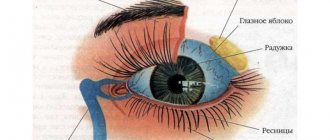
Previously, it was believed that the only function of blinking was protective (for example, from dust and from drying out). However, scientists have found that there is another function of blinking – psychological.
It is known that on average a person blinks about 15-20 times per minute. Thus, it turns out that ten percent of the time we are awake our eyes are closed. Yes, of course, with the help of blinking, the eyeball is moisturized and protected, but we blink much more often than necessary to perform such functions.
A group of Japanese scientists made a new discovery: when we quickly close our eyes, it helps us focus on the current situation and collect our thoughts.
Scientists made this conclusion after noticing a certain pattern: the occurrence of moments when we blink is not an accident. And despite the fact that it seems to us that we blink absolutely spontaneously, it turns out that this is not at all the case. Research has shown that we do this at expected times.
So, for example, when we read something, we blink after the sentence has finished. If we listen to someone, we often blink during the pause that the speaker makes between statements. When several people watch the same film, they blink almost simultaneously when the actions are delayed for a short time.
In the course of research, scientists were able to find out that people begin to blink subconsciously: in order to mentally relax or, if necessary, quickly focus on something.
To confirm or refute this fact, scientists conducted a study on 10 volunteers who then underwent magnetic resonance imaging and watched the TV show “Mr. Bean.” The scientists looked at which areas of the brain showed decreased or increased activity during blinking.
An analysis of the results showed that when blinking, brain activity increased in the so-called “passive mode network of brain functioning.”
This area of the brain operates when a person is in a state of waking rest. And it is this area that is responsible for that break that helps us improve attention after a person opens their eyes again.
Causes of pathology
Involuntary muscle contractions are not a cause for concern.
A healthy person is characterized by these processes if they rarely occur. Subtle twitching of the eyes or lips is caused by nervous overexcitation of a person, which disappears soon after taking sedative medications. Whether to contact a doctor in this situation or not is a person’s decision individually. It’s a different matter when eye tics recur regularly in children. This signals the seriousness of the situation. The factors that cause a child to blink and squint frequently have different origins. The reasons may be ophthalmological dysfunctions or malfunctions of the nervous system. The exact cause of the disease can only be determined by a specialist after diagnosis. Self-treatment is often useless or harmful. It's a waste of money.
Pathologies of the organs of vision
If the child blinks his eyes frequently, then the mother should seek help from an ophthalmologist. Dysfunction is often associated with disruption of the visual organs. These problems are observed due to the following reasons:
- Dryness of the cornea. This is a common occurrence among children and is caused by an unhealthy lifestyle. When a baby watches too much TV or does not take his eyes off the monitor for several hours in a row, he overloads his eyes. There is discomfort or itching, a feeling of sand in the cornea. Rapid drying of mucous membranes can be caused by low humidity levels in the room.
- Mechanical damage to the eyes. While playing with friends, the child may not notice it. The situation becomes more complicated when, after an injury, the eyes are rubbed with dirty hands. Because of this, infectious infection of the mucous membranes occurs.
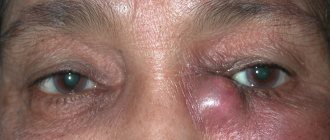
- Conjunctivitis. This inflammation causes swelling or swelling. To get rid of them, the child often closes his eyes.
- Partial loss of visual acuity. Modern children spend a lot of time using gadgets that impair visual perception. Good vision is becoming rare. At the initial stage of pathology, they squint or begin to blink frequently in order to better see the picture.
The given list of causes of pathology is basic, but far from complete. Children at 2 or 3 years old squint their eyes for a reason. Often the latter are hidden in physiological problems. Reflex contractions of the eyes appear after taking certain medications as a side effect. This happens after a traumatic brain injury.
The hereditary factor also plays a big role. There are a great many reasons, so only a specialist can understand them.
Pathologies of the nervous system
It is much worse if the baby blinks heavily or squints for other reasons. Such disorders require long-term treatment. These include the following:
- Stressful situation. It is not easy for children to tolerate nervous tension. The cause of stress can be a change in social circle, severe fear or quarrel. The result of a negative condition is an involuntary contraction of the eye muscles (or a nervous tic).
- Serious injuries to the head or eyes that affect the eye muscles.
- An allergic reaction (or side effect) after taking medications.
Often the cause of the defect is heredity. In this case, the disorder cannot be cured.
Psychological pathologies
The reason for involuntary muscle movement may lie in psychological childhood problems. In addition to the above contractions, the child may have twitching cheeks or mouth, headaches, and so on. This cannot be done without the help of a pediatric neurologist. Family conflicts are dangerous for a child’s psychological health. Negative experiences in the past prevent an adult from building healthy relationships.
Recommended reading: Eye twitching
As a result of family quarrels, the transmission of muscle impulses in the child’s body is disrupted. The amount of mediator produced in nerve tissues drops sharply. Such a deficiency causes nervous movements of the eye muscles. Nervous tics are especially typical for children 6-7 years old. It is not always associated with genetic inheritance.
Why does a person blink often?
Physiologically, a person should close his eyes no more than 4 times a minute.
If you blink 15 to 20 times, you must go to the hospital; this is considered a pathology. With each blink, a person loses about 400 milliseconds of visual time.
Blinking of the eyes occurs more often than necessary to lubricate the mucous membrane of the eyeball. This statement allowed doctors to conclude that the action was associated with other conditions.
Why do children blink often?
Parents believe that the cause is visual strain. Accordingly, they are trying to protect them from playing games on the computer, watching TV and other gadgets for long periods of time.
There are many factors that can cause the blinking effect in children. They can lead to unconscious active closure of the eyelids.
The reasons for this phenomenon may be the following factors:
- a complication caused by an acute respiratory disease or virus;
- allergy;
- nervous tic;
- drug overdose;
- TBI;
- concussion.
This action is carried out unconsciously in case of eye diseases. It is caused by dry keratitis, progressive myopia or hypermetropia, inflammatory processes and the entry of a foreign object.
Frequent blinking when talking
This means that the person is thinking about something else and has forgotten what he was talking about with his interlocutor. If he is lost in thought, the part of the brain that is responsible for processing the information received becomes less active and suppresses information coming from the interlocutor. One of the symptoms of this process is frequent blinking of the eyelids.
It indicates the nervousness of the interlocutor. For example, when speaking in front of a large audience or undergoing an important interview. Often this symptom indicates lies, deceit and insincerity. More often a person gets worried when he lies.
If a person blinks frequently, regardless of the situation, this is a mental disorder or another disorder of the visual analyzer.
Diagnostics
If the symptom is accompanied by dizziness, headaches, nervousness and irritability, make an appointment with a psychologist or neurologist. Most likely, the reason lies in the emotional state of the patient.
If other symptoms appear, contact a therapist, he will give a referral to the right specialist. For eye pain, redness, watery eyes, and increased sensitivity to light, a referral to an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist) is obtained.
The patient may also be referred to an allergist or infectious disease specialist. It all depends on the accompanying symptoms.
The doctor interviews the patient and collects anamnesis. Then allergy tests are prescribed, a blood test is taken, an MRI or CT scan is performed, and the visual analyzer is examined using an ophthalmoscope or other device.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
If the cause is an ophthalmological disorder, a course of physiotherapy is prescribed. Get a referral from a doctor; you should not engage in therapy on your own, because this technique is not suitable for all diseases.
Effective methods of therapy:
- electrophoresis with riboflavin;
- phonophoresis - medications are injected into the deep layers under the skin using ultrasound;
- magnetic therapy - improves blood microcirculation in tissues, restores, relieves swelling, has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect;
- laser therapy - stimulates the outflow of excess fluid, lowers intraocular pressure;
- ultrasound therapy - increases the hemato-ophthalmological barrier and sorption properties of eye tissues, accelerates the penetration of drugs, improves blood supply to tissues during degenerative processes in the retina;
- diadynamometry - sends pulsed currents;
- electrosleep - has a positive effect on the dynamics of vegetative-vascular and vegetative-cardiac disorders, has a beneficial effect on metabolic processes;
- acupressure.
Exercises
Gymnastics for the eyes allows you to strengthen the muscle fibers responsible for raising and lowering the eyelid. Special exercises help with rapid blinking due to nervous disorders.
Gymnastics:
- circular movements of the eyes;
- close your eyes and open wide;
- look up, then down for a few seconds, holding your gaze;
- close your eyes, place your index fingers on your eyelids and press lightly, in this position perform circular movements.
When performing gymnastics, make careful, slow movements. There shouldn't be any discomfort. If you experience pain, a feeling of eyelid tension or other symptoms that cause discomfort, stop doing the exercises and inform your ophthalmologist.
Prevention
There are no measures to prevent flashing. This is due to the fact that the symptom does not appear independently, it is a symptom of another condition.
What to do to prevent frequent blinking:
- avoid injury (protect your eyes when working with dangerous tools);
- have a good rest;
- do not stay in front of the TV or computer for a long time;
- promptly go to the hospital for treatment of diseases leading to this symptom;
- do not overwork physically and visually.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 2 4.00
Source: https://proglazki.ru/simptomy/chastoe-morganie/
What to do?
Please note that not all drugs for adults are suitable for children. They have contraindications and side effects. It is necessary to create a good-natured atmosphere in the home that develops positive emotions in the child.
To do this you should:
- Create trusting relationships and avoid quarrels.
- Alternate mental and physical work, taking rest.
- Diversify your child's leisure time.
- Do not impose activities on your child that cause irritation and negative associations.
- Perform an analysis of the situation that leads to a nervous tic.
- Avoid commenting to the child regarding frequent blinking.
- Agree with teachers and closest friends so that they do not attach importance to the child’s shortcomings.
Causes of nervous tics in children
Uncontrolled contractions of the eyelid (or both) have a paroxysmal nature, which occurs during nervous overexcitation. Some factors predispose to this:
- deficiency of nutrients (B vitamins, magnesium, potassium and calcium);
- genetic inheritance (tic is often passed on from parents);
- side effect from taking medications (the possibility of such a reaction is written in the instructions for use of the medicine);
- decreased immune defense of the body.
Severe childhood stress can be a catalyst for the onset of a nervous tic. The disease cannot be left untreated. An advanced disease progresses over time. Nerve contractions become more pronounced, and sometimes “spread” to the arms or legs.
The child's negative emotions, which cause tics, are not always obvious to his parents. Overexertion in a child, which adults do not know about, appears, for example:
- due to fear of the class teacher or other teachers;
- due to bullying from classmates;
- with fear of the dark;
- when moving to a new place of residence or transferring to another school;
- because of a quarrel between parents.
In order for therapeutic therapy to be effective for a child, it is necessary to find out the cause of his pathological condition.
What is an eye tic
This is an uncontrolled, frequently repeated contraction of the eye muscles. The tic occurs quickly, is stereotypical and short-term in nature. Tics (including eye ones) are called hyperkinesis, which means “super movement”. The appearance of hyperkinesis is most often associated with improper functioning of the brain, which issues an erroneous command to the muscles to contract.
An ocular nervous tic can occur constantly or occur sporadically when:
- nervous tension;
- exhaustion;
- excessive drop in body temperature.
If spasms pass quickly, appear rarely and disappear on their own, then there are usually no serious problems with nervous health. But sometimes they indicate the presence of problems either with the nerves or with the mucous membranes of the eyes. The eye tic itself is just a symptom that signals a nerve disorder or eye disease.
It is not dangerous, but still visually highlights a person’s facial expressions and can become a cause of ridicule in children’s and teenage groups. Most often, tics are observed in children over 3 years of age and during puberty, when the psyche is most vulnerable. In adults, eye tics can appear after shocking stressful events or nervous stress.
Head shaking combined with frequent contractions of the eye muscles indicates the presence of neurological problems. Treatment of these types of conditions can take a long period with stages of improvement and deterioration. Tics may go away completely, but return again in a stressful situation. Also, in some cases, tics are difficult to treat.
Parents and doctors should approach the issue of getting rid of tics comprehensively, using:
- medicinal adjustment with drugs;
- home recipes of traditional medicine;
- relaxing massages and techniques.
- psychological techniques.
First you need to imagine that the eyes are the wings of a butterfly.
- First you need to blink your eyelids hard - our butterfly wakes up. We close our eyes with tension and open them sharply. This must be done until tears appear.
- We wipe away our tears and gently massage the eyelid with our middle finger. To do this, we use circular movements.
- Now the butterfly takes flight. We blink quickly, imagining that eyelashes are wings. Exercise relaxes the muscles, which helps get rid of tightness. In addition, such exercise moistens the eyeball, this is necessary in order to treat nervous tics.
- The butterfly is tired. You need to close your eyelids halfway. They will begin to tremble. You need to concentrate and stop shaking.
Now you can rest. The pleasant treatment is over!
Diagnostics
It is important to distinguish nervous tics from frequent blinking, which appears for other reasons. Tics can have other manifestations, for example, motor (motor) and voice (vocal):
- Simple motor. They manifest themselves in the form of closing their eyes, twitching their heads, swallowing, grinding their teeth, sniffing, and shrugging their shoulders.
- Complex motor. Bouncing and echopraxia are observed.
- Simple vocals. This is revealed in the form of coughing, whistling, snorting, and grunting.
- Complex vocals. These are echolalia (reproduction of words) and coprolalia (obsessive swearing).
With tics, not only the eye may twitch, but other movements or sounds may also occur. The child is able to restrain the tic by willpower for a short time, but when attention weakens, the obsession returns.
With an ophthalmological disease, frequent blinking is accompanied by:
- irritation, dryness of the cornea, pain, discomfort, sensation of sand or a foreign body in the eye;
- decreased clarity or visual acuity.
Whatever symptoms prevail, the child should be taken to the pediatrician. It is especially important to do this if the signs have been present for a long time and are pronounced.
Frequent eye blinking in adults: causes, treatment
Blinking is a natural process necessary for the normal functioning of the eyes. A person repeats this action thousands of times throughout the day, practically without noticing it. Usually people blink once every 4-5 seconds. But sometimes an adult begins to blink his eyes too often. What does this mean?
Frequent blinking can be harmless, or it can be a symptom of a developing serious pathology in the body.
The mechanism of physiological blinking
Why does such a phenomenon as blinking occur? This is a natural involuntary process that moisturizes the organ of vision and protects it from drying out.
At the moment of closing the eye for a split second, the eyeball is cleansed and moistened with tear fluid. This also prevents eye infections.
Causes of frequent blinking in adults
The reasons for this phenomenon can be either directly related to ophthalmology or non-ophthalmological.
Neurological
In some cases, such a habit may indicate the development of a neurological disease.
The cause may be simple fatigue. To get rid of it, it will be enough to rest fully and get a good night’s sleep. On the recommendation of a doctor, you can take a course of mild sedatives.
It is very important to establish the correct daily routine. If these conditions are met, fatigue will pass and blinking too often will stop.
A severe stressful situation can provoke such a symptom in an adult. As a result of neurosis, a person may develop a nervous tic. Tics are divided into two types: primary and secondary. The first is associated with a disorder of the central nervous system, the second with problems in brain activity.
A neurological pathology accompanied by frequent blinking, tics, and uncontrolled behavior is the so-called Tourette syndrome. It can occur not only in children, but also in adults.
Other reasons
Most often, the cause of such rapid blinking can be a small foreign body that has entered the eye, for example, a speck. To eliminate the discomfort, it will be enough to remove it from the eye.
Dry eyes can also be a cause.
In some cases, frequent blinking is a harbinger of infectious eye diseases (conjunctivitis, keratitis).
Non-ophthalmological causes that cause this symptom may also include:
- Frequent smoking.
- Constant use of alcohol or drugs.
- Allergic reaction. In this case, in addition to blinking, there may be mucous, transparent discharge from the nasal cavity, itching, and burning.
- Reaction to taking certain medications. Manifestations are similar to allergic ones.
- Head injury.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Parkinson's disease.
- Epilepsy.
Usually, in the presence of pathologies, frequent blinking is accompanied by additional symptoms (pain in the eyes, burning sensation). If measures are not taken in time, they may also include:
- nausea;
- severe headaches;
- feeling of constant anxiety;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- changes in the skin of the eye;
- loss of consciousness.
Ophthalmological reasons:
- Reaction to bright light.
- Farsightedness.
- Myopia.
- Blepharospasm.
- Dry eye syndrome.
Frequent blinking can also be an accompanying symptom of some thyroid diseases.
When medical attention is needed
Frequent eye blinking is not always a harmless sign. In some cases, serious medical attention may be needed. It is important to visit an ophthalmologist for examination and prescribing the correct treatment.
Drug treatment
The ophthalmologist will conduct an initial examination, prescribe blood tests, and, if necessary, additional diagnostic procedures. Depending on the results, a diagnosis will be made.
At the discretion of the doctor, the patient may be recommended to visit specialists:
- Neurologist.
- Endocrinologist.
- Allergist.
- Cardiologist.
- Infectious disease specialist.
After diagnosis, specialists will jointly prescribe comprehensive treatment for the disease. First of all, the doctor will prescribe medications that can eliminate the cause of the disease, and the ophthalmologist will prescribe symptomatic treatment.
If there are inflammatory processes in the eye area, these may be:
- drugs with antibacterial action;
- complex of vitamins;
- local antiseptics;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- drugs with anti-inflammatory effects.
If the cause of blinking in adults is dry eyes, then drops are prescribed for instillation (Vizin, Tobradex). The dosage regimen is determined by the attending physician.
Dry eye treatment
There is no single treatment for the disease. After determining the cause of the pathology, specific therapy is prescribed. It includes adjusting the child’s daily routine and taking certain medications. For example, if blinking of the eyelids occurs due to fatigue, the following treatment is prescribed:
- Children’s access to modern gadgets (computers, consoles, phones or tablets) is limited, and time for rest increases;
- It is recommended to walk more in the fresh air;
- the diet is adjusted, which includes a large number of nutrients;
- Drinks containing caffeine are contraindicated.
The drugs can be used only as prescribed by the attending physician, strictly following the indicated course.
Treatment of nervous tics
This disease does not occur without a reason. The basis of any therapy is to find the source of the problem. Adequate treatment includes a whole complex. With the correct attitude of parents towards the baby, the disorder will quickly subside. Otherwise, the disease will only progress, aggravated by depression or childhood nervous breakdowns.
The therapy itself consists of the following:
- Competent diagnosis of the child in order to identify the primary source of stress.
- Correction of the child’s behavior by a child psychologist, who will help him cope with stress, adapt to a new team, and relieve fear. In other words, it will make the patient’s social life more comfortable for him.
- Parents themselves should strive to surround their child with a favorable atmosphere. Watch films or cartoons without scenes of violence and cruelty, do not sort things out between each other, etc.
- Give the patient a small dose of sedatives (Novopassit, tinctures of valerian or motherwort, etc.).
- Regular relaxing baths (pine baths, with sea salt) are effective.
- Drink chamomile tea before bed.
- Light massage with the index finger of the lower eyelid.
- Brief pressure on points located near the outer edge of the eye.
- Performing exercises that target specific muscles.
Therapeutic gymnastics includes the following complex:
- Squeezing and unclenching of the eyes. The movement is made abruptly. They close their eyes tightly and stick their eyes out until tears flow;
- Lightly and quickly blink your eyelashes for 30-60 seconds. This exercise will help cleanse the mucous membranes while moisturizing them.
- Covering the eyelids halfway for a long time. When trembling appears, you should try to stop it.
Facial massage gives good results. It is performed with slow movements, starting with stroking. You can’t put pressure on the skin, or resort to vibration. Be sure to use a massage gel or cream.
Why does a child blink his eyes often: causes and treatment methods
Exposure to certain methods for tic disorders enhances the beneficial effect in combination with the main methods of treatment, and sometimes is sufficient to get rid of nervous tics.
Alternative methods include:
- Massage treatments for the head, arms and legs for the purpose of relaxation in case of chronic fatigue and overwork. Improving blood supply to muscles and relieving increased tone reduces the excitability of the central nervous system. It is enough to do 10 sessions to improve the patient’s condition.
- Acupuncture. The ancient Chinese method is based on the impact of needles on certain areas of the human body. Acupuncture is based on ancient ideas about the concentration of vital energy on certain meridians of the human body.
- Electrosleep. A common and accessible method of reducing nervous excitability and normalizing mental state. Conducting low-frequency impulses to the brain is absolutely safe.
- Special exercises. A non-standard approach is effective if the eye twitches. Treatment is carried out independently.
- Charging begins with frequent blinking, then sharp squinting. The alternation of these phases is carried out until tears appear. Wetting the eyes is useful for relaxing the muscle and relieving tension. When fatigue sets in, you can close your eyes and rest.
A timely visit to a neurologist for consultation will help eliminate the tic. The specialist determines what to do to get rid of the disorder after diagnosing the disorder and assessing the person’s psycho-emotional state.
How is massage performed?
To complete it you need:
- Place the child on a chair with a soft back.
- Stand behind the child.
- Use a comb to part the hair on the head.
- After this, you can make massage movements using your index finger.
- Along the parting made, stroke with one finger, and then make light spiral movements.
- Using light pressure, kneading is performed.
- All massage movements alternate with stroking.
- Shock and vibration techniques are not used.
- After completing the cycle, perform the next parting, which is done with a deviation of 2 cm.
- In 1 procedure, you can perform 10-12 partings with a comb.
- After the procedures, the palms are placed in the forehead and back of the head and gentle movements similar to compression are performed (5-7 times).
- When performing a head massage, ointments, creams, and gels are not used.
Komarovsky about frequent blinking in children
The popular presenter claims that the cause of the child’s pathology is the unstable psycho-emotional state of the little patient. If an illness is detected, the child should be observed for 3-5 days.
If the blinking does not stop, then you should definitely contact a neurologist to prescribe therapy.
Parents are not allowed to demand that their child stop the tic on their own. Experts will help him with this. Adults should provide the patient with a comfortable sleep and wakefulness regime, feed him properly and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Why is this observed?
Frequent blinking of a child's eyes increases concentration. This will allow you to concentrate your thoughts to perform any action. When the eyelids periodically close, the nerve cells in the brain relax, which helps focus the gaze.
Frequent eye blinking in a child occurs from natural stimuli:
- penetration of dust and dirt;
- foreign body;
- strong wind;
- when reading and watching TV for a long time.
This condition should not lead to anxiety. If these causes are eliminated, eye function is restored and blinking is performed as usual. But there are situations when frequent blinking of a child’s eyes causes concern among parents, then there is no point in postponing a visit to the ophthalmologist.
Why is this happening
Increased blinking can be a reaction to bright light, especially if we leave a dark room and immediately find ourselves in a brightly lit room or outside on a sunny, clear day.
The frequency is individual for each person, so the above figures are averages.
- if we focus on some thought (at this moment it becomes more frequent);
In order to somehow organize them, we can conditionally divide all cases into 3 large groups:
ophthalmological reasons: this is a way to relieve tension (close your eyes tightly, blink), foreign body contact with the mucous membrane, dry eye syndrome, corneal injury, inflammation, etc.; neurological and other diseases not related to vision: neuroses, brain injuries, vitamin and mineral disorders, hormonal or metabolic disorders, Parkinson's disease, addiction to alcohol, drugs, negative drug reaction.
The first group of reasons should be addressed to an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist), who will prescribe appropriate treatment in each individual case. Some people complain not just of frequent blinking, but of a feeling of “sand” (dryness) in the eyes. But everything is interconnected. Naturally, in order to moisturize the eyeball, frequent blinking is simply vital.
It is necessary to identify the cause of dryness, which most often appears:
against the background of long reading, computer work, general fatigue, nervous tension, etc.; as an individual reaction to the dryness of the surrounding air.
Therefore, the first step is to eliminate the factors that caused dry eye syndrome. Perhaps, in addition to this, the specialist will prescribe eye drops that relieve fatigue, advise special exercises to relax the eye muscles, and everything will return to normal.
There is a whole set of exercises for the eyes, where you need to imagine that the eyelids are the wings of a butterfly, which either freeze (shrink), then open wide, or often flap in an impulse to fly away. Between these manipulations, it is necessary to lightly massage the closed upper eyelid with one of the fingers (the middle one is more convenient) in a circular motion.
Manifestations of nervous tics in adults for neurological reasons
The third broad group requires a more serious approach to treatment and you will most likely have to contact several specialists, because frequent twitching of the eye muscles is not a separate disease, but the end point of a long process of disorders. You will need a consultation with an ophthalmologist, traumatologist, infectious disease specialist, and neurologist.
Nervous tic is a childhood disease that is very rarely diagnosed after 18 years of age. And unless the cause of frequent blinking is not a birth injury or infection, but ordinary fear, then it is possible to do without medications at all, limiting ourselves to behavioral therapy.
Modern medicine distinguishes between primary and secondary tics. Primary refers to childhood nervous disorders that may return in adulthood. Experts associate secondary symptoms specifically with disturbances in brain activity. According to medical statistics, the percentage of the adult population prone to frequent blinking is limited to the range of 0.1-1%. Moreover, male residents of megacities most often suffer. The disease in adults is more difficult to treat.
In adults, blepharospasm (convulsive twitching) can occur against the background of atherosclerosis, calcium deficiency, organic lesions of the central nervous system, vascular diseases of the brain, etc. Why, depending on the underlying cause, complex treatment is required.
And, as a rule, drug treatment is combined with psychotherapy. Often, with severe nervous shock in adults, a tic may not appear immediately, but after some time. Psychotherapists believe that this applies more to those who are used to restraining their emotions.
Medicinal treatment of tics and other medical procedures
In extremely severe cases, a decision may be made to use surgery for the purpose of deep brain stimulation, but this method is in the testing stage.
Sometimes the smallest dose of Botox is enough to relieve upper eyelid spasm. However, as practice has shown, this method is also ineffective, because it gives short-term results for 3-5 months.
This outcome usually ends in a mild form of transient tic.
Drug treatment also cannot be called an absolutely optimal method, since it gives a positive result only in 30% of cases.
The following drugs are usually prescribed:
Is that all?