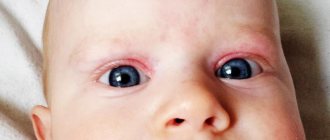
Swollen eyelids are a sign of various disorders in the body. The causes of this phenomenon may be allergic reactions, ophthalmological diseases and other factors. Swelling of the eyelids often occurs in children, especially preschoolers, as they are at risk for infectious eye pathologies. Let's look at the causes and methods of treating edema.
Inflammation of the upper or lower eyelid can be caused by various factors. Based on external signs, you can first guess what exactly caused the swelling. It depends on the degree of its severity, location, and whether it occurs in one or both eyes. Doctors also distinguish a separate type of edema, called reactive. It is named so because it develops literally in a matter of minutes. The location area can be any - both the upper and lower eyelids. This happens in some conditions. Let's look at the reasons why reactive swelling of the upper or lower eyelids may occur in a child.
Conditions under which reactive eyelid edema may develop
The skin around our eyes is the thinnest and most vulnerable on the entire body.
The development of eyelid edema is facilitated by its high extensibility, the rather loose structure of the subcutaneous fatty tissue and its ability to accumulate intercellular fluid. In ophthalmology, there are several reasons that can cause the development of reactive edema of the eyelids in a child:
- viral and infectious pathologies of the organs of vision (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, dacryocystitis, barley, chalazion, etc.);
- allergic reaction to various substances;
- diseases of the kidneys, thyroid gland;
- traumatic injuries;
- demodicosis;
- taking certain medications to which the body reacts individually;
- complications of sinusitis, sinusitis and other similar diseases;
- a bite of an insect.
In all of these cases, the child most often experiences severe swelling of the eyelids. In some conditions, reactive swelling of the eyelids pose a real health hazard - for example, during an allergic reaction.
Diagnosis and treatment
Many people are familiar with the situation when in the morning, instead of their own face, the puffy face of a stranger with heavy swollen eyelids and slitted eyes appears in the mirror.
But as the day progresses, this unsightly stranger transforms: the swelling subsides and the face takes on its normal appearance. The reasons for this unpleasant morning phenomenon may be:
- diseases of the urinary tract, kidneys
- drinking alcohol and salty foods at night
- allergies to used cosmetics
- blood flow disturbance
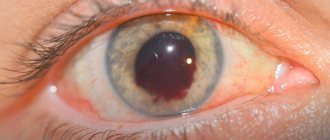
Sometimes swelling of the eyelids is accompanied by redness of the whites of the eyes, itching and a feeling as if sand had been poured into the eyes. The situation is extremely unpleasant and requires immediate treatment. Otherwise, painful wounds may appear in the areas of scratching, because the delicate skin of the eyelids is very easy to injure.
Eyelids swell and itch when working at a computer for a long time
But in order to begin treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause of swelling and itching of the eyes. The reason for this phenomenon may be:
- allergies (sometimes accompanied by a runny nose, lacrimation and even shortness of breath)
- infectious disease, conjunctivitis (may occur with discharge of pus from the eyes)
- stye - inflammation of the sebaceous gland
- blepharitis - inflammation of the edge of the eyelid due to a decline in immunity
- inflammation caused by dirt, dust, hypothermia under cold air flow (air conditioning, cold wind)
- congenital eye diseases: glaucoma, cataracts, corneal opacities
- contact lenses during the adjustment period or incorrectly selected lenses or glasses
- worm infection
- mosquito or other insect bite
There may be several causes of swollen eyelids in children, as well as in adults. The main ones are:
- conjunctivitis - the baby’s eyelids swell, the eyes itch, turn red, swell, and pus may come out of the eyes. Conjunctivitis can be either unilateral or bilateral. Drops of Tobrex and Levomycetin will help quickly. As a folk remedy, you can use rinsing with strong cold brewed black tea
- allergies - not only the upper eyelid swells, but also a small area around the eye. May be accompanied by lacrimation, itching, sneezing, and nasal discharge. It is necessary to give the child an antihistamine (Fenistil, Eden, Suprastin, Diazolin, Cetrin, Alerzin) as soon as possible and show it to an allergist.
- insect bite – important in the summer. Bites from mosquitoes, midges, and wasps in the upper eyelid can cause a similar reaction. Often the entire eye swells, there is redness at the site of the bite, and pain is noted. It is necessary to give an antihistamine and show the child to a doctor. Chamomile decoction is used as a folk remedy for rinsing. Gently wiping the eyelid with a weak soda solution will also help.
- barley - occurs when it is “blown” or “stretched”. It can also be a consequence of bacterial infection of the child’s body. Only a doctor should find out the cause and prescribe treatment. If in the first case warming up in the clinic can help, then in the second case you cannot do without an antibiotic. The site of inflammation is usually carefully cauterized with brilliant green, and also treated with antibacterial ointment twice a day. Under no circumstances should you try to squeeze out a stye for your child. This may lead to an even more serious infection.
- blow, bruise – a child’s upper eyelid may swell as a result of a bruise to the eye or upper part of the head. You need to briefly apply ice wrapped in a thin cotton towel or handkerchief (meat from the freezer will do) and go to the first aid station
If your newborn baby has swollen eyelids, do not immediately panic. Perhaps this is just a birth swelling that will go away on its own over time.
If the baby’s eyes and eyelids become swollen or swollen some time after birth, and after a while other parts of the body become swollen, the child has general swelling, which can be caused by:
- kidney disease
- liver dysfunction
- pathologies of the urinary system
- inflammation in the nasopharynx
- heart failure
- pathologies of the lymphatic system
- metabolic disorders
Allergies often affect the eyes, eyelids and surrounding skin. There is an inflammatory process that affects the membrane of the eye itself. Because of this, accompanying symptoms appear: burning, itching, redness, blurred vision, swelling of the eyelids.
The most common allergens that affect the eyes are:
- cold, low temperatures
- cosmetics
- pollen
- bird feathers
- animal fur
- medicines
To eliminate the unhealthy condition, you need to identify and remove the allergen as soon as possible and take an antihistamine (Ceterizin, Cetrin, Suprastin, Zyrtec, Eden). Apply drops of Lecrolin, Allomide or Allergodil topically. If allergic lacrimation and swelling of the eyelids is complicated by a bacterial infection, that is, discharge of pus from the eyes, it is necessary to add antibacterial eye drops, for example Levomycetin.
In cases of severe allergies, your doctor may prescribe hormonal eye drops or eyelid cream, such as Celestoderm or Advantam.
Lotions made from infusions of calendula, sage, chamomile and string will also help soothe irritation and relieve swelling of the eyelids. Cotton pads are soaked in the infusion and applied to the eyelids for several minutes. Then the disks are changed, and so on 5–7 times in a row.
If allergies are not treated, harmless swelling of the eyelids will soon lead to serious complications such as hyperkeratosis or keratitis.
Eden will help eliminate eyelid swelling and other allergy symptoms
In pursuit of fashion and beauty, girls have to pay not only with money, but also with their health. Understanding full well that eyelash extensions are not a harmless procedure, ladies continue to experiment with their own eyes. Trying to give the look sensuality and expressiveness, they sometimes get the opposite effect in the form of swollen eyelids and swollen eyes.
If after eyelash extensions your eyelids are swollen, it means that the body is trying to fight an unnatural pathological condition.
The main reasons why your eyelids may swell after eyelash extensions are:
- damage to the skin of the eyelids due to tools used
- allergic reaction to glue components
- use of cheap low quality materials
- rejection of a foreign body by the body
The first step is to get rid of artificial eyelashes as soon as possible. Eyelids cleared of glue will have to be treated for some time with special products, which will be prescribed by an ophthalmologist after assessing the situation.
You can use the following folk remedies yourself:
- Gently wipe your eyelids with cotton pads soaked in fresh potato juice for 3 to 5 minutes. Then apply nourishing cream to your eyelids
- Apply freshly prepared cucumber gruel to inflamed and swollen eyelids for 5 - 7 minutes 3 times a day
- Brew chamomile (1 tbsp) and oak bark (1 tbsp) in 1 tbsp. water, cool and strain. Pour the resulting liquid into ice cube trays and freeze. Gently wipe your eyelids with ice cubes wrapped in a cotton towel 3 to 4 times a day.
- Wipe your eyelids with a strong brew of black tea and make compresses 3 – 4 times a day
All of these methods will speed up recovery and contribute to the speedy restoration of the eyelids and skin around the eyes.
Permanent makeup allows a woman to always be “at her best” and significantly saves both time and money on purchasing decorative cosmetics. However, the tattooing procedure does not always go smoothly, and swelling of the eyelids is one of the most common phenomena when applying a design to the eyelids and eyebrows.
Swelling can be a natural reaction of the body to multiple micropunctures and the introduction of dyes under the skin. In this case, the swelling will go away on its own, and within a day there will be no trace of it left.
We suggest you read What to do if your baby spits up a lot
To minimize the negative consequences of permanent eye makeup, immediately after the procedure the eyelids are lubricated with Hydrocortisone ointment.
If after tattooing your eyelids are not just swollen, but also darkened or covered with crusts, severe itching appears, your eyes turn red and begin to water, consult a doctor. This is an abnormal condition that can only get worse.
Unfortunately, every woman is familiar with the situation when, after an evening spent in tears, the eyes swell and the eyelids become swollen. It is impossible to appear in this form at work or school, so urgent measures have to be taken to eliminate traces of grief.
The most effective methods are:
- Contrast washes - alternately applying cotton pads moistened with hot and cold water to swollen eyelids
- Tea compresses – moisten cotton pads with cold, strong tea leaves and leave on eyelids for 10 minutes
- Iced tea – freeze brewed black tea bags in the freezer, then apply to your eyes
- Diuretic tablets - if there is still enough time left before leaving home, take Furosemide, Diusemide, Trifas, Trigim, Veroshpiron or another diuretic drug
In this article
- viral and infectious pathologies of the organs of vision (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, dacryocystitis, barley, chalazion, etc.);
- allergic reaction to various substances;
- diseases of the kidneys, thyroid gland;
- traumatic injuries;
- demodicosis;
- taking certain medications to which the body reacts individually;
- complications of sinusitis, sinusitis and other similar diseases;
- a bite of an insect.
In this article
Allergic swelling of the eyelids in a child
Irritation can occur due to various substances.
Here are the most common factors that cause inflammation of the mucous membranes:
- Hay fever, or spring rhinoconjunctivitis, is an allergy to pollen from flowering plants. Occurs in the spring and summer season. Usually the reaction occurs to pollen from cereals, weeds and some trees (poplar, birch, alder). When allergen particles get on the mucous membrane of the eyes, reactive swelling of the eyelids often develops.
- Reaction to secretions of various glands of domestic animals.
- Food allergies. When consuming a product to which the body has an individual intolerance (often cereals, proteins), an allergic reaction occurs. Swelling of the eyelids may also be accompanied by a skin rash, upset stomach, and difficulty breathing as the throat becomes swollen.
- Reaction to certain medications.
- Insect allergy to insect bites, etc.
Any type of allergy in children is manifested by irritation and inflammation of the eyes, since the mucous membrane suffers first. Parents with redness and swelling of the eyelids should promptly consult a specialist to determine the cause. Allergic swelling can have dangerous consequences.
So, after an insect bite, reactive edema of the eyelids can develop within a short time - this is exactly what angioedema is called Quincke's edema. It manifests itself in the form of pronounced swelling on the lips, eyelids, cheeks, and oral mucosa. If the swelling spreads to the larynx area, then severe suffocation and death can occur. Due to the fact that in children under seven years of age the subcutaneous tissue is more pronounced, their tendency to swelling is an order of magnitude higher than in older children and adults, who are also at risk of such a reaction, but to a much lesser extent. Quincke's edema is dangerous because it sometimes develops very rapidly, and the baby requires urgent medical attention. In this case, reactive edema of the lower eyelid often occurs, in addition to the upper one. The child cannot open his eyes because the palpebral fissure closes.
The main treatment for allergies of various etiologies are antihistamine tablets and eye drops. The components included in their composition inhibit the effect of histamines on the body, which cause an irritable reaction. It is these substances that are responsible for the appearance of the most unpleasant signs of irritation - swelling, lacrimation, itching. In severe cases, intravenous corticosteroids may be prescribed.
Reasons why the upper eyelid may swell
What can cause eyes to swell? Swelling of the eyelids in the morning - one or two, without significant symptoms in the form of itching and burning, extensive swelling, often indicates a person’s disruption of sleep patterns and excessive visual strain. Also, the eyelids may swell due to excessive consumption of foods high in salt, which retains water in the body. In order to subsequently avoid such a phenomenon, it is necessary to protect the eyes from overwork, balance the diet, limiting the amount of salty, fatty and smoked foods, reduce the amount of salt consumed, and increase the volume of fluid.
Is your eyelid swollen? What could it be and how to quickly eliminate the swelling? Unfortunately, an unhealthy lifestyle may not be the only source of problems with puffy eyelids. Among the common causes are much more serious diseases caused by the activity of viruses, bacteria, weakened immunity, inflammatory and tumor processes. Two eyelids or one eyelid can swell at once.
Swelling of the eyelid - causes:
- allergies to pollen, dust, food, animal hair - with allergies, the eyelids of both eyes often swell, swelling of the entire face is also noted, and urticaria may appear;
- stye, boil, chalazion, dacryocystitis and other diseases of the eyelids - usually one eyelid swells, the disease should be treated only after consultation with a doctor in order to prevent complications;
- the eyelids may swell as a result of injury or tattooing - in this case, in addition to swelling, bluish hematomas will be visible;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system - with this cause of the disease, swelling of the eyelid is more pronounced in the morning, among the symptoms there may be swelling of the veins;
- difficult pregnancy - in the last trimester, many women have problems with their kidneys, which are under pressure from the fetus and amniotic fluid - the eyes, face and legs can swell because of this.
Swelling of the eyelids in a child due to viral and bacterial infections
Children suffer from infectious eye diseases several times more often than adults. Their level of personal hygiene is still quite low, and children often touch their eyes and mouth with dirty hands. This is a direct route for various viruses and bacteria that cause inflammatory diseases to enter the body: conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis, barley and other pathologies.
With viral and bacterial infections, swelling usually occurs in the upper eyelid, but in some cases swelling of the lower eyelid may develop. These symptoms include itching, lacrimation, severe hyperemia of the mucous membrane, and in some types of diseases - purulent discharge and other signs.
To treat bacterial infections, medications with antibiotics are prescribed, which are not absorbed into the blood, but act locally on the eye tissue, and therefore are completely safe for children. If there is no improvement within two or three days after starting to take the medications, then you need to stop using them and consult an ophthalmologist - he will prescribe another drug. Here is a small list of antibacterial drops and ointments that are used to treat childhood infections:
- "Tobrex";
- "Tetracycline";
- "Maxitrol";
- "Levomycetin";
- "Vitabakt" etc.
Causes
People often suffer from swelling in different parts of the body, which has many causes. Swelling in the eyebrow area is no different. The tumor can be caused by an external factor or an internal disease. The main reasons that can cause swelling of the eyebrows are considered to be the following:
NOTE. The information provided is not a substitute for an actual physical medical examination. Please visit your healthcare provider to determine the exact cause before starting medication.
Swelling due to illness and other factors
The first possible cause of eyebrow swelling is edema - this is swelling that occurs due to the retention of lymphatic fluid in the tissues and cavities of the body. In this case, a swollen eyebrow is the result of fluid leaking from the capillaries that are located around the eye. Symptoms appear gradually. This swelling may be caused by a hidden infection. Other possible causes include: prolonged sitting or standing, surgery, high altitude, sunburn, pregnancy, and complete lack of physical activity.
Serious medical conditions that can cause swelling are arthritis, pulmonary insufficiency, thyroid dysfunction, diabetes and liver disease. Associated symptoms will include:
- Swelling of the skin
- Itching
- Weight gain
- Increased heart rate
- Skin may appear glossy and tight
Treatment in this case most often involves eliminating the infection, if any. Otherwise, therapy will include:
- Diuretics are medications that help increase urination and remove excess fluid through the kidneys.
- Ranibizumab is a medicine approved in more than 85 countries that helps prevent and treat macular edema in diabetes.
- Control of blood vessel growth or therapeutic angiogenesis.
Injury
The eye is one of the most sensitive parts of our body. A hard object coming into contact with this area can cause damage, including a crack in the bone around the eye (orbital fracture), which can cause the eyebrow to swell.
Hard physical contact, such as a punch or ball to the eye, can cause this damage. A traumatologist should examine you and, depending on the extent of the damage, prescribe the necessary treatment.
Symptoms associated with orbital bone damage include red eyes, swollen eyebrows, and headaches. A combination of a warm compress and an anti-inflammatory will help relieve the swelling and pain it causes.
Epilation with thread or tweezers
While everything is clear with tweezers, not everyone knows enough about hair removal with a thread. This is an ancient method of hair removal that is more popular in the West. It is mainly done on the eyebrows for cosmetic purposes. This is one of the most hygienic treatments, no chemicals are used and the thread is only used once per person. This technique also reduces the likelihood of contact or atopic dermatitis, given that the only thing that comes into contact with your face is the thread.
Threading is an art and it is now becoming very difficult to find someone who can replicate the technique correctly. If done incorrectly, hair removal can damage the hair follicles, a condition known as folliculitis. Eyebrow pores can become clogged with dead skin cells and sebum or become swollen.
READ ALSO: How to visually hide a high forehead: successful women's haircuts
Eyebrow swelling caused by hair removal with thread or tweezers should not bother you. The symptoms will go away on their own in about a week. You need to keep your face clean and avoid further hair removal until the swelling goes down. Using a warm or cold compress twice a day will also help relieve swelling.
Botox injections
We all strive to maintain youth for a long time, especially women. Recently, cosmetic surgery and other facial procedures have become increasingly common. Research from one of the leading cosmetics companies has found that the number of people who resort to cosmetic procedures is increasing. One of these procedures is Botox injections.
Botox is used to treat certain muscle diseases and for cosmetic purposes to eliminate wrinkles by paralyzing the facial muscles. A drug made from botulinum toxin is injected into the facial muscles in specific locations.
When this procedure is performed poorly or too much Botox is injected, the muscles can swell. Therefore, Botox injections may be a likely cause of eyebrow swelling. Side effects of Botox include an allergic reaction, rash on the face and other parts of the body, itching, pain in the face or neck, muscle stiffness and nausea. If you experience the following symptoms, seek medical attention;
- Breathing problems
- Severe muscle pain
- Bladder control problems
- Itchy skin
- Vision problems
- Severe skin rash
- Irregular heartbeat
Ingrown hairs
Another reason for eyebrow swelling is ingrown hairs. This is a common occurrence among women due to the various methods they use to remove unwanted hair. These methods include waxing, tweezing, threading, and shaving.
When the above procedures are not followed properly, the hair follicles may become damaged. The pores become blocked, making it difficult for hair to penetrate the skin and it grows inwards. The pores can become filled with keratin, dead cells and tissue, forming a tumor, cyst or bump on the eyebrow.
Demodectic blepharitis
A common ophthalmological pathology, the causative agent of which is a mite of the genus Demodex. It measures 0.2-0.5 mm in size and is distributed in the ducts of the meibomian and sebaceous glands, at the base of the hair follicles of the eyelashes. Up to 25 individuals can live in one follicle, feeding on dead epithelial cells and gland secretions. This pathogenic microorganism is found in 90% of adults - they are simply asymptomatic carriers of it. However, when certain external factors arise, the mite becomes active, and then demodicosis begins to develop.
When demodicosis appears, the child begins to complain of burning and itching in the eye area, and these sensations intensify with heat (in the sun, in the bath), dryness and irritation. The edges of the eyelids are thickened and hyperemic. A characteristic initial sign of demodectic blepharitis is glued eyelashes, strewn with white particles at the base, as if frosted. Subsequently, pronounced swelling of the eyelids and ciliary edges occurs. With a long course of the disease, conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, trichiasis, and, as a result, dysfunction of the meibomian glands can develop. Elimination of demodectic blepharitis should be done in a timely manner so that it does not take an acute form.
For treatment, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of drops, for example, Carbachol, Acular, Okumetil, antibacterial ointments - Metronidazole, ointments - ichthyol and zinc, Tobrex, Tsipromed, antiseptics Vitabakt, Okomistin » as a prevention of secondary infection.
The most effective drops for the treatment of eye swelling
02.02.2019
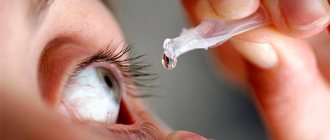
Eye swelling is a common problem. The reason may lie in allergies, infection, injury, previous surgery, or poor lifestyle. You can get rid of eye swelling using drops. This may be a universal drug or a medicine of a specific drug group. You need to use eye drops correctly.
Universal eye drops that relieve swelling
Such drugs are appropriate when the cause of ocular swelling is unknown or there are several negative factors at the same time. Universal drops are usually used as symptomatic treatment - they relieve swelling and a number of other unpleasant symptoms, but do not eliminate the cause of their occurrence.
Okumetil
These drops are considered antiallergic, but provide a complex effect thanks to three components in the composition: zinc sulfate, naphazoline hydrochloride and diphenhydramine hydrochloride. The combination of these substances provides a vasoconstrictor, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, astringent, and drying effect.
The drug is used for conjunctivitis, eye irritation accompanied by swelling, redness, itching, and foreign body sensation.
Okumetil (10 ml) costs an average of 200 rubles.
Antibacterial drops for eye swelling
Antibacterial drugs in ophthalmology are used to treat various infectious diseases. The patient can be prescribed a broad-spectrum medicine, but it is most effective to first identify the causative agent of the infection in order to select the most effective option in a particular case.
Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drops
Drugs in this group provide anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, which eliminate not only eye swelling, but also other symptoms. NSAIDs inhibit the action of the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which is involved in the production of prostaglandins involved in the development of the inflammatory process.
Antiallergic drops
These drugs are used for symptomatic treatment, as well as the prevention of allergic reactions. In addition to swelling of the eyes, allergies are usually accompanied by itching, watery eyes, and redness. Antiallergic drops can relieve these unpleasant symptoms.
This article will tell you how to choose the right eye drops for allergies.
Opatanol
These antiallergic drops are based on opatanol hydrochloride, a selective inhibitor of H₁-histamine receptors. This substance also provides a blockade of the release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells. The drug has a pronounced antiallergic effect and is prescribed for allergic conjunctivitis.
The cost of Opatanol (5 ml) is about 435 rubles.
Hormonal drops (corticosteroids)
Corticosteroid medications are often used for serious infections and autoimmune diseases. The advantage of corticosteroids is that they have a more pronounced effect. They provide anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and analgesic effects.
General rules for using eye drops
You need to use eye drops in accordance with the instructions, since different drugs may have their own application characteristics. Several general rules should also be highlighted:
- maintaining hygiene - before using the drops, be sure to wash your hands thoroughly with soap;
- During treatment, the use of decorative cosmetics and aggressive agents should be avoided;
- if a separate pipette is used to instill the drug, then it must be boiled each time or at least doused with boiling water;
- if the drops should be stored in the refrigerator, then they must be taken out an hour before use, otherwise the affected area may become hypothermic and the symptoms may worsen;
- when instilling, do not touch the eye with a pipette or dropper;
- while instilling the drug, you must lie down or tilt your head back - you must remain in this position for at least a minute after treating the eyes;
- when using several drugs in the form of drops simultaneously, wait at least 5 minutes between eye treatments;
- strictly follow the dosage regimen prescribed by the doctor or indicated in the instructions - duration of treatment and number of treatments per day;
- During treatment, contact lenses should be abandoned, especially for diseases of infectious origin.
Most ophthalmic drops have a shelf life of 2-3 years. This is only valid for unopened medicines. After opening the bottle, the drops can be used for a limited time - usually no more than a month. After this period, the drug cannot be used.
Eye drops are one of the main forms of ophthalmic preparations for topical use. They are used for the treatment and prevention of various diseases, allergic reactions and complications, including those accompanied by eye swelling. Eye drops must be used according to certain rules.
Source: https://telemedicina.one/zrenie/kapli-ot-oteka-glaz.html
Swelling of the eyelids in a child with barley
Children are often susceptible to this purulent inflammation because they do not keep their hands clean well and have the habit of touching their eyes with dirty hands and rubbing them.
Reactive swelling of the eyelids with this disease can occur even before the first pronounced symptoms appear. They turn red and swell, but the abscess itself (stye, or hordeolum) appears only after 3-4 days. When pressing with your fingers on the swollen eyelid, the child experiences pain. Sometimes the swelling is so developed that the eye stops opening.
2-3 days after the first signs of stye appear, a purulent head forms around the base of the eyelash, and the pain decreases slightly. After a day or two, the abscess opens, its contents come out, after which all symptoms gradually disappear. This process usually takes about seven days and leaves no scars or marks. But there are times when it leads to very serious consequences. Cellulitis of the orbit, sepsis, chalazion and other dangerous conditions may develop.
If parents notice swelling of the eyelids, they should definitely take the baby to the doctor and not self-medicate. You should also try to be with your child as much as possible during this time in order to control his behavior and distract him with activities if he tries to scratch his eye. It is important to prevent reinfection. To treat barley, antibacterial agents are prescribed.
Swelling of the eyelids in ENT pathologies
If complications develop due to inflammation of the sinuses, for example, with sinusitis or sinusitis, swelling of the eyelids may also occur. This is due to the close anatomical location of the nasal sinuses and orbit. If we are talking about children, then reactive swelling of the eyelids with these diseases is most typical for them.
If, with sinusitis or sinusitis, inflammation spreads to the orbit and the retina is involved in the process, then exophthalmos may be observed - protrusion of the eyeball forward, as well as to the side. The upper eyelid swells and noticeably increases in size and becomes very red. With severe swelling, the palpebral fissure may close completely. The child experiences noticeable pain in the affected eye, and the body temperature often rises to 38 degrees or higher. Visual acuity may also decrease. The progression of the disease can lead to atrophy of the optic nerve, swelling of the eye tissue, phlegmon and other complications.
For example, the danger of phlegmon is that it usually develops quite rapidly, sometimes in 10-20 hours, more often in babies of the first year of life or in children 7-9 years old. Phlegmon of the orbit of the eye is dangerous not only for vision, but also for the life of a small patient. When the purulent process spreads in the cranial cavity, meningitis, brain abscess, thrombosis, and sepsis develop.
If, against the background of acute inflammation of the nasal sinuses, the doctor notices severe hyperemia and swelling of the child’s eyelids, he will refer him to an ophthalmologist for a more complete diagnosis in order to exclude the spread of the inflammatory process into the orbit.
Traumatic swelling of the eyelids
Eye injuries can be of different types: chemical burn, mechanical injury, penetrating injury, etc. The degree of damage to the organs of vision in this case varies: from redness of the mucous membrane (for example, when contacted with soap) to severe damage to the eyeball due to contusions or penetrating wounds.
In case of injury, the eyelids, bones and tissues of the orbit, and the eyeball itself can be affected. Swelling of the eyelids occurs under various conditions. Even if an object during a mechanical injury did not directly touch the eye, but only adjacent structures (cheekbone, brow ridge), the swelling usually extends to the eyelids due to their high extensibility and the looseness of the subcutaneous tissue. They become red and swollen, and swelling may also spread to the other eye.
Swelling of the eyelids in a child with kidney disease
Edema due to kidney diseases is a very common phenomenon. Our kidneys work around the clock, removing excess fluid and toxins that accumulate as a result of metabolic processes. In addition, the kidneys regulate the acid-base balance, preventing the level of acidity in the blood. If the functionality of the kidneys is impaired, fluid begins to be retained in the tissues, which results in the occurrence of edema.
Reactive swelling of the eyelids in children can be a sign of a variety of diseases - ophthalmological, allergic, systemic, as well as a consequence of eye injuries. If swelling and redness of the eyelid occurs, you should take the child to a specialist who will make a diagnosis and prescribe proper treatment.