Urinary incontinence in older men is a syndrome that affects more than 13% of men aged 60 years and older. Effective and simple treatments can help you take control of your bladder.
Bladder problems are usually a topic of discussion for women. But they also affect men, especially those who have crossed the threshold of their 60th birthday. With age, the risk of experiencing urinary incontinence increases due to a decrease in kidney muscle mass. Metamorphoses also occur in the bladder and urethra due to natural aging. Taken together, this leads to the appearance of urological pathologies and associated unpleasant symptoms. In particular, older men often have an enlarged prostate, which causes urine retention and seriously impairs the normal functioning of the kidneys.
Male anatomy
To make it easier to understand the problem, you need to know how the male urinary system functions:
- The kidneys filter urine from the blood and empty it into the bladder, a hollow organ that holds fluid until a person feels the urge.
- When a man goes to the toilet, the pelvic muscles relax and the brain gives permission to the bladder to contract, squeezing fluid through the urethra.
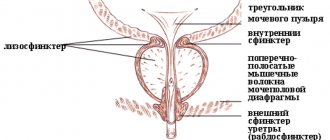
- When the bladder muscle contracts, the internal and external sphincters that hold the bladder channel (urethra) relax, allowing urine to pass. In men, the internal urinary sphincter is located just below the prostate gland, and the external sphincter muscle surrounds the entire urethra.
- The entire system is supported by the pelvic floor muscles, which run from the tailbone to the pubic bone (the front bone of the pelvis).
Urine is about 95% water and 5% waste. Some older men mistakenly believe that by drinking less fluid they will reduce the problem of incontinence (loss of urinary control). But urine becomes more concentrated (waste content increases to 10-15%) due to lack of fluid and can cause serious problems such as infections and dehydration. In addition, not drinking enough fluids causes constipation, which only makes the situation worse.
Types of male incontinence
In urology, types of urinary incontinence in men over 60 years of age are classified into several groups:
- Stress Incontinence - occurs due to natural physiological reflexes. Sneezing, coughing, and sudden exercise can trigger it. Often observed during heavy lifting or laughing.
- Urge Incontinence – characterized by a sudden desire to defecate and the inability to control the process before visiting the bathroom. Most often it occurs in patients suffering from diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, sclerosis or stroke survivors.
- Overflow Incontinence - Occurs when a small amount of urine leaks from the bladder. A man may have problems with incontinence if an enlarged prostate blocks the urethra. They provoke the appearance of diabetes syndrome and spinal cord diseases.
- Functional incontinence occurs in many older adults with normal bladder control. They simply have trouble toileting due to arthritis or other disorders that make it difficult to move quickly.
Fecal incontinence in the elderly - what to do?
Encopresis is characterized by loss of control over the act of defecation; feces are released randomly. If at first the problem is very small, gases and feces are released rarely and in small quantities, then if you do not seek specialized medical care in a timely manner, the disease progresses. There is a complete lack of control over bowel movements.
Fecal incontinence in the elderly
An elderly person can no longer go for a walk or go to the grocery store on his own; he has to use diapers and perform hygiene more often. In old age, doing all these manipulations becomes more and more difficult. A person needs help to bathe, get dressed, and change a diaper. The staff of the Long-Livers nursing home in Nizhny Novgorod will be able to help him with this.
Urinary incontinence in men - the main causes
The development of urinary incontinence in elderly men over 60 years of age is associated with many factors, both internal (diseases of the genitourinary system) and natural (aging). The following conditions most often form a pathological syndrome:
- chronic cough,
- constipation,
- obesity,
- genitourinary system infections,
- urinary tract obstruction,
- atrophy of the pelvic floor muscles and the bladder itself,
- dysfunction of the sphincter,
- prostate diseases, including cancer,
- neurological disorders that affect urinary control.
Bad addictions (smoking, alcohol abuse) and lack of normal physical activity have a negative effect on the functionality of the bladder. The risk group automatically includes men who have the following unfavorable factors added to their lifestyle:
- Age: Men are more likely to develop urological pathologies as they age. This is both the result of physical changes that make it difficult to hold urine, and side effects of certain diseases associated with old age, in which loss of bladder control becomes a secondary symptom.
- Lack of physical activity: Increased exercise can cause urine leakage. But, on the other hand, the lack of normal motor function increases the risk of weight gain, and, as a result, worsens the functioning of the bladder.
- Obesity: Excess weight, especially in the abdominal area, puts pressure on the bladder and causes leakage of urine.
- Concomitant diseases (prostate tumors, diabetes) and treatment can lead to temporary or chronic urinary incontinence.
- Neurological problems: Diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and multiple sclerosis can affect the brain's ability to properly signal the need to urinate.
- Birth defects: The urinary tract has not formed correctly.
Many men also experience short-term urinary incontinence after surgery on the prostate and genitourinary system in general.
Diagnosis and treatment
Urinary incontinence in men is a good reason to make an appointment with a urologist. To carry out diagnostics, he is obliged to familiarize himself with the patient’s medical history. The doctor will ask several questions related to your urination patterns. A physical examination will then be performed. A doctor can diagnose urinary incontinence based on your medical history and physical examination, but sometimes additional tests (such as urodynamic studies) may be needed. Treatment depends on the type of urinary incontinence the individual patient has. Prescribing effective therapy is the main task of the doctor. Our clinic in Moscow offers modern methods of treating the disease, which are successfully used all over the world. As a first line of treatment, your doctor may recommend the following methods to treat the problem:
- Lifestyle changes;
- Bladder training;
- Exercises on the pelvic floor.
Can also be used: Medicines; Fillers; Surgery; If the cause of the unpleasant symptom is prostate enlargement, the doctor prescribes one of the following medications:
- Alpha blockers. They relax the muscles in the prostate gland;
- Finasteride. It blocks the action of the male hormone testosterone on the prostate, causing it to shrink in size;
- Anticholinergic drugs. These remedies are used if symptoms are caused by an overactive bladder. They act directly on his muscles.
In addition, various combinations of drugs may be present. Depending on the cause, sometimes it becomes necessary to prescribe surgical treatment. In this case, surgery often involves removing excess prostate tissue to improve the flow of urine through the urethra.
| Code | Name | Price |
| 03.00 | Initial appointment with a urologist (candidate of medical sciences) | 2,000 rub. |
| 03.04 | Repeated appointment with a urologist (candidate of medical sciences) | 1,200 rub. |
| 03.60 | Initial appointment with a urologist (MD) | 5,000 rub. |
| 03.61 | Repeated appointment with a urologist (MD) | 3,000 rub. |
| All prices of the men's and women's health clinic | ||
Senile urinary incontinence in men after 70 years of age
The term “elderly person” is relative. A 70-year-old man living with a family and leading an active lifestyle is less likely to develop urinary incontinence syndrome. At the same time, a mentally and physically weakened 75-year-old single person can fully experience the consequences of age. The difference is small, but significant in terms of living environment.
However, most men who promptly report a problem to a urologist completely get rid of unpleasant symptoms, provided that the cause of the pathological condition is accurately determined. The first step is recognizing the problems that a 70-year-old man faces—this forms the basis of successful therapy.
When making a diagnosis, urologists often encounter several difficulties that may prevent them from prescribing adequate treatment:
- Negation
Older men often underestimate their incontinence. Experience shows that they view certain symptoms as normal consequences of the aging process and therefore unwisely omit the anxiety syndrome in a conversation with their doctor. In the case of an elderly patient who cannot adequately assess the primary signs due to stroke, dementia, or other pathological conditions, the closest relatives (guardians, neighbors, etc.) are interviewed in order to compile an accurate clinical picture.
- Physiological difficulties in urology
Most urodynamic studies are performed while the patient is awake so that he can personally assess and convey the sensation of bladder fullness and urge to void. Active patient participation during diagnostic procedures is necessary to accurately identify the cause. This may not be possible in some older patients due to illness or denial. Therefore, activities have to be rescheduled, repeated, or treatment is prescribed based on partial information.
- General condition of the patient
Urinary incontinence is significantly more common in men diagnosed with cancer, diabetes, heart failure, or neurogenic disorders. Comorbidities (vision loss, memory loss, decreased manual dexterity, cognitive dysfunction) or use of medications for other health problems make diagnostic evaluation and therapy more challenging.
Diagnostics
A thorough history is key, especially regarding urination and urine leakage, as this indicates the type of incontinence. Other important points include tension and discomfort, drug use, recent surgery and illness.
The physical examination will focus on looking for signs of conditions that cause incontinence, such as tumors that block the urinary tract, stool pressure, and poor reflexes or pain.
A frequently performed test is to measure bladder capacity and residual urine to identify poorly functioning muscles.
Other diagnostic measures include:
- stress test - the patient relaxes, then coughs vigorously while the doctor monitors urine loss.
- general urinalysis - urine is checked for infection, stones, etc.
- Blood tests - laboratory tests to look for substances associated with causes of incontinence.
- Ultrasound - used to visualize the kidneys and bladder.
- cystoscopy - a thin tube with a tiny camera is inserted into the urethra to view the inside of the urinary tract and bladder.
- urodynamics - various methods of measuring pressure in the bladder and urination.
Patients are often asked to keep a diary for a day or a week to determine their urinary patterns, noting the time and amount of fluid.
Help and care for incontinence in a nursing home for the elderly
Our home for the elderly and disabled provides meticulous care to each resident. We carefully ensure that each of our wards feels comfortable and cozy, both physically and mentally. Nurses help grandparents cope with difficulties and problems, provide hygiene, accompany them on walks, and take care of their skin. All our guests have their bed linen and clothes changed regularly. Cleanliness is the key to health, especially for patients with encopresis and incontinence.
Treatment of urinary incontinence in older men (after 60 years)
According to WHO medical statistics, about 200 million people around the world face the problem of incontinence. Almost 80% of men successfully undergo treatment and get rid of the syndrome. The main thing is to take the first step and consult a urologist.
There is no universal treatment regimen. Therapy will depend on the type, severity of the problem, and the patient’s lifestyle. Treatment measures begin with the simplest methods (exercises, developing useful habits). Many men after 60 years old regain control of urination by making a few lifestyle changes. If treatments don't work, drug therapy or invasive surgery may be tried. For some men, surgery becomes the last chance to return to a normal lifestyle and regain social connections.
Behavioral treatment
Kegel exercises for the treatment of incontinence are indicated for older men to tone the pelvic floor muscles. They aim to improve bladder efficiency, optimize muscle function and control urinary periods, significantly reducing urine leakage.
To obtain a positive result, it is necessary to repeat regular and correct contraction exercises for several weeks:
- First you need to find the right muscles to tighten them. To do this, it is advisable to sit down and take several tests. To identify them, it is necessary to imagine the situation and simulate the urge to urinate or release gas. If unsuccessful, it is better to seek help from a doctor or nurse.
- Once the muscles have been checked and pressure is felt on the back wall of the anus, the exercises can begin. At this stage, you need to take your time and stay focused, because contracting the “wrong” muscles will be of no use.
- Repeat the following exercises at least fifty times a day: contract the pelvic muscles, hold them and count to five each time. Release for five seconds and repeat. Additionally, the quick exercise involves squeezing and releasing your pelvic floor muscles as quickly as possible for one minute.
First, the exercises are performed in a lying position. When muscle exercises proceed according to all the rules, it is advisable to increase the load. A greater effect is achieved in sitting and standing positions. Patience is key with Kegel exercises. Only after 15-20 days will the first signs of improvement appear, and after 6 weeks it is possible to return to full control of the bladder.
Drug treatment
There are several pharmacological treatment regimens that have different effects on the ability of men 60 years of age and older to control their bladder. Some drugs are aimed at blocking the nerve signals responsible for urination, others slow down the filtration of urine, and others prevent muscle contractions of the organ. Most often, anticholinergic medications are prescribed to treat the bladder itself. The drugs are mainly used to treat incontinence. They block muscarinic receptors, which properly compress the bladder and reduce internal pressure. These are oxybutynin, trospium chloride, tolterodine, solifenacin and darifenacin. Side effects such as xerostomia (dry mouth), cognitive impairment and constipation may occur.
The doctor may also prescribe medications from the following groups for the treatment of incontinence:
- Alpha blockers
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Antispasmodic
The treatment regimen is developed individually and is kept under strict medical supervision. All drugs are available by prescription only.
Surgery
After exhaustive treatment with drugs, when the results obtained do not give the expected effect, surgical intervention is indicated. The goal is to eliminate chronic urinary incontinence in severe cases. Doctors perform three types of invasive procedures, depending on the severity and type of pathological syndrome.
- Treatment of prostate adenoma (benign tumor)
This is prescribed in cases of urinary incontinence due to overflow. The urethra can become clogged when the prostate gland is enlarged (adenoma) or when the urethra is narrowed (urethral stenosis). The surgeon performs an endoscopic resection to remove necrosis of the prostate or altered urethral tissue.
- AST balloon method against incontinence
It involves the placement of two inflatable and adjustable balloons implanted at the bladder neck to seal off the organ and prevent unwanted urine flow. The advantage of the operation is the ability to increase or decrease the swelling of the balloons by injecting saline.
- Placement of an artificial urinary sphincter
This surgical procedure is rarely prescribed for older men. Suggested for cases of severe and complex stress urinary incontinence. This is a prosthesis in the form of a silicone hydraulic ring located on the periphery of the urethra, which compresses it and is emptied using a pump. The method allows you to obtain satisfactory results - complete relief from the syndrome, urinary incontinence is eliminated.
Botulinum injections are also gaining popularity to treat urinary incontinence in cases of refractory bladder. It is injected into the bladder muscle in small doses when all other therapeutic measures have failed. Despite the effectiveness of the technique, it has not been fully studied and is currently the subject of research.
Alternative Treatments for Incontinence
In addition to traditional medication-based treatment or after surgery, the patient may also turn to solutions that involve maximal exercise to strengthen the perineal muscle, improve sphincter function, and reduce leakage.
The patient is prescribed a physiotherapeutic program of 10-20 sessions to reduce the perineum. Treatment of urinary incontinence in older men is carried out rectally.
Electrical stimulation for incontinence is also an effective way to reduce symptoms. A special probe is inserted into the anus to optimize the pelvic floor muscles and enhance the tone of the perineum.
Absorbent Products
Absorbent products, including shields, protective garments, briefs, and adult diapers, are the most well-known type of incontinence products. They are usually easy to get at pharmacies or supermarkets. The advantage of using them is that they do not require adjustment. Disadvantages of absorbent products are that they can be bulky, leak, have odors, and cause breakdown of the skin.