This phenomenon, such as burning when urinating , occurs in both men and women. Most often this happens due to urethritis, although there are other causes. One way or another, if you feel this way, you should consult a medical specialist so that he can accurately diagnose the disease and prescribe the correct treatment. In any case, you should not neglect the symptoms of burning.
The same urethritis may not have any pronounced symptoms at all, except for a slight burning sensation. The nonspecific type of this disease is caused by Escherichia coli, staphylococcus, and streptococcus. As for specific urethritis, it appears after pathogens enter the body.
Psycho-emotional factors
They cause a burning sensation during urination more often in women. And in men, this reason is an extremely rare case. Discomfort can be caused by depression and chronic neuroses.
Another reason may be trauma to the genital organs, allergic reactions to aggressive components in detergents. In women, allergies can be caused by the use of pads and tampons. The cause is neoplasms located near the organs of the genitourinary system. It is also worth noting that burning sensation in women occurs during the process of hormonal changes during menopause.
Finding out the exact cause of burning when urinating is possible only after contacting a urologist and conducting laboratory tests. After finding out the cause of the discomfort, it will be clear which treatment method is right for you.
Contact a specialist:
| Primary appointment with a urologist | 2000 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a urologist | 1500 rub. |
| Consultation with the chief physician or leading clinic specialist | 3500 rub. |
Go to Contacts Make an appointment
Burning in the urethra in men
severe burning in the urethra in men could be caused
In addition to non-infectious causes, severe burning in the urethra in men could be caused by:
- Cystitis,
- Prostatitis,
- Hormonal dysfunction,
- Urethritis (nonspecific or venereal)
This symptom most often occurs with specific infections (for example, chlamydia, trichomoniasis).
So, if the burning sensation does not disappear within 24 hours and/or is accompanied by any discharge, then we may be talking about sexually transmitted diseases.
In this case, it is necessary to consult a venereologist in our clinic as soon as possible.
You must remember that by not turning to a specialist, you risk not only your health, but also the health of loved ones and relatives who may become infected.
Burning in the urethra without discharge in men
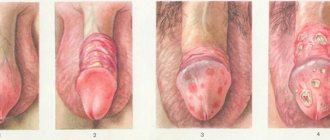
A burning sensation in the urethra with or without discharge, as well as a burning sensation in the urethra after urination in men, are signs of a disease such as urethritis.
Urethritis is an inflammatory disease that affects the mucous membrane of the urethra (urethra).
With insufficient treatment or without it at all, the process can develop into inflammation of the bladder (cystitis) or kidney inflammation - pyelonephritis.
Symptom - burning in the urethra is isolated in the following forms of urethritis:
- trichomonas, gonorrhea, mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, viral or fungal urethritis,
- nonspecific (caused by saprophytic staphylococci, Escherichia coli or Proteus),
- allergic, traumatic, radiation,
- acute or chronic urethritis,
- total urethritis.
If this symptom begins to appear after unprotected sexual intercourse (without the use of contraceptives), then it is advisable to consult a urologist or venereologist.
Since the cause is most likely gonorrhea or trichomoniasis.
In the presence of purulent discharge, we are most often talking about a bacterial process.
Viral urethritis and pathologies caused by protozoa often produce scanty mucous discharge.
With candidiasis, white mycelial threads are typically released in the morning or after urination or coitus.
Diagnosis of burning in the urethra in men caused by urethritis
If the doctor suspects urethritis, then after examination the patient will be offered a scraping of the urethral epithelium followed by a PCR test for typical or latent genital infections.
The venereologist will also prescribe a urine test (general or three-glass sample).
Depending on the results of laboratory diagnostics, treatment will be carried out or a conversation will be held about the prevention of STDs.
Treatment includes antimicrobials (antiviral or antifungal drugs) systemically or locally.
Local therapy is mandatory - urethral lavage or tampons.
A course of immunocorrection may also be recommended.
Treatment must be completed with repeated laboratory diagnostics. which should confirm relief from infection and inflammation.
If you experience any burning sensation in the urethra in men, contact the author of this article - a venereologist, a urologist in Moscow with 15 years of experience.
doctor
Specialized multidisciplinary clinic
Our staff consists of high-class doctors - members of the Russian and European Societies (EA).
We have a day hospital
We guarantee constant care for the patient and control over his recovery in the most comfortable conditions.
Low-traumatic treatment methods
We carry out operations with minimal intervention in the body using modern equipment of the new generation of intraoperative X-ray systems.
The main possible causes of burning after urination in women
- The leading cause of burning after urination is occupied by various infections. In women, due to the specific anatomical features - the proximity of the anal passage to the vagina and urethra, allows bacteria to freely penetrate into the urethra, then freely into the bladder and kidneys, because this canal in women is short and wide. A burning sensation can be a consequence of sexually transmitted infections - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, urogenital chlamydia and other diseases. Such diseases are accompanied by purulent or mucopurulent discharge.
- Another equally common reason is unclean sex, poor intimate hygiene and the use of low-quality contraceptives, which destroy the natural microflora of the vagina and can cause contact dermatitis. In this case, opportunistic bacteria begin to multiply very quickly, because the local immunity that restrains them is disrupted.
- Burning after urination occurs with urethritis and cystitis. It is also accompanied by pain in the canal and lower abdomen and a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied.
- Stones formed in the kidneys or bladder, when exiting through the urethra, injure its mucous membrane and provoke not only a burning sensation, but also the release of blood into the urine.
- Often, a burning sensation is caused by hygiene detergents due to an allergic reaction to the substances they contain.
Pain when urinating in men
03.07.2020
Sometimes men experience unpleasant phenomena in the form of pain when urinating . It may be itching, pain of varying degrees, or burning.
Pain may accompany the process of urination or appear immediately after this process. Most often, pain may be accompanied by strange discharge and discolored urine . If these phenomena take place, it means that inflammatory processes are going through in the man’s body, which have an effect on the urethra, internal genital organs , and kidneys .
Inflammatory processes are caused by the action of pathogenic bacteria, which include: E. coli, enterococci, Klebsiella, yeast-like fungi. Pain when urinating in men can be a consequence of diseases of the genitourinary system: chlamydia, gonorrhea, urolithiasis , urethritis , prostatitis , trichomoniasis.
Inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system in men tend to very quickly turn into chronic diseases, which ultimately complicates and prolongs the treatment process. A disease such as urethritis can contribute to the formation of very serious male diseases: male infertility , epididymitis, orchitis, cystitis .
Therefore, as soon as the first symptoms of pain when urinating , you should urgently consult a doctor . You need to contact doctors of narrow specialization: urologists , andrologists, venereologists. Only they will be able to competently diagnose diseases of an intimate nature and prescribe quality treatment.
Providing first aid for painful urination
If you experience a burning sensation when urinating , you should immediately reduce the amount of alcohol, tea and coffee, citrus fruits, and carbonated drinks. It is necessary to stop using hygiene products that contain chemicals. The use of soaps with fragrances and dyes, powder containing a large percentage of chemicals, and lubricated condoms can also cause pain when urinating .
To reduce pain, you can try rinsing the bladder . As soon as pain appears, drink two glasses of water. After these two glasses, you will need to drink another solution of baking soda at the rate of one teaspoon per 100 grams of water. After this, you will need to drink one glass of water every hour.
This simple procedure will help flush out the urinary tract from infection. If after this procedure the burning and itching does not stop, you should urgently consult a urologist .
Pain when urinating in men is often accompanied by a burning sensation. A burning sensation can be the cause of prostatitis , which is a process of inflammation of the prostate gland , occurring in chronic or acute form. If the process is advanced, then urination will be so painful that you will be unable to go to the toilet.
In the chronic form of the disease, prostatitis exhibits fairly moderate symptoms. This may include a slight increase in temperature, a slight burning sensation in the urethra , or a general feeling of discomfort. In many cases, men do not even pay attention to these signs, which is dangerous, since over time they become stronger and more pronounced.
The treatment process for prostatitis is carried out comprehensively: the use of antibiotics, massage of the prostate gland and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Prevention and treatment of urethral disease in men is carried out based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis. Before sending the patient for various tests , the doctor collects an anamnesis.
He finds out what other symptoms are bothering the patient: whether the color of the urine has changed, whether the color of the seminal fluid has changed and whether there is an odor in it, whether there is pain in the lower abdomen , whether redness, papillomas or pimples have appeared on the skin of the penis. The presence of these symptoms indicates the presence of an infectious disease already in its acute stage.
Published in Urological diseases Premium Clinic
Treatment of burning after urination
Treatment methods are chosen only by a specialist after a thorough examination and depend on the cause that causes the burning sensation. Inflammatory processes in the urethra and bladder are treated with antibacterial drugs, to which the bacteria causing the problems are not resistant. With the development of urolithiasis and the presence of salts in the urine, acidic or alkaline drinking is indicated, depending on the type of salts. In cases where stones have formed in the kidneys and ureters, it is recommended to crush them using a special ultrasonic device, and, in extreme cases, to remove them surgically.
Burning after urination is an unpleasant and dangerous symptom, so consultation with an experienced specialist and examination should be prompt.
Return to list
Diagnosis of urinary disorders
#QUOTE_1#
Should I see a doctor or not? For conscious people, the answer to this question seems obvious - of course, contact them. Moreover, it is advisable to undergo a full examination for the presence of infectious diseases in the body. When contacting a doctor, you should understand that with a high degree of probability he will prescribe one or more diagnostic studies, namely:
- medical history examination
- detailed external examination of the patient by a proctologist, urologist, infectious disease specialist or gynecologist
- analysis of patient's urine and blood
- scraping for bacterial culture from the urethra (for men) or smear for flora from the cervical canal (for women)
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs
- cystoscopy
- taking tests to confirm the presence of STDs using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) or ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) methods
- MRI (X-ray) of the spine, namely its lumbosacral region
These diagnostic methods will help determine the causes of urinary problems and prescribe the correct treatment.
Vesiculitis - symptoms and treatment
Diagnosis of acute vesiculitis
Diagnosis of acute vesiculitis is based on the patient’s characteristic complaints, the results of palpation examination of the area of the seminal vesicles, as well as data from laboratory and instrumental studies.
Inspection is the first stage of diagnosis. Includes examination of the genital organs and palpation (palpation) of the seminal vesicles. Palpation can be painful, so it must be performed extremely delicately.
Normal seminal vesicles cannot be palpated during digital rectal examination. With acute catarrhal vesiculitis in the area of the seminal vesicles, swelling, tissue compaction and pain are possible. This is especially clearly manifested in unilateral catarrhal inflammation of the seminal vesicle. If the lesion is deep, the vesicles are determined in the form of a dense, sharply painful cord or oblong formation, which can be felt at the level of the upper edge of the prostate gland.
With empyema of the seminal vesicle, a sharply painful flask-shaped tumor is palpated at the upper edge of the prostate, which changes shape with slight pressure. If the inflammatory process spreads to the surrounding tissues, then a sharply painful compaction without clear contours and boundaries will be felt at the site of the seminal vesicle. Typically, this lump extends beyond the prostate gland.
Laboratory examination is the second stage of diagnosis. It includes the standard minimum:
- Clinical blood test with determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) - leukocyturia and erythrocyturia (increased content of leukocytes and erythrocytes) are observed, which indicates the systemic nature of inflammation, and an increase in ESR.
- Biochemical blood test - possible increase in liver enzymes (ALT, AST and total bilirubin); with difficulty urinating, creatinine and urea levels sometimes increase.
- General urine analysis - as a rule, leukocyturia (increased white blood cell count) and erythrocyturia (increased red blood cell count) are observed.
- Urine culture for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics - it is possible to identify pathological flora from the lower urinary tract.
Instrumental examination is the third stage of diagnosis. An ultrasound examination of the seminal vesicles and prostate gland is performed. This study can be done with a transrectal or abdominal probe; maximum visualization will be with transrectal access (through the rectum). At the same time, the size, structure of the seminal vesicles and the presence of purulent foci in them are assessed.
In rare cases, computed tomography (CT) of the pelvis is performed to clarify the diagnosis [11].
Diagnosis of chronic vesiculitis
Diagnosis of chronic vesiculitis is based on an assessment of symptoms, ultrasound data, and microscopic examination of the secretion of the seminal vesicles.
The secretion should be obtained separately from each seminal vesicle. To do this, first massage the prostate gland, after which the patient is asked to urinate. Then the urethra is catheterized and washed with Furacilin solution so that a small amount remains in the bladder. After this, one seminal vesicle is massaged and its secretion is taken from the urethra. The patient is asked to urinate with the sterile solution remaining in the bladder, then the other seminal vesicle is massaged and its secretion is collected.
In chronic vesiculitis, the secretion contains leukocytes, erythrocytes and immobile sperm. Microbiological examination of secretions allows us to identify the causative agent of infection and select an antibacterial drug for adequate treatment. On ultrasound, the seminal vesicles will be enlarged, stretched and uneven.
In rare cases, similar symptoms can be observed with tuberculous lesions of the seminal vesicles, but this diagnosis is excluded by microbiological examination of the secretion. Seminal vesicle cancer is detected quite rarely. As a rule, it is a consequence of prostate cancer, and atypical cells and red blood cells will be detected in the secretion [12].
Causes of pain after urination
The main causes of pain after urination:
- Urolithiasis - stones have formed in the genitourinary system, which cause pain. With urolithiasis, there is a symptom of congestion - this is the cessation of urination and its resumption after a change in body position;
- Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease;
- Ureaplasmosis is a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease. In addition to pain after urination, there is clear discharge and pain in the lower abdomen;
- Urethritis - inflammation of the urethra;
- Trichomoniasis is a disease that causes pain after urination;
- Gonorrhea - in addition to pain after urination, there is inflammation of the gonads and swelling of the genitals.