The most common complications
There are the most common complications that occur in almost all patients. In this case, treatment may be completely absent or incorrect. Some of them are fixable, others cannot be eliminated. Therefore, it is necessary to find a competent specialist who will prescribe the right treatment that completely restores vision function.
To treat cataracts, medications and surgery are used. In both cases, the patient's condition may become more complicated.
Hemorrhage
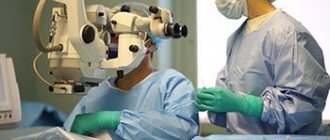
Eye surgery is classified as microsurgery. It is carried out using magnifying devices that allow you to closely examine the internal structures of the eyes. If the doctor incorrectly installed the intraocular lens, applied excessive pressure to any element of the eye, or made an incorrect movement, hemorrhage may occur.
In some cases, it does not form immediately, but after the operation is completed. This is the most dangerous option, since the entire internal cavity of the eye can fill with blood, this will lead to irreparable phenomena for the eyes, which will cause blindness.
In some cases, minor hemorrhage occurs, which resolves on its own. These are minor complications that do not require correction.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases
The internal structure of the eyes is an aseptic environment. When the eyeball is opened, pathogenic microorganisms enter it. These include bacteria, viruses, and fungi. If their number is insignificant, antiseptic agents will completely remove these microorganisms. Otherwise, infection of the internal structures of the eyes develops, and pus forms.
Infection often develops on the superficial structures of the eyes; pathogenic microorganisms enter the wound. This forms an infectious-inflammatory disease that spreads over the entire surface. To prevent the condition, the doctor prophylactically prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of drops to all patients.
Corneal edema
To penetrate the lens area, the doctor must cut the cornea. After the procedure is completed, swelling and inflammation will form. If the patient's condition is stable, medications, ointments, and solutions are prescribed. In case of extensive inflammatory processes, keratoplasty is indicated. This is a procedure to completely replace the cornea.
Postoperative astigmatism
For surgery, the eyeball must be cut. This changes its shape. There are often cases when it is not restored to its previous size. Astigmatism is formed, that is, the wrong shape of the eyes.
The patient does not clearly see surrounding objects, their shape and size changes. To correct the condition, special glasses and lenses are indicated.
Increased intraocular pressure
This condition is called postoperative glaucoma. Secreted fluid begins to accumulate in the chambers of the eyes, which expands them. Gradually they increase in size, squeezing the surrounding structures. This condition can lead to retinal detachment or degeneration. The optic nerve is also affected, losing its signal transmission function.
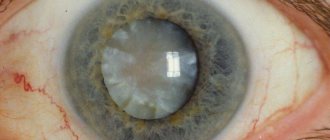
Secondary cataract
There is a pathology of the lens, for example, nuclear cataract, when it is necessary to remove not the entire element, but only part of it. In this case, the doctor needs to be very careful not to leave pieces of clouded tissue. If this happens, a secondary cataract forms. This condition is less amenable to correction, and most surgical treatments are not suitable. The patient's visual function begins to decline again, and blindness may occur.
Increased eye dryness
In the postoperative period, tear production often decreases. The surface of the mucous membrane becomes dry. This forms microtraumas and cracks in the cornea. The condition goes away over time. To maintain eye moisture, use drops (Defislez, Slezin).
Formation of floaters, dots before the eyes
If the vitreous body is damaged or compressed during surgery, non-existent elements form in front of the eyes. These include dots, flies, lines, stripes, lightning. They can be bright yellow or black. If this condition occurs several times and goes away, there is no need to worry.
Corrections require the constant formation of these elements.
Symptoms and causes of development
The first signs of recurrent cataracts appear at the stage after surgical recovery. This is due to the individual characteristics of the body. For example, if a patient suffers from trophic ulcers or diabetes mellitus, the risk of developing complications increases.
If you have high blood pressure, there is a high risk of cataract recurrence. A good doctor should especially carefully monitor the patient’s well-being if he knows about the presence of factors provoking the disease.
A dangerous disease that is easy to neglect is temporal arteritis.
Clinical picture of the disease
For what other reasons can a dangerous diagnosis be made after surgery:
- An allergic reaction to drugs used to restore the body after surgery can affect the appearance of cataracts.
- The advanced age of the patient becomes an incentive for repeated progression of symptoms.
- Proliferation of the skin epithelium associated with excessively active tissue regeneration.
- Bad habits.
- Mechanical damage can also lead to complications.
- The reason may also be hidden in an unprofessionally performed operation to replace the lens of the eye.
Radiation exposure and poisoning from toxic chemicals also contribute to the development of harmful symptoms. However, these reasons are rarely relevant, and more often recurrent glaucoma is associated with the patient's age or the use of inappropriate drugs.
We fight infection in a child correctly - Vitabact eye drops instructions for children.
The disease requires immediate response
In some cases, alarming symptoms appear within 1-3 weeks. However, more often discomfort and clouding of the lens develops after a few months.
It is not difficult to notice the problem, because it is accompanied by quite obvious symptoms:
- decreased visual acuity;
- blurred vision that progresses;
- the perception of colors and the panorama as a whole deteriorates;
- photophobia may occur;
- development of duality of objects and myopia.
Secondary cataracts can develop in one eye or in two at the same time. The problem is considered most dangerous if a cloudy lesion appears in the center of the lens.
More typical is a gradual increase in the symptoms of the disease, and a person may simply not pay attention to them. However, gradually the clouding and deterioration of perception will progress, which will ultimately lead to a sharp decrease in the quality of the visual apparatus.
Anti-inflammatory therapy will help avoid the development of complications
To eliminate the feeling of dry eyes, use special medications, such as Vitapos eye ointment.
Rare complications
There are complications that occur rarely in patients. Some of them can be corrected, others cannot be treated. In extreme cases, repeat surgery may be necessary to correct the person's vision function.
Lens rupture
The lens is a capsule containing a clear liquid. Particles spread throughout the internal structure of the eyes can damage these elements. For example, the vitreous body. This provokes an increase in intraocular pressure, the walls of the eye chambers begin to expand, gradually squeezing the retina and optic nerve. Their function decreases, and retinal detachment or optic nerve atrophy may occur.
Intraocular lens displacement
When cataract surgery is performed, an artificial model is implanted in place of the lens. It is called an intraocular lens. Around the lens are ligaments into which the lens must fit.
If the installation was performed incorrectly, it gradually shifts towards the retina. This leads to swelling, inflammation, and mechanical damage to the vitreous and retina.
Neurological disorders
The tissues of the eyes are not only well supplied with blood, but also innervated. If the doctor damages any nerve during the procedure, neurological disorders will occur. This may be twitching of the eye, the formation of nystagmus (involuntary eye movements). You need to contact a neurologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of IOL displacement
The main reason for this condition is damage to the ligamentous-capsular apparatus of the lens. This can happen both during surgery and after it, which is often caused by postoperative eye trauma. The incidence of SCA injury during surgery remains within 1-2%. Usually, it is not difficult to install the posterior chamber lens model into the capsular bag or into the ciliary groove, using fragmentary remains of the lens capsule as a support. In some cases, this requires an anterior vitrectomy or installation of intracapsular rings (the technique is used much less frequently).
Incorrect assessment by the surgeon of residual fragments of the SCA as a support or ignoring the above manipulations can provoke dislocation of the lens into the vitreous body, as well as onto the fundus. At the same time, such a condition can be complicated by hemophthalmos or proliferating vitreoretinopathy. In addition, it can cause chronic macular edema, retinal detachment, and indolent uveitis.
How to minimize the risk of complications
To reduce postoperative complications, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- staying at rest in a dark room so that negative environmental factors do not affect the eyeballs;
- use of sunglasses outdoors so that bright sun rays do not negatively affect the retina of the eyes in the postoperative period;
- postoperative antibiotic therapy, which eliminates the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- eating food rich in vitamins, nutrients, microelements necessary for normal metabolism and regeneration of damaged surfaces;
- lack of exercise in the first month after surgery, then exercises are prescribed on the recommendation of a doctor;
- the use of moisturizing drops that eliminate the risk of drying out the cornea.
Cataract removal is an operation that damages a small amount of tissue. Despite this, the patient may develop many complications, especially if he does not adhere to the doctor's recommendations. If a complication appears, you need to immediately contact a specialist so as not to lose vision function.
Late complications after cataract removal
This is a pathology that can develop at 2-3 weeks of the postoperative period and later.
Irvine-Gass syndrome
. This condition is characterized by the development of macular edema, which interferes with the perception of images by the retina. The treatment uses drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as glucocorticosteroids. If drug treatment is ineffective, intervention by an ophthalmic surgeon may be required.
Secondary cataract.
In some cases, secondary clouding of the lens may occur, which is localized in the posterior capsule. In such a situation, a capsulotomy using a laser is indicated, which again makes the lens transparent.
Cataract surgery at the Eye Surgery Center has reached a high level, which allows us to minimize the risks of complications.
You can make an appointment with our clinic specialists by calling: +7 (495) 727-00-44,.