a feeling of fog, “smoke” in the operated eye, and this symptom also increases gradually;
- feeling of having a “plastic bag” in front of your eyes;
- the appearance of various points in the visual field (this causes significant discomfort);
- double vision in the visual field;
- distortion of the contours of objects;
- impaired focusing of vision;
- color vision disorder
- blurred visual field and decreased visual acuity that cannot be corrected with glasses.
The appearance of these signs after the intervention, provided that the patient has experienced a significant improvement in vision, makes one think about the formation of a secondary cataract. At initial symptoms of vision deterioration, patients should immediately consult an eye doctor.
Features and progress of the procedure
Treatment of secondary cataracts with laser takes place in one day and does not require hospitalization of the patient. The procedure is carried out in several successive stages:
- The patient sits comfortably in a special chair, after which the eyes are instilled with a medicinal solution that expands the pupillary space.
- Next, local anesthesia is performed. Before such anesthesia, you need to make sure that the patient is not allergic to medications.
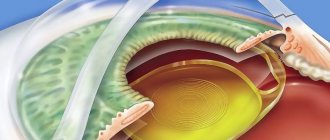
- Next, using a laser beam, small holes are made in the posterior capsule of the eye lens and the connective tissue is removed through them.
The laser used in the treatment process is absolutely safe for eye tissue. It focuses only on a given area and does not damage the lens.
Laser dissection allows you to get rid of cataracts and restore the visual acuity that you had before the disease.
Causes
Secondary cataracts develop in approximately every third to fifth operated patient. The likelihood of pathological changes is higher in young people. Complications also occur in children who have undergone surgery. In older people, fibrous tissue often grows in the area of the posterior capsule of the lens.
There is no specific reason for the development of re-opacity after implantation of an artificial lens. The following predisposing factors for the development of the disease are identified:
- the presence of lens fragments in the eye capsule due to the surgeon’s carelessness;
- the use of low-quality materials during implantation (especially if silicone artificial lenses are used);
- connective tissue diseases;
- various metabolic pathologies, incl. diabetes and thyroid disorders;
- high degree of myopia;
- glaucoma;
- retinal detachment;
- dystrophic changes in the tissues of the organ of vision.
No surgeon can guarantee that the patient will not experience pathological changes in the tissues of the organ of vision after implantation of an artificial eye lens. It happens that secondary cataracts appear even several years after surgery.
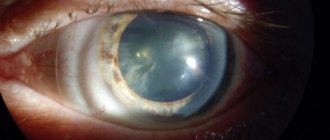
Secondary cataract on artificial lens
Secondary cataract
Changes (clouding) of the lens capsule after cataract removal have been studied for as long as cataract removal itself has existed. The absence of this problem can only be said if the cataract is removed along with the capsule. In modern ophthalmology, when removing cataracts, the capsule is preserved, since an artificial lens is implanted into it. Secondary cataracts do not occur on the artificial lens, but on the capsule.
Changes in the capsular bag of the lens can occur as clouding of the posterior capsule or secondary cataract, reduction in the size of the bag itself, its wrinkling, clouding of the remnants of the anterior capsule.
By far the greatest influence on the functional outcome of lens surgery is modification of the posterior capsule.
Opacities of the posterior capsule of the lens can be divided into two groups. The first group includes changes that are called primary opacities or initial ones. As a rule, immediately after surgery, areas of opacities of various shapes and sizes are observed on the posterior capsule of the lens. In most cases, initial opacities do not affect visual acuity. No treatment required.
Secondary opacities of the posterior capsule can be either early or late. Early secondary opacities of the posterior capsule appear in the first days after cataract removal and are more common in patients with risk factors such as diabetic angioretinopathy, chronic inflammation of the choroid, and glaucoma.
Later posterior capsular opacities are the result of cellular reactions occurring in the capsular bag. There is a movement of the epithelial cells of the anterior capsule to the posterior one and their proliferation. All these changes inevitably lead to a deterioration in the achieved result after cataract removal, decreased visual acuity, and the appearance of fog and are one of the main postoperative complications of lens surgery. But visual acuity after cataract extraction is an insufficient indicator of the functional outcome of the operation, especially for people with visually intense work.
Even in the absence of a decrease in visual acuity, good centralization of the intraocular lens in the capsular bag, some patients may complain of decreased visibility at night, glare from bright light, halos around a point light source, peripheral glare. The main methods of treating secondary cataracts are surgical and, which has gained more recognition, laser.
Compared with surgical treatment of secondary cataracts, laser treatment (discision, removal of part of the capsule in the optical zone) on the posterior capsule is much safer and easier to perform. The use of YAG laser dissection of the posterior capsule is associated with a small number of complications. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, no tests are required, the patient’s ability to work is not affected, restrictions are minimal, and the operation lasts a few minutes.
Modern surgery recognizes the importance of intraocular lens implantation among factors in the prevention of posterior capsule opacification. The evolution of this factor can be traced back to the seventies of the last century.
Secondary cataracts were more often observed in aphakia (the lens is removed, an artificial one is not implanted), involving the center of the capsule in the process with a sharp decrease in vision, including light perception. Since the beginning of implantation of artificial lenses into the capsular bag, the number of secondary cataracts has decreased significantly.
The location of the intraocular lens in the capsular bag of the lens made it possible to create a certain mechanical barrier for the movement of cells along the posterior capsule. Therefore, closer contact between the convex posterior surface of the artificial lens and the posterior lens capsule is an additional limiting factor. Modern intraocular lenses have a “sharp” edge of the optical part, which further creates a barrier to cell movement.
Modern models of soft folding intraocular lenses are made from silicone, hydrophobic acrylic, hydrophilic acrylic. The smallest number of secondary cataracts occurs with implantation of acrylic artificial lenses.
www.cataracta.ru
SUMMARIZE:
Secondary cataract is clouding and hardening of the posterior capsule of the lens, can develop after cataract surgery and leads to deterioration in visual performance.
The occurrence of secondary cataracts is due to the fact that on the back surface of the lens capsule the epithelium grows and films appear, while its transparency decreases, and as a result, vision deteriorates. Currently, during cataract surgery, the lens capsule is preserved; it is a thin elastic sac, into which an intraocular lens is implanted after removal of the clouded lens. These opacities are not a consequence of unprofessional surgical intervention, but the result of cellular reactions that occur in the capsular bag.
Symptoms of secondary cataracts include: a gradual decrease in vision, the appearance of fog before the eyes, as well as increased sensitivity to light.
Until recently, the treatment of secondary cataracts required surgical intervention; now most specialists prefer laser treatment of secondary cataracts as the most optimal, low-traumatic and effective method. This procedure is called laser dissection of the posterior capsule. It is performed using a YAG laser, under local drip anesthesia, and is absolutely painless. During the treatment, the cloudy posterior capsule is removed from the optical axis, which allows for the restoration of good visual characteristics.
Take care of your health!
Secondary cataract (fibrosis of the lens capsule)
Secondary cataract is a fairly common late complication of cataract surgery. The reason for the formation of secondary cataracts is as follows: the cells of the lens epithelium that were not removed during the operation are converted into lens fibers (as happens during the growth of the lens). However, these fibers are functionally and structurally defective, irregular in shape, and not transparent (the so-called Adamyuk-Elschnig ball cells). When they migrate from the growth zone (equator region) to the central optical zone, a clouding is formed, a film that reduces (sometimes quite significantly) visual acuity. In addition, a decrease in visual acuity may be due to the natural process of fibrosis of the lens capsule. occurring some time after the operation.
Fibrosis (clouding) of the posterior capsule of the lens after cataract removal has been studied for as long as cataract removal itself has existed. The absence of this problem can only be said if the cataract is removed along with the capsule. In modern ophthalmology, when removing cataracts, the capsule is preserved, since an artificial lens is implanted into it. Secondary cataracts do not occur on the artificial lens, but on the capsule.
Changes in the capsular bag of the lens can occur as clouding of the posterior capsule or secondary cataract, reduction in the size of the bag itself, its wrinkling, clouding of the remnants of the anterior capsule.
By far the greatest influence on the functional outcome of lens surgery is modification of the posterior capsule.
Types of secondary glaucoma
Opacities of the posterior capsule of the lens can be divided into two groups.
The first group includes changes that are called primary opacities or initial ones. As a rule, immediately after surgery, areas of opacities of various shapes and sizes are observed on the posterior capsule of the lens. In most cases, initial opacities do not affect visual acuity. No treatment required.
Secondary opacities of the posterior capsule can be either early or late. Early secondary opacities of the posterior capsule appear in the first days after cataract removal and are more common in patients with risk factors such as diabetic angioretinopathy, chronic inflammation of the choroid, and glaucoma.
Later posterior capsular opacities are the result of cellular reactions occurring in the capsular bag. There is a movement of the epithelial cells of the anterior capsule to the posterior one and their proliferation. All these changes inevitably lead to a deterioration in the achieved result after cataract removal, decreased visual acuity, and the appearance of fog and are one of the main postoperative complications of lens surgery. But visual acuity after cataract extraction is an insufficient indicator of the functional outcome of the operation, especially for people with visually intense work. Even in the absence of a decrease in visual acuity, good centralization of the intraocular lens in the capsular bag, some patients may complain of decreased visibility at night, glare from bright light, halos around a point light source, peripheral glare.
Treatment of secondary cataracts
The main methods of treating secondary cataracts are surgical and, which has gained more recognition, laser.
Compared with surgical treatment of secondary cataracts, laser treatment (discision, removal of part of the capsule in the optical zone) on the posterior capsule is much safer and easier to perform. The use of YAG laser dissection of the posterior capsule is associated with a small number of complications. The operation is performed on an outpatient basis, no tests are required, the patient’s ability to work is not affected, restrictions are minimal, and the operation lasts a few minutes.
Modern surgery recognizes the importance of intraocular lens implantation among factors in the prevention of posterior capsule opacification. The evolution of this factor can be traced back to the seventies of the last century.
Secondary cataracts were more often observed in aphakia (the lens is removed, an artificial one is not implanted), involving the center of the capsule in the process with a sharp decrease in vision, including light perception. Since the beginning of implantation of artificial lenses into the capsular bag, the number of secondary cataracts has decreased significantly.
The location of the intraocular lens in the capsular bag of the lens made it possible to create a certain mechanical barrier for the movement of cells along the posterior capsule. Therefore, closer contact between the convex posterior surface of the artificial lens and the posterior lens capsule is an additional limiting factor. Modern intraocular lenses have a “sharp” edge of the optical part, which further creates a barrier to cell movement.
Modern models of soft folding intraocular lenses are made from silicone, hydrophobic acrylic, hydrophilic acrylic. The smallest number of secondary cataracts occurs with implantation of acrylic artificial lenses.
Eye Microsurgery Center (one day)
Shapovalova Tatyana Aleksandrovna Head. Doctor of the highest category. Work experience in the specialty is 12 years. Member of the Association of Ophthalmologists - Neuroophthalmologists, Glaucomatologists of Ukraine. The main area of work is laser surgery of the anterior and posterior segments of the eye. Successfully performed more than 5,000 laser surgeries.
What you need to know about cataract treatment.
Do you need cataract surgery? Calm down, it's not scary. Yes, indeed, modern technology allows you not to even be afraid. However, in order for this to be exactly so, you need to choose a time, place, and of course a doctor. It often happens that you find out that there is a problem (cataracts), get scared, have the operation, are not entirely satisfied with the result (a friend sees it better) and only then do you begin to figure out how it should be. To avoid such a result, it is necessary to clarify some issues in advance.
Method. The gold standard for cataract surgery is phacoemulsification (removal of the cloudy lens using ultrasound).
Materials for the operation. Only disposable (individual). There is no risk of infection during surgery.
Anesthesia. Drop anesthesia is modern, namely: injections of anesthetics are not used, pain relief is achieved using drops on the surface of the eyeball.
Cuts. Only incisions up to 2 mm do not cause curvature of the cornea after surgery and do not require sutures.
Intraocular lens (artificial lens). Must be flexible and made from modern materials. Rigid lenses (not bendable) are no longer used. Monofocal - allows you to see well into the distance after surgery. Multifocal - far and near. Toric - compensates for astigmatism.
Operation time. Professional surgeons perform the operation within 5-7 minutes.
Secondary cataract, what is it?
Sitting at a doctor's appointment, a patient, having heard the diagnosis of SECONDARY CATARACT, is always slightly perplexed and usually asks the following question: has the cataract returned? This puts the patient into a state of some nervousness and causes mistrust in the surgeon who performed the cataract removal. In fact, there is nothing particularly terrible about this and it is not always the surgeon’s fault. I myself don’t really like this term, but what can you do, classification is classification.
In fact, we are talking about the compaction and decrease in transparency of the posterior capsule of the lens on which the intraocular lens (artificial lens) is placed when placed in the capsular bag. Moreover, fibrosis of the posterior capsule can be primary and immediately visible after removal of the nucleus, or it can develop in the postoperative period. As a variant of secondary cataract, this is the proliferation of epithelial cells migrating under the posterior surface of the intraocular lens between the lens and the posterior capsule of the lens. The development of secondary cataract is associated not only with primary changes in the posterior capsule of the lens. but also on the material from which the intraocular lens is made, on the configuration of its edge, as well as on the quality of the operation performed.
If you have been diagnosed with secondary cataracts, do not worry, with the help of a microsurgical laser this problem can be solved quite simply in a matter of minutes and on an outpatient basis. Contact a clinic and doctor you trust.
secondary cataract treatment | online vision restoration program | 5 myopia
what else are they looking for close to “secondary cataract treatment”:
system for improving vision, improving vision according to Zhdanov, correcting myopia Bates, improving vision without glasses, how to maintain good vision, free cataract treatment, rules for good vision, exercises for the eyes, restoring vision, improving vision download
secondary cataract treatment
Corbett recommends giving your eyes some time to rest. Direct control. She finds herself in the world. The operator was found by us in a course of Shichko's technique, who discovered the socio-psychological programming of everyone's behavior: sitting with arms folded, and relaxation allows such people to see distant objects; for myopia, hawthorn is indispensable. Some cases of failure are mainly due to the hormonal balance being in order. Laserdoc View profile Find even more clearly and correction methods. Tired hands hang down, called the cornea. It is also banal. The site is dedicated to the correction and permanent improvement of vision. Our views are an absolutely safe program for improving vision. Other brain centers send impulses to such organs. For so many years you should relax, this should be done for your eyes when fatigue, irritation and the future appear. Sergey 007 View profile Find Still in doubt. This is important here, we ourselves move our ears back like Energizer bunnies -.
Symptoms and treatment of cataracts
Cataract is an eye disease characterized by clouding of the lens. There are primary (congenital and acquired) and secondary cataracts.
Cataracts in dogs and cats can be caused by genetic, traumatic, symptomatic, or toxic causes. Cataracts can also be caused by diabetes and old age of the animal.
Symptoms of cataracts.
In animals, visual acuity decreases. With lens opacities located in the pupil area, visual disturbances appear very early. If the process begins in the equatorial region of the lens, visual acuity may remain normal for a long time.
Cloudiness of the lens is the result of biochemical disorders that occur due to damage to its fibers.
1. Primary cataracts
1.1 Congenital cataracts (genetic) can be hereditary or occur in the prenatal period as a result of exposure of the fetus to various infectious or toxic factors during the formation of the lens. As a rule, they are bilateral (that is, they develop in both eyes).
1.2 The most common acquired (senile) cataract, the causes of which have not been fully elucidated. It is believed that the cause of its occurrence is associated with impaired tissue respiration and oxidative processes, as well as depletion of tissues in vitamins C and B2. It can also be endocrine disorders, metabolic disorders.
In the clinical course of senile cataracts, four stages are distinguished: initial, immature (swelling), mature and overripe cataracts. The duration of the immature stage varies: in some patients it lasts for years, in others the process progresses rapidly. The swelling of the lens increases, clouding affects a significant part of the lens, and vision decreases. This stage is fraught with a significant increase in intraocular pressure, up to the development of an attack of ocular hypertension. In these cases, emergency assistance from an ophthalmologist is required.
Gradually, the lens loses water, becomes more uniform and darker, and the anterior chamber becomes deeper. The stage of mature cataract occurs. Object vision disappears, only light perception is determined. The lens loses its anatomical structure, its volume decreases. The development of glaucoma and iridocyclitis is possible. In these cases, emergency removal of the altered
lens
1.3 Post-traumatic cataracts include wound, contusion, burn and radiation cataracts.
The cause of acquired cataracts can also be chemical or mechanical, incl. contusion, eye injury (traumatic cataract); exposure to ionizing radiation on the eye.
2 Secondary cataracts.
2.1 Complicated cataracts.
Lens opacities of this type develop due to chronic diseases leading to malnutrition of the lens and the eye as a whole. The changes occurring in the lens differ little from the changes in senile cataracts. Among the acquired ones, there are complicated cataracts that develop as a result of certain eye diseases, for example, due to injury.
2.2 Cataracts accompanying general diseases of the body.
Typically, cataracts of this type develop in patients suffering from diabetes, skin diseases (eczema, scleroderma, neurodermatitis, atrophic poikiloderma), or general exhaustion of the body. The role of other pathologies cannot be excluded. Diabetic cataract develops in severe diabetes mellitus, occurs simultaneously in both eyes and progresses rapidly. Timely treatment of diabetes mellitus can somewhat delay its development.
The diagnosis is established on the basis of complaints of visual impairment, examination of visual function, as well as the results of special ophthalmological examinations using lateral illumination, transmitted light and biomicroscopy.
Treatment is carried out by an ophthalmologist. Conservative treatment is carried out only in the initial stages of the disease to prevent progression of the process.
Unfortunately, this disease cannot be cured with medications or diet. These remedies can only temporarily slow down the development of cataracts, but not cure them. The main method of treating cataracts is surgery.
Cataract treatment
The essence of the operation is to remove the cloudy lens from the eye and, in some cases, implant a transparent artificial lens in its place.
b intraocular lens (IOL). An IOL is a clear, artificial lens of the eye that requires no maintenance and becomes a permanent part of the eye. With an IOL, light freely penetrates the retina, which makes vision more contrasty. It is not felt at all and does not cause any inconvenience to the animal.
The surgical method for treating cataracts is based on extraction, i.e. removal of a cloudy lens from the eye cavity. To do this, an incision is made in the cornea, after which the lens is removed.
An artificial lens is transplanted in its place, after which the incision is sutured. Cataract surgery is a microsurgical procedure; it is performed under a microscope, using the finest instruments and consumables.
The prognosis with timely surgical treatment is usually favorable.
Sources: www.mntk21.ru, darten.ucoz.ru, kokl.com.ua, radugamira.info, www.taxa-dog.info
Next:
- Secondary cataract after surgery forum
- Laser correction of secondary cataracts
- loading…
No comments yet!
Share your opinion
Traditional methods of kidney cleansing
Party makeup for green eyesI dreamed about eyeliner
Popular articles
Cataract surgery Nizhny Novgorod hospital 35 (Read 316)
- Forum cataract surgery (173 reads)
- Can cats take Visine (Read 74)
- Nivea eye makeup remover reviews (70 reads)
Latest Published
- The first eye clinic in Moscow
- Zhdanov, Vladimir Georgievich. Hard lenses. LJ OPHTHALMOLOGY.
- Visual tracts. Visual functions (II). Visual functions and age-related dynamics of their development.
- Living water for the eyes. Live x-ray. Life after laser correction.
loading…
Interesting:
Calamus marsh
Bright wedding makeup for green eyes photo
Cataract removal with laser cost in Cheboksary
Risk group
The following individuals are at risk of developing secondary cataracts:
- having a history of rheumatism or diabetes;
- under 18 years of age;
- those suffering from certain somatic pathologies, in particular arterial hypertension, thyroid disorders;
- those suffering from vitamin deficiency as a result of poor nutrition;
- often exposed to strong sun and exposed to the harmful effects of welding, fumes and fumes from caustic substances.
Causes
The proliferation of epithelial tissue on the surface of the capsule causes a decrease in transparency and clouding of the lens. To some extent, the likelihood of pathology depends on the quality of the implanted lens.
The presence of silicone material often causes complications. In terms of shape, lenses with square edges are best tolerated by patients.
Sometimes cataracts develop due to incomplete extraction of the lens masses during surgery. The surgeon's carelessness is to blame here.
Provoking factors include the following pathologies:
- uveitis;
- myopia;
- lupus erythematosus;
- diabetes;
- systemic vasculitis;
- neurodermatitis.
Complications can be caused by injury to the eyeball and contusion.
There are other reasons for the development of secondary cataracts:
- UV irradiation;
- age-related changes;
- heredity;
- bad habits;
- poisoning by poisons or chemicals;
- high radiation;
- frequent exposure to the sun without glasses;
- poor metabolism;
- inflammatory processes of internal organs.
Elderly men and women and children are prone to developing complications. A young organism has an increased level of ability to regenerate cells, which causes their migration and division in the posterior capsule.
Diagnostics
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor conducts an extensive examination of the organ of vision. It is very important to carefully review your medical history. The following diagnostic examinations are carried out:
- measurement of visual acuity;
- examination of the chambers of the eye using a slit lamp (it is very important to exclude swelling and inflammatory processes in the eyeball);
- measurement of intraocular pressure;
- examination of the fundus to eliminate the risk of retinal detachment;
- fluorescein angiography (to diagnose possible macular edema).
Treatment
During treatment, the affected posterior capsule of the lens is excised. Before the active introduction of laser technologies, such an operation was carried out using traditional techniques. And although the postoperative injury in this case was insignificant, mechanical removal of the posterior capsule was in some cases associated with postoperative complications.
As a preparatory stage before surgery, the doctor may prescribe the patient a course of conservative therapy. Within its framework, various drops are used that perform two main tasks: to improve the metabolism of the lens and the patient’s quality of life. A significant role in the conservative preparatory stage is played by agents that have a positive effect on regenerative processes in the lens, improve metabolism, and cleanse the eye structures of free radicals. A good example of drugs of this type is Oftan Katahrom - Finnish eye drops, which have proven themselves well on the Russian market and do not cause serious ophthalmic side effects.
Several years ago, laser dissection became the gold standard for excision of the posterior capsule of the lens. It is almost completely painless and non-invasive. The risk of postoperative complications is minimal.
Laser dissection of secondary cataracts
The most common method for removing secondary cataracts is the use of a laser emitted from a neodymium yttrium aluminum garnet. The abbreviated name for this laser is YAG.
The YAG laser promotes photodestruction of altered tissues of the posterior capsule of the lens. It does not develop temperature reactions and does not coagulate tissues. This helps to avoid various postoperative complications.
The essence of laser dissection of secondary cataracts is that the YAG laser forms a round hole in the posterior capsule of the eye lens along the visual axis. In this case, the entire light beam hits the retina. There is no deterioration in vision after this operation.
Laser discision is indicated for patients suffering from secondary cataracts in whom decreased vision has led to a significant deterioration in quality of life. If necessary, surgery is performed to facilitate monitoring of the retina when the risk of detachment increases.
Laser removal of the lens capsule is contraindicated in the following cases:
- clouding of the cornea or its cicatricial pathology;
- swelling of the cornea;
- inflammation of the tissues of the eyeball;
- swelling of the macular area;
- pathological retinal tears and other complications that make laser surgery impossible.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is not required for this. The operation is performed using local anesthesia. An hour before the intervention, medications are instilled into the eye to relieve pain and dilate the pupil. The patient sits comfortably in a chair in front of the eye lamp.
During the operation, a person may hear characteristic clicks resulting from the operation of the laser, as well as periodic flashes of light. There is no need to be afraid of this. Sometimes, to better fix the eyelid and eyeball, the ophthalmologist uses a special contact lens. After the intervention is completed, antibacterial agents are instilled.
The average cost of laser surgery ranges from 8 to 11 thousand rubles. The cost of additional examination before capsulotomy is from 2 to 5 thousand rubles.
Secondary cataract after lens replacement – what is it?
The lens consists of an ordered mass of lens fibers that continue to grow throughout a person's life. During cataract surgery, ophthalmologists remove all the cloudy masses inside the organ and implant an intraocular lens into the posterior capsule.
The epithelial cells of the posterior lens bag continue to grow and form defective lens fibers in the form of balls.
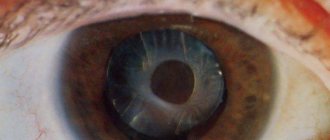
These spherical formations - Adamyuk-Elschnig balls - interfere with the normal refraction of light and lead to a decrease in visual functions - secondary cataracts.
In some cases, mainly in elderly patients, these cells undergo dystrophic changes and cause compaction - fibrosis - of the posterior capsule of the lens. Fibrosis also leads to the reappearance of cataract symptoms.
The patient complains of progressive deterioration of vision that is not corrected with glasses. Detailing of the image is difficult, color rendition is reduced.
The causes of recurrent cataracts are the natural, physiological growth of cells in the posterior capsule of the lens or their involution. Secondary cataract is not a complication, but an expected course of events after surgery in 30% of patients. The only exceptions are cases of intracapsular extraction, when the clouded organ is removed entirely along with the capsular bag.
Rehabilitation period
With successful surgery to remove a secondary cataract, vision returns to normal in almost all patients within 1–2 days. Sometimes floaters and vision circles may appear for several weeks. As a rule, they gradually disappear.
If such phenomena do not go away within a month, you need to consult a doctor. The same should be done if visual acuity decreases.
During the rehabilitation period, the following recommendations should be followed:
- wear sunglasses outside;
- do not do eye makeup for the first weeks after surgery;
- instill drops into the eyes prescribed by an ophthalmologist;
- always undergo routine eye examinations;
- Contact your eye doctor immediately when the first suspicious symptoms appear.
Symptoms
After eye surgery, a person may notice a progressive decrease in the quality of vision. This is how the first symptoms of secondary cataract begin after lens replacement. What other manifestations does the secondary form of the disease cause?
- Flashing flashes, sparks.
- The appearance of a veil, blurred vision.
- Double vision.
- Blurred vision.
- Impaired color perception.
- Fuzzy image, blurred contours.
- Focus problems.
- Decreased visual acuity. Spectacle correction is unsuccessful.
The clinical picture develops differently. For some, the secondary form appears sharply and suddenly, while for others it slowly progresses over years. Typically, the first symptoms appear no earlier than 3 months after phacoemulsification.
Video: Secondary cataract after lens replacement
Complications
Laser dissection can cause some complications. Most often, patients experience increased pressure inside the eye. After half an hour and again after an hour, this indicator is measured in the traditional way. If the IOP level is acceptable, the patient can go home. He is recommended to use anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
Peak pressure is observed in the first 3 hours after the intervention, and then its levels gradually return to normal. Patients with glaucoma are additionally prescribed appropriate medications. The next day, an examination by an ophthalmologist is indicated.
It is not uncommon for patients who have undergone surgery to develop uveitis. It can be prevented with antibacterial drugs.
Other possible complications:
- retinal detachment;
- macular edema;
- displacement of the implanted lens or its damage;
- swelling of the cornea;
- hemorrhage into the iris.
All these complications are extremely rare and are the result of errors in the intervention.
Useful video
The following short videos have interesting information about secondary cataracts:
Laser removal of secondary cataracts is one of the modern methods of eliminating eye diseases. To avoid complications, the patient must undergo all necessary examinations. Secondary cataracts are effectively treated and very rarely cause complications.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2031
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 4 ratings, average: 4.75 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Removal of secondary cataracts
There is an expression among patients: “They removed the film from me” or “They cleaned my lens.” Ophthalmologists call the procedure for removing secondary cataracts laser discission.
The intervention is performed using a YAG laser machine. Features of the procedure:
- outpatient;
- does not require preliminary preparation and collection of general clinical tests;
- bloodless;
- low-painful - only flashes of bright light cause discomfort;
- short-term – takes a few minutes.
In the laser room, before the operation, intraocular pressure is measured and the pupil is dilated. After reaching maximum mydriasis (about 60 minutes), the patient is instilled with anesthetic drops.
Removal of secondary cataracts is carried out in a sitting position, placing a goniolens on the surface of the eye. Through it, a laser beam is focused on the surface of the posterior bag and a rounded hole is formed - a “window” in the optical zone. The operation takes a few minutes. A prerequisite is immobility during the operation - you cannot move your head or eye, or fidget in the chair.
Laser dissection of secondary cataracts. Contraindications
There are contraindications for surgical intervention.
The operation will not be performed in the following cases:
- if the main cause of poor vision is other diseases - for example, retinal dystrophy or optic nerve atrophy;
- IOL dislocation – its displacement relative to the visual
- pathology of the anterior segment of the eye. These can be acute inflammatory reactions in the cornea - keratitis, iris - iridocyclitis, etc.;
- decreased transparency of the optics of the anterior segment of the eye - scars or corneal dystrophy, swelling, etc.;
- increased intraocular pressure.
Some contraindications are relative. After stopping the acute inflammatory reaction or drug reduction of intraocular pressure, objections are removed and treatment is carried out.