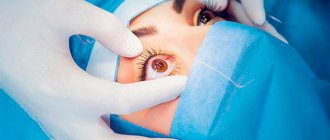
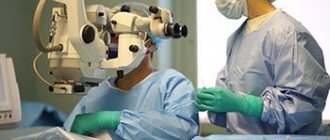
Important information about glaucoma
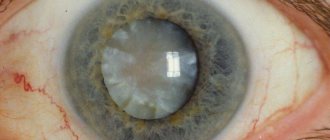
Translated from Greek, “glaucoma” is translated as “green color of the sea.” People usually start talking about glaucoma if a person experiences a persistent increase in intraocular pressure. This is due to stagnation of intraocular fluid, which can lead to destruction of the optic nerve.
Impaired outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyeball causes congestion and increased pressure in the eye. As a result, this leads not only to decreased vision, but often to its complete loss.
Ophthalmologists consider such visual pathology to be insidious: the symptoms of the disease can appear quite late. Typically, at an early stage, glaucoma has no symptoms at all.
Most often, patients begin to turn to ophthalmologists only when their vision begins to seriously suffer.
Postoperative stage
Modern technologies in ophthalmology make it possible to perform an operation within 20 minutes. In this regard, long-term bed rest is no longer required, and no one will categorically tell you how many days to spend in the hospital. Some specialists are ready to send the patient home after 1 hour, others will advise staying for 3-5 hours.
In some clinics, the person undergoing surgery remains under observation for as long as his health condition requires. But according to previous generally accepted standards, the period of hospitalization in this case should be 7 days. Everything directly depends on the type of surgery you underwent, the level of qualifications of the ophthalmologist and the reputation of the clinic you choose. If the operation was performed using the laser method, you can go home immediately, because no mechanical damage to the eye occurred during the process.
Regarding the removal of stitches, they are unlikely to immediately tell you the date when you need to come for this procedure. For each patient, the postoperative period is purely individual and it is almost impossible to predict for sure when the suture will heal. They can be removed either after 7 days or after 3 weeks.
It’s hard to believe, but it also happens that a patient walks with stitches for several months because the doctor lost sight of this point. This is another good reason not to neglect scheduled examinations and always show up on time throughout the entire rehabilitation period.
Necessary restrictions
Many people often wonder whether after surgery it is possible to watch TV, work on a computer and read. If the operation was successful and there are no serious complications noted, you can, but not earlier than 5 days later. And at the first slightest feeling of fatigue in the eyes, this load should be stopped and the necessary break should be taken from 1 to 3 hours.
Symptoms
The key symptoms of glaucoma are:
- blurred vision;
- the appearance of rainbow circles near light sources (light bulbs, headlights, candles, etc.)
When the patient begins to notice redness of the eyes and attacks of eye pain, this indicates that the pathology has entered the terminal or final stage, when it is no longer possible to cure.
Although you can get glaucoma at any age, this pathology is more common in older people.
The main symptom of glaucoma is increased intraocular pressure (or pressure with a difference in both eyes above 5 mmHg)
However, in addition to this feature, in patients with glaucoma, the boundaries of the visual field are disrupted and the fibers of the optic nerve are damaged. Therefore, with the development of this pathology, specialists also identify organic disorders in the structure of the eye (optic disc atrophy, disorders of ocular hydrodynamics, etc.)
The concept of “glaucoma” includes about 60 diseases that have a number of features such as:
- increased intraocular pressure;
- glaucomatous optic neuropathy (damage to the optic nerve) with its subsequent atrophy;
- visual impairment.
The main risk factors for the development of glaucoma are situations with:
- aggravated heredity;
- old age (over 65 years);
- anatomical features of the eyes.
Forms and types
Glaucoma is called primary if it occurs independently, or secondary if the pathology appears as the consequences of various disorders that change the condition of the vessels and the movement of blood in them.
Diseases in a patient such as:
- myopia;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- persistent hypertension or hypotension;
- migraine;
- diabetes mellitus
The main forms of glaucoma are:
- Open angle. The most common form, in which the function of the drainage system of the eyes is disrupted and eye pressure increases. It is often asymptomatic and quickly leads to blindness.
- Closed angle. A less common form in which intraocular fluid cannot enter the drainage system. This form has more pronounced manifestations in the form of pain, redness of the eyes and severe visual disturbances.
Glaucoma surgery prices
The cost of non-penetrating deep sclerectomy in our ophthalmology center starts from 30,00 rubles (for one eye) and depends on the surgical technique, as well as the use of drainage. You can find the entire list of prices for the treatment of glaucoma and other eye diseases in the PRICES section.
Microsurgical technique, the name of which is included in the title, refers to methods of treating glaucoma, and to understand the essence of this operation it is necessary to remember what we know about the disease itself.
The most common and, in principle, correct answer that can be heard to the question “What is glaucoma?” sounds something like this: “It’s pressure in the eye.” Indeed, glaucoma is a condition of chronically increased pressure of intraocular fluids, caused by their excessive secretion, violations of the natural drainage system of the eye, or a combination of these main reasons. In fact, this is not one disease, but a whole group of pathological conditions that differ in origin (congenital or acquired, i.e. primary or secondary glaucoma), anatomical features (open-angle or more rare closed-angle), course, prognosis, etc. Among the clinical variants of glaucoma, there is even such a seemingly paradoxical form as normotensive glaucoma, in which specific glaucomatous symptoms develop with relatively normal intraocular pressure (IOP).
One way or another, over time, disturbances in the natural hydrodynamics of the eye lead to degenerative changes in various intraocular tissues; The most dangerous is degeneration of the retina and optic nerve head, since this process leads to a progressive and irreversible decrease in visual function. According to statistics, today glaucoma is the second, after cataract, cause of acquired blindness in the world. As for the total number of people suffering from this disease, various sources provide estimates from 60 to 100 million people (at the same time, in developing countries the epidemiological situation with glaucoma is much worse than in developed countries). Most patients are mature and elderly people, although congenital and early, in particular, juvenile (adolescent) forms are also not unique. It should be noted, finally, that almost all serious medical and statistical studies reveal a significant trend towards an increase in the incidence of glaucoma.
The danger of glaucoma
Glaucoma can occur with more or less pronounced manifestations, but is always accompanied by a periodic or constant increase in intraocular pressure.
During an attack, the pupil dilates, loses mobility and acquires a greenish color (which is why this disease is also called “green cataract”).
The disease, if left untreated, results in complete loss of vision. It is in the rapid progression that the insidiousness of glaucoma lies.
Blindness due to glaucoma is associated with the destruction of retinal cells caused by high blood pressure, a disorder of the circulation of intraocular fluid and atrophy of the optic nerve. The damaged optic nerve stops transmitting visual signals to the brain normally. In a person with this condition, central and peripheral vision suffers, and the visual area gradually decreases.
Types and methods of operations
If conservative therapy does not produce any results, or the person experiences severe side effects, ophthalmologists may decide to perform surgical therapy.
- Laser surgery (trabeculoplasty)
This type of surgical intervention is becoming increasingly popular and is an excellent solution to the problem, although it cannot boast of long-term improvements.
The procedure is absolutely painless and is carried out within 15-20 minutes (the simplicity of the manipulation allows it to be carried out in an ophthalmologist’s office or in an outpatient clinic). The laser beam is focused on the trabecular meshwork of the eye, causing subtle changes in the drainage system of the glaucoma patient's eye. Thanks to this, the circulation of intraocular fluid improves and IOP decreases.
After completion of the procedure, the doctor will conduct a control measurement of IOP, and the patient is allowed to safely go home and do everyday activities. Many note a significant improvement in their condition, which makes it possible to undergo or eliminate the need for surgical intervention.
It may take several weeks for some people to feel improvement, during which time they may still need to take previously prescribed medications. Of course, some medications may not be necessary, but you cannot stop them on your own. Only a doctor, after conducting an examination, will decide which medications can be discontinued and which ones can be left in place.
- Trabeculectomy
If conservative treatment and/or laser surgery cannot affect IOP, specialists decide to use traditional surgery. The most widely known type of surgery, which is indicated for patients with all forms of glaucoma, is Trabeculectomy. During the operation, the surgeon creates a small passage in the sclera to ensure better circulation of excess eye fluid. A valve is surgically created that allows fluid to be released in the required amount, but does not allow the eye to drain completely.
A small bubble of fluid may appear in the area of the hole made in the eye, indicating that it is leaking into the area between the conjunctiva and the sclera. In certain cases, the piece drainage may become blocked and the pressure will begin to increase again. Such a course of circumstances is possible during the healing of an artificially created hole, because the body is trying to heal itself.
For this reason, many surgeons perform surgery using an antifibrotic agent that is injected into the eye during surgery to reduce scarring time. Half of the patients who have undergone surgery no longer require treatment for a long period of time. The 30-40% who are still being treated should have their IOP values checked regularly.
- Transplantation of artificial drainage system
Scientists have been able to develop simple devices that improve the circulation of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber, thereby achieving a significant reduction in IOP. Such devices have a simple structure, made of small silicone tubes passing to the anterior chamber of the eye. The tube is connected to plates sewn to the surface of the eye (they are almost invisible).
The liquid accumulates on this plate, after which it is absorbed by the tissues of the eye. There is an opinion that this type of surgical treatment does not reduce IOP as well as Trabeculectomy, but it is preferred for those patients whose IOP cannot be controlled by traditional surgery, or in the presence of old scars.
- Non-penetrating surgery
One of the innovations, non-penetrating surgery, during which the doctor does not penetrate the anterior chamber of the eye, shows great promise in preventing complications and reducing the risk of infection. But this type of treatment is not available to many doctors, because it requires great skill. It has not yet become widely used and is at the stage of clinical observations and trials.
Glaucoma Treatment Methods
Treatment of glaucoma is long and difficult. The choice of treatment method is determined by the doctor depending on the type of glaucoma, its course, and the patient’s health condition. The main ways to eliminate this eye pathology are treatment methods:
- conservative (medication);
- surgical;
- laser
- Drug treatment consists of instilling drops that reduce intraocular pressure. You have to use drops for life; in patients, instilling drops becomes as common a procedure as brushing your teeth. However, the drugs have many contraindications and are not always suitable for patients with serious concomitant diseases such as asthma or vascular pathologies.
- Surgery is used as a last resort when other methods are ineffective. Modern surgical techniques prefer gentle intervention, without perforation of the eyeball (non-penetrating sclerectomy). The surgical method is especially effective in the early stages of the pathology, as it stops its development, preventing the occurrence of atrophy of the optic nerve fibers. There are several methods of such operations. The most popular EX-PRESS technique uses a special valve made of medical steel to drain intraocular fluid. This treatment is well accepted by the patient’s body, and already on the day of surgery, most of them are already discharged home.
- Laser therapy for glaucoma has been used since the 70s of the last century and is excellent for those patients for whom the use of medications is not enough. We will analyze the essence of the laser method of treating glaucoma in detail.
How it is carried out and what the consequences may be
Surgeons offer several types of laser treatment for the disease. Each of them has its own characteristics. Laser vision correction has its pros and cons, and the opinion of specialists can be based on many individual characteristics.
Deep non-penetrating sclerectomy
The essence of this method is that the doctor makes a small incision on the cornea of the visual organ in the area of Schlemm's canal. With this method, the surface of the eye becomes thinner, so there is no need to make any holes . So the morbidity of this method is low, and the outflow of eye fluid occurs naturally.
Laser beams improve the accuracy of procedures and patient comfort. Find out about the effectiveness of glaucoma treatment with drops here.
Operation – laser iridectomy
This method of glaucoma treatment remains the most common today. A laser beam creates a small hole in the iris. It is this that acts as a kind of channel for increased outflow of fluid inside the eye. The result of the actions taken is the normalization of pressure inside the eye.
This type of laser intervention is prescribed for acute attacks of angle-closure glaucoma.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis. First, the patient is given local anesthesia. To do this, special drops with an anesthetic effect are used. In the field, drugs such as Travatan for glaucoma and similar drugs can already be prescribed. A goniolens is then placed on the cornea. Due to this, it is possible to direct the laser beam to the desired location.
If a repeat iridectomy is performed, only one pulse will be required.
You may also benefit from learning more about the signs of early-stage glaucoma.
Video: laser iridectomy:
Laser iridectomy has become widespread as a preventative measure to eliminate the symptoms of true narrow-angle glaucoma.
Find out when a scleral lens is needed.
When performing manipulation on one organ of vision, it is possible not only to improve its visual function, but also to prevent the development of pathology in the second organ of vision. Laser iridectomy should be used as a prophylaxis for patients who have been diagnosed with glaucoma in order to prevent its subsequent development.
More information about glaucoma treatment methods can be found here.
Laser trabeculoplasty for elderly and young patients
This method is distinguished by its safety and effectiveness. Thanks to the action of laser beams, it is possible to normalize intraocular pressure even in those patients for whom therapy with antiglaucomatous drops is contraindicated. Thanks to laser trabeculoplasty, it is possible to prevent the development of serious consequences, and also to do without surgical intervention.
After the manipulation, the patient can return to a full life. Thanks to trabeculoplasty, it is possible to restore the outflow of ocular fluid in open-angle pathology. Cataracts are also treated using a similar method. However, the symptoms and causes of cataracts are somewhat different.
Gillan Comfort drops can help with dry eyes.
Laser surgery cannot restore vision, but it can prevent the development of the pathological process.
It is also worth learning about how glaucoma is treated in the elderly.
The operation is performed on an outpatient basis. To do this, a high-energy laser beam is used. Before performing the procedure, the doctor administers local anesthesia to the patient by drip. Thus, it is possible to install a goniolens, with the help of which it is possible to focus the laser beams on the required area of the iris. It has a reflective surface. It is placed in the patient's eye. He must sit in front of the lamp, and the doctor will install a lens in one organ of vision, while the second is simultaneously fixed on a specific object.
You can find out about the best drops for eye pressure in this material.
Video: laser trabeculoplasty:
Often, the surgeon makes several holes in several segments of the iris at once. This is necessary to obtain long-term positive results. This procedure lasts half an hour. During this time, the patient usually observes flashes of laser or green light.
Find out what emergency care should be provided for an acute attack of glaucoma here.
Laser surgery for glaucoma
The laser is most effective at the beginning of the development of pathology, and this method is least effective in the advanced stage of glaucoma.
Laser treatment for glaucoma can be carried out by several types of laser units with different characteristics and parameters. For this purpose, technologies of this type of treatment are used in the form of:
- The technique of laser iridectomy and goniotomy, which involves artificially creating a hole for the outflow of intraocular fluid in the iris. A through hole in the iris leads to pressure equalization between the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye.
- Laser trabeculoplasty, used for open-angle glaucoma to restore the movement of intraocular fluid. With this technique, tiny burns are applied to the diaphragm, which leads to the expansion of the narrowed canal and improved outflow of intraocular fluid.
- Laser gonioplasty, which involves coagulation of the iris using an argon laser.
- Laser trabeculopuncture, the essence of which is to create slits in the scleral flap for the operation of the anterior chamber, used for complicated glaucoma.
- Laser descemengoniopuncture, used in the treatment of uncompensated glaucoma, allowing to supplement or replace the constant use of medications.
A variety of laser techniques allows the ophthalmic surgeon to select the most suitable treatment method for a given type of glaucoma. Laser correction can serve as an independent type of treatment, or be part of complex therapy and performed before microsurgical intervention.
Often, laser surgery alone is not enough to restore the outflow of intraocular fluid. Lack of retinal nutrition leads to atrophy of its light-receiving cells, even if intraocular pressure has been normalized. Therefore, to restore vision and prevent its deterioration, methods are used to improve the blood supply to the retina. The following methods can be used to improve blood circulation:
- laser stimulation;
- vacuum massage;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electrical stimulation.
Sometimes conservative methods are not enough, and to fully save vision, vasoreconstructive operations are used to redistribute blood flow and increase blood supply.
How is glaucoma surgery performed?
Glaucoma is a dangerous disease that leads to irreversible vision loss.
Surgery for glaucoma may be the only option to save you from complete blindness. Cataracts and glaucoma were previously considered the same disease until they were separated in 1705. This disease occurs latently, and when obvious symptoms occur, vision is already severely limited. It is impossible to reverse the process, so it is important to start treatment as early as possible.
At all stages of development, eye drops are used, but often this is not enough and there is a need for surgical treatment.
Indications for surgery
The goal of antiglaucomatous treatment is long-term normalization of intraocular pressure (IOP).
Antihypertensive drug therapy threatens complications not only from the visual organs, but also from the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems.
Indications for surgery for glaucoma cause a lot of debate, because the disease can behave unpredictably, some patients lose their vision even after successful intervention. Low blood pressure, even if IOP is low, accelerates vision loss.
You should also not underestimate the possible complications of the recovery period. If blindness has developed, the patient suffers from severe pain, and drug treatment does not help, eye removal is used for glaucoma. Indications:
- closed-angle form of glaucoma;
- the patient sees worse;
- fog appears before the eyes;
- pressure increases progressively;
- the patient himself chooses the surgical solution to the problem.
How to prepare?
Before the operation, the patient needs to undergo the necessary tests and be examined by a doctor.
During a planned operation, the patient undergoes a thorough examination and undergoes the necessary tests. A list of doctors whose opinions need to be obtained is given at the medical institution where the operation will be performed.
A hospital stay is recommended for 5 days before the procedure, and after the procedure the patient remains in the hospital for as long as his health condition requires. On the day of surgery, the anesthesiologist or ophthalmologist may prescribe additional medications. For proper preparation, the patient only needs to follow the instructions of the specialists.
If glaucoma is being treated surgically and the patient has a history of cataracts and needs a lens replacement, doctors will perform another operation.
Non-surgical treatment
Non-surgical treatment involves intervention in the structure of the eye without cutting. On the one hand, this method gives fewer side effects and negative consequences, and is characterized by rapid recovery after the procedure.
The patient does not need to stay in the hospital; he can go home a few hours after the procedure. On the other hand, the solution to the problem is temporary, the normalization of IOP is short-term, and repeated intervention is required.
It is used when surgical treatment of glaucoma is contraindicated.
Laser correction
If treatment for glaucoma does not improve vision, surgery is prescribed.
Laser treatment is performed in two ways:
- iridectomy;
- trabeculoplasty.
During an iridectomy, one or more holes are made in the iris to allow intraocular fluid to move between the chambers. Trabeculoplasty involves using a laser to target the trabecular diaphragm to improve fluid outflow. These manipulations are carried out under the influence of local anesthetic using a special lens. The procedure lasts about half an hour.
The advantages of laser treatment for glaucoma are the use of a local anesthetic rather than general anesthesia and minimal impact on the eye, which reduces the risk of complications.
The disadvantage of this method is the short-term effect. This procedure helps for a period of 1 to 5 years; with secondary correction, this period is reduced.
Possible adhesion of tissue at the sites of laser action or damage to the retina, iris or blood vessels.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction involves the effect of cold on the ciliary body. This effect is performed through the conjunctiva, sclera or directly. Used when there are contraindications to laser treatment. This method has a greater risk of complications and is not used in end-stage glaucoma. Contraindications are also:
- pain syndrome;
- unsuccessful surgical interventions.
Surgery
Surgery is used if glaucoma medications and non-invasive methods do not work. To prepare for such operations, IOP is reduced by medication to a minimum value and antihistamines are taken. If possible, eliminate inflammatory processes in the eyes or prescribe antibiotics.
Glaucoma surgery includes 5 groups of operations, from which the doctor chooses the most appropriate one.
Non-penetrating operations
This type of intervention does not involve creating through holes in the eyeball and is often used in conjunction with laser correction. Various adhesions and adhesions can form at the site of exposure, so sometimes special implants are additionally used. They prevent tissue fusion and provide a long-lasting positive effect after surgery.
Fistulizing operations
Fistulizing surgery is a method of surgical intervention with a simple technique and high results.
Fistulizing operations for glaucoma help normalize pressure in the eye at any stage of the disease in 85% of patients. Its essence is to create an additional channel for the outflow of fluid.
Moreover, in 20% of cases this canal can become scarred without the possibility of correction. In addition, there are other possible consequences:
- Destruction of the conjunctiva. This causes a watery tumor to form, causing pain and inflammation.
- Cataract. It develops due to problems with the nutrition of the lens and tabecula, since the intraocular fluid is not renewed well enough and does not pass through natural pathways in the required volume. In extreme cases, atrophy of the eyeball develops.
Drainage operations
During drainage operations, after a puncture is made to drain the fluid, a collagen tube is installed to provide drainage. Another option is to install a valve that allows fluid to enter the reservoir when a threshold IOP value is reached. Such drainage helps even with advanced forms of the disease; the newly formed canal does not scar.
Cyclodialysis
During the operation, the surgeon uses a scalpel to cut off the lens from the ciliary body that holds it, and then applies sutures. This manipulation creates an additional path for fluid movement from the anterior chamber, which normalizes the pressure. It may be complicated by hemorrhage, which resolves on its own without negative consequences. Cyclodialysis is often used in combination with other types of intervention.
Iridectomy
The main indication for iridectomy is angle-closure glaucoma. The operation involves cutting off part of the iris of the eye.
There are complete iridectomy, in which the ciliary and pupillary parts are cut off, incomplete, when only the pupillary part is excised, and basal, when the root of the iris is cut off.
After the manipulation, sutures are applied, which are removed after 7-10 days. Performed using local anesthesia. This operation eliminates fluid stagnation and ensures its movement.
Postoperative period
After surgery, patients are released from physical activity until the IOP stabilizes and vision becomes clear again.
Surgery to remove glaucoma most often takes place without negative consequences if you follow your doctor’s recommendations.
In the postoperative period, you may need to stay in a hospital, where doctors will promptly notice possible complications after the operation. You will need an eye patch for up to a week.
Also, during the week it is forbidden to strain your eyes - you should stop watching TV, avoid bright lighting, and wear sunglasses. Do not get your eyes wet for up to 10 days. During the recovery period, you should avoid physical labor and stop playing sports.
Alcohol and smoking are contraindicated. In your diet, you should reduce salt intake and foods that cause constipation. Regular examinations by an ophthalmologist for glaucoma after surgery are required.
Consequences
It is impossible to completely restore vision with either medication or surgery. The actions of specialists are focused on preserving vision and normalizing intraocular pressure.
After the operation, you need to undergo examinations on time, try to avoid stress and excessive physical activity. Since the processes that cause glaucoma have a destructive effect on the condition of the eye and optic nerve, this disease is often complicated by others, such as cataracts. In this case, it is recommended to immediately replace the lens with prosthetic lens during the operation.
Prognosis after surgery for glaucoma
Surgery in the early stages of the disease is highly likely to help preserve vision and avoid relapses. However, they usually operate on patients who present late, so often after several years, vision begins to deteriorate again. However, with timely intervention, two thirds of patients can maintain their vision for life.
Source: https://EtoDavlenie.ru/glaznoe/kogda-delayut-operatsiyu-pri-glaukome.html
Indications for laser therapy for glaucoma
The main indications for the use of laser therapy for glaucoma are situations related to:
- contraindications of drugs to reduce intraocular pressure;
- the impossibility of systematic drug treatment for this disease;
- the need to use a large number of medications to reduce intraocular pressure;
- ineffectiveness of long-term conservative treatment;
- a sharp decrease in vision or narrowing of the field of view;
- prevention of acute attacks of glaucoma.
Benefits of laser treatment
The laser is especially useful to use at the initial stage of the onset of this disease. Laser techniques make it possible to ensure normal outflow of intraocular fluid in a short time.
However, in advanced stages of the disease, laser treatment may be ineffective. However, there are situations where even advanced stages of glaucoma have been successfully treated with laser.
The benefits of laser treatment for glaucoma are associated with:
- minimal trauma to eye tissue during treatment;
- low cost;
- the ability to carry out treatment on both eyes in one day on an outpatient basis;
- minimum postoperative complications;
- the possibility of repeated laser procedures;
- painlessness;
- minimal rehabilitation period;
- carrying out treatment without the need to open the eye cavity and damage the eye membranes.
All laser techniques involve creating an artificial tunnel for the exit of intraocular fluid, as well as its thinning or expansion. An effectively selected technique allows you to stabilize intraocular pressure and eliminate the need for constant use of medications.
Laser treatment cannot restore vision, but this method can prevent the progression of the disease.
Flaws
Like any treatment method, the use of laser has disadvantages. The main one is the frequent fragility of the effect of laser correction and the need to re-use this technique. To maintain the effect of laser use, patients often have to use a number of medications.
Other disadvantages of laser treatment are related to:
- instability of the therapeutic effect and its ability to fade over time;
- the possibility of inflammation;
- sharp jumps in intraocular pressure in the first days after the intervention;
- constant lacrimation;
- in some cases, the possibility of damage to the lens of the eye or the walls of blood vessels;
- postoperative fusions at the site of laser exposure.
In some cases, laser treatment of glaucoma becomes ineffective, and then surgery has to be resorted to.
Indications for surgery
Is it worth having surgery for glaucoma? This question is asked by most people with increased intraocular pressure. Unfortunately, operating ophthalmologists do not always give their patients objective and useful advice. In an effort to earn more money, they can persuade people to undergo surgery without having good reasons for this.
Early, newly diagnosed glaucoma is preferably treated with medications. In most cases, 1-2 types of drops help bring intraocular pressure back to normal. Read more about the use of drops in the treatment of glaucoma →
If drug therapy does not produce the desired results or the disease has progressed too far, doctors consider surgery.
Indications for surgery for glaucoma:
- high intraocular pressure during treatment with antiglaucomatous drugs;
- rapid narrowing of visual fields, which indicates damage to the optic nerve;
- the patient’s inability or unwillingness to apply eye drops daily;
- progressive deterioration of vision with normal pressure;
- the patient’s desire to give up regular use of boring medications;
- absolute glaucoma, accompanied by complete blindness and severe pain in the eye.
Whether surgery is necessary for glaucoma is a complex and largely debatable question. When it comes to chronic disease, it can be difficult for doctors to make the right decision. There are many medications on the market that can bring intraocular pressure back to normal. However, they have side effects and do not always help. Therefore, in some cases it is better for the patient to agree to surgery.
Note that glaucoma can be not only chronic, but also acute. The second form of the disease develops very rapidly and after 1-2 days leads to irreversible blindness. A patient with an attack of angle-closure glaucoma requires immediate medical attention. If medications do not help, he undergoes surgery.
Contraindications to laser treatment
Laser treatment may not be suitable for all patients with glaucoma. Laser therapy should not be used in the following situations:
- under 18 years of age;
- complete loss of vision in one eye;
- glaucoma in closed-angle form;
- pregnancy or breastfeeding;
- viral eye diseases;
- autoimmune diseases;
- high degree of corneal opacification.
Preoperative preparation
It is important to comply with a number of conditions.
- Laser treatment is painless; you may feel a slight tingling sensation or light “clicks” in the eye area. The session lasts, depending on the surgical technique, from 5 to 60 minutes.
- Drinking alcohol is prohibited 2 days before treatment. It is also advisable to stop smoking on the day of surgery.
- On the day before the intervention, it is recommended to wash your hair and face and avoid the use of cosmetics (perfumes, deodorants, etc.)
- It is important to have identification documents with you (passport, insurance policy, medical card, research results).
- It is better to dress before surgery in a cotton T-shirt, blouse or wide-neck shirt. It is also important to have replacement shoes.
- A light breakfast is allowed on the day of surgery. You should also bring sunglasses with you.
Typically, medications are used before and after surgery: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, local painkillers, drugs to reduce intraocular pressure.
In case of severe pain syndrome in patients, local anesthesia (retrobulbar) can be used.
Cost of laser correction
Laser correction for glaucoma is performed in many clinics or medical centers. Most often, for this type of treatment, patients prefer to go to Fedorov’s clinic or its branches, located in 12 cities of Russia.
How much does laser treatment for glaucoma cost? The cost of the intervention depends on the level of the clinic, the city, the patient’s health condition, the chosen laser correction technique, and the complexity of the diagnosis.
The average cost of laser correction in Moscow is:
- from 12,500 to 17,500 rubles for keratectomy;
- from 12,000 rubles for laser iridectomy;
- from 13,000 rubles for laser trabeculoplasty;
- from 22,500 to 45,500 rubles for different types of LASIK surgery;
- from 65,500 rubles for combined treatment of glaucoma and cataracts.
Additionally, patients often have to pay for diagnostic tests or the use of medications during therapy, which will increase the overall cost of treatment.
Prognosis after surgery
The postoperative prognosis depends on the initial state of the visual organ and concomitant ophthalmological diseases. With timely diagnosis of glaucoma and surgical intervention, 90% of patients retain good vision.
Patients should understand that the remission time depends on the type of surgery, but on average it is 6-7 years. After this period, a gradual increase in pressure begins. It is important not to miss this moment in order to prescribe treatment in time and determine the timing of reoperation.
Reviews
Lilia, 62 years old
I was diagnosed with glaucoma and was offered to treat it with a laser. To my surprise, the effect of the operation on one eye was 100%. I am also going to treat the second eye.
Igor, 48 years old
Suddenly I was diagnosed with glaucoma. I was advised not to waste time on eye drops, but to undergo laser treatment. The effect of this treatment is simply excellent, and recovery takes place in the shortest possible time.
Irina, 41 years old
After laser treatment, my eyes stopped bothering me at all, and my vision became better than in my youth.
Glaucoma is a very insidious pathology prone to progression. The advanced stage of this disease often leads to blindness. The many advantages of laser correction prove the right of this method of therapy to exist and the need for further development.
However, one cannot fail to take into account that the best results are obtained by laser treatment in the initial stage of the pathology. Therefore, it is unacceptable to ignore any problems in eye health, as well as skip annual preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Sources used:
- Primary glaucoma in patients with myopia and hypertension / Elena Baudova. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2011.
- Diagnostic reference book for an ophthalmologist / P.A. Bezdetko, S.F. Zubarev, N.V. Panchenko. - M.: Phoenix, 2006.
- Ophthalmoscopy / Yu.S. Astakhov, N.Yu. Dahl. - M.: N-L, 2011.
- IU School of Medicine Department of Ophthalmology
Possible complications
In some cases, after surgery, patients experience unwanted complications. Fortunately, they are quite rare and can be treated. The main thing is to identify them in time and take the necessary measures.
Possible consequences of surgery for glaucoma:
- hyphema - hemorrhage in the anterior chamber of the eye;
- hypotension – excessively low intraocular pressure;
- inflammation of the internal structures of the eyeball;
- ciliochoroidal detachment - separation of the choroid and ciliary body from deeper structures;
- scarring, causing re-development of the disease after 2-3 years.
In patients with glaucoma over 75 years of age, unpleasant consequences occur much more often after surgery than in younger people.