“Furadonin” is one of the most common medications prescribed for a wide range of diseases of the genitourinary system. The drug is quite common, effective and affordable, which is why it is popular with both patients and doctors. However, for a complete cure, you need to take a whole course of the drug, which can take a couple of weeks. Of course, all this time it is difficult to maintain bed rest and adhere to a special diet. When planning your pastime, the reader may be interested: is it possible to take Furadonin with alcohol? Our article will answer the question.
What is "Furadonin"?
Talking about the compatibility of Furadonin and alcohol, first of all we will analyze the features of the drug itself. Its main active component is nitrofurantoin. The substance can not only destroy infectious agents, but also prevent them from multiplying and returning to the human body.
How do nitrofurans work? They inhibit the most important biochemical processes in the body of microbes, which leads to the death of the latter. In addition, the active component blocks the production of toxins by the microorganism. All this together allows you to improve the patient’s condition in a short time.
Another advantage of nitrofurantoin is that the substance activates the work of the body’s immune forces, provokes them to large-scale production of phagocytes, which are designed to destroy bacteria and foreign bodies.
The medicine today is presented in the form of tablets, powder, capsules. Take it on the recommendation of a doctor. It is best not to use such a serious drug for self-medication.
Effect of alcohol
When using the drug and alcohol, compatibility is low. This is due to the negative effect of ethanol itself on the body.
Taking tablets at the same time makes it difficult to convert ethanol into final products. The concentration of alcohol in the blood increases, which leads to corresponding manifestations.
The compatibility of the drug with alcohol is also expressed in a weakening of the therapeutic effect. Taking a small amount of alcohol, the patient reduces the effectiveness of the drug by 2 times, which leads to:
- Spread of inflammation.
- Penetration of pathogenic microbes into the ureters and kidneys.
- Deterioration in health.
- Lengthening the recovery period.
Alcohol in minimal concentrations can cause irreversible changes in organs such as the pancreas or intestines. People who took ethanol along with tablets developed hepatitis, pancreatic necrosis and bacterial sepsis.
When is the remedy prescribed?
The main reasons for a doctor to prescribe a drug:
- Cystitis in acute and chronic form.
- Urethritis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Pyelitis.
As a preventive component, Furadonin can be prescribed after certain diagnostic procedures (catheterization, cystoscopy), and surgical interventions.
The drug treatment regimen (frequency, duration of administration, dose) is selected by a specialist individually for each patient. The doctor also consults the patient about the compatibility of alcohol and Furadonin.
General ideas about the drug
The medicine is prescribed mainly for pathologies of the urinary system. It causes the death of most pathogenic microorganisms, therefore it is used by doctors for etiotropic treatment.
Belongs to the group of nitrofurans and affects enzymatic processes in the bacterial cell.
Taking the drug ensures a blockade of the production of toxins that have a negative effect on the condition of the body.
Additionally, an immunostimulating effect from long-term use of the tablets was noted.
The drug is prescribed for:
- Acute and chronic cystitis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Urethritis.
- To prevent complications after surgery in the urinary system.
After the first dose, there is an immediate decrease in pathogen growth and death. An anti-inflammatory effect develops, which ensures the recovery of patients.
The drug dosage regimen is prescribed by the doctor. It is highly not recommended to combine treatment with constant or periodic consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Contraindications
Like any other potent drug, this one has a number of contraindications. The instructions for its use also contain information about the impossibility of combining alcohol and Furadonin.
The main contraindications are:
- Allergy to any of the components of the drug.
- Acute form of porphyria.
- End-stage heart failure.
- Kidney diseases.
- Liver diseases.
- Lack of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the body.
The drug is contraindicated for children under 3. Pregnant women and nursing mothers should not take Furadonin.
Indications and contraindications for use
The medicine is intended for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ureteral system caused by microscopic organisms sensitive to the drug. The medication is used as a prophylactic composition when performing cystoscopy, urological operations, and catheterizations.
The drug is not prescribed to patients suffering from hypersensitivity to the drug, chronic failure of a paired organ, problems with the heart muscle, cirrhosis, hepatitis, or acute porphyria. It is not prescribed to pregnant women and nursing mothers, as well as to children whose age category has not reached one month.
While taking Furadonin, there is a possibility of allergic manifestations, gag reflex, nausea, dizziness, pain, hepatitis, pancreatitis, cough. Rarely, diarrhea and pain in the abdominal area occur.
Side effects
The instructions for the drug clarify that the combination of alcohol and Furadonin directly leads to the provocation of side effects. But they can manifest themselves without this reason.
To reduce the risk of side effects, it is recommended to use the product only after a good snack or lunch, and wash it down with plenty of drinking water.
Side effects of treatment with Furadonin are as follows:
- General malaise, weakness.
- Anemia.
- Migraine.
- Loss of appetite.
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Dizziness.
- Swelling.
- The appearance of a rash on the skin.
- Attacks of suffocation.
Rare side effects include hepatitis and jaundice.
Consequences of combination
If a patient takes Furadonin as prescribed by a doctor, then combining the drug with alcohol can cause the most unforeseen consequences. First of all, alcohol can greatly weaken the therapeutic effect of the medicine, and the treatment will be ineffective.
Often, due to the combination of alcohol and Furadonin, the following conditions and phenomena occur:
- Diarrhea.
- General weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Depression.
- Labored breathing.
- Feeling of bladder tightness.
- Depression.
- Temperature increase.
- Lack of appetite.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Edema.
- Chills.
- Asthma.
- Nagging pain in the abdomen.
- Increased pressure.
- Redness of the neck.
- Cramps.
To make side symptoms less pronounced, Furadonin should be taken with or after meals. The drug should be taken with milk or plenty of water. You should not drink carbonated water or energy drinks for this purpose. Taking liquids containing ethyl alcohol can provoke a painful reaction in the body.
If we remember that a person takes medicine not on a whim, but because of an illness, then we can understand that alcohol will never have a beneficial effect on an organism weakened by illness. It can only make the situation worse and cause harm.
Is it possible to combine alcohol and medication?
Are Furadonin and alcohol compatible? No. During this medication course, it is best for the patient to give up his favorite alcoholic drinks. There are several reasons for this.
We have already mentioned that alcoholic drinks provoke side effects from taking the drug. With cystitis and pyelonephritis, the patient's condition is always accompanied by poor health, general weakness, and unpleasant painful sensations. Intensified by alcohol, the side effects of the medicine will make it several times heavier.
We all know that ethanol has a negative effect on the body. And one of its harmful effects is a decrease in the effectiveness of the drug taken by a person. This is observed in the case of Furadonin and alcohol. Reviews also indicate that alcohol negatively affects the effectiveness of treatment.
Taking a potent medication is an additional (and sometimes very heavy) load on the body. This is the path the active component “Furadonin” takes in it:
- The substance dissolves and is absorbed in the intestines.
- Then it enters the blood and goes to the liver.
- In the cells of the organ, the substance awaits biotransformation - it turns into a metabolite.
- As a result of the process, about 50% of the active component will be excreted through the kidneys.
Hence the conclusion: taking Furadonin is an additional burden on the patient’s kidneys and liver. Therefore, contraindications include diseases and pathologies of these organs.
Is it possible to mix alcohol with Furadonin? Of course not! After all, alcohol has a toxic effect on the same organs - the liver and kidneys. Actively transforming in hepatocytes (liver cells), it is also excreted through the kidneys. And these organs already suffer additionally from the processing of the active component “Furadonin”.
Thus, a person combining medicine and alcohol deals a double blow to the kidneys and liver, doubling the load on them. And this can already lead to toxic hepatitis or general poisoning, intoxication of the body.
How dire are the consequences?
Taking the medication simultaneously with alcohol can also lead to negative side effects. Alcoholic drinks not only complicate the course of the disease, but also pose a potential danger to the patient’s health.
The following consequences are possible:
- increased heart rate;
- burning and cutting in the groin area;
- pain during urination;
- itching in the groin and urinary tract;
- frequent false urge to urinate;
- feeling of tightness in the bladder.
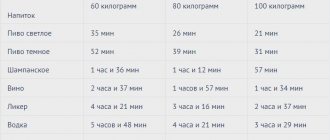
Furadonin and alcohol taken simultaneously always cause severe intoxication of the body. To find out whether you can drink alcohol after completing the course of treatment, you will need to know the time it takes for the medication to leave the body. This period is 2-4 hours.
Reviews from patients tend to suggest that the first use of alcohol should take place no earlier than a week after the last use of the medicine.
Furadonin is successfully used in medical practice. However, you should carry out the full course of treatment and not stop after the first improvements. The doctor must describe in detail the compatibility of the drug with alcohol when prescribing it to the patient.
However, the patient himself is also responsible for the correct intake of Furadonin. Knowing about possible negative reactions, you should categorically abstain from alcoholic beverages during treatment.
Mixing Furadonin with alcohol: consequences
We found out that medicine and alcohol are incompatible for three reasons: reducing the effectiveness of the drug, causing side effects, and increasing the load on the liver and kidneys.
It should, in turn, slow down the breakdown of ethanol into final products. The concentration of alcohol in the blood increases, which leads to additional negative consequences.
Based on studies and reviews about the compatibility of alcohol and Furadonin, it can be judged that alcohol-containing drinks reduce the effectiveness of the medicine by half! Moreover, we are not talking about strong variations, but about products that contain a minimum percentage of alcohol.
For the patient, all of the above threatens with the following consequences:
- Deterioration in general health.
- Active increase in the inflammatory focus.
- Delaying the moment of complete recovery.
- Penetration of pathogenic microorganisms that do not meet adequate resistance on their way further into the ureter and kidneys.
Reviews also say that combining Furadonin with alcohol can sometimes have a negative effect on the intestines and pancreas. The consequences here are quite serious - bacterial sepsis, pancreatic necrosis, hepatitis.
COCs and endometriosis: defense or attack?
Management of patients with endometriosis from the perspective of international and domestic clinical recommendations
World statistics on endometriosis have become especially alarming since the beginning of the 21st century. Currently, this proliferative disease affects 7 to 10% of women of reproductive age worldwide. At the same time, its prevalence clearly continues to increase; endometriosis is increasingly being diagnosed at a young age.
Pathogenesis news
As is known, the pathophysiology of endometriosis is based on the emergence and proliferation of endometrioid heterotopias in areas outside the normal location of the uterine mucosa. Morphofunctionally, the newly formed tissue is identical to the endometrium; it does not exhibit malignant properties, despite proliferative growth and the possibility of metastasis. At the same time, the diversity of the location of heterotopias determines the variability of the disease. Based on the characteristics of developmental mechanisms, clinical manifestations and recommended medical tactics, adenomyosis, cystic forms and deep endometriosis are distinguished - severe infiltrative forms, when heterotopias do not undergo regression, but, on the contrary, penetrate into the deeper layers of the peritoneum or other organs, forming infiltrates and adhesions
At the same time, all forms of endometriosis have common features: endocrine activity of foci, imbalance of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis and immunosuppressive conditions. Data accumulated over the last decade allow us to conclude that the decisive factor in the development of the disease is genetic, as evidenced by the high frequency of combination of endometriosis with connective tissue dysplasia syndrome, pelvic varicose veins, congenital malformations and underweight; moreover, they are not uncommon family forms. One of the recognized triggers of the disease is stress, which is noted in the anamnesis of up to 90% of patients with clinically manifest forms of endometriosis.
In general, endometriosis is considered a multifactorial disease, and it is characterized by three pathogenetically significant components.
1. Systemic inflammatory reaction aimed at clearing the abdominal cavity of retrogradely abandoned ectopic endometrial cells.
2. Impaired immune response, promoting cell attachment and progression of the endometriotic lesion.
3. Initiation of neoangiogenesis - vessels grow into the area of endometrioid heterotopia.
Why treat?
If endometriosis cannot be cured, why treat it? The answer to the question lies on the surface - this really makes a lot of sense.
1. The disease increases the frequency of reproductive disorders. Moreover, the risk of infertility or miscarriage depends not so much on the presence of endometriosis itself, but on its clinical form and location. After adequate comprehensive treatment, the likelihood of spontaneous pregnancy and favorable completion of the gestation period is very high, while the very fact of pregnancy ending in childbirth and lactation, in turn, significantly reduces the risk of relapse.
2. Endometriosis can affect organs the removal of which is difficult, impossible or physiologically inappropriate (bladder, intestines, eyes, lungs, gums, rectal sphincter, etc.). In addition, the forming adhesions change the anatomy and topography of the affected organs, with a possible disruption of organ functions.
3. Endometriosis significantly impairs the quality of life due to chronic pain syndrome, dyspareunia, menstrual disorders and infertility, which lead to anemia, asthenia and depression, sometimes over a fairly long period of life.
4. Cases of the occurrence of a specific cancer process in the endometrioid focus are described (in 1% of women with ovarian endometriosis and in 0.3% with disease of extra-ovarian localization).
Pathogenetic root of therapy
The concept of endocrine autonomy of endometriosis, coupled with the adhesive process typical of the disease in the area of the lesions, determines the priority of the surgical method of treatment.
In general, the surgeon’s task is to maximize the removal of visible and palpable lesions, which sharply reduces the amount and intensity of uncontrolled extragonadal conversion of estradiol (in addition to restoring normal anatomical relationships in the pelvic cavity).
But with widespread forms of the disease, the surgeon’s uncertainty about complete removal of the heterotopia, or a high clinical and anamnestic risk of relapse, drug therapy plays a role almost equivalent to surgical intervention, allowing one to move from “active defense” to “offensive” on active lesions and reduce the risk of repeated operations.
When it comes to adenomyosis in young nulliparous women or in patients planning a pregnancy in the near future, drug treatment remains the main or even the only option.
Surgery first
The American Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ASOS) has long established an algorithm for the management of patients with endometriosis, and laparoscopy is in the first place. This is justified for two reasons. Firstly, a clear idea of the severity of the process in external endometriosis can only be obtained during laparoscopy, and secondly, removal of foci of endometriosis is indicated for patients with a variety of, often combined, goals: to restore the anatomy of the affected area, relieve pain, eliminate hyperpolymenorrhea, prevent relapses. And, of course, one of the most sought-after treatment goals is to restore reproductive function.
Suppression for good
The main idea of drug therapy for endometriosis is to reduce the level of estradiol in peripheral blood below 40 pg/ml, which corresponds to a postmenopausal state. In this case, the prescribed treatment should maintain systemic hypoestrogenism for quite a long time - at least 6 months. It is this period of time that allows us to hope that irreversible atrophy will develop in active endometrioid lesions.
According to modern concepts, several groups of drugs can provide targeted hypoestrogenism in endometriosis.
- Combined hormonal contraceptives (optimal for adolescents and young women).
- Gestagens.
- Antigonadotropins.
- Antigestagens.
- Luteinizing hormone releasing factor (LHRF) agonists.
- Aromatase inhibitors.
Conversions of oral contraceptives
In healthy women taking oral contraceptives, the potential risk of endometriosis is significantly lower than in those who do not take them, since these drugs inhibit the functional activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, maintain a given level of estrogen in the blood serum, reduce the production of prostaglandins and reduce menstrual blood loss due to dystrophy or atrophy of the endometrium .
According to a meta-analysis of 18 clinical trials selected from 608, the overall risk ratio for endometriosis for current users of hormonal contraception was 0.63 (95% CI 0.47-0.85) - a woman taking COCs had a 37% lower risk of endometriosis. compared to the general population. However, there is a flip side to this coin - discontinuation of oral hormonal contraception increases the risk of endometriosis: in patients who recently stopped using COCs, the risk is 21% higher (OR 1.21; 95% CI 0.94-1.56), and in women who have ever taken contraceptives but do not currently use them - by 19% (OR 1.19; 95% CI 0.89-1.60).
From the above, a simple conclusion follows: discontinuation of the drug is advisable only in one case (not counting possible contraindications that arise during the period of use) - when planning a desired pregnancy - the best method of treating and preventing endometriosis, invented by nature.
Taking hormonal contraceptives is a very beneficial option for managing patients at risk for endometriosis. The use of COCs is considered in world practice as the first line of treatment for this disease in young women. They successfully relieve symptoms and can reduce the risk of relapse (with the exception of its infiltrative forms).
Progestational instruments
Progestogens do have therapeutic and prophylactic potential against endometriosis. They allow you to successfully relieve symptoms, reduce the frequency of relapses, and also complement complex treatment if it is necessary to restore reproductive function (maintaining the luteal phase, preconception preparation). For endometriosis, four substances of progestational nature are widely used.
- Medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Dydrogesterone
- Dienogest
- Levonorgestrel
Another method of hormonal contraception that has therapeutic benefits in patients with stage I-II endometriosis and after surgery is the intrauterine levonorgestrel-releasing system (evidence B). Its clinical effect is based on the monotonous local effect of 20 mg of levonorgestrel on the endometrium, which causes its dystrophy, even atrophy, and the development of reversible drug-induced uterine amenorrhea.
When the patient’s main problem is reproductive dysfunction, comprehensive overcoming of endometriosis is a mandatory stage that should precede measures aimed at combating infertility or miscarriage. LHRH agonists have traditionally been used as first-line therapy for endometriosis-associated infertility. Their advantages are that the point of application of the drug is the gonadophores of the pituitary gland
In case of miscarriage in patients with endometriosis, after complex two-stage treatment, it is customary to carry out rehabilitation and preconception preparation. The use of treatment regimens used for a condition defined as autoimmune chronic endometritis can be considered very justified, since in both cases the pathogenesis is based on a violation of endometrial receptivity.
The authors of the Canadian “Guide to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Endometriosis” (2010) succinctly summarize the current situation with this disease: today “... there is no specific treatment” that is universal for any patient. At the same time, “... it is necessary that the methods used are effective and safe and that they can <...> be used until the age of menopause or until pregnancy occurs, if desired.”
Based on materials from the Scientific and Practical Journal
for obstetricians-gynecologists
and specialists from the obstetrics and gynecology service,
# 2 (19) 04/2014 /StatusPraesens
Additional Side Effects
The person is prescribed Furadonin. Can I drink alcohol? No! Otherwise, the following side effects from the combination are possible:
- Heartburn, vomiting, nausea. In individual cases - diarrhea, enterocolitis, hepatitis.
- Negative effects on the central nervous system - insomnia, dizziness, nervousness, headaches.
- Allergic itching, urticaria. In individual cases - anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema.
If a patient, ignoring the doctor’s instructions, does not give up his favorite alcohol during the entire course of taking Furadonin, then such frivolity threatens him with the following:
- Jaundice (the liver cannot cope with double the load).
- Chronic vomiting, diarrhea.
- Small pinpoint rashes on the skin.
- Systematic headaches due to constantly increased intracranial pressure.
- Itching and burning in the perineum.
- Pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Flatulence.
This condition already requires special complex treatment.
Recommendations for taking the drug and side effects
This synthetic agent has a bactericidal effect. Its mechanism of action is associated with damage to ribosomal proteins and disruption of protein, DNA and RNA synthesis in bacteria.
Furadonin tablets are prescribed for the treatment of:
- inflammations resulting from infectious diseases of the urinary tract: acute cystitis, pyelitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, paranephritis;
- as preventive measures after urological surgery and diagnostics in the form of catheterization and cystoscopy;
- uncomplicated bladder infections.
Thanks to the active component of the drug (nitrofurantoin), pathogens stop producing toxins and an improvement in well-being occurs in a minimum period of time.
Possible side effects when taking the medicine are quite numerous:
- vomiting, nausea, jaundice, hepatitis;
- diarrhea and lack of appetite;
- dizziness and migraines;
- breathing problems (suffocation) and broncho-obstructive syndrome;
- swelling and paroxysmal cough;
- nystagmus and asthenia;
- chest pain, anorexia;
- drowsiness and fever;
- anaphylactic shock;
- increased blood pressure;
- chills and darkening of the eyes;
- peripheral neuropathy.
The use of the drug is recommended during meals or immediately after meals. In this case, the tablets should be washed down with plenty of still water.
The duration of therapy is usually seven to ten days. The recommended dose is 50 mg to 100 mg four times daily. If during this period of time relief of the condition does not occur, then further use is no longer effective.
What else is important to know about the drug:
During the entire course of treatment with this drug, a favorable result is achieved by increased protein intake in the patient’s diet. If, from the first day of taking the medicine, there are significant improvements in the condition, then you should not stop therapy. The course of taking the drug must be completed to the end. This will help avoid the transition of the disease from the acute phase to the chronic phase.
How to properly combine alcohol and medicine?
Experts advise completely abstaining from drinking alcohol for the entire duration of therapy.
However, if a situation suddenly arises where it is difficult or impossible to stop drinking alcohol, you should pay attention to these recommendations:
- The period of complete elimination of “Furadonin” from the body is 48-72 hours. Only after this period has passed can you enjoy your favorite alcohol without harm to your health.
- The minimum time that should pass after taking the medicine before a party is 24 hours. This is enough to save the body from severe toxic consequences, but will not protect against other side effects.
- If you drank an alcoholic drink the day before, then the course of treatment with Furadonin should begin 12-24 hours after that. Additionally, it is recommended to help the body remove ethanol by taking adsorbents (activated carbon).
- If you accidentally drank alcohol and took Furadonin almost at the same time, then you need to eat heavily. Give preference to fatty and high-calorie products - they slow down the absorption of alcohol into the blood and protect vulnerable organs.
Taking Furadonin with low-alcohol drinks
Since it is necessary to take the medicine with a large amount of liquid, some patients try to drink beer for this purpose, believing that a small proportion of ethyl alcohol in this low-alcohol drink will not have a detrimental effect on health and will not harm the treatment. But that's not true. The harm lies in the fact that beer can also reduce the effectiveness of Furadonin. In addition, ethyl alcohol, even in minute quantities, entering the brain, more precisely, the pituitary gland, causes a disruption in the mechanism of reducing the amount of urine and removing it from the body. By reducing the activity of the central nervous system, beer causes the call to urinate to arrive untimely and is delayed, which again leads to overfilling of the bladder, stretching of its walls and the growth of the inflammatory process. The patient's condition worsens.
In the distant past, the composition of beer was somewhat different than it is now; it did not contain ethyl alcohol, preservatives, thickeners, or flavor enhancers. These chemicals can cause the most unexpected side effects when used simultaneously with Furadonin, which will have a detrimental effect on the patient’s health. It is ethyl alcohol that is a substance that irritates the urinary system: kidneys, bladder, ureters, persistently causing a frequent urge to urinate. In addition, the process of removing alcohol from the body is slow, causing swelling of both the face and limbs.
It can be concluded that combining a course of treatment with Furadonin with taking any alcoholic drink, be it vodka, beer, wine, brandy, champagne, energy liquids, is strictly prohibited for both men and women.
The main dangers of the combination
In conclusion, we list the main dangers of combining alcohol and Furadonin:
- Electrolyte imbalance - effects on the cardiovascular system. These are cardiac pain, tachycardia, myocarditis.
- Pathological effect on the gastrointestinal tract, death of beneficial microflora, loss of accumulated vitamins and electrolytes.
- Kidney dysfunction, which can lead to nephritis.
- Negative effect on the liver and gall bladder.
The long-term consequences of such frivolity sometimes torment for a very long time - high blood pressure, itchy skin, chronic fatigue, anemia, mental disorders. Therefore, there is only one main piece of advice: during treatment with Furadonin, completely abstain from alcohol! A potent drug in itself is a big burden on the body.