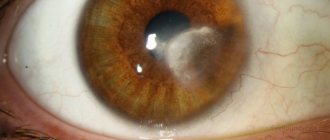
Causes of corneal swelling
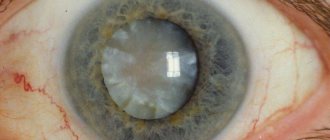
The cornea is the part of the eyeball located directly in front of the iris. This is the most convex part of the visual apparatus, which forms the optical system together with the lens. It has the shape of a spherical lens, ensures that light is refracted and projected onto the retina in the correct position. A condition called corneal edema causes blurred vision and blurred vision.
The cornea consists of three layers: endothelium, stroma and epithelium. Impaired water exchange in the stroma and epithelium can provoke corneal edema. A characteristic sign of edema is blurred vision. Typically, severe clouding is observed in the morning, and by the evening it disappears. Visual impairment due to corneal edema can be observed daily.
In addition to deterioration in the quality of vision, periorbital edema around the eye, redness, and swelling of the conjunctiva become visible. Such signs are often observed with inflammation and dystrophy of the visual organs.
Causes of corneal edema:
- Glaucoma. The cornea may swell due to increased intraocular pressure, when tissue metabolism is disrupted and fluid imbalance occurs. Swelling can be inside the eye and on the surface.
- Impact of a foreign body.
- Birth injury.
- Congenital endothelial dystrophy.
- Complications after glaucoma removal or vision correction.
- Allergic reaction.
- Development of pathogenic flora.
- Inflammatory processes (uveitis).
- Chemical burn.
Damage to the conjunctiva is observed with congestion or inflammation, panophthalmitis or a tumor of retrobulbar localization. Edema sometimes develops with exophthalmos. Periorbital edema is a common symptom of a variety of pathologies. Most often, the phenomenon is observed with a tumor or brain injury that disrupts the outflow of lymph and blood. Fluid can accumulate due to thyroid or kidney dysfunction.
Prevention
Preventive measures against corneal edema:
- Compliance with hygiene rules when caring for your face;
- Using hypoallergenic high-quality cosmetics;
- Regular measurement of intraocular pressure in patients over 45 years of age;
- Protect your eyes with special glasses to avoid injury to the organ of vision and the appearance of symptoms of swelling during hazardous work.
The correct selection of contact optics plays an important role in the prevention of pathological conditions of the corneal layer. Lenses must be of high quality, allowing oxygen to pass through to the eyes. You need to use lenses correctly.
Recommendations for following simple rules for using contact lenses:
- Remove and put on lenses only with clean hands.
- Wash the lens storage container after each use.
- Clean your lenses thoroughly with a special solution.
- Do not wear them for more than the service life indicated in the instructions.
- Give your eyes a break from contact lenses periodically.
- Use vision correction lenses that allow air to pass through.
Select cosmetics for eyelids and eyelashes from a health safety point of view; they should not contain allergens that cause swelling.
After removal of cataracts, glaucoma and other surgical interventions in different parts of the eye, do not burden your visual organs with computer work or reading, so as not to cause a relapse.
You need to choose a job that does not require strong physical activity or bending. When sleeping, you need to lie down so that your head is higher than your feet, which will ensure the necessary outflow of blood.
After treating edema, it is prohibited to swim or go to the sauna.
If you follow these rules, you can avoid repeated swelling of the cornea.
Symptoms of corneal edema
When the cornea edema, pain and pain in the eye are felt, lacrimation and photophobia increase. Blinking and moving your eyes causes discomfort. Vision may be blurred, making it difficult for the patient to see small details. Visual acuity decreases. Redness and inflammation are visually noted.
Chronic edema causes increased vascularization and impaired transparency of ocular structures. The condition, caused by the activity of bacteria, viruses and fungi, has similar symptoms. Discomfort with corneal edema is caused by its thickening and decreased transparency. Because the cornea is responsible for refracting light, clouding of the cornea causes a blurred or foggy sensation before the eyes. When wearing contact lenses, the discomfort increases.
Chronic edema is characterized by vascularization (the formation of blood vessels inside the cornea). It is very important to consult a doctor, because the complication does not manifest itself for a long time, and only an ophthalmologist can notice its signs during biomicroscopy.
Advanced vascularization affects the quality and acuity of vision. Often, surgical treatment is required to preserve visual function with chronic corneal edema.
Rare complications
There are complications that occur rarely in patients. Some of them can be corrected, others cannot be treated. In extreme cases, repeat surgery may be necessary to correct the person's vision function.
Lens rupture
The lens is a capsule containing a clear liquid. Particles spread throughout the internal structure of the eyes can damage these elements. For example, the vitreous body. This provokes an increase in intraocular pressure, the walls of the eye chambers begin to expand, gradually squeezing the retina and optic nerve. Their function decreases, and retinal detachment or optic nerve atrophy may occur.
Intraocular lens displacement
When cataract surgery is performed, an artificial model is implanted in place of the lens. It is called an intraocular lens. Around the lens are ligaments into which the lens must fit.
If the installation was performed incorrectly, it gradually shifts towards the retina. This leads to swelling, inflammation, and mechanical damage to the vitreous and retina.
Neurological disorders
The tissues of the eyes are not only well supplied with blood, but also innervated. If the doctor damages any nerve during the procedure, neurological disorders will occur. This may be twitching of the eye, the formation of nystagmus (involuntary eye movements). You need to contact a neurologist for diagnosis and treatment.
How is corneal edema diagnosed?
The primary diagnosis of corneal edema is carried out by an ophthalmologist. If necessary, a neurologist, endocrinologist, nephrologist, therapist and surgeon are involved.
The ophthalmologist uses various techniques to identify the factors that cause corneal edema. It is necessary to check for a viral or bacterial infection. Laboratory tests and biopsies may be performed. With edema, structural changes occur in the cornea, which can only be seen during biomicroscopy.
Biomicroscopy of the eye using a slit lamp reveals the following signs of corneal edema:
- microcysts on the epithelium;
- folding of the shell;
- increase in thickness;
- cloudiness;
- vertical lines in the stroma.
Signs of chronic corneal edema:
- vascularization;
- minor hemorrhages;
- swelling of the epithelium and stroma;
- strong increase in thickness;
- shell opacity.
Ultrasound scanning can detect intraocular edema. The Schirmer test makes it possible to determine the amount of tears produced.
Principles of treatment of corneal edema
Edema is treated by eliminating the cause. If there is a bacterial or viral infection, antibacterial and antiviral drugs must be used. Hard lenses are replaced with breathable ones. They also reduce the time they are worn to give the eyes a rest.
If swelling causes dry eye syndrome, artificial tears are prescribed (Oftagel, Vidisik, Systane-ultra). Severe cases of corneal edema require the use of hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Dexamethasone, Tobradex).
Choice of therapy for corneal edema
- Infectious lesions require the use of antibacterial drugs, additionally antiviral and antifungal drugs. In case of a calm course, ointments and eye drops are prescribed, and severe lesions are also treated with tablets and injections. During the treatment period, you should avoid using cosmetics and carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Allergic lesions are treated with antihistamines.
- Specifically, corneal edema requires the prescription of anti-inflammatory non-hormonal drugs. I stop the pronounced process with glucocorticoids (short course). It is better not to use contact lenses during treatment.
- For swelling of the conjunctiva, I prescribe anti-inflammatory and vasoconstrictor drops.
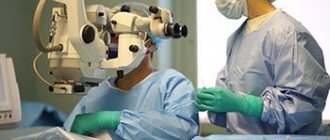
- If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment can be resorted to. If the cornea is damaged, it is transplanted or densified with ultraviolet light.
Incorrect use of lenses
The most common cause of corneal edema is improper use of contact lenses. Incorrect selection, prolonged wear, sleeping in lenses and using old ones that have expired - all this can cause swelling.
Eliminating these causes is simple; all you need to do is change the lenses, choose the right model that allows oxygen to pass through well, remove the lenses at night and when your eyes are tired, and additionally use moisturizing drops. It is important to care for your lenses and use special aseptic compounds to clean them.
An ophthalmologist may prescribe medications to speed up corneal recovery. Do not use contact lenses until swelling is eliminated. Exposure to a foreign body can aggravate the condition and injure the eye.
If the measures taken do not have the desired effect, and the swelling recurs, you must stop wearing contact lenses. Swelling caused by lenses should be treated by a qualified physician as there may be hidden risk factors. For swelling that is complicated by vascularization, on the contrary, it is recommended to wear hard lenses. Only an ophthalmologist can select and prescribe them.
Infection and allergy
For infectious corneal edema, diagnosis is aimed at identifying pathogens, and treatment at combating them. The patient is prescribed antimicrobial and antiviral drugs, usually drops with antibiotics (Levomycetin, Tobrex, Floxal, Tsiprolet). Additionally, eye ointments and tablets are prescribed.
If the cause of swelling is an allergic reaction, you need to visit an ophthalmologist and allergist. Contact with the allergen should be avoided and antihistamines should be used. Almost anything can be an allergen, so you need to conduct a test to identify the irritant in a specific patient.
With allergic edema, other symptoms usually also occur (itching, sneezing, runny nose, difficulty breathing). A comprehensive examination will reveal allergies in cases where swelling is the only symptom and there is constant contact with the allergen.
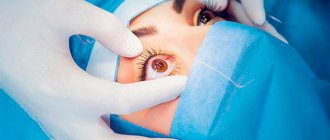
It is noteworthy that after surgical intervention in the eyeball, swelling is observed in almost all cases. If it does not disappear within 1-2 weeks, you should consult a doctor. Prolonged swelling after surgery, as a rule, does not disappear on its own. To eliminate swelling after surgery, drops are prescribed that accelerate tissue regeneration (Solcoseryl, Adgelon, Erisod, Emoxipin).
Eye after cataract surgery is red Rehabilitation after surgery VISION RESTORATION
There are the most common complications that occur in almost all patients.
In this case, treatment may be completely absent or incorrect. Some of them are fixable, others cannot be eliminated. Therefore, it is necessary to find a competent specialist who will prescribe the right treatment that completely restores vision function. To treat cataracts, medications and surgery are used. In both cases, the patient's condition may become more complicated.
Hemorrhage
Eye surgery is classified as microsurgery. It is carried out using magnifying devices that allow you to closely examine the internal structures of the eyes. If the doctor incorrectly installed the intraocular lens, applied excessive pressure to any element of the eye, or made an incorrect movement, hemorrhage may occur.
In some cases, it does not form immediately, but after the operation is completed. This is the most dangerous option, since the entire internal cavity of the eye can fill with blood, this will lead to irreparable phenomena for the eyes, which will cause blindness.
In some cases, minor hemorrhage occurs, which resolves on its own. These are minor complications that do not require correction.
Vision can be restored without surgery
Non-surgical eye treatment in 1 month...
>
Infectious and inflammatory diseases
The internal structure of the eyes is an aseptic environment. When the eyeball is opened, pathogenic microorganisms enter it. These include bacteria, viruses, and fungi. If their number is insignificant, antiseptic agents will completely remove these microorganisms. Otherwise, infection of the internal structures of the eyes develops, and pus forms.
Infection often develops on the superficial structures of the eyes; pathogenic microorganisms enter the wound. This forms an infectious-inflammatory disease that spreads over the entire surface. To prevent the condition, the doctor prophylactically prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of drops to all patients.
Corneal edema
To penetrate the lens area, the doctor must cut the cornea. After the procedure is completed, swelling and inflammation will form. If the patient's condition is stable, medications, ointments, and solutions are prescribed. In case of extensive inflammatory processes, keratoplasty is indicated. This is a procedure to completely replace the cornea.
Postoperative astigmatism
For surgery, the eyeball must be cut. This changes its shape. There are often cases when it is not restored to its previous size. Astigmatism is formed, that is, the wrong shape of the eyes.
The patient does not clearly see surrounding objects, their shape and size changes. To correct the condition, special glasses and lenses are indicated.
Increased intraocular pressure
This condition is called postoperative glaucoma. Secreted fluid begins to accumulate in the chambers of the eyes, which expands them. Gradually they increase in size, squeezing the surrounding structures. This condition can lead to retinal detachment or degeneration. The optic nerve is also affected, losing its signal transmission function.
Secondary cataract
There is a pathology of the lens, for example, nuclear cataract, when it is necessary to remove not the entire element, but only part of it. In this case, the doctor needs to be very careful not to leave pieces of clouded tissue.
If this happens, a secondary cataract forms. This condition is less amenable to correction, and most surgical treatments are not suitable. The patient's visual function begins to decline again, and blindness may occur.
Increased eye dryness
In the postoperative period, tear production often decreases. The surface of the mucous membrane becomes dry. This forms microtraumas and cracks in the cornea. The condition goes away over time. To maintain eye moisture, use drops (Defislez, Slezin).
Formation of floaters, dots before the eyes
If the vitreous body is damaged or compressed during surgery, non-existent elements form in front of the eyes. These include dots, flies, lines, stripes, lightning. They can be bright yellow or black. If this condition occurs several times and goes away, there is no need to worry.
Corrections require the constant formation of these elements.
Prices for cataract removal:
| № | Service name | Price in rubles | Make an appointment |
| 2009003 | Optical-reconstructive intervention in the anterior segment of the eye for cataracts and post-traumatic and post-traumatic changes | 90000 | Sign up |
| 2008047 | Phacoemulsification for complicated, mature and overmature cataracts, category 3 of complexity | 86880 | Sign up |
| 2008046 | Phacoemulsification for complicated, mature and overmature cataracts, category 2 of complexity | 79650 | Sign up |
| 2008045 | Phacoemulsification for complicated, mature and overmature cataracts, category 1 of complexity | 77400 | Sign up |
| 2008044 | Phacoemulsification for initial and immature cataracts, category 3 of complexity | 71220 | Sign up |
| 2008043 | Phacoemulsification for initial and immature cataracts, category 2 of complexity | 67080 | Sign up |
| 2014001 | Penetrating keratoplasty + phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation (complexity category 2) | 96000 | Sign up |
| 2014003 | Penetrating keratoplasty + reconstruction of the anterior chamber with iris plastic surgery, phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation | 120000 | Sign up |
| 2014005 | Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty + phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation (complexity category 2) | 108000 | Sign up |
| 2014007 | Posterior layered endothelial keratoplasty + phacoemulsification or cataract extraction with IOL implantation | 84000 | Sign up |
| 2008041 | Discision of secondary cataract | 9000 | Sign up |
| 2008053 | A set of consumables and an imported intraocular lens for phacoemulsification of cataracts with cataract removal. | 42000 | Sign up |
| 2008005 | Ultrasound phacoemulsification with IOL implantation for initial and immature age-related cataracts | 79650 | Sign up |
| 2008007 | Ultrasound phacoemulsification with IOL implantation for complicated, mature and overmature age-related cataracts | 84440 | Sign up |
| 2008012 | Cataract removal without phacoemulsification + IOL | 40200 | Sign up |
| 2008021 | Cataract extraction with implantation of an artificial lens of the first category of complexity | 40500 | Sign up |
| 2008022 | Cataract extraction with implantation of an artificial lens of the second category of complexity | 45600 | Sign up |
| 2008023 | Cataract extraction with implantation of an artificial lens of the third category of complexity | 50400 | Sign up |
Making an appointment Today: 8 registered
Rare complications
There are complications that occur rarely in patients. Some of them can be corrected, others cannot be treated. In extreme cases, repeat surgery may be necessary to correct the person's vision function.
Lens rupture
The lens is a capsule containing a clear liquid. Particles spread throughout the internal structure of the eyes can damage these elements. For example, the vitreous body.
This provokes an increase in intraocular pressure, the walls of the eye chambers begin to expand, gradually squeezing the retina and optic nerve.
Their function decreases, and retinal detachment or optic nerve atrophy may occur.
Skolkovo talked about the possibility of complete restoration of vision
A new drug for the treatment of vision was presented at the innovation center. The medicine is not commercial and will not be advertised...
Read completely
Intraocular lens displacement
When cataract surgery is performed, an artificial model is implanted in place of the lens. It is called an intraocular lens. Around the lens are ligaments into which the lens must fit.
If the installation was performed incorrectly, it gradually shifts towards the retina. This leads to swelling, inflammation, and mechanical damage to the vitreous and retina.
Neurological disorders
The tissues of the eyes are not only well supplied with blood, but also innervated. If the doctor damages any nerve during the procedure, neurological disorders will occur. This may be twitching of the eye, the formation of nystagmus (involuntary eye movements). You need to contact a neurologist for diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of corneal edema
Swelling of the cornea of the eye does not go unnoticed. The first sign of edema is a change in visual acuity. The patient complains that he sees poorly. Captivity appears before your eyes. Using contact lenses causes discomfort. Even with the naked eye, folds and stripes can be seen on the cornea. With prolonged swelling, a network of blood vessels appears on the cornea.
Symptoms of corneal edema also include:
- image distortion,
- photophobia,
- pain in the eyes (burning and stinging),
- sensation of a foreign body (usually sand),
- redness of the eyeball.
Various eye diseases lead to swelling of the cornea of the eyeball. The symptoms are similar, regardless of the cause. In rare cases, the disease is asymptomatic.
How to minimize the risk of complications
To reduce postoperative complications, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- staying at rest in a dark room so that negative environmental factors do not affect the eyeballs;
- use of sunglasses outdoors so that bright sun rays do not negatively affect the retina of the eyes in the postoperative period;
- postoperative antibiotic therapy, which eliminates the risk of developing infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- eating food rich in vitamins, nutrients, microelements necessary for normal metabolism and regeneration of damaged surfaces;
- lack of exercise in the first month after surgery, then exercises are prescribed on the recommendation of a doctor;
- the use of moisturizing drops that eliminate the risk of drying out the cornea.
Cataract removal is an operation that damages a small amount of tissue. Despite this, the patient may develop many complications, especially if he does not adhere to the doctor's recommendations. If a complication appears, you need to immediately contact a specialist so as not to lose vision function.
Causes
The causes of corneal edema may be the following:
- Development of infectious inflammation associated with various microorganisms;
- The development of allergic inflammation caused by contact of allergens in the eye (cosmetics, skin care products, dust, pollen, animal hair, etc.);
- Injuries in which an aseptic component of the inflammatory reaction is present;
- Incorrectly selected contact lenses;
- Glaucoma;
- Surgical interventions on the eyes.
Treatment
Therapy depends entirely on the cause that provoked the pathology. Diagnosis is carried out by an ophthalmologist. To exclude infections, laboratory tests are prescribed.
The degree of corneal edema is assessed using a technique called in medicine corneal pachymetry (measuring thickness using ultrasound or optics).
If necessary, the ophthalmologist can prescribe a Schirmer test, which will determine the level of tear fluid produced by the eye.
Medically
Treatment tactics with medications are selected depending on the cause that provoked corneal edema.
Reason: contact lenses
If the source of the problem is contact lenses, the first thing to do is stop using them until the symptoms disappear completely.
Bacterial infection often results from improper lens wear. Corneal edema is provoked by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and amoebic infection.
Treatment in this case consists of local use of antibacterial agents such as Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin. The antibiotics contained in these drugs will quickly and effectively help the patient.
Cause – complication after cataract surgery
Corneal edema after cataract surgery sometimes occurs the next day after the phacoemulsification procedure. The cause of swelling in this case is the large amount of fluid that passes through the eye during crushing and washing out the replaced lens of the eye. The denser the cataract and the poorer the vision, the more likely it is to develop postoperative corneal edema.
As a rule, corneal edema after surgery does not require additional treatment. Disappears on its own within 1-2 weeks.
In rare cases, swelling is relieved with injections and procedures, which, if necessary, are prescribed by the attending physician.
Source: https://PrimaMed-kzn.ru/bolezni/pokrasnenie-glaza-posle-operacii-katarakty.html
Surgical treatment of corneal edema
It is very important to monitor the patient's condition after cataract surgery, as the risk of endothelial dystrophy, which is characterized by corneal edema, increases. This complication is rare, but has dangerous consequences. The patient is prescribed long-term antiviral drugs or undergoes a corneal transplant. Keratoplasty restores the transparency of the cornea, stops its pathologies and ensures the functionality of the eye.
Based on the size of the area to be replaced, keratoplasty can be total, local, and subtotal, and based on the layers being replaced, there are end-to-end, anterior, and posterior layer-by-layer keratoplasty. During the operation, the doctor creates a flap using special instruments or a femtosecond laser. Donor material is implanted into the vacant space and sutured to the periphery of the cornea. After surgery, the patient must wear a bandage or protective lenses for some time.
Keratoplasty is performed in one procedure, most often under local anesthesia. A few hours after the operation, the patient is sent home. Recovery after a cornea transplant takes a year. The stitches are removed after 6-12 months. After keratoplasty, you should avoid heavy loads and aggressive effects on the eyes.
Modern medicine also offers an innovative method of cross-linking. The procedure promotes the fusion of collagen fibers, which are the basis of the cornea, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The shell becomes dense and withstands loads. The operation eliminates complications and swelling, as well as reduces astigmatism and improves vision.
Inflammation of the cornea after cataract surgery - elimination of complications
The modern method of cataract removal by phacoemulsification is used all over the world and is as safe and reliable as possible. The risks of postoperative complications are minimized, but still present.
Inflammation of the cornea after cataract surgery is an early postoperative complication, which with timely treatment is quickly eliminated.
It is for this reason that it is important not to skip follow-up examinations after surgery.
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation after cataract surgery may occur due to excessive exposure to ultrasound during phacoemulsification. Prolonged exposure to ultrasonic waves on a clouded lens is required in cases of removal of mature cataracts.
In this case, the density of the opacity is high, so the lens is difficult to crush. The duration of exposure to ultrasound increases, which in turn negatively affects the entire eye as a whole.
Viscoelastic is used to protect nearby elements of the visual organ, but in rare cases this is not enough.
Inflammation can also occur as a result of IOL implantation through a large incision. As the incision increases, the risks of inflammation increase significantly.
To eliminate this risk, soft intraocular lenses are used, which are inserted into the anterior chamber through a minimal incision in a folded form. The high qualifications and experience of the surgeon performing the operation guarantees accurate and careful insertion of the IOL.
When forming a microincision with a femtosecond laser, a more accurate incision profile is achieved, as well as faster healing and a reduction in corneal swelling after surgery.
In very rare cases, during the first 24 hours after surgery, non-infectious inflammation may occur, a sign of which is swelling of the cornea and a sharp deterioration in vision.
The cause of this reaction may be a toxic reaction to the irrigant solution used during phacoemulsification.
A reaction may also occur to remnants of viscoelastic that were not completely removed after the procedure.
What other complications could there be?
Early complications also include hemorrhages after cataract removal, which may be a consequence of the traumatic impact of the fixing elements of the intraocular lens design.
Such damage can occur as a result of traumatic impact on the eye, pressure, manual friction and careless behavior in the first days after surgery. As a rule, this complication is eliminated with the help of drops that help resolve the hemorrhage.
It is also worth noting that the monoblock design of the intraocular lens made of soft material eliminates this risk of injury to the eye.
Increased intraocular pressure can be caused by problems with the drainage system of the eye, which occurs as a result of insufficiently thorough washing of the viscoelastic. To eliminate the complication, drug therapy is prescribed.
Displacement of the artificial lens can occur in the event of traumatic impact on the eye in the early postoperative period. Also, in extremely rare cases, the size of the intraocular lens may be incorrectly selected, which, because of this, is not sufficiently securely fixed inside the capsule.
Preventing and eliminating complications
In the postoperative period, you need to follow simple rules:
- take all medications prescribed by your doctor;
- monitor your health and, if you notice any unpleasant symptoms, contact an ophthalmologist;
- limit physical activity;
- exclude alcohol consumption to eliminate the risk of injury and increased intraocular pressure;
- do not rub your eyes and avoid getting water and soap into them during hygiene procedures;
- give up cosmetics;
- limit visual stress, monitoring eye fatigue and providing them with timely rest;
- refuse to visit the pool, sauna and open water;
- Use sunglasses when spending long periods of time outdoors.
To prevent the development of inflammation in the postoperative period, artificial tear preparations are mandatory.
Medicines are also used to stimulate regeneration processes and reduce corneal swelling in the first days after surgery.
Visual rehabilitation in the case of regular use of medications prescribed by an ophthalmologist proceeds quickly and without complications. It is also important during this period to follow a schedule of follow-up examinations and adhere to restrictions on physical activity.
Source: https://mgkl.ru/patient/stati/vospalenie-rogoviczyi-posle-operaczii-kataraktyi
Traditional medicine recipes for corneal edema
Self-medication for corneal edema can be very harmful and require serious and long-term therapy. Traditional medicine can only be used as an additional symptomatic effect, but only with the permission of the attending physician.
Proven methods for treating inflammation in the eye:
- Honey. Add a little honey to boiled water (1:2). Place 2 drops into eyes twice a day.
- Onions and horseradish. Grind the ingredients and dilute with water (1:1). Leave for 15 minutes until the bitterness goes away. Moisten a cotton pad and apply to your eyes.
- Mulberry. For swelling and pain in the eyes, a decoction of mulberry leaves and bark helps: boil a large spoonful of the ingredients (a glass of water) in a water bath for 15 minutes. Instill a few drops 3-5 times a day. Effective for dry eyes.
- Potato. Swelling can be eliminated with raw potatoes. You need to grate one tuber, put the pulp in gauze and put it on your eyes for 20 minutes.
- Onion. You can make an eye wash from onions. You need to boil a medium onion and add a couple of drops of boric acid to the broth. Use twice daily.
- Herbal mixture for severe pain. Mix flaxseed, cornflower and elderberry (a small spoon each), pour boiling water (2 cups), leave for 8 hours and strain. You should rinse your eyes several times a day.
- Prevention of corneal edema involves careful facial care and proper personal hygiene. It is necessary to use only high-quality and hypoallergenic cosmetics, as well as hygiene products. Contact lenses must be selected correctly and purchased at a specialized salon. People over 45 years of age should monitor intraocular pressure and protect their eyes from ultraviolet radiation. It is important to consult a doctor promptly if visual discomfort occurs.
Sources used:
- Modern pharmacotherapy of ulcerative lesions of the cornea / Olga Krivosheina and Igor Zapuskalov. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2013.
- New technologies in the treatment of corneal diseases / ed. H.P. Takhchidi. - Moscow: Mir, 2004.
- Cornea. Atlas / Jay Crutchmer, David Paley. - M.: Logosphere, 2007.
- National Eye Institute
Definition of disease
The cornea of the eye is the main component of the refractive system. This convex-concave lens, which is no more than one millimeter thick, has 6 transparent layers.
The cornea not only refracts light, but also protects the eyes from negative external influences, for example, from dust particles floating in the air. Having high sensitivity, the cornea saves the eye from clogging by closing the eyelashes, as well as washing away particles with tear fluid. As the lesion develops, its properties change, light transmission decreases, photophobia develops, and vision decreases significantly, especially in the morning and evening hours.
As a result of the pathological process, edema in the cornea can contribute to the destruction of the substance of the corneal layer, and then to its necrosis.