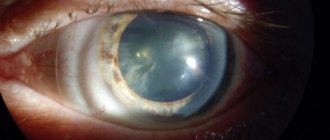
Diseases of the retina are variable, but most of them negatively affect vision, distorting visibility. They affect any part of the thin layer of tissue on the inner wall of the eye. Innovative retinal treatment in Israel helps get rid of unpleasant symptoms and restore vision.
The Tlv.Hospital company offers examination at the best Israeli clinics and subsequent correction of detected problems under the supervision of the country's leading ophthalmologists.
We guarantee increased attention to Russian-speaking patients, professional treatment methods, and the latest rehabilitation techniques at affordable prices. Having worked in the medical tourism market for over 10 years, we deservedly enjoy the recognition of thousands of people who have regained their health with our help.
What are the dangers of retinal diseases?
The retina contains millions of light-sensitive cells (rods and cones), nerve endings, which together provide visual perception of the world around us. The retina carries information to the brain via the optic nerve, allowing us to see. Therapy is provided for all types of abnormalities. Depending on the patient’s condition, the goals of treatment may be to stop degradation processes, slow down the pathogenic effect of pathology, and improve and restore vision. If you delay contacting a doctor or receive services from a non-professional specialist, there is a risk of loss of vision and complete blindness.
Symptoms of diseases
Most retinal diseases have similar features and manifest themselves with identical symptoms:
- Floating spots, feeling of cobwebs before the eyes.
- Blurred contours of surrounding objects, distorted features.
- Impaired lateral vision (darkening, glare, light spots).
- Loss of visual acuity.
If these signs appear, contact your ophthalmologist immediately.
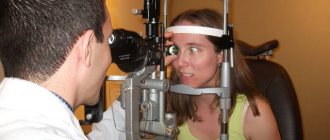
Diagnosis of retinal diseases
Retinal diseases can be associated with aging, diabetes, eye injury, and due to genetic factors. To make a diagnosis, a thorough examination is carried out, searching for abnormal areas of the structure of the visual analyzer. The following tests are used:
- The Amsler grid test tests the clarity of central vision. The doctor asks the patient which lines appear faded, broken, or distorted. Depending on this, the degree of retinal damage is determined.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) - This test is designed to provide precise images of the retina to diagnose epiretinal membranes, macular holes, and edema. Performed to monitor the severity of age-related wet macular degeneration and response to treatment.
- Fluorescein angiography - the doctor uses a dye to highlight the blood vessels in the retina under a special light. This helps identify closed, damaged, abnormal vessels, changes in the back of the eye.
- Indocyanine green angiography - profile dye lights up when exposed to infrared light. The resulting images show the blood vessels of the retina and choroid.
Ultrasound is performed to detail the internal structures of the eye, which helps identify certain tissue characteristics for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors. CT and MRI may be recommended to assess damage.
When is retinal surgery needed?
Surgery on the retina is a necessary measure in case of retinal detachment. During this pathological process, the inner layers of the retina are separated. As a result of this separation, fluid begins to accumulate in the eyeball. The extrascleral filling procedure is designed to bond the layers in order to restore vision to its functionality.
For mechanical injuries to the head and visual organs directly, which result in a rupture, the laser coagulation technique is used. This method is also popular in the treatment of peripheral retinal detachment. As a result of the intervention, breaks in the shell remain, but their edges are sealed with special coagulants. This operation is of an emergency nature when there is an urgent need to stop the progression of the disease.
Vitrectomy is performed in cases where the doctor identifies pathologies in the vitreous body. The operation is usually performed when there is extensive damage to the retinal layer, changes in the structure of the vascular system and hemorrhages in the localization of the vitreous body.
Main symptoms
If a person has a thinned retina, then he experiences the following clinical signs:
Redness of the organs of vision and dryness of the mucous membrane may be symptoms of the development of pathology.
- presence of black spots before the eyes;
- photophobia;
- lacrimation;
- headache;
- pressing sensations in the eye sockets;
- disturbance of general well-being;
- difficulty working with small objects and reading;
- inability to distinguish colors;
- sharp deterioration of vision in the dark;
- distortion of the shape of objects;
- redness and dryness of the eye mucosa.
Contraindications to surgery
Each of the above methods has its pros and cons. There is a special group of people for whom such treatment methods are contraindicated.
Contraindications to the vitrectomy procedure:
- clouding of the cornea of the eyeball;
- the appearance of white spots on the organs of vision;
- severe changes in the structure of the retina and cornea.
If these symptoms are detected, the vitrectomy procedure will not bring positive effects.
Contraindications to the extrascleral filling procedure:
- vitreous haze;
- swelling on the sclera.
Contraindications to the laser coagulation procedure:
- hemorrhage in the fundus;
- pathological changes in the vascular system of the iris;
- opacity of certain areas of the eyeball;
- high risk of increasing the area of delamination.
Retinal detachment is the separation of a layer of photoreceptor cells - rods and cones - from the outermost layer - the retinal pigment epithelium.
The procedure can also be refused if there is an allergic reaction to the anesthetic, or restrictions on anesthesia. Surgery for retinal detachment is not performed if the disease is in the stage of active inflammation. Before the procedure, it is necessary to conduct special tests, take X-ray photographs, and cure caries.
Factors provoking the development of pathology
The main cause of retinal dystrophy is natural wear and tear of the organs of vision and age-related changes in the body. But this phenomenon is not at all necessary in old age; not all older people develop dystrophy of the visual organs. The risk group includes:
- those suffering from diabetes mellitus, kidney and adrenal dysfunction;
- hypertensive patients;
- patients diagnosed with high and moderate myopia - in this case, the retina overstretches, becomes thinner in certain areas and ultimately ruptures;
- people prone to vascular diseases;
- victims of severe intoxication.
It has already been proven that dystrophic changes in the retina are caused by genetic predisposition and can be inherited. For this reason, children of parents who have been diagnosed with such a pathology should especially carefully monitor the condition of their visual organs.
This is interesting: according to research, atrophic changes in the retina are more common in females with fair skin and blue irises. Moreover, the symptoms of dystrophy often begin to express themselves clearly during pregnancy in women.
Carrying out the procedure
Laser coagulation
This operation does not require anesthesia, and its duration is up to 20 minutes. In specialized institutions, the operation is performed on an outpatient basis, and the patient goes home on the same day. The patient is observed in hospitals for one week.
During laser coagulation, instead of anesthesia, special eye drops and an anesthetic are used. After their application, the patient is injected with a drug that enlarges the pupil. As soon as the drug begins to act, the doctor installs a special optical lens that focuses the laser beams. With the help of such a device, individual rays are collected into a beam and directed to the area of detachment. As the operation progresses, areas appear where, as a result of protein breakdown, the retina is “soldered together.” Such “adhesions” will prevent further detachment.
The patient is placed in a special chair, in a sitting position. During exposure, slight discomfort may be felt due to the action of the laser, expressed in bright flashes of light. Some patients may experience dizziness or nausea as a result of these outbreaks. The process of complete adhesion of the detached areas takes about two weeks. After this period, the patient must visit a doctor to diagnose the results obtained.
Laser photocoagulation is used to limit the area of rupture and thinned areas of the retina
Extrascleral filling
Before performing this operation, the patient is prescribed bed rest. At rest, the liquid accumulated in the localization of the detachment forms a kind of bubble and acquires clear boundaries. This approach allows you to very accurately determine the areas that need to be affected.
The operation consists of several stages. First, the outer layer of the eyeball is cut. Using a special device, pressure is applied to the sclera of the eyeball. After the sclera is tightly pressed to the retina, the doctor marks all damaged areas and makes special fillings.
The main material for their manufacture is most often silicone. This filling is installed under the retina and adheres to the sclera. To prevent the filling from moving, it is secured with special threads. The liquid that accumulates at the rupture sites is absorbed by the pigment layer. In the later stages of the disease, when its amount is several times higher than normal, an incision of the sclera may be required in order to remove it.
Sometimes additional mesh fastening may be required. In such cases, a special mixture of gases is pumped into the vitreous body. In order for the gas to reach the required point, the patient must focus his vision on a certain point indicated by the doctor. In situations where it is necessary to restore the volume of the vitreous body, an isotonic solution is injected into it. After all the manipulations, the outer layer of the eyeball is sutured.
The extrascleral filling procedure is highly complex, and can only be entrusted to a true professional. In ninety-five percent of cases, specialists are able to succeed and stop retinal detachment. The main point in this issue is the timely detection of the disease.
Scleral filling is the bringing together of the layers of the retina by creating an area of scleral depression from the outside.
Vitrectomy
This method of surgical intervention is performed in a hospital, and most often has the nature of additional treatment after extrasleral filling. The procedure is performed under anesthesia.
The doctor makes holes in certain areas of the sclera. Special tools are inserted into these holes. After this, the specialist begins to directly influence the vitreous body, partially or completely removing it. Instead, a special mixture of gas or silicone oil is installed.
Treatment
The prescribed treatment is directly influenced by the degree of development of the pathology and its type. Unfortunately, in advanced cases of the disease, it is not possible to restore the original quality of vision. To treat the disease in its onset stages, medications with vasodilating properties are used. In addition, vitamin complexes and drugs that strengthen the body’s vascular system are prescribed. Very often, specialists allow the possibility of using physical treatment methods. Such techniques include:
- therapy using microwaves and ultrasound;
- laser therapy;
- influence using electrical impulses.
Today, laser therapy is one of the best measures for the prevention of diseases of the visual organs. This method is used when patients cannot undergo surgery.
The tendency to thin the retina is inherited
Complications and their consequences
The following complications often occur after surgery:
- Inflammation. It manifests itself as redness of the eyeball, severe itching and lacrimation. As a preventive measure, eye drops containing an antiseptic can be prescribed.
- Changes in visual perception. After the procedures, vision may temporarily lose its sharpness. Ophthalmologists recommend wearing special glasses during the postoperative period. The recovery period can take up to three months.
- Strabismus. This side effect was found in almost fifty percent of patients who underwent extrascleral filling procedures. Usually caused by damage or improper fusion of muscles.
- Increased pressure in the visual organs. Such consequences after surgery develop very rarely. Sometimes they cause glaucoma. Given the complexity of the disease, there may be a possibility of a repeat procedure in order to remove the filling.
- Narrowing of visual perception. This side effect is the result of improper laser coagulation of the retina. In rare cases, the pathology is associated with a progressive stage of the disease.
The likelihood that the disease will spread to other areas of the retina is about twenty percent. In order to avoid this, it is sometimes necessary to re-correct.
If you know the primary symptoms of detachment, then recognizing it will not be so difficult
Symptoms
Different types of the disease have their own distinct symptoms. Thus, with the peripheral form of retinal thinning, the initial stage of the disease occurs without certain pain or visual defects. The first symptoms may appear only at the stage of retina rupture. Very often, patients at this stage complain of bright flashes of light and the appearance of black spots in front of their eyes.
The wet form of the disease leads to visual distortion of the shapes of observed objects. The visual field can be significantly narrowed, which leads to the fact that some areas simply fall out of the visual field.
The risk group includes people suffering from myopia, as well as those who have vascular diseases, diabetes, hypertension
The following signs should be considered common symptoms of the disease:
- decreased visual acuity;
- difficulty navigating in a poorly lit room;
- impaired “twilight” vision;
- problems with color perception;
- the appearance of veil and cloudiness.
Diagnostics
You can suspect that the retina is discharged and the number of light-sensitive cells on it has decreased if the patient has a clinical picture characteristic of this disease. To confirm the diagnosis, an ophthalmoscopic examination of the fundus is performed. To better identify structural abnormalities of the macula, the pupil can be pre-dilated. An ultrasound examination of the eyeball and its optical tomography are also performed. To identify abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels, angiography is performed, where an abnormal arrangement of blood vessels is detected, which means the wet form of macular degeneration. You can measure intraocular pressure and study the visual fields. It is also necessary to undergo a general and biochemical blood test.