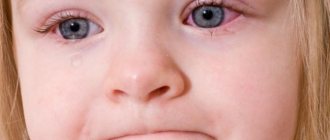
Why does a film appear on the eyes of a newborn? When a baby is born, clouding of the eyes may be observed. Why does this happen? The appearance of a “gelatinous film” may indicate inflammation that occurs in the tear ducts.
This is a fairly rare occurrence and occurs in approximately 5% of babies. Doctors call this disease dacryocystitis.
- V.Rohto Cool eye redness drops help relieve redness and dryness;
- Restore mucosal metabolism;
- The drug acts very quickly, brings noticeable relief and cooling;
- Suitable for daily use.
Causes of purulent discharge from the eyes in children
Eye diseases that can cause purulent discharge from the eyes in newborns and infants:
Dacryocystitis of newborns
Many children are born with poorly developed tear ducts. This means that tears cannot drain properly into the nasal cavity. Because of this, secretions from the eyes accumulate in the lacrimal sac and inflammation begins. In this case, as a rule, only one eye of the baby becomes watery and purulent.
Treatment in the first 3 months of the child is carried out with medication. Anti-inflammatory drops are instilled and massage of the lacrimal sac is applied. In most cases, dacryocystitis goes away. Sometimes it is necessary to probe the lacrimal ducts.
Neonatal conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye during the period 28 days after birth is called neonatal conjunctivitis.
Bacteria that cause inflammation: Staphylococcus aureus, chlamydia, streptococcus, etc.
Gonococcal infection of newborns
With gonococcal infection, newborns have very profuse purulent discharge, with pronounced swelling of the eyelids. Damage to the cornea and development of corneal ulcers may occur.
Eye injury during childbirth
In case of pathological birth, eye damage and infection of the eye are possible.
Inadequate eye care immediately after birth
Immediately after birth, newborns are given special antiseptic drops for prevention. In the case when drops are not used, the risk of developing conjunctivitis in newborns is increased.
Inflammation of the mother's genital tract
Inflammation of the mother's genital tract leads to infection of the child and the appearance of signs of eye inflammation.
Causes of yellow discharge
- 3.1 Drug therapy
The composition of the secretion varies in consistency, color and volume. The most common causes of the symptom are the following diseases.
Acute conjunctivitis
This is the most common cause of yellow discharge in children. Usually the disease is caused by staphylococcus and streptococcus. The pathogen enters the organ of vision with the hands, and is introduced from the skin, nasopharynx, middle ear and sinuses. Only one eye is affected, but the infection can spread to the other after a few days.
Additional manifestations of the disease:
- the child has difficulty opening his eyes, because the eyelashes on the eyelids stick together;
- redness of the conjunctiva of the eyelids and eyeball occurs;
- severe itching and burning appears;
- The baby complains of photophobia.
Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Most often it is diagnosed in newborn children who became infected from the mother during their passage through the birth canal. The disease is characterized by copious yellowish discharge, swelling of the eyelids, severe redness of the mucous membrane of the eyeball and eyelids. If the symptoms are ignored, the pathology quickly spreads to the cornea, causing an ulcerative process there.
Dacryocystitis of newborns
The congenital form of the pathology develops in the first weeks of life due to impaired development of the lacrimal apparatus. Secondary – appears later in children and is caused by anomalies and diseases of organs adjacent to the lacrimal ducts.
The main cause of dacryocystitis is the failure to open the nasal opening of the nasolacrimal duct, which ends in a blind sac, at the time of birth. As a result, tears cannot flow into the nasal cavity. Conditionally pathogenic microflora penetrates the sterile lacrimal ducts of newborns from the maternal birth canal.
Additional signs of the disease:
- the appearance of slight mucopurulent discharge from the eye;
- secretion of copious and liquid secretions.
Keratitis
Rarely detected in children. The disease begins acutely and is most often caused by bacteria and viruses (adenovirus, herpes virus). If the pathology is bacterial in nature, a rounded gray-yellow infiltrate forms on the cornea. The virus develops against a background of reduced immunity. In the herpetic form, blisters form on the cornea, which burst and turn into ulcers. The latter can merge to form a tree-like pattern.
Main manifestations of pathology:
- sharp severe pain in the affected eye;
- blurred and severe vision impairment;
- blepharospasm;
- severe lacrimation, photophobia;
- redness of the eye;
- the appearance of a mucous-yellowish secretion;
If the disease progresses, it can develop into a corneal ulcer and threaten perforation of the membrane.
Prevention methods
It is impossible to avoid the development of dacryocystitis, since you cannot influence the rupture of the protective film in any way. But massage and regular eye washing will help avoid serious complications.
But you are quite capable of preventing the development of viral and bacterial infections:
- every day, carry out hygiene procedures 2-3 times, in the first month it is better to rinse your eyes with saline solution or a weak solution of Furacilin, then you can use ordinary boiled water;
- do not touch the baby’s face with dirty hands;
- If you have a cold, be sure to wear a gauze bandage before feeding and interacting with your baby.
The best way to avoid infectious pathologies is to strengthen the immune system early and regularly.
Air and sun baths, daily gymnastics are beneficial for babies; be sure to maintain the temperature in the room within 18-22 degrees, humidity - 50-70%.
Before proceeding to treatment of the pathological process, it is necessary to accurately establish the cause of its development. To do this, the doctor carries out standard measures, which include establishing the visual acuity and field, examining the fundus, as well as in direct and transmitted light. In addition, the doctor takes a smear from the conjunctival cavity to perform a bacteriological examination. This will allow you to accurately identify the pathogen and correctly design antibacterial therapy.
Prevention of conjunctivitis begins in the prenatal sanitation of pregnant women with further treatment and use of drops with antibacterial and antiseptic effects for newborns
Prevention involves following simple rules:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- hardening;
- proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of infectious eye diseases.
In order to select the most effective treatment regimen, it is necessary to determine as accurately as possible the cause of the occurrence and development of the pathology. For this purpose, special medical procedures are carried out.
A smear must be taken for bacteriological examination, during which the causative agent of the disease is identified. Additionally, the fundus is examined and visual acuity is determined. Based on the results of the tests, treatment is prescribed.
The very first procedures to prevent eye diseases are carried out when the baby is not even born. They involve the rehabilitation of the expectant mother. And immediately after birth, the baby’s eyes are washed with antiseptic antibacterial drops. In the future, prevention is simple and does not require much effort or expense. You just need to follow simple rules:
- Maintain personal hygiene. At first, this is the concern of the parents, but over time it is worth teaching the child to do this on his own.
- Strengthen the immune system, do not ignore hardening procedures
- Watch your diet. The main criteria are varied, healthy, rich in vitamins.
- Have regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist
The basis for preventing eye suppuration in children is sterility, cleanliness and hygiene. Symptoms of eye blepharitis can be found here.
READ MORE: Uric acid in the blood: normal and increased, treatment, symptoms and causes
Basic rules of prevention include:
- It is necessary to instill in a child a love of cleanliness and neatness;
- Make sure that your child does not come into contact with sick animals, friends, or relatives who have viral eye diseases;
- Do not let your child rub his eyes with dirty hands;
- Constantly wash your child’s hands, treat them with antiseptics for children;
- The child's clothes, towels and bedding should be changed regularly and belong only to him.
You can find out how dangerous dirofilariasis is here.
Thus, children’s eyes fester for two main reasons: infection from an infected person, animal, or independent introduction of the virus into the area of the visual organ. It is important to diagnose the disease in time, prescribe therapy and know what to do. Surround your child with love, care and attention so that he does not experience extreme stress during the treatment period.
Causes of purulent discharge from the eyes in pregnant women and children over one year old
ARVI and influenza
Pus that may be present in your child's eyes may be due to a viral infection. Knowing the causative factors, as well as how to cope with them, can prevent the development of purulent discharge from the eyes in an infant.
Sinusitis
If your baby has a cold, he may develop sinusitis (inflammation of the sinuses). Important symptoms: fever, pain in the forehead and eyes, lacrimation and suppuration of the eyes.
Allergy
If your baby has a runny nose and you notice redness and small mucous-yellow discharge, then it may be an allergy.
Conjunctivitis
The eyes of children and pregnant women often fester due to infectious inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by both bacteria and viruses. Symptoms of conjunctivitis begin in one eye and then spread to the other eye.
Mechanical damage to the eye
Inflammation and suppuration can occur if a mechanical particle gets into the baby’s eye:
- eyelash;
- fly or other insect;
- cotton wool or fabric fibers;
- chemical splashes;
- splashes of hot oil;
- plastic flake;
- a piece of glass;
- metal or wood shavings.
In this case, first aid is required:
- The inflamed eye is washed with saline solution, a decoction of chamomile, calendula or warm black tea. If you have a solution for soft contact lenses, you can use it.
- It is necessary to determine whether a foreign body has come out of the eye.
- If it is impossible to independently determine the extent of the damage, then the child urgently needs to be shown to a specialist who will examine the eye using special equipment.
How to treat the disease in newborns?
If the diagnosis of dacryocystitis is confirmed, doctors prescribe stimulation of the nasolacrimal ducts. To do this, the duct, which is located on the lower eyelid of the inner corner of the eye, is massaged with light movements towards the nose. This procedure is done 5-7 times during the day. As a result of constant pressure, the closed membrane of the duct ruptures, the channel becomes open. If the canal does not open before 6 months from birth, surgery is necessary. It is simple and is carried out by an ophthalmologist in the clinic’s office. The doctor inserts a thin probe into the canal and opens it. In rare cases, this operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Until the channel opens, the eye must be constantly washed. This will prevent complications of the disease and prevent the infection from spreading to the other eye.
If after opening the canal the suppuration does not disappear, you should consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor may prescribe antibiotic treatment.
If the doctor has diagnosed bacterial conjunctivitis, he will first prescribe rinsing. When such treatment does not help, the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy. Viral conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral drugs. Medicines may be in the form of drops or ointments. Sometimes you may need to take medications orally in tablet form.
The foreign body will be removed by an ophthalmologist. Trying to remove the irritant on your own is not recommended. It is strictly forbidden to use various objects, especially sharp or hard ones.
You can try dripping boiled water into your eye to wash away the foreign body. But a visit to the ophthalmologist is mandatory in any case. Even a successfully removed foreign body could scratch the mucous membrane. Timely treatment will help avoid complications.
Barley in a baby
Caused by infection of the eyelash follicles, a swelling on the eyelid that leads to the formation of pus is called a stye . The bacterial infection enters the hair follicles and sebaceous glands, which are located near the eyelashes. In mild cases, barley goes away on its own. But if the child has a weakened immune system, then it can develop into a boil . Two or three days after the eyelid becomes red and swollen, the eye begins to fester.
Under no circumstances should you squeeze out pus or open a stye. It must ripen itself and release dead cells. That is why his treatment is aimed at accelerating the process. For this it is recommended:
- Apply compresses of warm mashed potatoes wrapped in a wide bandage or clean gauze. Keep it until it cools down.
- Dry heat is very effective in treating barley. You can consult a doctor to prescribe a course of UHF for your child.
- The eyelid must be treated with antibacterial drugs - 1% Erythromycin, Tetracycline ointment or Ciprofloxicin. Albucid is instilled into the eye.
- Several times a day, compresses are made from warm chamomile infusion. To do this, moisten a cotton pad or swab and apply it for 5–7 minutes.
- You can use flaxseed, 2 tbsp. l. which is heated in a frying pan, poured into a clean bag and applied to the eye for 7-10 minutes five times a day.
Warming the stye must be used very carefully, since with this method of treatment it can open and infect the eye. Therefore, if a stye appears on the eye, it is better to take a child to a specialist.
Parents must remember that the baby's health is in their hands. Therefore, at the first appearance of symptoms of eye inflammation, you should consult a doctor. Only in this case, treatment of the disease will not take much time and will not cause complications.
A child's eye is festering, treatment
Situations that require immediate attention and medical attention include the following symptoms:
- severe swelling of the eyelids and very profuse purulent discharge
- increase in body temperature
- the child complains of decreased vision and pain in the eyes
- child rubs his eye
- eye redness and watery eyes
It is important to know that the spread of infection in children occurs very quickly and rapidly. Therefore, it is necessary to seek medical help in a timely manner.
During treatment, when using eye ointments and drops, it is necessary to first remove pus from the eye. Any types of medications (drops and ointments) are effective only after rinsing the eye.
How to treat conjunctivitis with medication?
Conjunctivitis in a 4-month-old child can be cured with a limited amount of medication. The reason is that not all medications are suitable for infants. Many drops and ointments that are designed specifically to treat conjunctivitis cannot be used on four-month-old infants due to the high likelihood of side effects. After examining the child, the ophthalmologist will prescribe those medications that he considers the most gentle for the child’s body. It is customary to treat conjunctivitis in newborns with eye drops and ointments with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. The following drugs have proven themselves to be the best:
- "Tobrex" is an eye ointment with an antibacterial effect. It must be placed in the corner of the eye once a day for 10 days. It is best to do this before bed;
- "Ophthalmoferon" is a drug that has an antiviral effect. It is used 1 drop every 2 hours, after which the number of instillations is reduced to 3-4 times a day;
- "Vitabact" are eye drops that are used for at least a week, but no more than 10 days. The drug should be administered 4 times a day, one drop;
- "Tetracycline ointment" is one of the most common drugs used to treat conjunctivitis in four-month-old children. It is placed 2-3 times a day in the corner of the eye after washing it;
- "Albucid" - the children's version of these drops should be a 1% solution. It is allowed to use it up to 8 times in the first two days of illness, then up to 4 times a day.
Even if only one of the baby’s eyes is affected by conjunctivitis, drops must be instilled into both: into the sick eye for treatment, and into the healthy eye for prevention. During instillation, it is important not to touch the baby’s cornea with the pipette or “spout” of the bottle. By the way, the pipette can only be used with a rounded end. If this happens, then the pipette must be disinfected before the next use of the drops. This is necessary so that re-infection does not occur and the infection does not “spread” from the diseased eye to the healthy one.
First aid
Even if you have made an appointment to see a doctor as soon as possible, it is important to relieve your child's condition before visiting the hospital. The main method is washing. When rinsing, it is important to use a separate cotton swab for each eye to avoid spreading infection. You can rinse with clean warm water, chamomile decoction, saline solution (purchased at a pharmacy or made yourself), furatsilin or chlorhexidine.
Eye rinsing should be done moving from the outer corner of the eye to the inner corner so that accumulated secretions come out.
If the discharge has a very thick consistency, then parents should first lightly massage the child’s eyelids, and rinse a little later, when the discharge comes out. Massage should be done in the same way as rinsing: from the outer corners of the eyes towards the nose.
Parents often notice an accumulation of purulent discharge in the corners of the eyes in their children. This symptom is quite dangerous, as it may indicate the presence of a certain illness. It needs to be treated immediately at the initial stage, before serious complications arise. The doctor will be able to prescribe treatment only after he can understand what led to the development of such unpleasant symptoms.
When a child’s eyes fester, it is most often caused by some kind of disease. It is characterized by the following clinical picture:
Each child’s body reacts differently, so the pathological process can manifest itself in different ways. But if at least one of the above symptoms occurs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to properly wash a child's eyes
Pediatricians recommend rinsing the vision organs twice or thrice a day. Too frequent procedures are undesirable, because... may lead to irritation of sensitive mucous membranes.
There are several ways to wash your eyes:
- Using cotton products.
- Using a pipette.
- Using a syringe.
To complete the first version of the procedure, you will need to prepare:
- eye treatment composition at room temperature;
- several cotton pads (or tampons);
- clean, lint-free wipes.
When washing the eyeballs, do not use wet wipes with fillers, fragrances, or alcohol-based rags. All items must be clean and new and used once.
A cotton pad (tampon) is moistened in the medicinal product, then squeezed out so that liquid does not drain from it. Next, wipe each eye in turn, moving from the outer edge to the inner. A new disc is used for each organ of vision. Any liquid that gets on the patient's face is carefully wiped off.
The duration of therapy should be agreed with the children's doctor. Most often, procedures are performed until the negative symptoms completely disappear.
When carrying out rinsing, it is necessary to ensure that the composition used is free of dust, lint, hairs or pet hair. In order not to injure the patient’s organs of vision, it is necessary to get rid of long nails and carefully file them. All movements must be smooth and careful.
For patients under 12 years of age, the eyes can also be irrigated using a dropper. For this purpose, you will need to pull back the lower eyelid and lift the upper one, then introduce 1-2 drops of the cleansing composition, instilling it closer to the corners. After these manipulations, the eye should be closed and the remaining product should be carefully removed with a clean cotton pad.
To carry out the procedure on an older child, a rubber syringe can be used. Immediately before the procedure, it will need to be sterilized by boiling. Next, take a little solution into a syringe and direct the liquid into each eye in turn.
Conjunctivitis in infants
The disease can be viral or bacterial. With bacterial conjunctivitis, a child experiences the following symptoms:
- severe lacrimation;
- redness of the eyes and eyelids;
- covering the eye with a thin whitish film.
Types of conjunctivitis
This inflammation begins in 1 eye and then moves to the second. With purulent conjunctivitis, a baby has the following symptoms:
- secretion of a large amount of purulent fluid, which sometimes completely clogs the eyes;
- eyelids are difficult to open after sleep due to their sticking together;
- sudden swelling;
- secretion of a large number of tears;
- irritation of the cornea.
Viral conjunctivitis is more dangerous for a baby than bacterial conjunctivitis. A viral infection can spread throughout the body, causing disruption of all its functions.
In young children, inflammation of the conjunctiva occurs for the following reasons:
- underdevelopment of immune defense;
- intrauterine infection;
- herpetic infection of the mother;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene requirements;
- getting dust or foreign matter into the eyes.
The child is prescribed Levomycetin drops. It is recommended to wash the eye with antiseptic solutions such as Furacilin and decoctions of medicinal plants. Only a doctor can select a highly effective remedy against conjunctivitis.
Sometimes this disease can last a long time. This depends on the state of the immune system and the severity of the inflammatory process. Parents need to be patient. It is very important to continue the previously prescribed therapeutic course to achieve maximum effect. If everything is done correctly, the baby’s eyes will soon be cleared of pus.
You should not rely on traditional medicine and the advice of friends. Only with timely consultation with a doctor can a complete recovery be guaranteed.
Prevention of eye inflammation
Inflammatory purulent eye diseases can be prevented. This is much easier to do than to treat them. Parents should heed these recommendations:
- It is necessary to toilet the eyes. Moreover, it should be performed every day, even if at first glance there are no visible signs of the inflammatory process, and the eyes are clean. The frequency of such procedures is 2 times a day.
- Sterile wipes are used for washing. It is better not to use cotton wool, because lint may remain in the eyes, and this will lead to suppuration.
- For hygienic purposes, it will be enough to use clean boiled water.
- Keep the child clean and prevent dust and dirt from coming into contact with his face. Then the risk of purulent inflammation is reduced.
- Pregnant women regularly visit antenatal clinics.
- Before conception, it is advisable to be examined for the presence of STDs, and if they still exist, to cure them.
Purulent inflammation of the eyes cannot be safe for a baby. If their first symptoms become noticeable, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
How to cure conjunctivitis in a child quickly at home
Dr. Evgeniy Komarovsky emphasizes that before treating conjunctivitis in a child, first determine the cause and form of inflammation.
Viral form
Viral conjunctivitis in children is treated with local antiviral agents: eye drops, ointments. If viral inflammation of the conjunctiva develops against the background of ARVI, then complex treatment will be required. The doctor will prescribe tablet forms of antiviral drugs.
Komarovsky says that the immune system of a small person is able to cope with viruses on its own. In 5–7 days, the inflammatory symptoms will subside even without medication. We need to wait until the immune system develops protection.
Komarovsky notes that treatment of herpetic infection requires the prescription of medications, since the herpes virus can cause severe damage to the visual organ.
Bacterial form
Bacterial conjunctivitis is treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics. The instructions for some drugs indicate age restrictions. This suggests that clinical studies have not been conducted on children, so the pharmacological company cannot approve the use of the drug in children. But Komarovsky allows the use of some prohibited antibiotics in consultation with a doctor.
For purulent conjunctivitis, antibacterial ointments and eye drops are suitable. Rinse your baby's eyes first, soak them and remove any dried crusts.
Watch a video about the concomitant disease and why it overlaps with the bacterial form:
Allergy
The allergic form of inflammation requires identification of the allergen. This is not an easy process, because anything can be an allergen. Start by eliminating the most common ones: pet hair, laundry detergents, food allergens, dust.
Drug treatment includes antihistamine drops and tablets. Sometimes, to relieve severe inflammation, the doctor may prescribe glucocorticosteroids. Hormonal drugs act more quickly and powerfully than antihistamines.
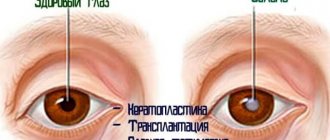
Symptoms of diseases
The film on the eye causes a feeling of discomfort. It may vary in intensity and duration. Most often, this condition occurs in the morning or after hard work at the computer. In some cases, the unpleasant symptom disappears if you blink your eyes. Moisturizing the organs of vision and wiping are often required. Such conditions are often accompanied by other symptoms, including:
- itching and unpleasant burning sensation;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- the appearance of spots and “flies”;
- general weakness.
A film on a person’s eyes, which is accompanied by similar signs, may indicate the development of diseases not only of the visual organs, but also of the nervous system. That is why you should seek help from ophthalmologists. Specialists will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate therapy. Often the development of a film on the eye is observed in older people. The neoplasm consists of an overgrown conjunctival membrane.