Probing or bougienage of the lacrimal canal is a procedure that allows you to get rid of dacryocystitis.
The disease is characterized by stagnation of tear fluid in the lacrimal sac and obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct.
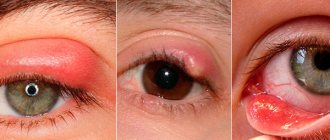
As a result, a good environment is created for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. The child experiences a painful swelling in the area of the lacrimal sac, narrowing of the palpebral fissure, swelling of the eyelid, and redness of the affected area. The use of antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory drugs only temporarily helps with dacryocystitis. Then relapses occur.
The frequency of complications depends on the age of the patient. According to statistics, probing of the lacrimal ducts in newborns is more successful than after a year. During the postoperative period, it is important to follow the recommendations and doctor’s orders and use prescribed medications.
Preparing a child for sounding
The optimal period for probing is a newborn or age 1-5 months. If the operation is postponed until a later date, the likelihood of complications increases, in particular, re-occlusion and the need for another probing. In addition, at a younger age the child does not feel pain or discomfort. As the film grows older, it hardens and its removal is not so painless.
Before piercing the canal, the child should visit an otolaryngologist. If a deviated nasal septum is detected, surgery is not advisable. Another surgical intervention is required.
Before surgery, the newborn should not be fed for 1.5-2 hours to prevent regurgitation. To prevent accidental movements of the arms and legs, it is advisable for children to swaddle tightly. If it is necessary to use medications, consult a doctor about their compatibility with the medications used during and after the intervention.
Before the operation, the following activities are performed:
- diagnosis of dacryocystitis, differential diagnosis;
- visiting a pediatrician to exclude diseases and inflammatory processes that serve as a contraindication to probing during a certain period;
- taking a general blood test;
- visits to an allergist to prevent the development of intolerance to anesthesia, adverse reactions, and identify possible allergies;
- analysis of the contents of the lacrimal sac, identification of pathogens for subsequent prescription of medications during the rehabilitation period after probing;
- blood clotting test;
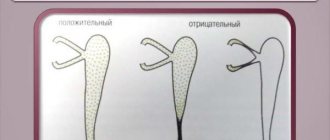
- determining the degree of canal blockage using the Vesta test, when a colored liquid is dropped into the eyes, a tampon is inserted into the nose, conclusions are drawn based on the amount of staining.
The limitation to surgical intervention is the acute stage of dacryocystitis, accompanied by copious discharge of purulent exudate. This is due to the danger of pus penetrating into the second, healthy eye, ear, and further infection.
Probing algorithm
The procedure is performed in a manipulation room in a clinical setting by a highly qualified ophthalmologist. During the preparation period, it is necessary to visit a professional otolaryngologist to exclude the presence of a deviated nasal septum. Also, before the procedure, the doctor must prescribe a blood test and a blood test for coagulation.
The duration of the procedure is a total of 5 to 10 minutes. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. Drops with an anesthetic effect are instilled into the eyes twice. After this, using a special conical instrument (Sichel probe), the ducts are dilated.
Next, the doctor takes a longer instrument (Bowman probe) and inserts it to the required depth, breaking the interfering film. After breaking the film, the doctor thoroughly rinses the tear duct and disinfects it. For this manipulation, drugs that are safe for the mucous membranes of the eyes and saline solution are used.
After all the manipulations have been carried out, the doctor makes sure that it was successful. To do this, the Vesta test is repeated. If drops of paint appear on the swab, this is an indication that the film has been successfully broken and the conjunctiva has been completely cleaned.
If massage and drug treatment do not help solve the problem, and the probing procedure is simply necessary, you will have to endure all the discomfort. This is especially true for small children. Although the procedure is carried out exclusively after anesthesia, the child will still cry - and this is a natural reaction of a newborn, since he is touched, a lamp is shining in his face, and there are strangers around him. After the procedure, the discomfort quickly disappears.
Progress of the operation
The duration of the surgical intervention is 5-20 minutes. There is no need to stay in a hospital. After probing, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and instructions and promptly come for an examination to an ophthalmologist at your place of residence.
At the beginning of the operation, the skin around the eye is treated with antiseptic and disinfectant medications in the form of solutions, and an age-appropriate local anesthetic is injected into the eyes.
To expand the lacrimal ducts, giving them an accessible and passable form for intervention, a Sichel probe is inserted into the lumen of the canal. Once the desired size is reached, it is removed and a Bowman probe of smaller size and diameter is inserted. The ophthalmologist moves it along the lumen of the lacrimal canal, thereby destroying the purulent plug.
At the end of the manipulation, the skin around the eyes is treated with a disinfectant, antiseptic solution, and the remaining plugs and pus are washed away.
Complete probing of the lacrimal ducts is determined by pouring disinfectant liquid through the nasal passage. If necessary, the procedure can be repeated.
Instead of a probe, a special small ball can be used. When it is filled with air, it passes through the tear ducts and breaks the integrity, removing the plug.
Risks and forecasts
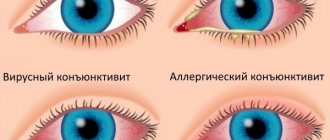
Often, parents of sick children confuse obstruction of the lacrimal duct with conjunctivitis due to some similarity of symptoms. Incorrect treatment of conjunctivitis begins immediately, which helps only for a short period, and the cause of the disease is not eliminated.
The consequences of such therapy are expressed in the accumulation of a large amount of pus and the baby’s poor health. Next, painful swelling and induration appear, and the newborn’s temperature rises and he becomes restless. Consultation with an ophthalmologist will help determine the exact disease and the need for surgical intervention.
A characteristic feature of dacryocystitis is the discharge of pus from one or both eyes . If the course of therapeutic massage does not produce results, it is necessary to operate the lacrimal canal. Indications for probing are also narrowing of the lacrimal canal and other pathologies in its development, the presence of a chronic process in the eyes, excessive lacrimation at any age.
In newborns, the probing procedure is prescribed from two months, but in severe cases the operation is performed at a younger age.
It is important to exclude the presence of pathological processes in the nasal septum before probing, so that there is no risk of developing complications after surgery. The prognosis is favorable, especially when contacting a doctor was timely.
Rehabilitation and post-operative care
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to monitor your general health, avoiding colds, ARVI, and follow the recommendations of an ophthalmologist.
To prevent infection, antibacterial drops and ointments are prescribed:
- Phloxal;
- Tobrex;
- Tobriss;
- Tobramycin;
- Vigamox;
- Vitabact;
- Levomycetin;
- Tsipromed and Tsiprolet (from 1 year).
The drops are used in a course determined by the doctor.
To wash the eyes before instillation, use an aqueous solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate of low concentration, chamomile decoction or tea leaves. All liquids should be at room temperature and freshly prepared.
After probing, you can perform the usual actions and procedures - wash your face, take a bath, etc. However, many experts advise monitoring the condition of your eyes for a month. Boiled water should be used for washing. Swimming in open water is not advisable.
For better results, after probing, massage of the lacrimal canals is necessary for 7 days or more. Before performing massage actions, mother needs to cut her nails short or file, wash her hands and wipe dry.
After probing, symptoms may persist: discharge for up to 1-2 days after surgery, lacrimation for up to 2-3 weeks.
Complications after the procedure
Any surgical intervention has its complications, and probing of the lacrimal ducts is no exception. After all, each patient has an individual body and each reacts differently to anesthesia and to the surgeon’s intervention. Among the frequent complications, it is worth noting scarring of the canal puncture site. The scar can cause re-clogging of the canal. In order to prevent scarring, it is necessary to follow the doctor’s recommendations as accurately as possible after probing.
It is important to closely monitor the condition of your eyes and the condition of the eyes of newborns (the disease is most often visualized in children from 3 to 6 months), and if you experience any discomfort, souring of the eyes, inflammation of the corners of the eye, be sure to consult a doctor . It is important to remember - no self-medication, as this can cause serious side effects.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
Possible complications and consequences
The likelihood of complications depends on the age of the patient, the neglect of the condition and the accuracy of following the recommendations and instructions of the ophthalmologist, and the characteristics of the child. Thus, after probing in children of the first year of life, adverse consequences occur only in 10% of cases, in the remaining 90% of cases there are no complications.
A few days after the intervention, provided the recommendations are followed, children’s eyes stop tearing and festering.
Possible complications:
- increased tearing after surgery;
- irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyelid;
- conjunctivitis;
- a small scar after bougienage of the lacrimal canal, leading to re-obstruction in the future;
- low risk of bleeding and infection, despite the safety of the operation, the absence of incisions and impact on vital organs;
- bleeding from the nose;
- nasal congestion.
If complications occur, you should not self-medicate; you should consult an ophthalmologist. A visit to the clinic is also required for the following conditions:
- temperature increase;
- weakness, lethargy, nausea and vomiting;
- profuse lacrimation that does not go away after 14 days;
- bleeding, redness of the eyes;
- conjunctivitis, purulent discharge from the organ;
- no tears when crying.
To prevent the development of consequences, the formation of adhesions and repeated obstruction of the lacrimal canal, it is important to promptly use eye drops and other prescribed medications, follow the doctor’s recommendations and regularly massage.
It is also important to avoid contracting colds during the rehabilitation period. To do this, do not contact sick people, do not visit crowded places, and limit your presence in kindergarten or school. In the postoperative period, the child is susceptible to bacterial and viral diseases, which can lead to relapse and the need for repeated probing.
After surgery, you should not rub or touch your eyes, except for rinsing and massaging.
Probing the lacrimal duct in young children
Dacryocystitis in young children
In a third of newborns, the tear duct is completely or partially closed by the so-called germinal film. As a rule, it disappears (resolves) on its own, but in some children it remains. This creates obstruction of the lacrimal canal and does not allow it to perform its function - draining fluid from the eye into the nasal cavity. The fluid stagnates in the eye and accumulates in the lacrimal sac (a small physiological cavity that is located between the corner of the eye and the nose). As a result, obstruction of the lacrimal ducts leads to inflammation against the background of stagnation - dacryocystitis.
Symptoms of the disease
In a child with dacryocystitis, the first thing that attracts attention is the constant stagnation of tears in the eye and lacrimation. When the inflammation turns purulent, in the morning accumulations of pus and crusts begin to appear, which stick the eyelashes together. If you press on the area where the lacrimal sac is located, then pus comes out from the lacrimal openings - they are located on the mucous membrane of both eyelids closer to the inner corner of the eye.
Subjectively, dacryocystitis is manifested by lacrimation and purulent discharge, but the eye may not bother the baby and remain “calm.”
In severe cases, swelling, edema, and redness form over the area of the lacrimal sac due to its inflammation. Such symptoms should alert parents, since it is important to consult an ophthalmologist in time to prevent a serious complication - phlegmon of the lacrimal sac. Therefore, treatment of dacryocystitis in newborns should be carried out before such serious disorders occur. Dacryocystitis can be unilateral or bilateral.
Treatment Options
Dacryocystitis can be treated conservatively and surgically.
For therapeutic purposes the following is carried out:
- Rinsing the nasolacrimal duct to restore its patency
- Massage the area of the lacrimal sac to “develop” the canal
- The use of antibiotics, in drops or systemically, to suppress the inflammatory process
- Probing the lacrimal canal in children under one year of age
- Opening of the lacrimal sac, or dacryocystostomy: used extremely rarely and only in severe cases of the disease
In most cases, treatment consists of probing the lacrimal canal in newborns, followed by lavage. The operation is carried out quite quickly and, when performed professionally, takes about 10 minutes. It is cosmetic and does not require hospitalization of the patient, but is carried out as follows:
- Anesthesia is performed
- Using a special conical probe, the doctor carefully expands the entrance to the canal; the end of the probe is blunt, so tissue damage is excluded
- Then, using a long thin thread probe, the specialist passes the entire length of the canal. This leads to the dissection of films and adhesions inside it, to the destruction of purulent and mucous “plugs” and the release of the lumen
- Finally, the canal is washed with sterile liquid under low pressure. Patency is checked by instilling a colored solution into the eye, which, if the canal is passable, should flow out of the nose. This completes the probing of the lacrimal canal in the infant.
The child does not need supervision.
What parents need to know
- Probing is a highly effective procedure that you should not be afraid of; Probing the lacrimal canal means saving the child from potential chronic dacryocystitis, problems with excessive lacrimation and other disorders in the future
- If signs of dacryocystitis appear in a child, you should consult a doctor.
- It is better to carry out probing before the patient is 4 months old; if the manipulation is performed later, a relapse of dacryocystitis may develop
- Before probing, you must undergo a standard examination: consultation with a pediatrician, general blood and urine tests, blood clotting test
- 1-2 hours before the procedure, the patient should not be fed or given water.
- After probing, you need to carefully monitor the child’s condition for 24 hours.
- On the day of the procedure, you should not bathe the child, walk with him, or give him a massage.
- Be sure to follow the recommendations given by the ophthalmologist on eye care and instillation of antiseptic solutions
Indications for reoperation
Repeated probing of the lacrimal canals is carried out if the first operation is ineffective - insufficient puncture of the plug, non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations in the postoperative period, a cold and relapse of dacryocystitis.
The technique of repeated probing is no different. In some cases, a silicone tube is inserted into the tear duct to prevent blockage. The tube is removed by a specialist 6 months after installation.
The postoperative period and care after re-probing are no different.
To prevent re-operation, it is advisable to puncture a child up to 5, maximum 8-12 months.
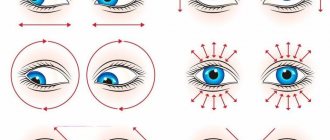
How to do a massage correctly: technique and execution scheme
During massage procedures, the baby should lie on a hard surface. The head does not need to be specially fixed. Actions must be fast and accurate. Each sliding pressure should be for 2 seconds and no more. The procedure will cause slight discomfort to the baby. It should be borne in mind that the older the baby is, the more painful the procedure will be. Lazy eye in adults can be a consequence of diseases such as astigmatism, myopia, and color blindness.
The baby's eyelid should be closed and drawn along it from the back corner to the bridge of the nose. This is done so that the mucous membrane is moistened and thus removes impurities. After light pressure on the eye sac, the finger should slide down to the wing of the nose. Such actions are repeated several times. When massaging in the area of the lacrimal sac, you can make stroking, jerking, vibrating movements. All actions must be careful and gentle, since in the first months of life there is no bone tissue in the sinuses of the nose. Reviews of eye drops aloe extract according to Fedorov can be found here.
massage scheme for lacrimal ducts in newborns
As a result of pressure, pressure increases in the nasolacrimal duct. This leads to a gradual thinning of the membrane and its rupture. During the procedures, pus may be released, which is removed with a cotton swab. It is necessary to ensure that the secreted pus does not get into the nose or ear. The discharge of pus indicates that the procedures were carried out correctly. The baby may cry. Therefore, there is no need to worry about this, since tearing will help flush out the pus. After the procedure is completed, the baby’s eyes are instilled with drops prescribed by the doctor. Vitobact and Levomecitin are usually prescribed. But analogues of Diclof can be found on our website.
The fact that a membrane rupture has occurred can be seen from the following symptoms. When pressing on the lacrimal sac, no pus will be released. Tears flow from both eyes. The baby becomes calm.
How to Avoid Probing
Piercing the lacrimal canal is performed when drug treatment for dacryocystitis and conservative therapy are ineffective. First, during the initial treatment, specialists prescribe eye drops, eye rinsing and a special massage. In some cases, following these recommendations gives good results and allows you to avoid probing.
For dacryocystitis, therapeutic massage is performed by a professional or mother after training. Duration, frequency and technique are determined individually. Massage movements are performed in light circular movements with the little finger.
Before performing a massage, you should cut your nails short, wash your hands thoroughly, and wipe dry. This reduces the risk of eye injury to the baby and undesirable consequences.
A special massage technique can improve the patency of the lacrimal ducts, remove purulent fluid and break through the gelatinous film. At the beginning of the procedure, the eyes are cleaned with a cotton swab with furatsilin. Then press up to 10 times on the area above the lacrimal sac and move it to the base of the nose.
After the procedure, it is necessary to remove the released exudate with an aqueous solution of chamomile or furacilin, or tea leaves. For this, only freshly prepared liquid at room temperature is used.
After cleansing the eyes, antibacterial drops - Tobrex, Tobriss, Vitabakt, Vigamox or others approved for age. It is extremely important to observe the dosage, frequency of use and duration.
Massage for newborns is carried out immediately before feeding or during up to 5-6 times a day for 14 days. If there is no improvement, you should not self-medicate or resort to traditional methods. Timely consultation with a doctor will help avoid complications and advanced forms of disease.
Lacrimal duct lavage in newborns
Due to the physiological characteristics of the structure, the nasolacrimal ducts of a baby can be blocked to a greater extent by a gelatinous film, which should self-destruct 15 days after the birth of the child. In standard cases, this process is not facilitated by medication - it occurs independently under the influence of tears.
However, the film does not always dissolve naturally, which may indicate its excessive density or a congenital anomaly in the structure of the skull or tear ducts. In such cases, doctors recommend postponing rinsing the baby's lacrimal canal. As a rule, the procedure should be delayed until the child is at least 2 months old. In some cases, ophthalmologists prescribe a special massage to the baby, which helps clean the tear ducts without additional intervention. In the first stages of therapy, the child's mother can massage the required area on her own. The set of exercises is not that complicated. For example, after each feeding, the mother massages the baby’s tear duct up and down with force 6-10 times. However, it is important to perform the massage correctly. It must be preceded by a mandatory consultation with a specialist.
If a set of exercises does not help, the lacrimal canal is washed in newborns. During medical intervention, before the procedure begins, the doctor administers local anesthesia to the child for pain relief.
A special rinsing kit is then used, which may include:
- Conical instrument (Zakhil probe);
- Bowman's probe, which has a pointed base (with its help, the doctor pierces the gelatinous film that interferes with the outflow of tear fluid);
- Special blunt needles, etc.
Before surgery, the lacrimal canals are disinfected with a solution. The final stage of washing involves disinfection by introducing antibiotics, which subsequently eliminates the risk of inflammation and the development of infectious diseases.
What to do if massage does not work
You actively massaged your child for 2–3 weeks, regularly instilled eye drops with the prescribed remedy, but recovery did not come, the tear ducts did not become patent.
Then you should try to break the membrane with an antiseptic solution. For this purpose, drugs such as Trypsin and Lidase are used, which are proteolytic enzymes and under their influence the membrane tissue can dissolve. They are introduced under pressure.
If this method does not help, the eye continues to fester, then you will have to resort to mechanical rupture of the membrane. This method is called probing. This procedure is performed with local anesthesia.
As a rule, after one such session, the disease is stopped. But you will have to use drug treatment and rinsing therapy for 3 months. It is better to carry out the probing procedure when your child has reached the age of 4 months. But sometimes the doctor decides to perform it earlier.
There are cases when even several repeated probings do not lead to a cure for this disease. Then, at an older age - at 2-3 years old - the introduction of special spacers into the lacrimal ducts and dacryocystorhinostomy are used. An anastomosis is formed, connecting the nasal cavity with the lacrimal sac.
Causes
Obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct can be caused by many reasons. Among them:
- Congenital narrowing of the canal, absence of the canal inlet.
- Inflammation of the lacrimal sac (dacryocystitis). Occurs when debris, foreign objects, or irritating reagents enter. Actively walking dogs and hunting breeds are especially susceptible. The most common cause of inflammation is grass seeds and plant thorns.
- Turning of the eyelids. In this case, mechanical injury and irritation of the mouth of the duct are observed.
- Infection.
- Allergy.
- Foreign object in the duct.
- Sinusitis, rhinitis.
- Tumor of the conjunctiva, middle eyelid, nasal passages.
- Glaucoma.