All the variety of forms of eye cataracts can be divided into two main groups - congenital cataracts and acquired cataracts.
Congenital cataracts account for more than half of all congenital visual defects. Cataracts can develop in one eye or in both eyes at the same time, and can also be combined with another pathology. With congenital cataracts, opacities in the lens, as a rule, are limited in area and stationary, that is, they do not tend to progress.
Unlike congenital cataracts, acquired cataracts have a progressive course. Acquired cataract is the most common among all types of lens opacities.
The role of the lens in the visual system
The lens of the human eye is a transparent natural lens that acts as part of the optical apparatus. It is located behind the pupil and iris. It is noteworthy that the lens does not contain blood vessels or nerves, but is “nourished” through the intraocular fluid in which it is immersed.
Without the lens, light impulses cannot be transmitted and light cannot be refracted. This element of the eye provides accommodation (adjustment). It is the lens that divides the eyeball into anterior and posterior sections. It protects the vitreous body from microbes when inflammation of the anterior chamber of the eye develops.
The lens is a very sensitive element of the eyeball. Under sudden influence and in poor conditions, dangerous processes begin in it. Even with a mild injury, the lens may begin to become cloudy and stop performing its functions.
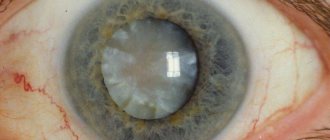
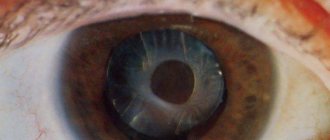
Cloudiness of the lens is called a cataract. This condition is characterized by a gradual decrease in vision, difficulty determining the boundaries of objects, and the inability to distinguish objects in poor lighting. Patients with cataracts note that they have to look at the world as if through foggy glass.
Postoperative period
After cataract surgery, after a few days in hospital, the patient is discharged from the hospital. The recovery period takes 1.5-2 months, during which you will need:
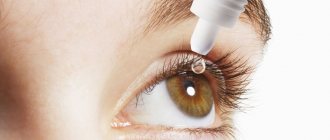
- instill special medications into the eyes,
- wear a bandage that protects the eye from dirt, water, smoke,
- be constantly monitored by an ophthalmologist.
Recommendations for patients to speed up the healing process of the eye and prevent displacement of the artificial lens:
- Do not sleep on the side of the operated eye;
- Do not tilt your head down;
- Do not lift weights exceeding 5 kg;
- Do not drive;
- Do not rub your eye or put pressure on it;
- Wear sunglasses;
- Avoid getting soap and water into your eyes;
- When washing your hair, tilt your head back, not forward.
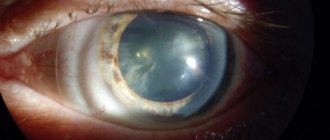
Types of traumatic cataracts and their symptoms
Traumatic cataracts can be partial or complete (local and total). There are also semi-resolved cataracts and dense ones.
Types of cataracts according to the position of the lens:
- membranous (normal position);
- subluxation (partial shift);
- luxation (complete shift to the fundus).
Types of cataracts by type of injury:
- contusion (blunt eye injuries);
- toric (damage from chemicals);
- wound (penetrating injuries);
- radiation (damage from ionizing radiation).
Symptoms of traumatic cataracts will depend on the location of the opacities. If there is a posterior subcapsular cataract, symptoms are usually severe and extensive. Cortical and sclerotic opacities add less discomfort to the patient.
The most common type of cataract is contusion cataract. Damage can occur with direct concussion, that is, with a blow with a blunt object, and indirect (to the head). The cause of toxic cataracts is all kinds of burns of the eyeballs with aggressive liquids. In addition, clouding can develop in case of severe poisoning with ergot, nitro dyes, trinitrotoluene and other substances.
Radiation opacities are predominantly ring-shaped. With radiation cataracts, colored spots are visible on the gray background of the lens. This feature is used for differential diagnosis.
Modern medicine offers only surgical methods for treating traumatic cataracts. Such eye injuries, which can cause clouding, often end badly because they damage the structures of the posterior segment of the eye. Patients often develop retinal detachment, macular fibrosis, and optic neuropathy. Sometimes afferent pupillary failure and iridodialysis are also detected.
Cataract
Syphilis
Diabetes
426 06 November
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Cataract: causes, classification, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Description
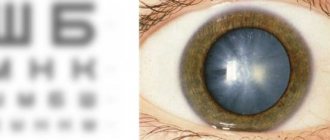
Cataract is a disease characterized by clouding of the lens of the eye, which leads to partial or complete loss of vision. According to the World Health Organization, about 17 million people over the age of 60 suffer from cataracts. In developed countries, a 40% incidence is recorded. Ophthalmologists around the world, having examined and observed over time a huge number of patients with cataracts, came to the conclusion that about 70% of clinical cases have an average progressive rate of development of the disease. This means that within approximately 6–10 years, cataracts will require surgery to replace the clouded lens.
A healthy lens has a transparent structure and acts as a natural lens that transmits light rays, focusing them on the retina.
As soon as the lens loses its transparency, its transmission capacity is weakened and a person’s vision deteriorates. In the later stages of the disease, clouding of the lens reaches such proportions that it becomes completely white and practically impenetrable to light stimuli, and the person goes blind.
Causes of cataracts
There are many reasons for the development of cataracts.
- Infections: viral (more typical for congenital cataracts, when infection occurs in utero from the mother), non-viral - syphilis (caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum), toxoplasmosis (caused by the parasite Toxoplasma).
- Rhesus conflict between mother and child. In some cases, if the child's father has Rh-positive blood and the mother has Rh-negative blood, the mother may produce antibodies (immune response proteins) against the child's cells, which is harmful to his health.
- Age-related degeneration of the organ of vision.
- Intraocular inflammatory processes.
- Eye injuries.
- Metabolic disorders - diabetes mellitus, vitamin deficiency, calcium deficiency, galactosemia. Galactosemia is a hereditary disease, an enzyme pathology, in which complete intolerance to formula or breast milk develops, delayed psychomotor development, liver damage, cataracts, water-electrolyte and protein disorders.
- Toxic – exposure to ionizing radiation, taking certain medications.
- Already existing eye diseases – high myopia (myopia), glaucoma.
- Hereditary predisposition.
In addition, there are risk factors that can become a trigger for the development of cataracts.
- Diseases of the internal organs, in which the vascular wall and microcirculation in the organs are affected.
- Bad habits, such as smoking, which impair microcirculation and the supply of tissues (including the eyes) with nutrients and oxygen.
- Chronic or past eye infections or injuries.
Classification of the disease
1. Congenital cataract.
2. Acquired cataract:
- senile (senile, age);
- arising against the background of existing eye diseases (myopia, infections, uveitis, iridocyclitis - inflammatory diseases of the choroid);
- traumatic;
- “cataract of systemic diseases” – develops with existing chronic diseases;
- medicinal – develops as a result of taking certain medications (corticosteroids, antiarrhythmics);
2.1.
radiation – when exposed to radiation, infrared radiation. By stages of development and severity of symptoms
The following types of cataracts are distinguished separately:
- Initial cataract.
- Immature cataract.
- Mature cataract.
- Overripe cataract.
Depending on the location of
the area of lens opacification and depending on its shape, several types of cataracts are distinguished: anterior and posterior polar, cortical (the vast majority of clinical cases of senile cataracts, more than 90%), total, nuclear, fusiform, layered, subcapsular, etc. .
Symptoms of cataracts
The main symptom of cataracts at all stages, regardless of the location of the lens opacification, is a progressive decrease in visual acuity.
In the initial stages, a feeling of a veil before the eyes and the flickering of “black flies” may be disturbing (in this case, the “front sights” can move in the direction of gaze, or can be fixed in one place). As the disease progresses, double vision, dizziness, rapid visual and general fatigue, and discomfort in the eyes may occur. A person begins to make more and more efforts to focus his gaze, especially while driving or driving.
Then the patient stops recognizing faces and reading, as the ability to distinguish small details and font is lost; subsequently, in the absence of treatment, only the ability to differentiate between light and dark is retained.
It is much more difficult to identify the symptoms of congenital cataracts, because a newborn child cannot complain of poor vision. When examining a child, the doctor reveals clouding of the pupil (complete or partial). Normally, a child is able to focus his gaze on the faces of his parents or large objects from two months. Young patients with cataracts do not demonstrate this skill, which gives reason to suspect the presence of this pathology. Another alarming sign is when a two-month-old child does not follow moving objects or always turns to the toy or parents with the same side (the same eye in case of a unilateral lesion). If the mother of the child in the first trimester, when the embryonic formation of the fetal neural tube, from which the visual organs will later develop, has suffered an infectious disease or gestational diabetes mellitus was detected during pregnancy, the likelihood of developing cataracts in the child increases. More often, the rubella virus, affecting pregnant women, causes fetal defects that are incompatible with life, but in some cases it is also possible to give birth to live children with cataracts.
Diagnosis of cataracts
Mandatory for this pathology is an examination by an ophthalmologist, measurement of visual acuity, examination in transmitted light (allows you to identify the localization of the cloudiness and its degree, while the doctor monitors whether the passage of the light beam through the eye changes and asks the patient to periodically change the direction of gaze), tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure) and biomicroscopy (used in the diagnosis of diseases of traumatic, inflammatory origin and neoplasms, detects lens opacities of various sizes).
If the development of Rh conflict between mother and fetus is suspected (when the father of the child has Rh-positive blood and the mother has Rh-negative blood), an ultrasound scan of the fetus is performed according to gestational age and, if necessary, the woman is given anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin.
How does traumatic cataract develop?
With a closed eye injury, cataracts develop in 11% of cases. During injury, the eyeball is subject to impact and counter-impact forces. A strike is a direct force, and a counterstrike is a reflected force. It is the counterblow that damages the lens more strongly. When subjected to mechanical action, the eyeball shortens, the lens capsule ruptures, and the ligaments of zonules are torn off. And everything happens at the same time. The more precise mechanism of damage to the lens capsule during trauma is not clear.
The capsule is able to quickly regenerate (properties of subcapsular epithelium), so damage up to 2 mm is quickly restored. If damage exceeds 3 mm, opacification occurs: rupture of the capsule leads to intraocular fluid entering the lens.
Capsular injuries may suddenly open days or months after the injury. In this case, secondary glaucoma, severe inflammation and cataracts often develop. And although most often traumatic cataracts are not associated with damage to the capsule, this factor cannot be excluded.
In most cases, traumatic cataract occurs due to the fact that at the time of contusion, subcapsular opacities are formed in the cortical layers of the lens. Such opacities have the shape of petals and spokes, diverging radially.
Without treatment, traumatic cataracts can progress to the point that fundus examination becomes difficult. As cataracts mature, vision decreases, intraocular pressure increases, and inflammation recurs.
Diagnosis of cataracts and preoperative examination
You need to schedule a visit to the doctor if you notice deterioration in vision and loss of clarity. Only comprehensive diagnostics using special equipment can identify the causes of the violation.
Examination for cataracts includes the following measures:
- visual acuity testing (visometry);
- determination of the degree of refraction of the eyes, measurement of the curvature and refractive power of the cornea (computer keratorefractometry);
- study of the anterior segment of the eye, assessment of the condition of the lens and iris (biomicroscopy);
- checking the angle of the anterior chamber (gonioscopy);
- determination of visual fields (perimetry);
- checking the level of intraocular pressure (tonometry);
- assessment of the condition of the optic nerve and retina (ophthalmoscopy);
- measurement of the thickness of the cornea and lens, the depth of the anterior chamber, assessment of the condition of the vitreous body and retina (ultrasound scanning);
- comprehensive study of the anterior segment, detailed examination of the cornea (keratotopography).
Since cataracts are often treated with the installation of intraocular lenses, during the diagnostic process it is necessary to study the condition of the cornea in detail. The radius of curvature of this shell allows us to calculate the necessary lens parameters. If a traumatic cataract is suspected, it is important to perform a B-mode ultrasound scan. This allows you to find breaks and timely determine the presence of retinal or choroidal detachment.
Before the operation, you should undergo a thorough examination, if necessary, visit other specialists and make sure there are no contraindications. The purpose of ophthalmological diagnosis is to detect or exclude phacodonesis and vitreous hernia, and examine the posterior capsule. Before surgery, it is important to check the condition of the ligaments of Zinn.
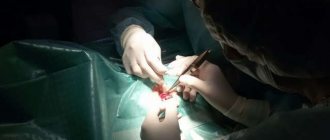
Surgical treatment of traumatic cataracts
The timing of opacification removal will depend on the severity of the inflammatory process, the need to restore vision (this applies to children with an increased risk of amblyopia), future operations and the general condition of the patient. The treatment method and timing should be determined by the doctor, taking into account the vision prognosis and the presence of concomitant pathologies. The surgical plan will be based on the severity and location of the cataract.
The most common method of cataract removal is phacoemulsification, but surgery is contraindicated for brown cataracts. The lens is removed using ultrasound through a small puncture. The entire procedure takes up to 20 minutes. The doctor breaks up the cloudy masses and sucks them out of the capsule in order to insert a special lens into the vacant space. Modern implants are no different in functionality from a natural lens. The rehabilitation period does not take much time, and postoperative recommendations do not complicate the patient’s life. In the vast majority of cases, surgery provides a complete cure for cataracts.
Sometimes they resort to extracapsular extraction. This method is used less and less, although it remains acceptable if the ligaments of Zinn are weak and there is no vitreous hernia. Technologies that make it possible to implant intracapsular rings and capsular hooks are used when removing traumatic cataracts using an anterior approach. In the presence of severe phacodonesis, lens subluxation and capsule damage, another method of removing the opacities should be considered.
Primary extraction of traumatic cataracts is advantageous in that it eliminates the cause of inflammation, normalizes the level of intraocular pressure and carries out visual rehabilitation. Disadvantages of the procedure include a long rehabilitation period and an increased risk of inflammation. It may also be that the cataract did not affect your visual function and surgery will not help restore it.
Implantation of an intraocular lens
Implantation of an intraocular lens can be carried out after cataract removal by any method (provided that there is no inflammation and the risk of infection is low). The lens can be installed in the capsular bag, anterior chamber, ciliary groove, and fixed near the sclera or iris.
In children, clouding of the lens greatly increases the chances of developing amblyopia (lazy eye syndrome). Since rapid opacification of the posterior capsule often occurs after extraction, capsulotomy and vitrectomy (anterior) must be performed along with it. When operating on a child, the doctor must minimize the impact on the developing eye.
Opacities do not always progress, so the doctor must determine the advisability of surgery. If other structures of the eye have not been damaged, unnecessary intervention can only cause harm. When cataracts do not impair vision or provoke inflammation, infection or glaucoma, dynamic monitoring of the condition of the lens is recommended.
Traumatic cataracts are not always treated surgically. In cases where the clouding is not localized in the center of the lens and is not very dense, optical correction can be done. This is due to the fact that such cataracts do not interfere with normal vision.
Taking tests
A few weeks before the procedure, it is necessary to identify the condition of the internal organs and systems. For this purpose, instrumental and laboratory tests are performed:
- General blood analysis. It indicates the state of the circulatory system, the presence of hypoxia (oxygen starvation). An increased number of ESR and leukocytes means that the inflammatory process has spread in the body. If the data in the analysis is overestimated or underestimated, this is a reason for additional testing of the body and treatment before surgery.
- General urine analysis. The condition of the urinary system and kidneys is revealed. For some diseases, general anesthesia is not permitted because it affects the kidneys.
- Blood chemistry. Indicates an enzymatic composition. For example, the enzymes ALT and AST are determined, which indicate the condition of the liver tissue.
- Rh factor, blood group. The analysis is necessary if an emergency blood transfusion is needed.
- Test for hepatitis B and C, HIV infection. If an exacerbation of hepatitis is detected, treatment is carried out, only then surgery is prescribed. The doctor should be alerted to the presence of these infections in order to be especially careful. It is important to sterilize all instruments after the patient to prevent the spread of hepatitis or HIV.
- Fluorography. The condition of the pulmonary system is determined; if an inflammatory disease is detected, the operation is postponed. During its implementation, the patient's condition will worsen.
- Electrocardiography. Since the operation uses anesthesia, it may be contraindicated for people with serious cardiovascular disorders.
Based on laboratory and instrumental research methods, the doctor judges the patient’s health status. There are contraindications for which the procedure is not performed.
Traditional methods of treating cataracts
It must be remembered that no remedy can completely cure lens opacity. Traditional medicine in the treatment of cataracts can only be considered as an additional therapy that will stop the progression of the disease.
So, for cataracts, it is recommended to drink a drink daily with the juice of carrots, celery and parsley, where the carrot part is 40%. Adding blueberries and mulberries to your diet helps improve the functioning of the visual system.
There are many recipes with honey. You can prepare drops based on it: dilute liquid honey with an antiseptic (20% sodium sulfate solution). This treatment is effective after 3-4 weeks of three daily instillations.
Before using any products, you should consult a doctor, but most often ophthalmologists do not recommend self-medication for cataracts due to its absolute ineffectiveness. Cloudiness can only be removed from the eye through surgery; it is not for nothing that there is no effective conservative treatment for cataracts.
Drops for cataracts
The modern pharmaceutical market offers hundreds of drugs for a variety of pathologies of the visual system, and cataracts are no exception. Typically, doctors prescribe drops only to relieve symptoms, since there is no sufficiently effective remedy on the market to resolve opacities.
For cataracts, Vitafacol, Quinax, Vitaiodurol, Taufon and Oftan-catachrome are often prescribed. However, replacement therapy (drugs with substances, the deficiency of which presumably causes cataracts) is ineffective for the traumatic nature of opacification. The eye may be completely healthy before the injury and not need additional “nutrition.”
Notably, most cataract drugs are not independently tested. The manufacturer himself organizes an effectiveness study, the results of which are not always reliable. Therefore, the effectiveness of numerous drugs for cataracts has not been scientifically proven, and therefore their use may be inappropriate.
Separately, it is worth mentioning Quinax drops. Only this drug has shown real, albeit insignificant, effectiveness in the treatment of senile, diabetic and other forms of cataracts. This drug is unique in its kind: its active substances are able to activate enzymes in the intraocular fluid and enhance the process of resorption of lens proteins. To achieve results, you need to use drops for years, which is unacceptable if the disease progresses quickly.
Cataract drops can only be effective at the initial stage of the disease. Existing dense opacities can be completely cured only with surgery, so you should not postpone surgical treatment.
Prevention of cataracts
If in the case of age-related opacification it is almost impossible to avoid it, then it is possible to delay damage to the lens. The only measure to prevent traumatic cataracts is protection from damage.
To strengthen the visual system, you need to follow the norms and rules of a healthy lifestyle. Smoking and alcohol abuse are the main irritants of the whole body, so you need to give up bad habits.
You can increase the body's protective functions through physical exercise, weight control, and the prevention of nervous disorders. It cannot be said that these measures protect against cataracts, but failure to comply with them often contributes to the disease.
Special prevention of traumatic cataracts:
- protection of the visual system from ultraviolet and microwave radiation;
- adequate intake of drugs that increase tissue photosensitivity (steroids, antiallergic drugs, antidepressants, tranquilizers, contraceptives);
- dosed consumption of coffee and products containing it;
- glucose control and proper treatment of diabetes.
It must be remembered that eye drops do not help get rid of the disease, they only stop its progression. You can even say that a clouded lens can no longer be saved, only replaced with an intraocular lens.
Sources used:
- Eye diseases. Modern view of treatment and prevention / O.V. Stepanova. - M.: IG “Ves”, 2005.
- The most important things about eye diseases and vision restoration. - M.: Vector, 2013.
- 100% vision / Mitchell H. Friedlander, Steph Donev. - M.: World of Books, 2005.
- Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov
Preparing for surgery
To perform eye surgery, all patients should prepare:
- 1 week before the procedure, all medications that affect blood composition are discontinued. It is especially important to eliminate drugs that thicken or irritate it.
- 1 week before the procedure you should not drink alcoholic beverages. The same applies to time during the rehabilitation period.
- If the patient used contact lenses before the procedure, they are removed 1 week before treatment. Use only glasses to eliminate injuries to the mucous membrane.
- The last meal should be at least 8 hours before the procedure. Usually the operation is scheduled for the morning, since food and liquids should not be consumed before the operation.
- Before surgery, you can shower using germicidal soap. There should be no foreign particles, dirt or grease on your hair and face. They may get into your eyes.
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to remove hair if it reaches the eyes.
- On the day of surgery, a woman should not wear makeup. Any makeup carries an increased risk of bacterial infection.
- On the day of surgery, the patient is given a sterile suit to change into.
Following these rules will prevent bacterial infection and unwanted reactions for the body.