Stenosis of the lacrimal canal is a diagnosis that is quite common in newborns. Otherwise, this condition is called “standing tear,” since due to obstruction of the canal, the natural outflow of tear fluid does not occur. In our case, the problem turned out to be hereditary - almost 30 years ago, my parents also faced a similar diagnosis, made to me at the age of three months. Therefore, when my daughter’s eyes began to water, I had no reason to panic, because the most likely reason was already known.
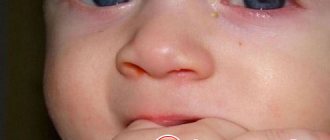
I noticed that the baby’s left eye began to leak while still in the maternity hospital on about the 3rd day. The neonatologist decided that the reason was that skin particles had gotten there. Just at this time, my daughter’s dry skin began to peel off, the top layer of which should have completely come off, so the theory could very well turn out to be correct. We were advised to wash our eyes with boiled water more often and after a couple of days we were sent home.
But regular rinses had no effect.
, and when the doctor came to us after discharge, both eyes began to water and even fester. We were prescribed drops and a decoction of chamomile or a weak solution of furatsilin to clean the eyes, since they were supposedly infected in the maternity hospital. A week later, despite following all the recommendations, things did not get better, rather, quite the opposite, and by the time the doctor visited us again, the eyes were already quite festered.
As a result, Lisa was prescribed two more types of eye drops, one of which was an antibiotic. The situation improved a little, but my eyes continued to water. The suspicion that infection is not a cause, but a consequence, became increasingly substantiated.
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself with quite specific symptoms, so it is not difficult for an experienced doctor to make an accurate diagnosis.
In general, patients or their relatives may notice the following symptoms characteristic of nasolacrimal duct stenosis:
- constant excessive tearing for no apparent reason;
- blurred vision;
- photophobia;
- the appearance of a tumor in the area of the corner of the eye, where the lacrimal sac is located, when pressed, purulent exudate is released from the lacrimal openings;
- over the affected eye, the eyelids are slightly drooping and the skin is red and hot;
- redness of the ocular conjunctiva due to the inflammatory process, which was caused by narrowing of the lacrimal canal and impaired fluid outflow;
The swelling in the corner of the eye grows over time, the skin over it becomes thinner and spontaneously opens, and a fistula appears in this place. This situation is quite dangerous for the patient’s life. Opening the tumor is accompanied by the release of pus, which spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body. And since the pathology develops near the brain, this can lead to serious consequences and even death. To prevent such developments, it is necessary to consult a doctor when the first signs appear.
Diagnostics
The initial examination in adults is carried out by a therapist (you can consult an ophthalmologist yourself). If a child is sick, parents should contact a pediatrician.
Diagnostic measures begin with a medical history, during which the doctor asks about disturbing symptoms. Then carry out:
- physical examination;
- tonometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- assessment of total tear production (Shimmer test);
- Ultrasound, MRI, CT scan of the sinuses;
- examination of the channel contents to identify bacteria.
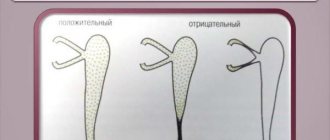
A collarhead test or Vesta test is mandatory. A dye is dropped into the eye. A cotton swab is inserted into the nose and wait 10 minutes. If during this time the cotton wool becomes colored, this means that the test is positive and the nasolacrimal ducts are passable. If the turunda remains clean, then we are talking about a violation of the patency of the canals.
Root canal treatment
The most important step during root canal retreatment is treatment of the affected area. For more reliable canal cleaning, modern dentistry uses instruments made from an alloy of titanium and nickel. The use of the latest tools allows you to efficiently clean the canal from infection and prevent further development of the disease. In some cases, special medications are used to remove the infection.
Our dentists (Chelyabinsk) have been successfully performing repeated root canal treatment for several years!
Our doctors have mastered the art of treatment using a microscope:
- Markova Natalya Aleksandrovna, Dentist-therapist.
- Evstunina Elena Nikolaevna, Dentist-therapist.
- Pankratova Dobryan Igorevna, Dentist - Therapist.
- Ignatova Elvina Nailievna, Dentist-therapist. Head of the therapeutic department.
- Leontyeva Anna Vasilievna, Dentist-therapist of the highest category. The specialist is certified training. Provided dental care to more than 2,000 residents of our city. Specializes in endodontic treatment using a microscope.
- Avdeeva Natalya Viktorovna, Dentist-therapist.
- Goldina Maria Sergeevna, Dentist-therapist.
To make an appointment, call us: 731-11-11!
Treatment methods
Some people try to eliminate dacryostenosis on their own, which is not recommended at all. The therapeutic method should be chosen by the doctor based on the degree of narrowing of the ducts. To treat stenosis of the lacrimal canal, it is washed with solutions of glucocorticoids, antibiotics, and proteolytic enzymes.
Obstruction is usually eliminated with the help of drops and ointments. They must be prescribed only by a doctor who will determine the dosage. Vigamox, Tobrex, Oftaquix, Levomycetin, Gentamicin and Dexamethasone ointments are usually prescribed. To wash the eyes, antiseptic solutions of Furacilin and Chlorhexidine are prescribed.
In more complex cases, the following procedures are prescribed:
- Intubation.
To do this, a tube made of polymer materials is inserted into the duct, through which excess liquid is drained. After 6 months it is removed. - Balloon angioplasty
. A tube is inserted into the narrow lacrimal canal, at the end of which a balloon is attached. It is carefully inflated, gradually expanding the walls of the ducts.
Massage
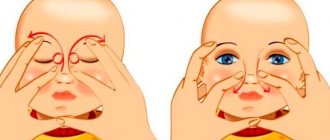
In childhood, narrowing of the lacrimal canal is eliminated with the help of massage, as a result of which the embryonic membrane ruptures and the patency of the lacrimal ducts is restored. The procedure boils down to 7-10 jerking movements of the inner corner of the eye.
Before performing a massage, you must wear sterile medical gloves. Wipe the child's eye with a cotton swab dipped in chamomile infusion from the temple to the nose. Carefully feel a small bump in the inner corner of the eye with your finger and begin to massage it. In this case, pus should be released, which should be removed by washing with antiseptics.
After completing the eye massage, Levomycetin drops or Vitabact are instilled. Massage should be performed 5-6 times a day.
If after 3 months of regular procedures the problem has not been resolved, the doctor will suggest an operation to probe the nasolacrimal duct. A probe is inserted into it, with the help of which the embryonic film is broken through. In particularly difficult cases, dacryocystorhinostomy is required.
What is tear trough contouring?
The tear trough starts from the inner corner of the eye and runs down along the nose. If it is in order, it does not stand out under the skin in any way. And if deformation begins, the defect clearly appears, and then the appearance of dark circles or tired, haggard eyes appears. The older a person is, the more the furrow sags and darkens. This problem occurs quite often, and previously it could only be solved with the help of blepharoplasty.
Modern cosmetology tries not to resort to surgical intervention, but to limit itself to injections of fillers to fill the groove of the tear trough and the surrounding area.
As a result, the procedure does not require long-term recovery, but the effect of the injections cannot last forever. Approximately once every 6-12 months the procedure must be repeated.
There are several drugs that are specifically adapted for injection into the tear trough for the purpose of its correction. They have increased density and low hygroscopicity (which is why swelling practically does not occur). High-quality gels should not cause allergic reactions. The following drugs are currently used in tear trough contouring:
- redensity;
- Yvoire;
- Restylane;
- Artefill;
- Sculptra;
- Radiesse;
- Juvederm.
Fillers in the nasolacrimal groove: what does the patient need to know? About this in the video:
Prevention
The congenital form of dacryostenosis cannot be prevented. The embryonal film is formed in each fetus during intrauterine development. And if it does not burst at the first cry of the child, you will need to eliminate it yourself or with the help of doctors. Acquired lacrimal canal stenosis can be prevented using basic hygiene rules. You should not touch your eyes with dirty hands, you should use contact lenses correctly and visit an ophthalmologist regularly.
These methods will prevent the development of dacryostenosis and will significantly increase the effectiveness of therapy when pathology is detected.
Dacryocystitis in newborns accounts for 6-7% of all cases of eye diseases. Violation of the outflow of tears provokes stagnation and inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis), and then conjunctivitis, due to which parents do not notice the true cause of the disease. At the same time, they struggle with the clinical consequences for months.
Constant crying is common for a newborn baby. But if you begin to notice problems in one or both eyes after sleep, signs of inflammation or discharge of pus, and the treatment you have chosen does not bring results, perhaps it is time to reconsider the diagnosis.
Obstruction of the lacrimal canal is observed in all newborns. This is an anatomical feature of embryo development. During the formation of the respiratory system in the mother's womb, the lacrimal canal is closed by a thin epithelial septum (film), which protects the baby's respiratory system from the ingress of amniotic fluid.
When the baby was born, took air into his lungs and cried for the first time, the film breaks under pressure, freeing the patency of the lacrimal canaliculi.
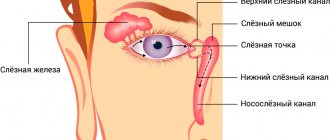
Tears are produced in a gland located under the upper eyelid. It washes the entire eyeball and accumulates in the corners of the eyes near the nose. There are lacrimal openings - these are two openings behind which there are lacrimal canals, the upper (absorbs 20%) and the lower (80%). Through these tubules, tears flow into the lacrimal sac and then into the nasal cavity.
A blockage, obstruction, stenosis, mucus plug or simply a narrow tear duct in a child that leads to stagnation of tears and subsequently becomes inflamed is called dacryocystitis.
There is congenital (primary) dacryocystitis in newborns, which manifests itself immediately after birth, and eventually goes away on its own in children up to one year old. And there is secondary (acquired) dacryocystitis, it does not appear immediately, does not go away after a year or longer, and is a consequence of blockage of the tubules after birth.
Tears are responsible for moisturizing the eye, nourishing the cornea, and contain dissolved immune complexes to fight bacteria that enter the eye from the air. Together with the lipid layer, tears form the eye film, which, in addition to protecting against drying out, reduces friction between the eyelid and the eyeball. Therefore, any narrowing or stenosis of the lacrimal canal disrupts the process of natural tear formation and natural circulation, which leads to complications.
Consequences of dacryocystitis in children:
- purulent, infectious conjunctivitis;
- decreased visual acuity;
- phlegmon of the lacrimal sac;
- the appearance of fistulas of the lacrimal sac;
- development and generalization of infection.
Canal probing operation – is it worth worrying about?
Probing of the lacrimal canal is usually carried out at the age of three months to a year (Lisa was already 5.5 months old). During the operation, performed under local anesthesia, a probe is inserted into the lacrimal duct, which pierces the film covering it, after which the canal is washed generously with a disinfectant solution. The duration of the operation is only 5-10 minutes.
I don’t think that surgery is always the best way out of a situation, and I’m even glad that in our country doctors have finally begun to believe that the best surgery is the one that was avoided. But in this case, I weighed all the pros and cons and decided in favor of probing. My opinion was largely influenced by the fact that I myself underwent a similar intervention as a child, which was relatively painless for me and without any consequences.
The older the child, the more stress he experiences from such manipulations, so to wait a few more months, subjecting my daughter to daily execution in the form of a massage (remember, 6 times a day!) and the risk of a new infection, and therefore taking antibiotics, I was not ready.
Even though surgery is always a risk. In this case, as a result of medical errors, bleeding, inflammation or scarring may have occurred, as well as the need for repeated probing.
For the niece of one of my good friends, the parents were able to clean the channel themselves. This took 7 months of active work.
Before probing, we had to take 2 blood tests, get a certificate from a pediatrician (or neonatologist) and a referral from an ophthalmologist from the children's clinic. This is unless you count a whole pile of photocopies of all kinds of documents. On the day of the operation, we had to arrive at the hospital in the city center by 9 am, so we took a taxi and, fearing traffic jams, ended up arriving much earlier. The doctor was another 20 minutes late. The procedure itself really took no more than 5 minutes.
. The fox was taken from me, taken to the office and almost immediately returned, bawling, but absolutely unharmed. They prescribed regular drops and copious rinsing of the nose 3 times a day to avoid re-clogging the canal due to swelling.
Dacryocystitis in newborns accounts for 6-7% of all cases of eye diseases. Violation of the outflow of tears provokes stagnation and inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis), and then conjunctivitis, due to which parents do not notice the true cause of the disease. At the same time, they struggle with the clinical consequences for months.
Constant crying is common for a newborn baby. But if you begin to notice problems in one or both eyes after sleep, signs of inflammation or discharge of pus, and the treatment you have chosen does not bring results, perhaps it is time to reconsider the diagnosis.
Obstruction of the lacrimal canal is observed in all newborns. This is an anatomical feature of embryo development. During the formation of the respiratory system in the mother's womb, the lacrimal canal is closed by a thin epithelial septum (film), which protects the baby's respiratory system from the ingress of amniotic fluid.
When the baby was born, took air into his lungs and cried for the first time, the film breaks under pressure, freeing the patency of the lacrimal canaliculi.
Tears are produced in a gland located under the upper eyelid. It washes the entire eyeball and accumulates in the corners of the eyes near the nose. There are lacrimal openings - these are two openings behind which there are lacrimal canals, the upper (absorbs 20%) and the lower (80%). Through these tubules, tears flow into the lacrimal sac and then into the nasal cavity.
A blockage, obstruction, stenosis, mucus plug or simply a narrow tear duct in a child that leads to stagnation of tears and subsequently becomes inflamed is called dacryocystitis.
There is congenital (primary) dacryocystitis in newborns, which manifests itself immediately after birth, and eventually goes away on its own in children up to one year old. And there is secondary (acquired) dacryocystitis, it does not appear immediately, does not go away after a year or longer, and is a consequence of blockage of the tubules after birth.
Tears are responsible for moisturizing the eye, nourishing the cornea, and contain dissolved immune complexes to fight bacteria that enter the eye from the air. Together with the lipid layer, tears form the eye film, which, in addition to protecting against drying out, reduces friction between the eyelid and the eyeball. Therefore, any narrowing or stenosis of the lacrimal canal disrupts the process of natural tear formation and natural circulation, which leads to complications.
Consequences of dacryocystitis in children:
- purulent, infectious conjunctivitis;
- decreased visual acuity;
- phlegmon of the lacrimal sac;
- the appearance of fistulas of the lacrimal sac;
- development and generalization of infection.
Causes
Obstruction of the lacrimal canal in a newborn or infant is explained by the lack of rupture of the protective film that was given to us at birth. Or the presence of accompanying adhesions or mucus plugs, which the newborn could not get rid of with the first cry.
Causes of dacryocystitis in newborns:
- anatomical underdevelopment of the lacrimal system;
- excessive tortuosity or narrowing of the tubules;
- anomaly in the location of the lacrimal sac;
- curvature of the bones of the facial skull;
- polyps, growths, tumors that physically block the outflow.
Dacryocystitis in older children occurs due to trauma, physical damage, inflammation, or as a complication of a more serious disease.
Symptoms of the disease
Blockage of the tear duct in children is often confused with the usual problem, and the wrong problem is treated for weeks. To distinguish conjunctivitis from dacryocystitis, you need to take a closer look at the newborn baby.
- You may notice that your newborn's eyes will occasionally tear from one or both eyes for no apparent reason when the baby smiles. This suggests that the tears simply have nowhere to go, and the excess flows down the cheeks.
- Then stagnation occurs. Dirty tears that washed the eyeball accumulate in the sac, forming a “swamp”. At this stage, the inflammatory process occurs, we see redness, swelling, swelling, all signs of conjunctivitis.
- At the next stage of dacryocystitis, the newborn’s eyes begin to sour, at first only after sleep, then constantly.
- Then they appear, and when you press on the swelling in the projection of the lacrimal sac, pus flows out of it.
- Over time, the process worsens, and antibacterial treatment gives only temporary results.
Diagnostics
Only an ophthalmologist can accurately diagnose dacryocystitis in newborns. At the first stage, if you suspect that the child’s tear duct is clogged, you can contact pediatricians at an appointment or a visiting nurse, and then you need to visit an ophthalmologist.
At the appointment, the doctor will examine the newborn, prescribe the necessary procedures, tests, and tests. Using a dye (collargol or fluorescein solution) and the Vesta test, the presence of blockage is checked. In this case, drops of dye are dropped into the eye and the time of their appearance is noted, as well as the amount on a cotton swab in the nose.
Sometimes it is necessary to consult related specialists and examine an otolaryngologist to determine the structure of the nasal sinuses or septum. If necessary, ultrasound, computed tomography of the facial bones, and laboratory tests are prescribed.
When inflammation occurs, a bacteriological sample of discharge from the eye is taken to determine the flora and sensitivity to antibiotics.
Video: Health Guide: Dacryocystitis
How to treat dacryocystitis in children
Dacryocystitis of newborns involves three treatment options:
- conservative methods;
- wait-and-see tactics;
- surgical intervention.
Your doctor will determine which treatment method is right for you when examining your newborn. Do not self-medicate or use unconventional folk methods. A newborn is not a field for experimentation.
Conservative methods of treating dacryocystitis include medications and massage. Combining these two methods can significantly speed up the healing process and alleviate the condition of the newborn baby.
Use drugs only in children's dosages and strictly follow the rules and techniques of massage.
Drug treatment
Obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct in children is treated mainly with drops and ointments. The choice of antibacterial agent should be based on seeding and seeded microflora. Drops are instilled during the day and after a massage, and ointments are placed behind the lower eyelid at night. The dosage and method of administration are prescribed by the doctor.
Drops and ointments for dacryocystitis for the treatment of newborns:
- "Albucid".
- Vigamox.
- Tobrex is often prescribed to infants.
- "Levomycetin".
- Gentamicin ointment.
- Dexamethasone ointment.
- Oftaquix.
- A solution of furatsilin or chlorhexidine for washing and wiping the eyes.
Before use, the drops must be warmed to body temperature in the palm of your hand or in a water bath. Since opened medications must be stored in the refrigerator, it will be very unpleasant for the baby to drop cold medications into the eye.
Video: Dacryocystitis or sour eyes in infants
Massage
How to pierce the tear duct yourself without surgery? The main method of treating dacryocystitis in newborns is. The movements resemble pressure from the corner of the eye to the tip of the nose along the nasal septum. This physically pushes out any blockages and helps the tubules free up.
Massage technique for newborns with dacryocystitis:
- First of all, you need to wash your hands, remove all jewelry, and trim your nails so as not to injure the newborn or cause an infection.
- If purulent discharge is present, first, using a bottom-up motion, it is necessary to squeeze out the purulent contents. Wipe your eye with a cotton pad or gauze soaked in an antiseptic solution.
- Then instill the antibiotics in drops and now push the drops from top to bottom through the tubules into the lacrimal sac and beyond. Drops must be instilled several times.
- Repeat these movements ten times, two to three times a day. At night, place ointment behind the lower eyelid.
Video: How to massage the tear duct?
Operation
Surgery is the most radical method for dacryocystitis in young children and is used only if previous methods have not worked. Patency is then surgically restored. The procedure takes place in a hospital setting, under local or general anesthesia.
If, after conservative treatment of dacryocystitis, the lacrimal canal in the newborn has not opened, use:
- Artificial puncture of the lacrimal canal in newborns.
- Canal plastic surgery for structural anomalies.
- Bougienage, probing the lacrimal canal.
The most popular is probing. In this case, a small thin probe is inserted into the opening of the lacrimal canal, which breaks through plugs, breaks films, adhesions, and also expands the patency of the lacrimal ducts. The procedure takes a few minutes, is painless, but unpleasant for a newborn baby. In some cases, probing is repeated after a couple of months.
Save the article about childhood dacryocystitis in your bookmarks and share it with your friends on social networks. This information will be useful to anyone who already has a baby or those who are just preparing to become parents.
Stenosis of the nasolacrimal duct is a pathology of the structure of the nasolacrimal duct, which occurs as a result of its chronic inflammation.
If left untreated, the risk of tear duct obstruction increases. There is a congenital form of stenosis pathology.
Pathology of the lacrimal ducts
Home / Treatment of diseases / Pathology of the lacrimal ducts
- Lacrimal ducts (canals): signs of obstruction
- Treatment methods for lacrimal duct diseases
- Cost of diagnosis and treatment of lacrimal duct diseases
- Make an appointment
- Useful articles
Lacrimal ducts (canals): signs of obstruction
Tear fluid is constantly produced by the lacrimal gland. Tears cleanse the eyeball and prevent the cornea and conjunctiva from drying out. The tear fluid flows through two pinholes into the lacrimal canaliculi. The lacrimal canaliculi unite into the lacrimal sac, which passes into the nasolacrimal canal. The latter opens into the nasal cavity, where tears flow, which becomes obvious during crying.
Many children are born with partial obstruction of the tear ducts, which is manifested by recurrent inflammation of the eyes, swelling and redness in the area of the lacrimal sac. In most cases, the patency of the tear ducts is restored spontaneously, without surgical intervention.
With congenital blockage of the tear ducts, the child experiences constant lacrimation and periodic purulent discharge from the eyes.
Acquired diseases of the lacrimal gland and lacrimal ducts can be the result of infectious diseases, inflammatory diseases of the eyes and nose, tumors and injuries.
Signs of obstruction of the lacrimal ducts can be very different, depending on the severity of the disease; as a rule, diseases of the lacrimal ducts begin with mucous or purulent mucous secretions, due to which inflammation of the lacrimal ducts occurs
The most common diseases of the lacrimal apparatus:
- dacryocystitis - inflammation of the lacrimal sac
- dacryostenosis - narrowing and inflammation of the lacrimal ducts
- canaliculitis - inflammation of the tear ducts
- congenital anomalies of the lacrimal ducts (aplasia, fistulas, diverticula, etc.)
- neoplasms (tumors) of the lacrimal ducts
- dacryoadenitis - inflammation of the lacrimal gland
It is necessary to treat diseases of the lacrimal apparatus, especially in the case of congenital pathology, in a timely manner, since the accumulation of tears can lead to suppuration and the spread of infection to the eye and brain.
Treatment methods for lacrimal duct diseases
In the conditions of Yekaterinburg there is an operating room for plastic and reconstructive operations in the orbit, on the adnexal apparatus of the eye (eyelids, lacrimal ducts, extrabulbar muscles). Operations are performed for friendly, paralytic, traumatic, and previously operated strabismus. Surgical correction of congenital developmental anomalies and acquired cosmetic defects is carried out - epicanthus, blepharoptosis, lagophthalmos; elimination of symblepharons, deformations of the palpebral fissure, entropion and eversion of the eyelids, dermoids and lipodermoids, fatty hernias, blepharochalasis.
Surgery of the lacrimal ducts using endoscopic and laser equipment is developing. Plastic surgery of the lacrimal canaliculi is performed in case of narrowing, eversion or atresia of the lacrimal openings, traumatic obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculi; various types of dacryocystorhinostomy, including laser intracanalicular and surgical endonasal endoscopic with intubation with silicone stents; endoscopic intubation methods for the treatment of stenosis of the nasolacrimal duct; lacorhinostomy with permanent intubation; probing for dacryocystitis in newborns.
When referring patients for surgical treatment of lacrimal duct obstruction, it is necessary to have a conclusion from an ENT doctor, excluding rhinogenic causes of the disease, and the results of computed tomography of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
In case of severe dry eye syndrome, obturation of the lacrimal openings is performed (silicone obturators from FCI, BVI).
In conditions requiring removal of the eyeball (lack of visual function with pain, threat of sympathetic ophthalmia or disfiguring appearance), along with traditional enucleation, in most cases, evisceroenucleation is performed with the implantation of various grafts using original technology to achieve a better cosmetic effect.
A relative contraindication to evisceroenucleation is the presence of a tumor process.
In case of anophthalmic syndrome, plastic surgery of the conjunctival cavity is performed with implantation of inserts made of various materials into the orbit (carbotextim, hydroxyapatite, polytetrafluoroethylene, Radiesse). When referring patients with anophthalmos for such interventions, a preliminary computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the orbits is necessary to visualize the anatomy of the orbit and the condition of the extraocular muscles.
Correction of post-traumatic dislocations of the eyeballs due to fractures of the orbital floor and walls is performed with plastic surgery of the orbital walls with titanium mesh and various implants.
For endocrine ophthalmopathy, diplopia is corrected by operations on the extraocular muscles, levator recession during retraction of the upper eyelid, and other operations.
For paralytic lagophthalmos and lower eyelid inversion, frame plastic surgery of the lower eyelid, recession with levatoroplasty of the upper eyelid, canthoplasty and other operations are performed.
When removing tumors of the orbit, eyelids, and bulbar conjunctiva, a radio wave knife “Surgitron” or “Wiftronic” is used, and a histological examination of the removed tumors is also performed.
Removal of pterygium is performed using traditional methods, as well as with barrier plastic surgery and transplantation of autolimbal flaps.
The following operations are performed in Ekaterinburg:
- Rinsing the lacrimal canals (tear ducts), bougienage and intubation of the canal with a temporary silicone tube to prevent secondary closure.
- Expansion of the tear ducts using a balloon (Dacryoplasty).
- Intubation (introduction into the tear ducts) of permanent tubes (Jones tube).
- Creation of bypass routes using drainage tubes -Dacryocystorhinostomy-DCR. The method is used when the canals are completely closed and in the absence of effect from the previous treatment. The operation can be performed endoscopically, through the nasal cavity.
Cost of diagnosis and treatment of lacrimal duct diseases
Vision diagnostics
Cost of vision diagnostics – eye examination:
| № | Name of service | Cost (in rubles) | ||||
| planned reception | extraordinary reception | |||||
| 1 | Diagnostic tests | |||||
| 1.1 | Comprehensive diagnostic examination * | 2 800 | 3 500 | |||
| 1.2 | Comprehensive diagnostic examination of children under anesthesia (patient) | 6 950 | ||||
| 1.3 | Repeated diagnostic examination using a short method on an outpatient basis and in a day hospital | 1 150 | 1 320 | |||
| 1.4 | Diagnostic examination using a short method in the early postoperative period - within 1 month (on an outpatient basis and in a day hospital) on the recommendation of the Center’s doctors | 600 | 700 | |||
| 2 | Diagnostic examinations in enhanced comfort conditions | |||||
| 2.1 | Comprehensive examination | 6 000 | ||||
| 2.2 | Examination using a short method | 3 500 | ||||
| 3 | Special methods | |||||
| Name of service | 1 eye | 2 eyes | ||||
| 3.1 | Quantitative threshold perimetry (accounting unit - eye) * | 800 | 1 170 | |||
| 3.2 | Ultrasound biomicroscopy (accounting unit - eye) * | 840 | 1 230 | |||
| 3.3 | Standardized echography of the eye and orbit (accounting unit - eye)* | 850 | 1 100 | |||
| 3.4 | Electrophysical studies (EPS) * | 2 450 | ||||
| 3.5 | Determination of the threshold of electrical sensitivity of the retina and lability of the optic nerve (electrophosphene) * | 440 | ||||
| 3.6 | Rinsing and probing of lacrimal ducts * | 1 370 | 1 750 | |||
| 3.7 | Endoscopy of the nasal cavity and lacrimal sac * | 1 170 | 1 170 | |||
| 3.8 | Optical coherence tomography of the anterior segment of the eye * | 990 | 1 120 | |||
| 3.9 | Optical coherence tomography of the posterior segment of the eye * | 1 030 | 1 280 | |||
| 3.10 | Examination of the anterior segment of the eye using a Scheimpflug camera | 970 | 1 220 | |||
| 3.11 | Analysis of material for pathogenic microflora * | 850 | 1 400 | |||
| 3.12 | Endothelial microscopy | 370 | 500 | |||
| 3.13 | Analysis of tear fluid osmolarity | 1 450 | 2 710 | |||
| 3.14 | Dynamic Pascal contour tonometry | 400 | 720 | |||
| 3.15 | HRT retinal tomography (accounting unit - patient)* | 1 100 | 1 100 | |||
| 3.16 | Study of tear production and drainage (patient) * | 220 | ||||
| 3.17 | Ultrasound B-scan of the eyeball * | 360 | 490 | |||
| 3.18 | Keratotopography | 640 | 840 | |||
| 3.19 | Scanning laser polarimetry (GDX VCC) | 660 | 1 140 | |||
| 3.20 | Fluorescein angiography** | 2 900 | ||||
| 3.21 | Confocal microscopy of the cornea | 1 080 | 1 350 | |||
| 3.22 | Indocyanine angiography | 6 900 | 12 900 | |||
*Free medical care for this service is provided in accordance with territorial programs of state guarantees of free provision of medical care to citizens of the Russian Federation if they have a passport and a valid compulsory health insurance policy (CHI).
**Currently, the procedure is not carried out (until the drug is registered in the Russian Federation).
Consultative and diagnostic appointments and surgical treatment of patients under the compulsory medical insurance system in Yekaterinburg are carried out by appointment:
— for residents of the Sverdlovsk region — based on a referral from an ophthalmologist,
- for residents of other regions of the Russian Federation - in the direction of a medical institution, certified by a seal.
The relevance of compulsory medical insurance policies can be checked on the websites of the Territorial Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund of your constituent entity of the Russian Federation, or by contacting the medical insurance organization that issued the policy. For residents of the Sverdlovsk region, the official website address is:
www.tfoms.e-burg.ru (section “Check policy”)
Treatment of lacrimal duct pathology
Cost of lacrimal duct treatment:
| № | Name of service | Cost (in rubles) | |
| In order | Out of turn | ||
| 1 | Surgical operations by complexity categories | ||
| 1.1 | Highest category* | ||
| 1.1.1 | Closed lacrimal duct reconstruction with temporary intubation with silicone drains | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.2 | Bougienage, probing of the nasolacrimal canal with closed temporary intubation with drains | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.3 | Open lacrimal duct reconstruction with intubation with silicone drains | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.4 | Lacorhinostomy with intubation | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.5 | Laser antegrade intracanalicular dacryocystorhinostomy with lacrimal duct intubation (LADCR+I) | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.6 | Endonasal endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with intubation (EDCR+I) | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.7 | Lacorhinostomy with implantation of lakoprosthesis | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.8 | Lacorhinostomy with permanent intubation | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.9 | Excision of scar tissue in the rhinostomy area with reintubation of the silicone system | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.1.10 | Repeated endonasal endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy | 28 900 | 36 200 |
| 1.2 | First category* | ||
| 1.2.1 | External canaliculo-cryocystorhinostomy with lacrimal duct intubation (NDCR+I) | 22 400 | 28 000 |
| 1.2.2 | Probing of lacrimal ducts under anesthesia for dacryocystitis of newborns | 22 400 | 28 000 |
| 1.3 | Second category* | ||
| 1.3.1 | External dacryocystorhinostomy without lacrimal intubation (DCR) | 13 300 | 16 600 |
| 1.3.2 | Extirpation of the lacrimal sac | 13 300 | 16 600 |
| 1.3.3 | Partial resection of the lacrimal gland | 13 300 | 16 600 |
| 1.3.4 | Surgical correction of narrowing, eversion of lacrimal openings | 13 300 | 16 600 |
| 1.3.5 | Activation of the superior lacrimal canaliculus | 13 300 | 16 600 |
| 1.3.6 | Plastic surgery of the inferior lacrimal canaliculus according to Sultanov | 13 300 | 16 600 |
| 1.3.7 | Implantation of a punctal obturator | 13 300 | 16 600 |
| 1.4 | Third category* | ||
| 1.4.1 | Suturing of the lacrimal punctum with autoconjunctival plastic surgery | 9 500 | 11 900 |
| 1.4.2 | Opening of phlegmon of the lacrimal sac with external drainage | 9 500 | 11 900 |
| 1.5 | Dacryocystorhinostomy using endoscopic technologies (cold plasma) | 60 000 | |
| 1.6 | Dacryocystorhinostomy using endoscopic technologies (laser, radio wave or shaver) | 37 800 | |
Attention!
The cost of treatment for one eye is indicated.
*
Free medical care for this service is provided in accordance with territorial programs of state guarantees of free provision of medical care to citizens of the Russian Federation if they have a passport and a valid compulsory health insurance policy (CHI).
Consultative and diagnostic appointments and surgical treatment of patients under the compulsory medical insurance system in Yekaterinburg are carried out by appointment:
— for residents of the Sverdlovsk region — based on a referral from an ophthalmologist,
- for residents of other regions of the Russian Federation - in the direction of a medical institution, certified by a seal.
The relevance of compulsory medical insurance policies can be checked on the websites of the Territorial Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund of your constituent entity of the Russian Federation, or by contacting the medical insurance organization that issued the policy. For residents of the Sverdlovsk region, the address of the official website is: www.tfoms.e-burg.ru (section “Check the policy”)
Useful articles
- Intervention that does not interfere (Business quarter No. 42 (852) 11/12/2012)
- It’s not dust in the eyes, or dry eye syndrome (Ural Medicine No. 3 (338) April, 2009)
- Secrets of Bright Eyes
Symptoms
When the nasolacrimal duct is narrowed, fluid is unable to leave the conjunctival sac in the usual way. It accumulates in the lacrimal cavity, and when it reaches the edges of the eyelids it pours out of the bag. Based on this, the main symptom of lacrimal duct stenosis is excessive lacrimation.
Due to the fact that the natural outflow of tears is disrupted, harmful microorganisms and mechanical particles remain in the lacrimal cavity, as a result, an inflammatory process occurs. This manifests itself in the form of redness of the conjunctiva of the eye. The lacrimal cavity enlarges, the skin over it becomes thinner. A swelling occurs at the inner corner; if you press on it, pus or mucus is released from the lacrimal opening.
Diagnostic procedures
The doctor conducts:
- Test for reflux of a dye solution from the tear ducts.
- Nasal test.
- Diagnostic lavage of the lacrimal canal.
To identify pathology, an x-ray with contrast is performed. If necessary, the doctor prescribes diagnostic probing of the tear duct. To assess total tear production, a Shimmer test is performed. Ultrasound examination, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography can determine the condition of the lacrimal ducts and lacrimal gland.
Treatment methods
The treatment method is chosen depending on the degree of narrowing of the nasolacrimal duct.
Drug therapy involves washing the lacrimal ducts with special drugs. To treat nasolacrimal duct stenosis, disinfectant solutions, antibacterial agents, glucocorticoids, and proteolytic enzymes are used. Laser using a mixture of helium and neon is effective in treating dacryostenosis.
Some doctors are against probing the nasolacrimal duct, arguing that this procedure is quite traumatic and its effect is insignificant.
For dacryostenosis, intubation of the nasolacrimal duct is performed. In this case, a tube made of high-quality polymer materials is used. The tube is inserted into the nasolacrimal duct and removed after six months.
Balloon angioplasty is an effective method of widening narrow tear ducts. To do this, a tube with a balloon is inserted into the nasolacrimal canal, which must be inflated so that the walls of the duct move apart.
When the nasolacrimal duct is blocked or narrowed, adults can develop a dangerous eye disease - dacryocystitis. Without proper diagnosis and quality treatment, this disease is fraught with irreversible consequences, which in advanced cases can even lead to the death of the patient. Therefore, in this article we will consider all aspects of this disease, symptoms and modern treatment methods.
Detailed description of the procedure
The most common question regarding the specifics of this procedure is: does it hurt? It is this factor that makes many people put off visiting the dentist until the last moment.
Modern equipment and innovative techniques reduce the discomfort from cleaning the tooth canals to a minimum, and all major activities are carried out with anesthesia.
The standard procedure algorithm consists of several stages.
Examination by a dentist
This step is very important in the success of the treatment, since the presence of voids or, on the contrary, excessive application of filling material is fraught with serious complications.
All root canals of the organ are hidden from the pulp chamber by a narrow passage, which visually looks like a small gap. Finding these orifices, as well as correctly determining their number, is the doctor’s main task when examining a tooth to be filled.
X-ray
X-ray examination of the organ affected by the pathology is a mandatory requirement , since the channels are characterized by different sizes, can be straight, or can be branched. And the direction of their growth is different in each specific case.
A photograph obtained as a result of X-ray irradiation allows the dentist to see the real situation and decide how to carry out the manipulation in the most efficient manner. And this procedure is absolutely safe.
Anesthesia
If the situation is not associated with aggravating factors, pain relief is carried out locally by administering an anesthetic injection.
Depending on the components of the drug, the effect occurs after 7–15 minutes . If the clinical picture requires additional surgical procedures, the patient can be given general anesthesia, before which a test for individual intolerance is taken.
Anesthesia not only eliminates pain, but also improves the psychological state of the patient during the procedure.
Insulation
The affected organ is isolated by using a special rubber device. This is a necessary measure that prevents the disinfectant from entering the oral cavity - the product is too aggressive and can cause a burn to the mucous tissue.
In addition, such an overlay prevents the penetration of salivary fluid into the cavity of the canals prepared for filling, since under the influence of anesthetic drugs salivary secretion is produced in excess.
Opening access to channels
To gain access to the canals, the doctor drills out the organ . If the situation allows, this is done directly in the area of the caries lesion. The manipulation is done extremely carefully, using special tools. The specialist first prepares the tooth cavity, and then removes a thin layer in the area of the pulp chamber.
Don’t know what to do if your tooth starts to crumble? We will tell you what to do first. From this article you will find out whether candidal stomatitis is contagious in adults.
Using Tools
The expansion of the canals begins by using the thinnest devices that are strong enough and yet flexible. The cavity is processed as follows: the dentist gradually screws the file into the cavity, increasing the diameter of the instrument.
This is done until the canal is completely free of pulp fragments. Thorough cleaning of them is the key to ensuring that no complications arise later.
Disinfection – dry cleaning
After the mechanical treatment of the organ fragments is completed, the doctor proceeds to disinfect the cavity, since a minimal amount of pulp tissue, as well as pathogenic microorganisms, still remain. They are washed with a special chemical, which is passed through the dental cavity and the canals are washed. The solution will neutralize the remaining soft tissue.
In many clinics, this procedure is performed using ultrasound equipment. Wave fluctuations deliver the train to the most remote areas of the canals.
Sealing
Before proceeding to the final stage of the procedure - filling the canals, they should be thoroughly dried . In order for the component that will fill the cavity to firmly set, its inner surface must be absolutely dry.
Modern materials used as a filling agent are subject to strict requirements. These must be high-quality hypoallergens, durable and reliable, with a high strength coefficient.
In addition, the filling must withstand temperature changes, not accumulate X-rays, but transmit them into the deep layers of the hard tissues of the organ. It must be resistant to the negative effects of aggressive compounds and acids contained in products and oral care products.
The following video shows how canal filling is performed:
Repeated x-ray
This is done upon completion of all manipulations so that the dentist can make sure that everything was done efficiently , the cavities are filled, and there are no fragments of medical instruments left in the canals, which sometimes happens.
Based on the results, the tooth cavity is closed and a permanent filling is placed. What it will be depends on the opinion of the specialist, the patient’s preferences and the capabilities of the clinic.
Do you know how to treat flux with antibiotics and how effective these remedies are? Here: https://dentist-pro.ru/lechenie/desny/gingivit/kak-pravilno-i-chem-vospalenie.html - we will tell you how to get rid of inflammation of the gums around the tooth.
Does your jaw click when you open your mouth? Possible causes for this phenomenon are listed here.
What it is?
Dacryocystitis is an infectious and inflammatory disease characterized by damage to the lacrimal sac of the eye. Typically, this disease is most often observed in people aged 30-60 years. In women, this disease occurs more often due to the narrower anatomical structure of the nasolacrimal ducts.
As a rule, in adults, the lesion with dacryocystitis is always one-sided.
The disease occurs due to blockage of the nasolacrimal canal. As a result, tear fluid accumulates in the lacrimal sac and cannot penetrate outside. Due to the disruption of the outflow of tear fluid, active proliferation of microorganisms occurs, which leads to inflammation and the formation of mucopurulent discharge.
Manifestation of dacryocystitis in adults
In adults, dacryocystitis occurs due to narrowing and closure of the nasolacrimal duct. Due to the narrowing of the channels, fluid circulation is disrupted. As a result of this, stagnation of the tear secretion occurs, in which microorganisms begin to actively develop.
Swelling of the tissues surrounding the nasolacrimal duct occurs as a result of inflammatory diseases of viral or bacterial origin (respiratory infections, chronic rhinitis, sinusitis).
The disease can also be caused by:
- fractures of the bones of the nose and orbit; damage and disruption of the integrity of the lacrimal canaliculi; nasal polyps; penetration of debris, dust and other foreign bodies into the eye.
Also, the following factors may contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- metabolic disease; diabetes; weakening of the immune system; allergic reactions; interaction with chemicals hazardous to the organs of vision; sudden temperature fluctuations.
The following clinical manifestations occur with dacryocystitis:
- constant lacrimation; mucopurulent discharge from the eyes; hyperemia and swelling of the lacrimal caruncle, conjunctiva and semilunar fold; swelling of the lacrimal sac; sore eyes; narrowing of the palpebral fissure; increased body temperature; general intoxication of the body.
Dacryocystitis can have an acute or chronic form of the disease. Clinical manifestations of the forms of the disease vary.
In the acute form of the disease, clinical symptoms manifest themselves most clearly.
In the area of inflammation of the tear ducts, sharp redness of the skin and painful swelling occur. Due to swelling of the eyelid, the palpebral fissures become very narrow or completely closed. The patient may experience pain in the eye area, chills, fever, and headache.
Advanced stage of dacryocystitis
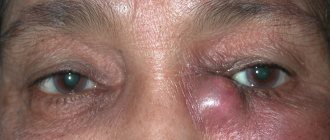
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by constant lacrimation and swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac. When pressing on this area, mucopurulent exudate is released from the lacrimal canals. A swollen neoplasm forms in the area of the lacrimal sac, visually resembling a bean.
As it develops, it becomes densely elastic.
Inside the cavity of this neoplasm, pus accumulates, which, when pressed, is released out. With further development of the infection, phlegmon of the orbit or fistulas may occur.
Plastic punctum
Plastic surgery of the lacrimal punctum is a surgical operation performed by excision of the inner edge of the lacrimal punctum and plastic surgery of the eyelid in order to eliminate pathologies of the lacrimal duct of the eye due to congenital developmental anomalies or injuries.
The content of the article:
- The course of plastic surgery of the lacrimal punctum
There are a number of pathologies of the lacrimal punctum of the eye that require surgical correction of this area. These include:
- absence of lacrimal opening;
- underdevelopment of the lacrimal opening;
- narrowing of the lacrimal opening;
- dislocation of the lacrimal opening;
- dry eye syndrome;
- pathology of the lacrimal ducts as a result of frequent damage to the conjunctiva by infectious diseases.
The above pathologies can be either congenital or acquired.
The absence of the lacrimal punctum is defined by the term “aplasia”, underdevelopment - “hypoplasia”, narrowing - “stenosis”. Both the lacrimal openings of each eye and one can be affected. In this case, the patient suffers from constant lacrimation and accumulation of tear fluid in the corner of the eye. However, with the normal state of the second lacrimal punctum and its optimal functioning, problems associated with pathologies of the first lacrimal punctum may not appear, which means that the operation will not be urgent.
Eversion of the lacrimal opening is also an indication for surgical intervention. It is this pathology that is the most common among those acquired, less common as a congenital abnormality. The state of the lacrimal punctum can be called normal when it is facing the eyeball and hidden by the lower eyelid. When everted, it is noticeable even without retracting the lower eyelid. Discomfort in this case is due to constant lacrimation. Like others, this anomaly can only be corrected surgically.
It is worth noting that plastic surgery of the lacrimal punctum can be carried out only after the formation of the lacrimal ducts, nasolacrimal duct, skull bones, and nasal cartilage has been completed. As a rule, this operation becomes possible once the patient reaches 14 years of age. Individual cases are determined by a specialist.
Plastic surgery of the lacrimal punctum of the eye is one of the operations of high complexity.
Initially, it is worth considering the structure of the lacrimal ducts of the eye. They consist of the lacrimal canaliculi, lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct. Tears are discharged into the nasal cavity using the nasolacrimal duct, into which the lacrimal sac passes into its lower part. Various pathologies of the lacrimal opening require their own algorithm for performing the operation. For example, when the lacrimal punctum is underdeveloped (atresia), the film covering it is pierced or cut crosswise. Thus, the specialist restores patency, then within two days the point must be bougienage.
With aplasia, the point must be formed and then connected to the lacrimal canaliculi.
Stenosis of the lacrimal opening is often accompanied by inflammation in this area, which is chronic in nature. Since in this case the operation is significantly complicated, initial treatment is required - rinsing the nasolacrimal duct. If this is not possible, intubation is performed with a specialized tube, and then the operation itself can be performed.
In the case of dry eye syndrome, surgical intervention can be avoided: initially, the problem is usually eliminated with conservative treatment, and if the required result is not achieved, the specialist is forced to perform surgical intervention.
Dislocation of the lacrimal opening is corrected by several methods. Fazakas' operations for dislocation of the inferior lacrimal punctum suggest focusing on excision of the lacrimal papilla using various methods. Operations using the Nemeth method are used for anterior and posterior dislocation and involve the introduction of a thin conical probe into the lacrimal canaliculi.
Most plastic surgery clinics in Moscow offer lacrimal punctal plastic surgery. Detailed information about them, including contact details and price list, is available on our website.
Diagnostics
In order to identify the disease, the patient must be examined by an ophthalmologist. As a rule, dacryocystitis is quite easily diagnosed due to its characteristic clinical symptoms. During the examination, the doctor conducts an external examination and palpation of the area of the lacrimal sac, performs the West lacrimal-nasal test, instillation fluorescein test, and radiography of the lacrimal ducts.
First of all, the ophthalmologist listens to the patient’s complaints and carries out an external examination of the lacrimal sac area. When palpating this area, purulent secretion should be released from the lacrimal canaliculi.
The most commonly performed test is the West nasolacrimal test.
It is one of the most common diagnostic techniques. During this procedure, a solution of collargol or protargol is instilled into the conjunctival sac. These staining substances are used to determine the patency of the lacrimal canal. A cotton wool or turundum swab is inserted into the sinus. Traces of the coloring substance should appear on the tampon no later than after 5 minutes. A delay in the entry of the substance into the nasal cavity or its absence indicates a violation of the patency of the nasolacrimal duct.
The degree of patency of the entire lacrimal drainage system, as well as the level and localization of areas of obliteration, are determined using contrast radiography. During this diagnostic method, iodolipol solution is used.
If it is necessary to identify microbial pathogens of dacryocystitis, bacteriological culture is performed.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient must undergo an additional examination by an otolaryngologist. As a rule, an otolaryngologist performs rhinoscopy for dacryocystitis. The patient may also need to consult a dentist, traumatologist, neurologist or neurosurgeon.
As a rule, if dacryocystitis is without complications, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Treatment of dacryocystitis, first of all, depends on the form of the disease and the causes of its occurrence.
The treatment process for dacryocystitis is generally divided into two parts:
- restoration of patency of the nasolacrimal canal; anti-inflammatory therapy.
When treating dacryocystitis in adults, bougienage and rinsing of the nasolacrimal duct with disinfectant solutions and the use of antibacterial drops and ointments are performed.
Bougienage is the most common, gentle method of restoring the patency of the nasolacrimal canal. During this procedure, the blockage of the nasolacrimal canal is physically removed using a special rigid probe (bougie).
Initially, patients suffering from dacryocystitis are prescribed enhanced antibacterial treatment to avoid infectious complications. This is necessary because with dacryocystitis there is a possibility of a purulent form of encephalitis or a brain abscess.
Dacryocystitis in old age
The acute form of the disease is treated in a hospital setting. As a rule, in this case, intramuscular injections of benzylpenicillin sodium salt
(3-4 times a day) or oral administration
of Tetracycline
(4 times a day),
Sulfadimezine
(4 times a day).
If an abscess of the lacrimal sac has formed, it is opened through the skin. Before opening the abscess, systemic vitamin therapy and UHF therapy are performed. After opening, the wound is drained and washed with antiseptic solutions of Furacilin, dioxidin, hydrogen peroxide
.
Levomycetin, Miramistin, sodium sulfacyl, gentamicin
) and antibacterial ointments (
Erythromycin, tetracycline, floxal
are instilled into the conjunctival cavity .
In addition to local treatment, systemic antibacterial therapy with broad-spectrum drugs is carried out. For this purpose, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, and penicillins are used.
In advanced forms of dacryocystitis, when standard drug treatment is ineffective, Dacryocystoplasty
or .
Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy
Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy
is a surgical procedure used to treat dacryocystitis in adults. Special modern minimally invasive equipment is used to perform the operation. Dacryocystorhinostomy can only be performed on patients who do not have an allergic reaction to anesthetic drugs. During the operation, a special flexible tube is inserted into the tear duct - an endoscope with a microscopic camera. An endoscope is used to make an incision in the blocked tear duct. The rehabilitation period after surgery is 6-8 days. To avoid inflammation of the cornea, he prescribes a course of antibiotics. The advantage of this operation is that it does not leave visible skin scars on the face or damage to the tear ducts.
Balloon dacryocytoplasty
In most cases, balloon dacryocystoplasty is used.
This is a safe operation that can be performed even on children over 1 year old. During the operation, a special thin conductor is inserted into the nasolacrimal canal through the corner of the eye, which is equipped with a microscopic expanding balloon filled with liquid. In a blocked area of the nasolacrimal canal, the balloon expands and opens the duct using pressure and is then removed from the canal. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. After the operation, a course of antibiotics and eye drops are prescribed to prevent the development of infection.
Complications
Dacryocystitis is a rather dangerous disease, since if left untreated it can cause various complications.
The chronic form of the disease is especially dangerous.
In this case, infection of other membranes of the eye is possible.
There is a possibility of developing concomitant diseases - Blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis
. With the further development of chronic dacryocystitis, the cornea is affected and a purulent ulcer is formed. As a result of the occurrence of a corneal ulcer, a cataract may subsequently develop, which can become not only a cosmetic defect, but also reduce the quality of vision.
Further development of the ulcer can also lead to endophthalmitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the internal structures of the eye.
A significant complication can be the development of life-threatening diseases that can lead to disability or death in the patient:
- sepsis; orbital phlegmon; thrombophlebitis of the orbital veins; thrombosis of the cavernous sinus; inflammation of the meninges and brain tissue.
Plastic surgery of the eyelid and lacrimal canal
Author: Erbol Hello. The fact is that 3 months ago (09/17/2017) I suffered a moderate injury. Namely, a rupture of the lower eyelid and tear duct in the left eye. As part of emergency care in the hospital, within 2 hours I underwent surgery to restore the integrity of the torn lower tear duct and plastic restoration of the torn lower eyelid of the left eye. The gap in the eyelid came from the corner of the eye (near the caruncle) and went downward in an arc. The length of the tear was approximately 1 cm. Also during the operation, a small ring ligature was applied to restore the function of the lacrimal duct. The ligature was a thin double thread made of some synthetic material (possibly nylon). The ligature passed into the lower lacrimal punctum and came out of the upper lacrimal punctum. The sutures on the eyelid were removed 11 days after surgery (09/28/2017). At the hospital I was told that the recovery period is 2 months and after this period the ring ligature from the eye will be removed. 50 days after the operation (11/06/2017), the ophthalmic surgeon removed the ligature and prescribed antibiotics. On the same day when the ligature was removed, the surgeon tried to wash out the lacrimal canal. But unfortunately, it turned out that the function of the tear duct was not restored. At that point, when 68 days had already passed after the operation, the ophthalmologist again tried to rinse, but the result was the same. When washing the lacrimal canal through the lower lacrimal punctum, the rinsing liquid does not pass into the nasopharynx and comes out back from the same lacrimal punctum. When the liquid is introduced through the upper lacrimal punctum (the upper lacrimal canal was not damaged), the liquid passes into the nasopharynx normally.
In the conclusion of ophthalmologist E.M. Molokotin. it is said: “The ligature has been removed from the tear ducts. The nasolacrimal duct is washed. Fluid passes through the superior lacrimal punctum. Through the bottom no.
An X-ray examination of the lacrimal ducts with contrast was also performed. The following assessment was received: “When administered through the superior lacrimal duct, the contrast passes into the nasopharynx. When administered through the lower lacrimal canal, the contrast partially passes into the nasopharynx, but is retained in the anastomosis of the lacrimal canals.”
Thus, when the ophthalmic surgeon rinses the lacrimal canals, the liquid does not pass through the lower lacrimal punctum and comes out back. However, according to the X-ray examination, for some reason it follows that the contrast passes, but is retained in the anastomosis. Since the contrast was introduced not only through the lower lacrimal opening, but also through the upper one (and in this case it passes normally), it is possible that the contrast that passed into the nasopharynx from the upper point confused the radiologist and he made an incorrect assessment.
I think it’s also worth noting that after the injury and surgery, and to this day, a small amount of light yellow, thick mucous discharge appears in my eye every day. About the size of a match head. This discharge accumulates in the corner of the eye near the caruncle. I remove them with a cotton swab.
I have a question. What can be done about the obstruction and how can the function of the lower lacrimal duct be restored. What is the most optimal surgical operation with the lowest probability of relapse in this case to solve the problem of obstruction? I also wouldn’t want to put the remaining working upper tear duct at risk.
Thank you.
Answered by: ophthalmologist at the Moscow Eye Clinic
Hello, Erbol! Your question has already been answered earlier. This condition is subject to examination by a plastic ophthalmic surgeon.
Make an appointment with an ophthalmologist
Fill out the form and get a 15% discount on diagnostics!