A complaint such as itching in the genital area due to cystitis does not occur in all women.
Therefore, when faced with it, some patients experience a feeling of anxiety.
The localization of itching varies, as do the causes and time of appearance.
Sometimes itching begins simultaneously with the appearance of the first manifestations of cystitis.
And sometimes the symptom appears at the start of treatment.
Some experience burning and itching in the vagina after a course of therapy.
The condition is exhausting, layered with the symptoms of cystitis, and it greatly reduces the quality of life.
There is no need to exhaust yourself with patience: modern medicine has enough opportunities to relieve itching.
You just need to seek help from a qualified dermatologist or urologist.
Causes of itching with cystitis
Cystitis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the bladder.
It is caused by various factors:
- nonspecific flora is the most common option
- causative agents of sexually transmitted infections or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
- allergic processes
- diabetes
- some medical procedures
And a few more less common triggers.
Some diseases that cause cystitis are themselves accompanied by itching.
For example, allergic urticaria or diabetes.
In other cases, itching in the vagina or perineum begins precisely because of cystitis.
The main role in this is played by urine leakage and the action of pathogenic flora.
The disturbing symptom must be treated, as itchy surfaces require scratching.
Excoriations (the so-called scratches) on the skin of the groin become infected very quickly.
As a result, it turns out that itching complicates the course of cystitis due to a bacterial infection of the skin.
Therefore, it cannot be ignored.
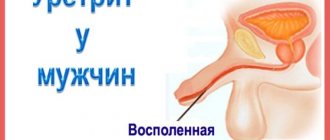
Pain after urination in men
In men, pain after urination may occur due to:
- Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland. This disease begins after bacteria enter the prostate from the urethra. Prostatitis appears against a background of weakened immunity, stress, and concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system. Symptoms: pain after urination, abdominal pain, pain during ejaculation, difficulty urinating, pain in the testicles;
- Phimosis is a disease during which the foreskin narrows. This disease is provoked by infection, injury, and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Symptoms: pain after urination, difficulty urinating, pain during ejaculation.
Itching due to cystitis caused by bacterial infections
Almost 80% of cases of the disease are of an ascending nature.
That is, first the pathogenic microflora inoculates the urethra, and then, after a few days, penetrates the bladder.
One important factor contributes to this development of events: high bacterial contamination of the vulva and vagina.
That is, previous inflammation of the external genitalia, more or less pronounced.
Against this background, itching of the vulva, genitals and vagina itself is quite a common occurrence.
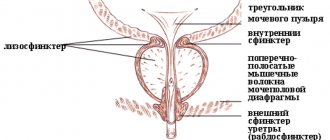
The mechanism is simple: swelling of the mucous membrane of the bladder does not allow the internal sphincter to reliably block the outflow of urine.
And it constantly seeps in drops from the urethra and leaks.
Salty and microorganism-rich liquid enters the mucous membrane of the vulva, which provokes irritation of the delicate epithelial lining.
And it becomes inflamed and begins to itch.
Among the pathogens, nonspecific flora predominates - Klebsiella, Escherichia coli, staphylococci and streptococci.
As for STDs, the leaders here are chlamydia and trichomonas.
All these microbes feel quite comfortable on the epithelium of the genital organs and on the mucous membrane of the bladder.
It often happens that inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder coincides in time with an active process in the genital organs.
A woman with cystitis perceives this combination as itching.
In fact, two inflammatory processes take place at once: in the mucous membrane of the bladder and in the vagina (vaginitis, colpitis, vulvitis).
Such situations are characterized by discharge from the genitals, unpleasant odor, burning and pain in the vagina, and dyspareunia.
In this particular case, cystitis, as a manifestation of an STD, can be considered contagious to a woman’s sexual partner.
The incubation period for different microorganisms is different:
- 1. Nonspecific flora is activated within 24-48 hours from the moment it enters the bladder. And the first symptoms will be from the bladder.
- 2. With an STD, the genital organs are primarily affected, and for such processes, itching in the intimate area can become primary, and the symptoms of cystitis appear after 4-5 days.
Based on these signs, preliminary conclusions can be drawn about the cause of inflammation.
But laboratory research methods play a decisive role in diagnosis:
- clinical urine tests
- sediment microscopy
- genital smear
- urethral smear
- immunological reactions
A venereologist or dermatologist prescribes tests.
He, as a rule, collects diagnostic material himself and interprets the results.
Treatment
You can remove burning and itching in the intimate area with infectious cystitis only by recovering from the main cause - infection.
To do this, you need to identify the pathogen and test it for sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs.
Then carry out a full course of therapy for the underlying disease and concomitant pathology.
With an unprofessional approach or attempts at self-medication, cystitis and STDs readily transform into chronic forms.
The second negative aspect of unqualified use of antibiotics is the destruction of normal bacterial flora.
This creates favorable conditions for the development of fungi.
How to fix
If after treatment the signs of cystitis do not disappear, you need to contact a urologist who will prescribe repeated urine and blood tests, ultrasound of the bladder and cystoscopy. A woman needs to visit a gynecologist who will help identify the reasons for the persistence of unpleasant signs.
If after treatment the signs of cystitis do not disappear, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the bladder.
Drugs
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms use:
- Antibiotics (Nolitsin, Nitroxoline). These drugs are effective against most pathogenic microorganisms. Resistance to them develops slowly, which makes it possible to use such drugs for cystitis that is difficult to treat.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin). Used to relieve persistent inflammatory processes.
- Uroseptics (Canephron, Cyston). They accelerate the healing of injured tissues, relieving discomfort, and prevent the spread of infection.
- Vaginal suppositories (Betadine, Polygynax). Restores the microflora of the genital organs in women, relieves itching and burning in the vaginal area.
Folk remedies
Drug therapy is combined with the use of:
- Bearberry. 1 tbsp. l. the herbs are poured with 200 ml of cool water and left for a day. The infusion is taken 100 ml 3 times a day.
- Bath with chamomile, oak bark, string and calendula. 100 g of raw material is boiled in 2 liters of water for 15 minutes. The finished broth is poured into a basin with 10 liters of warm water. Take a bath for half an hour, after which you put on warm underwear.
- Rosehip decoction. 4 tbsp. l. crushed rhizomes, pour 1 liter of water, boil for 15 minutes. Drink 0.5 cups of the decoction before each meal.
[morkovin_vg video=”dAh1mBvFDqI, Treatment of cystitis in women and men; dIXIAbUDovk, Cystitis – symptoms, treatment; aViOsAlPaRQ, Inflammation of the bladder – treatment”]
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures enhance the effect of drugs, facilitating their penetration into tissues. This treatment has no side effects or contraindications. To get rid of the unpleasant signs of cystitis use:
- electrophoresis;
- inductothermy;
- magnetic therapy;
- magnetophoresis;
- ultrasound therapy;
- hyperthermia (local increase in temperature);
- pulsed electroanalgesia (pain relief).
Nutrition
Drinking enough fluid (at least 2.5 liters per day) helps get rid of the signs of cystitis. Avoid foods that make urine concentrated - spicy and salty foods, sour fruits, marinades, garlic, radishes, and onions. Products rich in magnesium are useful for cystitis - buckwheat and millet porridge, dried fruit compotes. The diet involves limiting the amount of legumes, fish, and dairy products consumed. Drinks made from lingonberries and cranberries help normalize urination.
Itching with cystitis caused by fungal infections
Yeast fungi of the genus Candida live in minimal quantities on the mucous membranes of a healthy person.
And under any favorable conditions, they begin to actively multiply, provoking candidiasis.
One of these favorable conditions is the uncontrolled use of antibiotics.
Many women, having discovered symptoms of cystitis, begin treatment on the advice of friends or information from unverified sources on the Internet.
Often the cynic manifestations actually subside, the disease seems to recede.
And after one or two days, the process begins again, with renewed vigor.
Itching in the genital area and vagina after treated cystitis is almost always associated with the active proliferation of yeast.
Antibiotics do not help in such situations.
Since candidiasis is already a complication of improper treatment, and because of this, severe itching appears on the genitals.
The symptoms of the process resemble typical thrush (which is what it is):
- burning and redness of the mucous membrane of the vaginal vestibule
- white plaque on inflamed surfaces
- sour smell
- itching in the affected areas
It happens that a bacterial infection in the bladder resolves safely even with self-medication.
But when itching in the vagina after cystitis remains, does not go away, and even intensifies, this is a sign of candidiasis, which has complicated antibiotic therapy.
Treatment
You can relieve itching only by dealing with candidiasis.
For this purpose, systemic antifungal drugs are used.
At the same time, you need to prescribe such medications in the form of vaginal tablets, suppositories, baths, and so on.
Ideally, an antifungal drug should be added to the antibiotic regimen for bacterial or STD-associated cystitis from the very beginning.
This will help you achieve full recovery more quickly.
It will provide certain guarantees that the itching of the intimate area will not return in a few days or weeks.
In addition, contacting a specialist will help prevent another unpleasant moment.
That is, increased itching in the first phase of antimicrobial therapy, associated with allergies to certain medications.
Itching with cystitis caused by allergic processes
Sometimes our body reacts too strongly to certain substances.
The phenomenon of allergic cystitis is much less common than bacterial or candidal cystitis.
But here, itching is the main symptom.
The disturbing sensation is very intrusive and pronounced.
Itching of the urethra, vulva area.
On the part of the bladder, typical signs of inflammation are observed, but much less pronounced when compared with the infectious process.
Each person has their own provoking factors, and allergens are individual.
Almost always, the process is accompanied by characteristic urticaria-type rashes on the skin of the body: in the groin, on the thighs, and external genitalia.
You should also expect the addition of lacrimation and rhinitis.
It is very rare, but there is an isolated reaction of the bladder mucosa to drugs that are used to treat cystitis and are excreted unchanged in the urine.
For example - furamag, nitroxoline.
Then there may not be skin reactions like urticaria.
But allergy mediators will certainly provoke symptoms very similar to the manifestations of cystitis.
Even in the urethra it can itch, and when urinating, a burning sensation can appear due to irritation of the mucous membrane with urine.
Treatment
Before you try to relieve the itchy component of the allergy, you need to make sure it is present.
Thus, sometimes an exacerbation of chronic interstitial inflammation is mistaken for allergic cystitis.
The problem is that urine leaks can cause irritation and itching on the skin of the groin, which an inexperienced eye can easily confuse with hives.
It is better to entrust the diagnosis to a dermatologist.
An examination may be sufficient to clarify the diagnosis.
Sometimes you will need to take laboratory blood tests for immunoglobulins and allergy tests.
The first thing to do to get rid of itching is to stop contact with the allergen.
If these are medications, then you need to change them to ones that are equally effective, but safe.
Special antiallergic drugs will help relieve itching faster:
- loratadine, included in such drugs as Claritin, Agistam and others
- Desloratadine, the next generation of such drugs, is the active ingredient for Fribris, Eden
- Cetirizine, perfectly relieves itching, is used to prevent allergic relapses, serves as the basis for “Cetrin”, “Zodak”
- Diphenhydramine, the most famous drug, known for its strong antipruritic effect, but also has unpleasant side reactions
All drugs on the list are intended for systemic use and are taken orally.
In case of severe reactions of the mucous membrane of the genital organs, vulva, urticaria on the skin of the groin, it may be necessary to add local treatment - ointments based on corticosteroids.
But you need to understand that such drugs reduce local immunity.
With unqualified treatment, allergic itching can give way to candidiasis.
Localization and character
If after cystitis there are unpleasant sensations in the form of itching, burning and frequent urge to urinate, the patient’s quality of life worsens. The localization and intensity of symptoms varies, which is explained by the severity of the disease and the treatment methods used.
Itching
This symptom brings the greatest discomfort to the patient. It is localized in the area of the external genitalia and remains after treatment. Itching is accompanied by irritation of the mucous membranes of the urethra and vagina.
Burning
Unpleasant sensations are localized in the urethra, in the lower abdomen, in the area of the head of the penis in men and at the entrance to the vagina in women.
They intensify at the beginning or end of urination, gradually subsiding after its completion.
Pain
The pain remaining after cystitis is aching or pulling. It occurs in the pubic area, spreading to the lumbar region, perineum and anus. Intensifies with urination, physical activity, and sexual intercourse.
Itching with cystitis caused by diabetes
A very specific option, but this disease is becoming more common.
It is characterized by decreased immunity and dry mucous membranes.
Cystitis in diabetics is a fairly common occurrence.
Skin itching, unfortunately, too.
The dry mucous membrane of the vulva, vagina, is very easily irritated by leaking urine.
And if it is also infected, then colpitis may also develop.
Both bacterial and candida.
Treatment
The only way to help diabetics get long-term relief from itching is to effectively control their blood sugar levels.
Antipruritic drugs such as diphenhydramine should be used with caution and only after consulting a doctor.
Topical use of hormone-based ointments is not indicated.
For such patients, creams with emollients are a good alternative.
For example - shea butter, avocado, canola.
Emollients moisturize, soften and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Safe, can be used in childhood.
Itching with cystitis after medical procedures
Strictly speaking, three points can be attributed here:
- injury to the bladder during any instrumental research, for example, cystoscopy
- radiation cystitis that occurs after X-ray irradiation for tumors of the pelvic organs
- complication of the bacterial process by candidiasis with unbalanced antibiotic therapy
Unfortunately, all three options simply cannot be excluded.
When performing cystoscopy, a thin endoscope is passed through the urethra and inserted directly into the bladder, the mucous membrane of which is inflamed and swollen.
The same applies to the urethra.
Microtraumas can almost never be avoided.
Therefore, itching may occur in the urethral area as a result of healing of microtraumas.
If there are no signs of infection (pain, burning, swelling), then there is no need to worry.
It is enough to relieve the itching with medications or traditional methods.
A similar mechanism is typical for pouring drugs into a bubble.
But attention is needed here: itching from instillations may be the result of an allergic reaction.
X-ray therapy, unfortunately, is rarely without negative consequences.
Often, a course of irradiation of the pelvis leads to the development of radiation cystitis, and a parallel reaction of the skin results in itching.
How to relieve such symptoms is always decided individually by an oncologist.
We have already mentioned those situations when cystitis went away from antibiotics, but the itching in the vagina remained.
This sign is typical for the final phase of treatment.
When antibiotics destroy the vaginal flora and candida begins to multiply there.