Enuresis is usually called urinary incontinence during sleep - nighttime and daytime. This unpleasant disease is diagnosed in children and adults at any age, but adolescents under 15 years of age (up to 3%) and older people are especially susceptible to it.
Cost of urologist services in our clinic
| Initial consultation with a doctor with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Consultative appointment with a doctor based on test results and ultrasound results | 500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys in standard mode and using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the bladder | 500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) | |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
Urologists say that nocturnal enuresis (NE) is curable in many cases, the main thing is to find the cause of the pathology. Therefore, do not hide the problem from doctors - make an appointment with a urologist and undergo an examination.
Why do people pee: the brain argues with the kidneys
The content of the article
The causes of urinary incontinence are well known: enuresis is caused by pathologies of the central nervous system, incoordination of the bladder and brain, nocturnal polyuria (increased urine production) associated with hormonal abnormalities, and kidney disease.
Hormonal causes of enuresis were previously practically not considered, but it is now known that hormone imbalance is the cause of almost half of the cases of the disease. Moreover, the failure can occur at any level - in the pituitary gland, thyroid gland or respiratory organs.
Thus, apnea (respiratory arrest due to adenoids, snoring, obstructive bronchitis, etc.) leads to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain (hypoxia), which in turn leads to a lack of production of vasopressin (ADH), a hormone responsible for the proper functioning of the kidneys.
The less ADH is secreted, the more urine is produced: some patients can accumulate up to 20 liters per night! No bladder can hold such an amount.
In addition, the lack of certain sex hormones leads to weakening of internal muscles, in other words, to their aging. The organs sag and put pressure on the bladder, reducing its volume. This phenomenon is often observed in women during menopause. It has been established that women suffer from enuresis three times more than men.
Scientists say that most patients with enuresis have genetic prerequisites for this. A gene responsible for the development of NE has been discovered. Another cause of enuresis is sleep disturbances, when the patient sleeps “like dead” and does not feel the urge.
How is urinary incontinence treated?
In case of urinary incontinence in women, appropriate therapy is necessary. If this is possible, drug treatment is carried out first. Certain groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Estrogens. They increase muscle tone, improve the elasticity of ligaments, and therefore are an effective remedy for stress urinary incontinence. Such therapy is carried out only if doctors confirm the fact of estrogen deficiency.
- Driptan and Spazmex are used for urge incontinence (overactive bladder).
- Antidepressants that show their effectiveness even in severe forms.
The list of medications is quite extensive, so they are selected based on a specific clinical case. You need to understand that many medications have contraindications and quite serious side effects.
Why you need to treat nocturnal enuresis
There is not a single person who would like to sleep in diapers or wake up in a puddle of urine. A constant smell, wet underwear and judgmental glances from even the closest people are the eternal companions of people with NE.
Patients with nocturnal enuresis cannot live a normal life: travel is excluded for them, and they have to sleep alone. This is oppressive, an inferiority complex develops, and the psyche is destroyed.
As for health, enuresis is often only a symptom of a disease that requires mandatory treatment, especially when it comes to the kidneys or hormonal imbalance.
About urinary incontinence in women at night
Millions of women around the world suffer from involuntary loss of urine during sleep, called incontinence. Women may leak a few drops of urine, while others may experience a strong, sudden urge to urinate before the fluid comes out in a large volume. Sometimes women experience both symptoms. For women, the risk of public embarrassment prevents them from engaging in many activities with their family and friends. Urine may leak involuntarily during sexual activity and cause emotional distress.
Urine leaking uncontrollably is always due to problems with the muscles and nerves that help temporarily hold or release urine.
How is nocturnal enuresis treated?
There is no magic pill that could be prescribed to every patient with NE, because the treatment method completely depends on the cause of the pathology. The doctor first sends you for tests (urine, blood) and diagnostics - ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys, x-rays. Then, having received the results, he draws conclusions. Sometimes the data obtained is not enough, then additional research will have to be done.
Treatment of enuresis can be conservative and surgical. If the cause can be eliminated without surgery, then enuresis is treated with medications and psychotherapy, otherwise surgical intervention is required. The help of a psychotherapist is often required even after treatment: many patients have difficulty getting used to life “without diapers.”
Drug treatment can include various drugs: hormonal problems are eliminated with hormone therapy, infections are usually treated with antibiotics. There are medications that reduce urine production at night and restore sensitivity to the nerves of the bladder.
As for operations, there are now many methods that correct pathologies of the urinary system, including low-traumatic ones. Such interventions are carried out through punctures in the abdominal cavity or natural access (urethra), so after them everything quickly heals and is forgotten.
Treatment with drugs and lifestyle changes
If it is not possible to achieve a positive effect when using special exercises, the woman may be prescribed pharmaceuticals. Their use allows you to eliminate involuntary urination. However, the use of such means will be effective only in cases where incontinence is provoked by urgent factors. If we are talking about stress incontinence, medications will not have the expected effect. Changing your usual way of life can also be effective:
- It is recommended to visit the toilet as often as possible in order to constantly leave the bladder empty;
- it is advisable to completely or completely reduce the consumption of alcohol and coffee, as they aggravate the problem;
- It is important to adhere to the drinking regime by limiting the amount of drink before going outside and before going to bed;
- The “leg-to-leg” pose, practiced by many women, contributes to the formation of pathology.
Special pads can also be a good help, although they cannot be classified as therapeutic methods. However, it is the doctor who decides on the final treatment option.
Our silicone urethral pessaries are an effective measure for the prevention and treatment of urinary incontinence. The products have passed all the necessary clinical tests and have all the necessary certificates and permits.
Are there pills for enuresis?
Urologists are often asked what medications should be taken for nocturnal enuresis in adults. This question can only be answered by knowing exactly the cause of the disease:
- A drug that contains antidiuretic hormone and reduces nighttime urine production may be prescribed.
- For neurotic enuresis, sedatives and mild antidepressants are prescribed.
- There is a method that involves taking combination drugs containing ephedrine. These powerful medications are available by prescription.
But it is not possible to cure enuresis with dietary supplements, since they do not contain real drugs.
What are the treatment methods?
At the initial stage, treatment methods are quite simple; surgical intervention, as a rule, is not required; conservative measures, non-drug and medicinal, are used:
- Kegel exercises strengthen muscle tissue.
- Special devices can be inserted into the vagina to stimulate the functionality of the organs with electrical impulses.
- Biofeedback therapy is carried out using sensors attached to the patient’s body. They transmit a signal to the monitor when the perineum is tense and relaxed, focusing on the resulting image, the woman learns to control the pelvic muscles.
- Another method of strengthening the muscular system is to place weights in the vagina, which need to be held there using muscle strength. As the muscles strengthen, the weights of the weights are increased, which allows you to develop self-control skills when urinating.
- As a therapeutic measure, it is recommended to normalize body weight, avoid smoking, which provokes coughing, and heavy physical activity.
- Drug therapy involves the use of antidepressants, hormonal drugs, and estrogens.
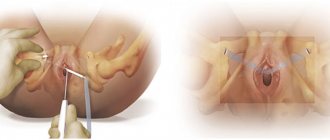
In the later stages, it is rarely possible to do without surgical techniques. Modern medicine prefers treatment using sling urethropexy with a synthetic loop. With this intervention, after inserting it into the patient’s body, the loop is placed under the urethra - the middle part of the organ - which allows it to be stretched to the required state. The surgeon makes the necessary adjustments and fixes the loop. The operation can be performed using local anesthesia. After the procedure, relapse is possible in 10-20%.
In addition to the loop, hydrogels can be used, which are inserted into the sphincter area. Such substances maintain weak muscles in the desired tone, organizing a locking effect. But this method has certain disadvantages - the biocompatibility of the drugs is too low, moreover, they quickly dissolve and can move in the tissues.
Also, to eliminate the pathological condition, anterior colporrhaphy, urethrocystoscopy, and an artificial sphincter are implanted. This list can be further expanded, since over 200 methods of surgical intervention have been developed for this type of incontinence.
It should be noted that the treatment methods for men are in many ways similar to those used in cases when it comes to the fairer sex. Men can be prescribed training of the muscle tissue of the pelvic floor using Kegel exercises, using the biofeedback method. They use behavioral therapy and quite actively use neuromodulation based on electrical stimulation, for which the nerve fibers responsible for the functionality of the urination mechanism are stimulated with very weak electric current discharges. Stimulation of the sphincters, the muscle tissue of the pelvic floor, is especially effective.
Urine leakage in men and women
Urine leakage in men and women usually begins to become more pronounced after the age of 60.
Urine leakage occurs much earlier in women than in men.
Most often, the disease manifests itself against the background of hormonal changes in the body (menopause in women), that is, during the transition to physical old age.
Urine leakage in men and women occurs for the following reasons:
- Diseases of the spine and spinal cord;
- For spinal injuries;
- For bladder tumors;
- With a neurogenic bladder;
- Serious inflammation of the bladder, which is chronic (tuberculosis);
- Prolapse and prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls;
- Difficult long labor, or, conversely, too fast labor;
- Gynecological surgery, such as removal of an interligamentous tumor, uterine extirpation;
- Operations that are endourethral in nature;
- Perineal injuries in women;
- Serious inflammatory processes in the genital organs of a woman;
- Prostate diseases in men, prostate adenoma and prostatitis.
Types and symptoms
The disease can be classified depending on its symptoms and etiology. The “nocturnal” subtype is called nocturia, when nocturnal diuresis predominates over daytime diuresis. Urine does not linger in a relaxed body. This phenomenon is not normal, even if you wake up when urine is released, or even during the process.
Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition where damaged nerves send signals to the bladder at the wrong time, causing the bladder muscles to contract without warning, causing urine to leak.
Symptoms of OAB:
- urinary frequency - bothersome urination eight or more times a day;
- Urinary urgency - a sudden need to urinate immediately;
- persistent incontinence - urine is released after a strong, sharp urge;
- nocturia - the patient wakes up at night to urinate, or urine is released directly during sleep.
Urinating up to seven times a day is normal for many women, but women with OAB may find that they need to urinate even more often, including while sleeping.
Functional
People with specific health problems that interfere with normal movement, communication, or decision-making may have difficulty choosing where and when to urinate. For example, a person with Alzheimer's disease may not think well enough to schedule a bathroom visit. It may also be difficult for a person in a wheelchair to get to the toilet on time. Functional incontinence is the result of physical and medical conditions. Conditions such as arthritis often develop in older women in nursing homes.
Overflow incontinence
Urine tends to leak out if the bladder is full. This occurs when the bladder does not empty properly, causing it to leak. Weak bladder muscles or a blocked duct can cause incontinence. Nerve damage from diabetes or other diseases can cause bladder muscles to weaken; tumors and urinary stones can block the urethra.
Other types
Combinations of different forms of incontinence are called mixed type. Most women do not have the pure form, and many studies show that mixed incontinence is a common type of nocturnal urine loss in women.
Transient incontinence is the temporary version. Medicines, infections, mental impairment and limited mobility can cause temporary incontinence. Severe constipation can cause temporary incontinence when affected stool presses on the urinary tract and obstructs flow. As a result, it becomes difficult to urinate on a schedule.