Kidney pain - causes
The most common cause of kidney pain is kidney inflammation. It could be:
- Glomerulonephritis.
Most often the disease is caused by bacteria or viruses. Usually appears a week or two after infection. The healing process of the primary disease is interrupted, and health worsens. Sometimes there is loss of appetite and stomach problems. There may also be swelling of the face and legs, problems with urination, and signs of high blood pressure. Rarely, the disease is accompanied by fever. - Interstitial nephritis.
In most cases (about 70%) acute interstitial nephritis is associated with the use of so-called nephrotoxic drugs, which lead to drug-induced nephropathies (drug-induced kidney damage). Symptoms of the disease: fever, pain in the lumbar region (described as dull), skin rash (in different places), oliguria. Joint pain, hematuria, and decreased urine output may also occur. - Pyelonephritis.
Symptoms are similar to those that occur with interstitial nephritis.
Pyelonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
Diagnosis of kidney diseases
If you suspect a dysfunction of the filtration organ, the doctor will first talk with you and examine external signs that can clarify the essence of the ailment:
- swelling of the face;
- pallor;
- pain when tapping in the lumbar region;
- high blood pressure;
Then he will prescribe you a set of laboratory tests, which may vary significantly depending on the disease. However, some tests for kidney disease are standard:
- blood chemistry;
- general blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- ultrasound diagnostics.
For special indications, you may be prescribed:
- kidney biopsy
- excretory urography,
- computed tomography,
- Zimnitsky's tests.
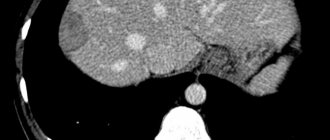
Causes of pain in the kidneys (kidney): renal colic
Renal colic occurs when there is a sudden increase in pressure in the upper urinary tract caused by residual and rising urine levels. This condition results from the ureter being blocked by a urinary stone.
A sign of renal colic is sudden, very severe pain. It begins in the kidney area (lumbar region), from where it goes down to the bladder, urethra and outer thigh.
Associated symptoms:
- painful urination;
- frequent urination;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating.
Painful urination
Bloating
Vomit
Symptoms of kidney diseases
Lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue, weakness; increased blood pressure and, as a result, headache; the appearance of swelling on the face and legs, which is usually noticeable in the morning and smooths out in the evening; increased body temperature, chills, sweating; nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting; frequent or painful urination; the intensity of pain does not depend on body position.
Urine may also change: it becomes rich in color or, conversely, colorless, contains blood, mucus or sediment.
The location of the pain is very important. Many people do not know where the kidneys hurt and what the characteristics of the pain are. With kidney diseases, pain occurs more often on one side - to the left or right of the spine. It is localized just below the ribs and can radiate to the lateral surface of the abdomen and groin, along the ureter, to the external genitalia, and inner thighs.
Causes of pain in the kidneys (kidney): hydronephrosis
The cause of pain in the kidneys may be the accumulation of urine in the organ due to its difficult outflow, that is, hydronephrosis. Hydronephrosis is usually detected by chance, as it is asymptomatic. Moreover, if the pathology gives symptoms, they are uncharacteristic.
- Children most often complain of digestive problems: abdominal pain, lack of appetite, flatulence, diarrhea. There may also be a fever, which indicates a urinary tract infection, often associated with hydronephrosis.
- In adults, a characteristic symptom is a dull pain in the lumbar region, which spreads to the pubic symphysis, and in men - to the testicles. Associated symptoms include gastrointestinal complaints: nausea, vomiting and bloating. There may also be problems with urination.
Hydronephrosis
Treatment and diagnosis of burning in the kidney area
To identify the cause of the problem as accurately as possible, first of all, you need to consult your doctor.
This kind of disease will require a number of diagnostics:
- Urinalysis - necessary to detect red blood cells and increase white blood cells. Salts can be debugged;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys - will help determine the cause of inflammation and check for the presence of a cyst;
- X-ray of the kidneys - can identify possible kidney stones, find out their exact location, and determine the causes of faulty urine flow.
If small kidney stones or sand are present, litholytic treatment is usually carried out with various drugs. This helps to reduce the size of stones and allows them to pass through urine.
In the presence of large stones, surgical intervention is required. It is also possible to get rid of stones using ultrasound, which breaks large stones into small ones, after which they are excreted in the urine.
Cyst-like causes of pain are not treated. Here, as a rule, the cyst is pierced with a needle and the contents of the cyst-shaped cavity are removed.
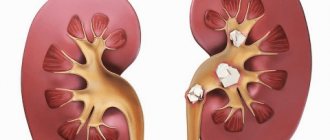
Causes of pain in the kidneys (kidney): cyst
A kidney cyst is a fluid-filled bubble with thick walls located in the kidney parenchyma. Cysts can be congenital, acquired and genetically determined. When kidney cysts are small, they usually do not cause symptoms.
As the cyst enlarges, it gives the following symptoms:
- pain is localized most often in the lumbar region, as well as on the sides of the abdomen;
- discomfort or unpleasant feeling of tightness in the abdomen;
- gastrointestinal disorders, such as nausea.
Most often, a kidney cyst does not require treatment.
Diagnostics
In order to make the most accurate diagnosis, a specialist will examine the patient and palpate the kidneys and peritoneum. If the right kidney also hurts and the patient does not know what to do, then it should be remembered that self-treatment is fraught with serious consequences. It is necessary to go to the hospital as soon as possible. Here the task of the attending physician is to make an accurate diagnosis. To do this, the specialist will perform the following activities in order to make the most accurate diagnosis:
- Interview the patient to collect the most detailed medical history;
- Examine the patient and palpate the kidneys and peritoneum;
- Prescribe blood and urine tests;
- Perform an ultrasound of the kidneys and abdominal organs.
In addition to these measures (if no pathologies of the urinary system are identified), a specialist may prescribe the following procedures:
- MRI of the spine;
- X-ray of the kidneys;
- Angiography of the urinary system;
- Kidney urography.
Causes of kidney (kidney) pain: cancer
Kidney cancer is more common in men over 45 years of age. Women usually develop kidney cancer between the ages of 55 and 74. The most dangerous thing for the kidneys is smoking cigarettes, namely, toxic substances in tobacco smoke are very harmful.
Kidney cancer
Symptoms that doctors call the classic triad (that is, hematuria (blood in the urine), pain, and palpable swelling) affect only 7-15% of patients. The presence of such signs usually indicates significant progression of the disease.
Certain symptoms are more common, for example, hematuria is observed in 40-60% of patients. The pain that accompanies the disease may resemble colic or be dull and manifest in the lumbar region. Patients experience a range of unpleasant symptoms: fever or heat, night sweats, weight loss, high blood pressure and polymyositis.
The most effective treatment for kidney cancer is surgical removal of the tumor, since this type of tumor is moderately sensitive to chemotherapy and radiation (radiation therapy).
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
How to determine if your kidneys are hurting
In order not to confuse unpleasant sensations with back pain, you need to know about the peculiarities of the manifestation of the symptom. What to do, how to check and determine if the kidneys are hurting? Recommendations:
- Think about what might have caused you to get sick. If you understand that you have been engaged in heavy physical labor, have been in an uncomfortable position for a long time, there is a high risk of diseases of the lumbar muscles and spine. If you are hypothermic, this indicates that the organ of the urinary system is not in order.
- The urinary organ is mainly disturbed at night, rarely during the day, and painful sensations in the musculoskeletal system occur periodically, more often after movement.
- Pain in the urinary organ is accompanied by specific symptoms: constant thirst, temperature, changes in urination, loss of appetite.
Find out in more detail what a kidney cyst is - symptoms and treatment of the disease.
The kidneys are a unique organ that works continuously throughout life. 24 hours a day, the kidneys actively distill blood several times, cleanse it of toxins, and remove excess moisture from the body, redirecting it to the appropriate tubules.
The structure and position of the organ is no less unique. Unlike other paired organs, the kidneys are located asymmetrically - one is slightly higher than the other. The difference in position gap depends on the characteristics of human anatomy, age and type of activity.
Due to this interesting situation, when the kidneys hurt, the pain radiates to a variety of parts of the body - the back, stomach, lower back.
Interesting! In fact, the kidneys are located above the lower back, almost in the middle of the back.
To determine where the organ is located, you need to feel the lower rib with your finger and draw an even line from the edge of the rib back strictly parallel to the thigh.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of pain in the right kidney, preventive measures are taken. They are:
- Giving up bad habits.
- Proper nutrition.
- Compliance with drinking regime.
- Playing sports.
- Avoiding hypothermia.
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene (which is especially important for female representatives, who often experience kidney inflammation due to anatomical features).
- Disturbance of innervation of the bladder: causes, diagnosis and treatment
- Necrotizing nephrosis - clinical picture and treatment methods
- How to restore the bladder mucosa: methods and preparations
- Macrophages in urine: what does it mean, why is it dangerous and what to do
- Aminoaciduria: what it is, causes, classification and treatment
It should be noted that a number of medications, if taken uncontrolled, can cause pain in the area of the right kidney. Nephrotoxic medications include antibiotics, analgesics, cytostatics, anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs, sulfonamides, and indomethacin. Therefore, such products should be used only as prescribed by a doctor and in the recommended dosage.
To exclude the development of pathology, it is recommended to periodically undergo a preventive examination, take blood and urine tests, and do an ultrasound.
New on the site
Copyright 2021 All about kidney health. All rights reserved.
Leave a comment 97,829
People often wonder: what to do if your right kidney hurts? It should be noted that pain does not just arise and is a signal of the development of a disease, which only a specialist can diagnose and treat. Therefore, it is important to understand the symptoms that accompany colic and cramps on the right side, and when they appear, do not delay visiting a doctor.