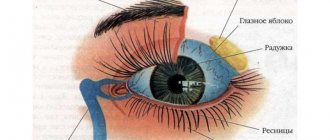
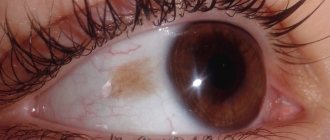
Accompanying symptoms
Often, yellowing of the sclera or the appearance of yellow spots on the whites of the eyes is accompanied by other symptoms, which are divided into local and general. If the cause of the change in the color of the sclera is an ophthalmological disease, against its background the following may also occur:
- Pain or itching in the eyes.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
- Discharge from the eyes.
- Inflammation of the edges of the eyelids.
- Decreased visual acuity.
And if the cause of yellow spots is a general disease, as a rule, general symptoms also appear, including loss of appetite, feeling tired, nausea, feverish conditions, chills with fever.
Dark stain
When a dark spot appears in the eye, then the situation is more dangerous. Typically, the patient complains of “floaters” in the eyes, which can move from object to object as the patient looks.
Often such a dark spot indicates initial destructive processes in the vitreous body. This suggests that that part of the organ of vision that is located between the lens and the retina begins to collapse. It acquires a jelly-like state. In most cases, black spots appear on the periphery, but it can also happen that they appear directly on the pupil. According to statistics, this disease is considered age-related, but can also occur in people suffering from myopia.
If the problem is advanced, there is a risk of developing a complication such as retinal detachment on the vitreous body. Here it is necessary to urgently contact a specialist, since it may be necessary to perform laser surgery, which allows you to fix the site of the rupture.
When, in addition to a dark spot, additional symptoms appear, then a person is simply obliged to consult an ophthalmologist.
These include situations:
- if there is a dark spot in the eye that seriously impairs vision;
- “special effects” appear before your eyes - lightning, colored spots, etc.;
- if in the eye or eyes, when you look, not one, but several black spots begin to appear;
- when a “veil” appears, affecting partially or completely the entire eye.
Such deterioration indicates a serious development of the eye disease, so help is simply necessary in such a situation.
To help the patient, the ophthalmologist can prescribe special resorption therapy that will help get rid of opacities. Drug treatment is aimed at stimulating metabolic processes in the vitreous body. In parallel with this, the patient needs to take eye vitamins and use physiotherapeutic procedures. If all these methods do not give a positive result, then surgical intervention is used.
It is also worth noting that “black spots flashing before the eyes” is observed with high blood pressure.
This phenomenon is often accompanied by a headache in the back of the head, nausea and vomiting. It is worth measuring your blood pressure for several days and, if it is elevated, consult a therapist.
If the symptoms increase - the pain intensifies, the person suffers from vomiting, is anxious, lacks air, then you should seek medical help immediately to avoid possible complications in the form of stroke, heart attack, cerebral edema, etc.
General reasons
Yellowing of the sclera of the eye is one of the most typical symptoms of jaundice. Jaundice develops when bilirubin metabolism is disrupted in the body. The main organ involved in this process is the liver. The inability of the liver to remove bilirubin may depend on various factors, but in the end, it begins to be deposited in the skin, including the mucous membranes of the eyes, which causes a change in their color.
Diseases leading to jaundice are considered to be:
- Cirrhosis of the liver, which in most cases is caused by alcohol abuse.
- Hepatitis caused by a viral infection of the liver.
- Liver cancer.
- Obesity, which leads to fatty hepatosis (dystrophy) of the liver.
- Stones in the gall bladder.
- Anemia.
Any general diseases that lead to the appearance of yellow sclera require a thorough medical examination of the patient and emergency care.
Eye diseases
Yellow spots on the white of the eye usually occur in connection with diseases of the organ of vision, which do not cause irreversible consequences and do not cause complete loss of vision. These include:
- Pingwekulu. The pathology is a benign yellow growth in the conjunctival area. At the same time, yellow spots appear symmetrically, both on the outside and in the corners of the eye. Typically, the disease is more common among the elderly, since the development of pinguecula is caused by the natural aging of the mucous membrane of the eye.
- Pterygium. This is a growth or thickening of the mucous membrane of the eye in its inner corner. It looks like a triangular yellow spot and does not cause pain. In some cases, the pterygium may turn red, becoming bright pink. The disease is caused by aggressive influence of external factors. Among its causes, the following are especially often cited: dry, hot climate, intense UV radiation, exposure to strong winds.
- Dermoid cyst of the conjunctiva. This birth defect is a benign neoplasm and is characterized by a dense capsule containing a fatty substance. Dermoid cysts tend to grow and increase in volume.
- Conjunctival cyst. It is an epithelial growth with fluid inside. It may be yellowish in color and appear as a small spot on the conjunctiva.
- Nevus. It is of the same nature as moles on the skin. It is a yellowish or brown spot localized in any area of the sclera, including its inner and outer corners. If overgrown, it can pose a threat to vision.
- Horner-Trantas spots. The cause of their appearance is considered to be allergic reactions. Such spots are small yellow “grains” localized on the white of the eye around the cornea. The cause of their appearance is usually allergic conjunctivitis, less often allergic keratitis.
What is the danger of such symptoms?
Any formation on the eyeballs is potentially dangerous. For example, if it appears along with headaches and nausea, then it is likely a precursor to a migraine.
Yellow spots become a side symptom of the underlying disease. It happens that they can change size depending on the lighting. A characteristic feature is that when you look into the distance, you see a floating formation in front of your eyes.
Such signs relate to diseases of the vitreous body, namely its destruction. If a person sees bright flashes, this may mean that the posterior part of the vitreous has detached. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Yellow spots before the eyes can be accompanied by significant vision impairment. In this case, a person has difficulty seeing objects even at close range. This is often caused by swelling of the retina. In this process, fluid accumulates in the central part, or macula.
The tissue in the eye begins to swell. This happens if a person suffers from diabetes or diseases of the cardiovascular system. This manifestation also develops as a result of allergies to medications taken.
Bleeding inside the eye may also occur. Outwardly, it will not appear in the form of red spots, but yellow, brown and even black formations will be visible.
Destruction of the vitreous body
There is also degeneration of the macula, the center of the retina where the light beam is focused. This is an age-related disease. It affects older people. At first, dots may appear before the eyes and the patient’s vision deteriorates.
The disease progresses quickly, and the person is at risk of completely losing his vision. The patient has damage to the retina in the central part.
There is a hereditary Stargardt disease. It is associated with genetic abnormalities. The disease manifests itself at a young age of 6 years. The obvious signs are:
- Yellow spots before the eyes.
- Colorblindness.
- The child sees poorly in the dark.
Treatment
Prescription of treatment when yellow spots are detected on the whites of the eyes occurs only after a complete examination and identification of the causes of this condition.
In case of nevus, the patient needs dynamic observation by a specialist. The initial stages of pterygium and pinguecula are treated with drops and gels with moisturizing properties for the conjunctiva. If there is eye irritation with redness, a course of anti-inflammatory therapy is recommended. If the effect of therapeutic treatment is insufficient, surgery may be prescribed.
Severe cases of conjunctival cysts are treated only with surgery. In this case, the patient may be offered cauterization or laser treatment. Horner-Trantas spots disappear after drug therapy for the underlying disease.
In the medical department, everyone can undergo examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on the results, receive advice from a highly qualified specialist. The clinic provides consultations to children from 4 years old. We are open seven days a week and work daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Our specialists will help identify the cause of vision loss and provide competent treatment of identified pathologies.
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure or make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by calling 8 (800) 777-38-81 (daily from 9:00 to 21:00, free for mobile phones and regions of the Russian Federation) or using the form online entries.
Causes of occurrence and treatment recommendations
Vitiligo is never congenital : such a disease, due to a number of reasons, can appear starting from about ten years of age and mainly against the background of autoimmune pathologies.
These are diseases that arise due to dysfunction of the immune system . Often the disease is hereditary .
Keep in mind! Other reasons and contributing factors are:
- Experienced stress and psycho-emotional disorders . In such cases, circles under the eyes can form over a long period of time, developing from individual dots and spots. In such cases, cosmetic procedures are powerless; it is possible to prescribe a course of immunomodulatory drugs - cyclosporine or isoprinosine.
- Infectious dermatological diseases . Vitiligo in such cases spreads almost immediately after the disease or after some time. Effective methods of treatment are courses of antibacterial drugs or taking corticosteroids if the diseases are accompanied by inflammatory processes with subsequent disruption of the structures and functions of soft and bone tissues (prednisolone, betamethasone).
- Sometimes white circles appear after prolonged contact with synthetic materials . For example, if a person wears surgical masks due to professional activities. In such situations, antiallergic therapy may be prescribed, and during treatment it is allowed to use masking cosmetics.
- Vitiligo under the eyes can develop due to a lack of vitamins and microelements in the body , which leads to disruptions in the functioning of the immune system. The main treatment option in this case, in addition to the use of immunomodulators, may be a course of fortification (this disorder is mainly characteristic of a lack of vitamins E, C, B9, B6 and B1).
- Sometimes helminthiases lead to disruption of the endocrine glands, which leads to a lack of copper in the body and provokes the development of the disorder. Treatment involves taking anthelmintic drugs.
- If this phenomenon is associated with diseases of the liver and digestive tract (disruption of the processes of production of various enzymes and pigments occurs in such cases), it is possible to prescribe the drugs dalargin, phosphogliv or essentiale.
Note! In itself, such a symptom has no consequences other than psychological discomfort.
But it can indicate malfunctions of the thyroid gland, skin diseases (including psoriasis), diabetes, psychological problems, pneumonia, and sometimes the pathology even speaks of progressive myopia.
accurately determine the cause of the disease only after a medical examination , based on the results of which specific treatment is prescribed :
- restoration of skin color using an excimer laser;
- PUVA therapy (a complex of taking psoralen drugs, which, with simultaneous ultraviolet irradiation of the affected areas of the skin, reduces the skin's susceptibility to such radiation and the risk of developing the disease due to exposure to sunlight is reduced);
- use of narrow-wave irradiation;
- regular use of hormonal ointments (protopic or epidel), which prevent the destruction of pigments. The course is complemented by oral administration of melagenin, which enhances the production of natural melanin.
In severe cases with extensive and irreversible damage, the patient may need skin grafts.