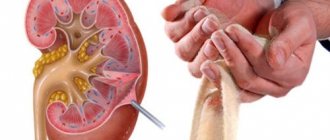
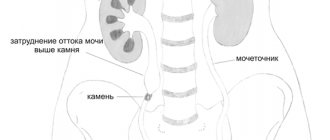
Urolithiasis, or urolithiasis, is one of the kidney pathologies associated with metabolic disorders in the body. The disease has no age restrictions; it can be found in both newborns and adults. First, microliths (“sand”) are formed, from which stones are subsequently formed. Kidney stones themselves rarely cause concern to the patient. Significant clinical manifestations occur if stones migrate into the ureter, causing blockage. As a result, the outflow of urine from the kidney is disrupted, and severe pain occurs (renal colic).
This situation can cause acute, life-threatening inflammation of the kidney or disruption of its function. In such cases, the patient requires emergency surgery. It is very important to treat the disease at the stage of its occurrence: this will avoid complications and bring the body back to normal in a short time.
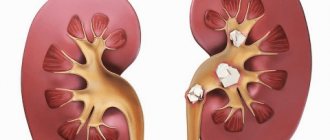
Types of stones:
- Calcium-oxalate - dense, grayish-black in color, with spiny growths.
- Calcium phosphate - quite soft, with roughness, light gray in color.
- Urates are hard, smooth and yellow (due to uric acid).
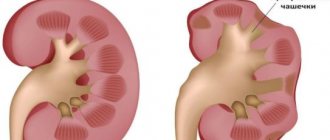
All of these types of stones can be localized in the kidneys, bladder or ureters.
Features of the course of urolithiasis in women and men
People aged 20 to 55 years are at risk. The highest incidence rate is observed in the countries of Asia Minor. Urolithiasis is diagnosed three times more often in men than in women. However, it is women who tend to form coral-shaped studded stones, which cause many painful symptoms.
Symptoms are almost the same in both sexes. The main difference: in men, pain during renal colic radiates to the penis, and in women, to the labia. Quite rarely (in only 17% of cases) diseases of a bilateral nature occur, i.e. the formation of stones in both kidneys.
Sand in the kidneys - symptoms during pregnancy
Sand in the kidneys of pregnant women often appears as a result of metabolic disorders, which can be triggered by altered hormonal levels. Diagnosis of pathology during pregnancy is difficult due to the inadmissibility of certain studies. In addition, painful sensations in the lower abdomen can be considered by a pregnant woman as a result of increased fetal activity. Many expectant mothers are in no hurry to tell the doctor about this. The presence of sand in the kidneys in pregnant women is accompanied by the same symptoms, these are:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- pain when urinating;
- acute urinary retention;
- the appearance of traces of blood in the urine;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms of urolithiasis
- Pain in the waist region (this can be continuous or periodic dull or sharp pain).
- Renal colic (spontaneously occurring severe pain, which indicates blockage of the ureter).
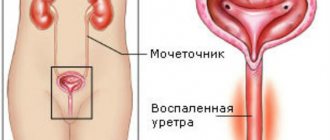
- Pain when urinating and change in urine color (frequent need to urinate, blood or pus in the urine).
- Nausea, vomiting, high blood pressure and temperature, bloating.
In children, the symptoms of urolithiasis often do not coincide with those indicated. In any case, only a qualified specialist can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
How does sand manifest itself in the kidneys?
The size of the grains of sand is so small that their presence in the kidneys often does not affect the well-being of patients. These formations are not capable of causing difficulty in the outflow of urine like kidney stones. In this regard, the pathology in most cases is diagnosed accidentally, during a comprehensive examination of the pelvic organs.
A gradual increase in the size of sand grains and their merging with each other leads to the appearance of concretions (stones). At this stage, patients learn about sand in the kidneys, the symptoms of which in women manifest themselves as follows:
- pain in the lower abdomen, projected to the area of the ureters;
- change in urine color (red tint);
- painful urination;
- burning in the perineal area.
Pain due to sand in the kidneys
Patients who suspect that they have this pathology ask specialists whether their kidneys hurt if there is sand in them. As noted above, urolithiasis is asymptomatic for a long time. Only when the outflow of urine is disrupted do patients begin to notice the first painful sensations.
At first, these are mild, slightly pulling discomfort in the lower back and sides. Over time, the frequency and intensity of pain increases. When conducting diagnostics, some patients indicate the lower abdomen on the side as the localization of pain. The ureters are located in this place, the movement of grains of sand along which causes pain.
Urination due to sand in the kidneys
Difficult, painful urination along with a change in the nature of urine excreted are the first signs of sand in the kidneys. Prolonged presence of salt deposits in the kidneys leads to the formation of small stones. When they get stuck in the ureters, they cause problems with urine output. Urination becomes unproductive: the urge to empty the bladder is often false. Patients learn how sand comes out of the kidneys by the following signs:
- change in urine color to scarlet or pink;
- burning in the groin area;
- painful sensations on the sides of the abdomen.
What are the causes of urolithiasis?
The causes of urolithiasis are often associated with heredity, namely metabolic disorders. As a result, changes occur in the chemical and water-salt structure of urine, in particular, excess content of:
- uric acid;
- oxalate salt;
- calcium salts;
- phosphate salt.
Internal causes include digestive diseases, dehydration, infections, vitamin D deficiency and poor diet.
There are also external factors:
- the water we use, or rather its chemical composition;
- climate, amount of ultraviolet rays;
- conditions at work and at home (sedentary lifestyle or, conversely, heavy physical activity).
Sand in the kidneys - reasons
The causes of sand in the kidneys in women are practically no different from the factors that provoke its appearance in men. It should be noted that the detected fine mixture is not essentially sand. By its origin, it is more of a sediment that is formed from salts. The diameter of an individual grain of sand cannot exceed 0.9 mm. Sand and kidney stones are different concepts.
Doctors believe that the main reason for their accumulation in the kidneys (urolithiasis) is a metabolic disorder and the patient’s dietary habits. Among other possible factors that provoke sand in the kidneys (symptoms in women are listed below), it is necessary to highlight:
- Genetic predisposition.
Doctors have proven that metabolic characteristics can be inherited. This is indicated by their frequent coincidence among close relatives. - Poor quality of drinking water.
The high content of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus salts in tap water, which is the main source of liquid, increases the risk of stone formation. - Features of climatic conditions.
High humidity and hot climate reduce the volume of secretion produced by the sweat glands. As a result, trace elements accumulate in the bloodstream, which enhances renal filtration. - Same type, unbalanced diet.
The predominance of meat dishes in the daily menu leads to acidification of urine. If the basis is plant products, alkalization develops. The appearance of sand in the kidneys can only be avoided by combining these components. This factor is especially common in women who follow various diets. - Vitamin imbalance.
Increasing the concentration of vitamin D with a simultaneous decrease in the level of vitamins A and C. - Hyperthyroidism.
An increase in the size of the parathyroid gland provokes an increase in the concentration of calcium in the blood, which partially settles in the kidneys. - Urinary tract diseases.
Congenital malformations, frequent inflammatory and infectious processes contribute to stagnation of urine.
Diagnosis of urolithiasis
As soon as the first signs of urolithiasis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. In order to correctly determine how to treat urolithiasis, it is necessary first of all to identify the causes of this disease.
What diagnostics can modern medicine offer?
The main diagnostic methods that allow us to determine all the features of the course of the disease include the following:
- A general blood test and biochemistry are mandatory procedures for identifying inflammatory processes (leukocyte levels) and pathological changes in the very structure of the organs.
- General urine analysis - allows you to determine the chemical composition of impurities contained in urine.
- Ultrasound examination is the most common method, which has minimal negative effects, and therefore is not contraindicated even for pregnant women. This method allows you to detect even small formations.
- Excretory urography - X-ray imaging of the urinary system. Specific stones can form in the human body, which are not a barrier to X-rays and therefore are not diagnosed by this method.
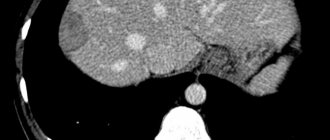
- Computed tomography is a three-dimensional image that allows you to obtain the most complete information about the presence of foreign bodies. It is one of the most advanced diagnostic methods.
Treatment of urolithiasis
There are several basic treatment methods that can complement each other:
- Drug treatment of urolithiasis. Special preparations dissolve stones and promote their removal from the body. This type of treatment is more effective together with herbal medicine, but, unfortunately, in most cases it is not effective.
- Shock wave lithotripsy. The crushing of the stone occurs due to the rapid pulse of the shock wave. This method is the most painless, but not always effective.
- Ureteroscopy. Crushing through a thin instrument inserted into the ureter.
How do sand come out of the kidneys in women?
- If sand comes from the kidneys, then the symptoms in women may coincide with various female diseases, from cystitis to inflammation of the appendages.
- They can also be confused with an ectopic pregnancy or even appendicitis.
Severe pain
It is in this regard that it is important to understand that constant symptoms of sand leaving the kidneys are:
- The presence of aching or, conversely, stabbing pain in the lines coinciding with the urinary ducts and descending to the groin from the navel. When urine comes out , grains of sand come out with it, after which pain relief is felt.
- Pain in the hypochondrium caused by irritation of the kidney tissue and inflammation in it. Typically, women feel such pain after physical activity, which causes the sand in the kidneys to move. The pain may be sharp or intensify gradually.
- The stomach or separately the lumbar region may , sometimes radiating to the groin or intestines. And until the grains of sand come out in the urine, the painful attack continues. These sensations are less painful than those caused by kidney stones , since the sand is much finer.
- Turbidity and red coloration of urine due to the fact that sand injures the mucous membranes of the ureter.
- More frequent urge to urinate, but less total urine per day.
- Pain and burning sensation when urinating, especially in the final stage.
- Relief after finishing urination.
Prevention is the key to your health!
If a person has had urolithiasis, treatment does not guarantee that it will not return. Therefore, prevention of urolithiasis is necessary, which includes:
- getting rid of bad habits;
- proper nutrition and limiting salt intake;
- establishing the correct drinking regime;
- avoiding hypothermia, especially in the lumbar region;
- lack of stress;
- playing sports without excessive strength loads;
- trips to specialized sanatoriums.
All this will avoid the need for surgical treatment of urolithiasis.
At the Urology Clinic of the Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry, you will be provided with any type of assistance, will conduct a full diagnosis and prescribe the most effective method of treatment. The availability of modern equipment, as well as many years of experience of specialists, makes it possible to identify the disease even at the earliest stages.
Sand in the kidneys - what to do?
Talking about how to remove sand from the kidneys, doctors draw attention to the need to change lifestyle. Reviewing your diet and drinking only purified drinking water quickly reduces the concentration of salts in the body. Increasing physical activity, swimming, and yoga help normalize metabolism in the body. It is important to drink at least 2 liters of purified water per day. It is recommended to exclude the following foods from the diet:
- coffee;
- strong tea;
- spices;
- marinades;
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- meat and fish (with urates);
- sorrel, rhubarb, acidic foods (with oxalates).