Cerebral hemorrhage is a process in which accumulated blood enters the brain matter .
This disease is quite serious and common, because according to statistics, cerebral hemorrhage ranks 2nd among other types of strokes.
Most often, this disease affects older people, but recently one can observe changes in the picture, according to which hemorrhage occurs in people over 30 years of age.
Basically, nothing can foreshadow a sudden cerebral hemorrhage; it usually occurs spontaneously during the daytime from physical overexertion or strong emotional experiences.
Often, such a disease can lead not only to paralysis of some limbs or the entire body, but even to the death of the patient.
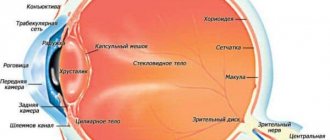
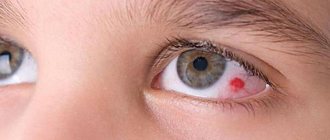
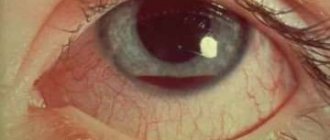
What is hemorrhage in the eye?
Damage to the small blood vessels in the eye causes the eye to become red or bleed. Depending on the location of the damaged vessel, the following are distinguished:
● subconjunctival hemorrhage. The vessels of the mucous membrane of the eye are damaged. As a rule, they are spontaneous and develop without an obvious reason.
● Hyphema. Hyphema is a collection of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye (between the cornea and iris). Typically the result of blunt trauma to the eye. Accompanied by severe pain and blurred vision. Such hemorrhage in the eye requires emergency care.
● Hemophthalmos. Vitreous hemorrhage inside the eye. In other words, internal hemorrhage in the eye. With hemophthalmia, a pronounced fog appears before the eye. In the case of complete hemophthalmos, vision loss occurs. Hemophthalmos is a severe eye lesion. Without treatment, permanent vision loss is possible.
● Retinal hemorrhage. Retinal hemorrhage develops as a result of bleeding from the vessels of the retina. The retinal tissue is very sensitive and thin. Therefore, even small hemorrhages can lead to significant vision loss and the development of retinopathy.
Consequences
If adequate assistance was provided in the first hours after the discovery of hemorrhage, this greatly increases the likelihood of a favorable outcome, but in some cases patients lose some of their basic vital functions.
As a rule, extensive hemorrhage in the brain has serious consequences - paralysis of one side of the body (right or left), less often an arm or leg.
Sometimes there is a disturbance in speech, facial expressions, and coordination of movements.
Despite this, if all necessary rehabilitation measures are carried out, although this is a very long process, the patient has the opportunity to restore at least partial capacity, which is already a very good outcome.
Causes of hemorrhage in the eye
There are the following reasons for the appearance of this symptom:
- Eye injuries.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye caused by viruses.
- Sudden and rapid increase in blood pressure.
- Severe cough, vomiting.
- Taking blood thinning medications (aspirin, salicylates, anticoagulants).
- Vitamin K deficiency.
- Blood clotting disorder.
- General diseases: Diabetes mellitus, Hypertension, systemic vasculitis.
- After eye surgery.
Blood emergencies
In memory of Seryozhka S., who became infected with HIV while giving birth to some drug addict on a train
APPENDIX 1
An emergency situation means contamination of the skin, mucous membranes, as well as the overalls of medical workers, equipment, table surfaces, and floors with blood and other secretions of the patient..
Blood is the most potent source of hepatitis B virus or HIV infection in the workplace.
Therefore, measures to protect against the hepatitis B virus and HIV infection consist primarily of preventing their transmission through blood, as well as vaccination against hepatitis B.
Although the modes of transmission of hepatitis B virus and HIV are the same, the risk of contracting hepatitis B virus in the workplace is higher than that of HIV infection (this is due to the fact that the concentration of the virus in the blood of HIV-infected patients is much lower).
Emergency model No. 1: damage to the skin (cut, puncture)
The probability of contracting HIV when puncturing or cutting the skin with instruments contaminated with HIV-infected blood is 0.3-0.5%. The probability of contracting the hepatitis B virus in this emergency situation is 6-30%.
If a cut or puncture occurs, you must immediately remove gloves or expose the wound area. Squeeze the blood out of the wound; wipe off the blood with a swab soaked in 70% alcohol. Then, if the wound allows, wash your hands thoroughly under running water with soap twice. Lubricate the wound with a 5% iodine solution. After 15 minutes, repeat the treatment with alcohol; cover with a bactericidal plaster.
Emergency Model No. 2: Blood on exposed body parts
The probability of contracting HIV when infected blood comes into contact with intact skin is estimated at 0.05%.
If blood (or other biological fluid) comes into contact with intact skin, immediately treat it with a swab moistened with a disinfectant solution or 70% alcohol solution for 0.5-1 minutes.
Do not rub! Then wash twice with warm running water and soap and wipe dry with a disposable napkin or individual towel. After 15 minutes, repeat the treatment with alcohol (for more details, see
file Hand treatment).
Emergency model No. 3: blood gets into the eyes, nasal mucosa or oral cavity
The probability of contracting HIV when infected blood comes into contact with mucous membranes is estimated at 0.09%.
If blood gets into your eyes, you should immediately rinse them with distilled water from a first aid kit to prevent HIV infection (or with a freshly prepared 0.05% solution of potassium permanganate - dilute 100 mg of potassium permanganate in 200 ml of distilled water). To wash your eyes, use glass baths: fill them with water or solution, apply to your eyes and rinse, blinking for 2 minutes. Drop 2-3 drops of a 20% albucid solution into each eye.
If blood gets on the nasal mucosa, you should immediately rinse your nose for 2 minutes in a freshly prepared 0.05% solution of potassium permanganate (dissolve 100 mg in 200 ml of water). Drop 2-3 drops of a 20% albucid solution into each nasal passage.
If blood gets on the oral mucosa, you should immediately rinse your mouth with 70% ethyl alcohol or a freshly prepared 0.05% solution of potassium permanganate (dissolve 100 mg in 200 ml of water) for 2 minutes.
Emergency model No. 4: blood got on a gown or other protective clothing
If blood gets on the gown, the overalls are carefully removed (rolled up with the contaminated side inward) and immersed in a disinfectant solution for the required time (use 5 liters of disinfectant solution per 1 kg of dry linen).
Then rinse in water and wash as usual. The skin under contaminated clothing is treated as indicated in paragraph “2” of these instructions.
Shoes are wiped twice with a disinfectant solution (hands are protected with gloves, the cleaning cloth is disposed of after disinfection).
Emergency model No. 5: blood on equipment, table surfaces, floor
If drops of blood come into contact with equipment or furniture surfaces, they should be immediately wiped with a cloth soaked in a disinfectant solution. Repeat the treatment after 15 minutes. The wipe is then disinfected and disposed of.
If there are large quantities of blood and liquids containing blood (for example, vomit) on the floor, you should wear gloves, moisten a rag in a disinfectant solution and collect the blood in a container. Then add disinfectant solution into the container in a ratio of 1:4. Exposure according to the instructions for the disinfectant.
The contaminated area is wiped again with disposable wipes soaked in a disinfectant solution. The treatment is repeated after 15 minutes. If there are large pools of blood on the floor, the use of disposable waterproof shoe covers should be considered; if there is a risk of splashing, glasses and a waterproof apron should be used.
When removing contaminated shoe covers and aprons, wear gloves.
Contaminated cleaning material should be soaked in a disinfectant solution (concentration and exposure time - see instructions for the disinfectant) in a ratio of 1:4, and then disposed of in accordance with the instructions for the disposal of class B waste.
APPENDIX 2
Contents of a first aid kit:
PurposeName and quantity
| For treating wound surfaces |
|
| To disinfect material that comes into contact with the skin |
|
| For disinfection of material contacted with mucous membranes |
|
| For instilling medicine into the eyes and nose | |
| To wash the eyes with a 0.05% solution of potassium permanganate |
|
| To stop bleeding | |
| Dressing |
|
Additionally, it is necessary to provide in the department:
- instructions for carrying out emergency preventive measures in case of emergencies;
- working disinfectant solutions in the disinfection corner, an irreducible supply of tap water for washing hands in a 5-liter container, toilet soap, individual napkins for blotting hands.
To clean up large pools of blood you may need: disposable waterproof shoe covers, rubber gloves, rags. If there is a risk of blood splashing, wear glasses or a protective face shield or a waterproof apron.
A first aid kit for the prevention of HIV infection should be stored in a separate labeled box in the treatment room. Responsibilities for monitoring the storage and replenishment of the first aid kit are assigned to the head nurse of the department.
Source: https://www.spruce.ru/infect/HIV/accident2.html
When should you see a doctor urgently?
Contact your doctor immediately:
- hemorrhage occurred simultaneously in 2 eyes at once
- sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- strong fog before the eye
- hemorrhage is accompanied by pain and decreased vision
- hemorrhage in the eye occurred as a result of an eye injury
- you are taking blood thinning medications
Treatment methods
If a patient is suspected of having bleeding in the brain, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible, and in no case should you move the patient yourself or allow him to move on his own.
The sooner you start treatment for cerebral hemorrhage, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome; basically, you need to carry out all the necessary procedures and examinations in the first few hours after the attack.
First aid
First aid should be provided by emergency physicians.
They must reduce or completely eliminate brain swelling with the help of special medications, stop the hemorrhage, normalize the patient’s blood pressure and, of course, deliver him to the intensive care unit or intensive care unit.
Treatment may also include surgery.
Basically, operations are carried out in the first three days after the discovery of the disease by a neurosurgeon.
In this case, a series of procedures are performed to remove excess blood from the aneurysm, which helps reduce intracranial pressure and increases the patient’s chances of recovery.
In addition to surgical intervention, drug treatment , which is mainly aimed at maintaining normal blood pressure and the general condition of the patient.
How to treat bleeding in the eye
Subconjunctival hemorrhage in most cases does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
If you experience pain and discomfort, your doctor may prescribe decongestant and anti-inflammatory drops. For concomitant eye infections, antibacterial or antiviral drugs are prescribed. As a rule, subconjunctival hemorrhage resolves within 2 weeks, without complications.
In other cases of hemorrhages in the eye, immediate treatment is required in an eye hospital.
Diagnostic techniques
In order to diagnose a cerebral hemorrhage, you need to carefully question the patient about his complaints.
If the patient has not retained the ability to speak adequately, it is necessary to find out from relatives whether he had high blood pressure, which could precede hemorrhage.
The main deviations can be noticed even with the naked eye; it is enough just to talk to the patient, ask him to move his arm or leg, so that we can definitely talk about damage to the brain tissue.
If the patient is unable to move independently or express himself verbally, this may indicate more serious brain damage.
In addition to the neurological examination, it is necessary to conduct a hardware examination.
Most often they use a computed tomograph , as this is a fairly effective examination method, with which you can not only determine whether the brain is affected, but also identify the size and location of the affected tissues.
In addition, other devices are used, such as MRI, which can show even minor abnormalities, but this device is quite expensive to use.
Drops to strengthen eye blood vessels
To strengthen the blood vessels of the eyes for various diseases associated with both external and internal factors, there are drugs in the form of drops. They are based on a vascular strengthening or angioprotective effect.
They not only restore the walls of damaged blood vessels in the eye, but also restore blood microcirculation in the structures of the eye, tissue nutrition and respiration. Descriptions of some of them are provided below.
Emoxipin
This is a synthetic antioxidant with a vascular strengthening effect. The latter property is expressed in the ability of the drug to increase the elasticity and strength of capillary walls in the structures of the eye.
In addition, Emoxipine has antiplatelet properties. That is, it reduces the adhesion of blood elements and the formation of blood clots. Thus, the viscosity of the blood decreases and its fluidity improves.
Reducing the permeability of vessel walls prevents the formation of hemorrhages. Available as a 1% solution in 5 ml dropper bottles.
It is widely used in ophthalmology for various pathologies:
- in case of circulatory disorders in the brain,
- with intraocular hemorrhages of various etiologies,
- for diabetic retinopathy, etc.
Emoxipine helps eliminate minor hemorrhages, strengthens the blood vessels of the eyeball, and reduces the permeability of the vascular walls. This leads to increased blood flow in the structures of the eye.
Under the influence of the drug, processes such as retinal dystrophy and diabetic retinopathy are suspended. Visual acuity improves, blood clots in blood vessels dissolve, and impaired blood circulation is restored.
The course of treatment ranges from a week to three months. The drug is instilled into the eyes, 1-2 drops three times a day.
Potassium iodide 3%
An antimicrobial and antisclerotic drug, promotes the resorption of hemorrhages into the vitreous body, restores damaged blood vessels, and acts as an antiseptic.
Apply 1-2 drops to the eyes two to four times a day.
Contraindications for the use of the drug are hypersensitivity to iodine, thyroid tumors, hemorrhagic diathesis.
Diclofenac
A drug with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Diclofenac is used as an element of complex treatment of intraocular hemorrhages. One drop is instilled up to 5 times a day for 1-2 weeks.
Hyphenation
The drug is used in a complex of therapeutic measures for the treatment of ocular hemorrhages. Promotes their rapid resorption and regeneration of eye tissue. The drug is instilled into the affected eye up to 8 times a day.
How to treat wounds of an infected person
During emergency care for a person with hepatitis C, it is necessary to prevent contact of your blood with the patient’s blood. It should not come into contact with exposed skin or mucous membranes. To protect yourself, you should:
- use rubber gloves;
- apply disinfectant solutions or ointments with cotton swabs;
- dispose of bloody bandages and cotton wool.
If contaminated biomaterial gets on the skin or mucous membranes, use strong antiseptics.
Treatment at home
Cold compresses and herbal infusions are considered the most effective for bruises in the eyes. Alternative medicine offers several effective recipes to solve this problem. By the way, all of them can be used for bruising in the eye in newborns.
- Compress with tea leaves. Prepare strong black tea, let it cool and soak a cotton pad in it. Apply damp cotton wool to the damaged eye for 15-20 minutes.
- Compress with chamomile. Pour boiling water over the dried flowers, let the product cool and brew. Then strain the resulting tea, soak a bandage or cotton wool in it and apply it to the eye. Leave the compress on for half an hour.
- Lotion with cottage cheese. Wrap the milk product in a bandage and apply it to the injured eye. The same compress using serum will be no less effective.
- Lotion with cabbage. The cabbage leaf must be crushed to a puree. The resulting paste should be wrapped in a bandage and applied to the eye. You can use freshly squeezed cabbage juice in the same way. This compress should be done several times a day to get a quick effect.
All of these remedies have proven themselves in the treatment of bruises in the eye. In a child, hemorrhage can be eliminated using any of them. The main thing is to follow all the rules for using the chosen product.
List of the best drops for hemorrhage
Considering the cause of such unpleasant symptoms, the doctor prescribes certain ophthalmic solutions in the form of drops. It is worth considering that they can only be used after a doctor’s prescription and follow the recommendations in the instructions. If adverse reactions develop, you should stop treatment and consult an ophthalmologist.
Emoxipin
The active ingredient of this medicine is methylethylpyridinol. Therefore, the drops have such a pronounced medicinal effect:
- produce an antioxidant effect;
- help strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- influence the normalization of blood clotting;
- reduce the risk of blood clots.
The drug has the ability to effectively eliminate hemorrhage. But there is a significant drawback - the risk of developing an allergic reaction. This causes itching, burning, and redness of the conjunctiva. The course of treatment lasts 1 month. Emoxipin should be instilled 1 drop 4 times a day.
When using several ophthalmic drugs, the interval between them should be 10-15 minutes. These drops are instilled last.
Taufon
The drug is widely used in ophthalmology. The active substance is the amino acid taurine. This component accelerates the regenerative processes of the mucous membrane and tissues of the eyeball. Additionally improves the functioning of membrane cells. Helps quickly eliminate hemorrhage and improve the patency of nerve structures.
In most cases, they are prescribed to eliminate the consequences that arose after a blow. Sometimes Taufon can cause an allergic reaction. Instill 1-2 drops 3 times a day. The course of drug therapy is 30 days.
Vixipin
The composition of this drug is similar to Emoxipine. Its use helps strengthen blood vessels. Prescribed for the prevention of thrombosis. Thanks to such actions, the elimination of hemorrhage is accelerated. Among the contraindications, it should be noted the presence of individual intolerance or hypersensitivity to the composition. It is prohibited for women to take during pregnancy and lactation.
Standard dosage: 1 pot 4 times a day. Treatment usually lasts 30 days, but in some cases it can be extended to 6 months.
Albucid
Antibacterial drops popular in ophthalmology. They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Prescribed for inflammatory, bacterial eye damage. Effectively help eliminate hemorrhage. Pharmacology offers a solution for children (20%) and adults (30%). Instructions for use: Albucid is instilled 2 drops 5 times a day, observing hygiene rules. The drug is well tolerated.
Potassium Iodide
This drug contains potassium iodide. This substance has a pronounced antimicrobial, antiseptic, and antiatherosclerotic effect. This promotes rapid resorption of blood clots. Treatment lasts 2 weeks. It is necessary to instill 1 drop 2 times a day. It is forbidden to take Potassium Iodide to patients with nephritis or thyroid dysfunction. Take only after doctor's prescription.
Diclofenac
The name of this drug is familiar to many. The main substance is sodium diclofenac. This component helps quickly eliminate hemorrhage, reduces swelling, redness, and pain. After the first instillation, a short-term burning sensation, uncontrolled lacrimation, redness, and an allergic reaction may occur.
Interaction with drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid is prohibited. Use Diclofenac 4 times a day, 1 drop. Treatment lasts 2 weeks.
Hyphenation
This drug is usually used as an adjuvant therapy. The active ingredient is hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Thanks to this substance, the mucous membrane is moisturized. In addition, it produces a protective function for tissues. Complex treatment with other ophthalmic drops speeds up the process of eliminating hemorrhage.
Promotes regeneration of mucous membranes and tissues. You can instill Defislez 8 times, 2 drops each. At the same time, maintain a certain time interval between instillations.
How to wash soiled items
In cases where the blood of a hepatitis patient gets on things, furniture, floors and other household items, disinfection is carried out. To destroy the virus, detergents containing chlorine additives are used. No less effective:
- Sanox;
- Santry gel;
- Sanfor;
- Domestos.
If clothes are dirty, wash them using rubber gloves in water at a temperature of 60°C. But it is best to boil it for at least 5-7 minutes. White items are soaked for 30 minutes in a chlorine solution.
Hepatologists recommend washing clothes of people with hepatitis separately from things of healthy household members. This will reduce the risk of contracting HCV infection to a minimum.