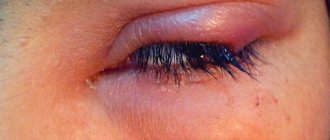
Headache and swelling of the eyelids occur simultaneously quite rarely. Usually these two signs are not related. Sometimes their appearance indicates the development of severe pathologies of internal organs. In what cases should you definitely see a doctor? Let's consider the causes of swelling of the upper eyelids in the presence of a headache.
Headache and swelling of the eyelids
Swelling of the upper eyelid is a very common symptom. It is characteristic of many eye diseases and various pathologies of internal organs. Also, the eyelids swell even in the absence of diseases. In rare cases, another symptom develops in parallel with this symptom - headache. This sign also cannot be called specific. Its appearance does not always indicate the presence of a pathological process in the body. As a rule, with the development of these two symptoms, others appear - increased body temperature, weakness, weight loss, etc. Let's consider the main causes of swelling of the upper eyelids and headaches.
The upper eyelid is swollen - what could be the reasons?
This symptom can appear for completely different reasons. They are not always associated with diseases. So, the eyelids swell due to hormonal imbalances. In such cases, bilateral swelling is observed. As a result of injuries, after an insect or animal bite, swelling develops in one affected eyelid. These reasons do not lead to headaches. However, it can occur in a person after drinking alcohol.
Ethyl alcohol in large quantities causes not only swelling of the eyelids, but also the entire face. A person is also worried about nausea, dizziness, headache, weakness, and loss of appetite. Severe poisoning may require medical attention. In most cases, you just need to drink a lot of water and get enough sleep. Headache and swelling will go away in a day or two, depending on the condition of the body and the amount of alcohol consumed the day before.
In addition, common causes of eyelid swelling include:
- late dinner;
- overwork;
- several glasses of water or tea drunk before bed;
- insomnia.
The main factor leading to swelling of the eyelids and the appearance of bags under the eyes is the accumulation of excess fluid in the intercellular space. Various parts of the body swell, but the skin of the face, and especially the eyelids, is the thinnest. In this regard, swelling is primarily noticeable in the eyes. Moreover, mainly the upper eyelids swell. The lower ones swell, as a rule, with infectious eye diseases.
In what other cases is swelling of the upper eyelid accompanied by headache? Both of these symptoms can be disturbing in various eye pathologies that are inflammatory in nature. Including:
- conjunctivitis;
- blepharitis;
- dacryocystitis;
- barley;
- keratitis;
- chalazion.
The symptoms of these ailments are similar, so we will consider them separately.
Swelling under the eye on one side: causes and solutions
The asymmetrical appearance of swelling on the face can tell a doctor a lot.
For example, in such cases, heart disease is often excluded, since pathologies of this organ are usually characterized by the uniform distribution of accumulated fluid under the skin, although cardiac problems cannot be completely excluded.
Most often the problem is localized. In women, the pathology may be hormonal in nature, for example, speak of an imbalance in this area or be a manifestation of pregnancy. Let's look at the main causes of edema.
Allergy
Swelling in this case is an accumulation of immune cells that the body has directed to fight the allergen.
The localization of this process can be located in both eyes, or it can be asymmetrical, on the left or right side.
Most often, allergies in this area appear due to low-quality cosmetics, but food products, household products and plant pollen cannot be ruled out.
Quincke's edema
In essence, this is the same allergic reaction, but in a more severe form. This covers a significant part of the body: subcutaneous fat, eyes and even the respiratory tract.
The latter localization is especially dangerous, since swelling of the tissues of the respiratory tract is fraught with their closure, and this has a high probability of death.
It is necessary to act immediately, and the actions must be as correct as possible.
Cold
With a cold, swelling to varying degrees is observed throughout the body. This is due to the deterioration of lymphatic flow. But if a person has swelling under the eye on one side, then there is a high probability of a unilateral inflammatory process in the sinus or maxillary sinuses. The diagnosis will accordingly be sinusitis or sinusitis.
Insect bites
Surprisingly, this is the reason that seems most unlikely to people, because it seems that it is very difficult to miss close contact, and especially an insect bite. But many of them, such as mosquitoes, numb the bite site before the process. Only bees and wasps sting in such a way that it is impossible not to notice it. In these cases, swelling appears only under one eye.
Hit
Mechanical damage to the mucous membranes and eyelids is accompanied by swelling of the soft tissues on the right or left side, depending on the location of the collision.
Liquid accumulates inside, thus forming a bag. By the way, the hematoma can migrate to neighboring areas. Over time, such a hematoma should resolve without consequences.
You can speed up the process by using local agents with a resolving effect.
Diseases that cause edema
This can include several different diagnoses. Conventionally, they can be divided into several groups:
- Inflammatory processes localized in the tissues of the eyes. These are conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis. The clinical picture of the diseases is quite obvious and affects only these areas, and therefore it is difficult to doubt them.
- Pathologies of the oral cavity and teeth. How can teeth relate to the organs of vision? These tissues are located very close, and therefore inflammation in the oral cavity can cause swelling in the lower eyelids. In this case, inflammation in the oral cavity can affect the gums, and the process can become purulent. By the way, swelling often appears immediately after treatment, installation of dentures or crowns, as well as tooth extraction.
- Pathologies of the facial nerves. This neurological condition is accompanied by the appearance of pain in the head or neck, as well as the appearance of swelling in various areas of the face.
- Intervertebral hernia in the cervical spine. This condition is accompanied by impaired muscle tone, pain in the head and neck, swelling on the face and other symptoms. By the way, the appearance of swelling in one eye may indicate the progression of the disease.
- Diabetes. When the level of sugar in the bloodstream increases, especially if there are also elevated lipid levels, the viscosity of the blood increases significantly (the blood becomes thick). Metabolic processes slow down. Edema in such patients appears much more often than in others. By the way, this pathology has a particularly negative effect on the organs of vision, since microscopic blood vessels are located here - capillaries, which are more sensitive to changes in blood density.
Which doctor should I contact?
If there is swelling under the eye, it is advisable for a person to go to a therapist, but not every general practitioner is able to see the scope of pathology in a particular patient. In practice, the patient is then referred to other specialists - a cardiologist, neurologist, ophthalmologist, allergist, surgeon.
This does not mean at all that a person will become a patient of all these doctors. It’s just that this method makes it possible to exclude possible areas of pathology, and diagnosing the state of the body is never superfluous.
Finally, many diseases are hidden, and a complete examination will allow them to be identified at an early stage.
Diagnosis of diseases
Diagnostic procedures must include:
- blood and urine tests;
- conducting an ECG;
- CT or MRI, as well as x-ray of the skull (especially for injuries);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs (in some cases, MRI of these parts).
In the future, more detailed examinations may be required, for example, measuring intraocular pressure.
How to remove puffiness under the eyes
The simplest methods for eliminating swelling under the eyes are based on the need to accelerate the outflow of lymph and narrow the local blood vessels. Any cold compress will do for this.
The easiest way is to place a cotton pad soaked in clean water in the freezer for a few seconds, then apply it to your eyes. The duration of such a compress is a couple of minutes.
Any product from the freezer, pre-wrapped in cotton cloth, is also suitable for quick cold.
An excellent way to relieve swelling and increase local tone are compresses from tea bags. To do this, just dip the bags in hot water for a couple of seconds and immediately apply to the swollen areas around the eyes. The duration of this compress is 5 minutes.
Pharmaceutical products that have absorbable and blood-thinning properties work better.
Here you can note such local preparations as troxevasin ointment, Lyoton gel, Troxerutin, as well as more expensive cosmetics - Skin Doctors Eyetuck, Lierac Dioptigel, La Rosche-Posay Hydraphase Intense Yeux. They can be purchased at pharmacies or specialized cosmetic stores or salons.
If you have the financial opportunity, you can resort to cosmetic procedures. Specialists can offer such types of manipulations as darsonvalization, electrical stimulation, mesotherapy.
By the way, today you can also purchase devices for home darsonvalization.
If you strictly follow the instructions, then in addition to relieving swelling, a person will notice a significant increase in skin turgor and an improvement in complexion.
Some people try to remove swelling under the eyes with diuretics. Diuretics remove water from the body, but at the same time change the concentration of its components. This is especially important, and it is the violation of salt metabolism that subsequently becomes an even greater problem, and therefore this method can only be used after the recommendation of the attending physician.
A good way to get rid of swelling is to massage this area. This will improve lymph flow. Massage is done only on cleansed skin. The lymphatic drainage effect can be achieved with these exercises:
- On the temples you need to make 10 circular movements clockwise. It is better to carry out movements with the middle finger.
- From the outer corner of the eye to the inner corner along the bottom line, you need to apply soft pressing movements with your fingers. Along the top line, such movements are carried out in the opposite direction. Repeat 3 times.
- Using your fingertips, press first on the upper and then on the lower eyelid. Each movement is 10 seconds.
- Using patting movements with your fingertips, draw from the bottom of the eye from the outer corner to the inner, and vice versa from above.
- Wash with cold water and apply healing cream.
And of course, if this pathology is a symptom of a disease, then it must be treated. Removing swelling under the eye in this case will be useless until the impaired functioning of the system or organ is restored. If swelling is caused by prolonged lack of sleep, then it is better to correct the situation with good sleep.
Possible complications
Complications and consequences can sometimes be irreversible, that is, it is not always possible to eliminate them and restore former vision, even with the help of the most modern means and technology. If timely medical care is ignored, the patient may encounter the following conditions:
- Exophthalmos. This is a forward displacement of the eyeball. In this case, a person begins to experience difficulty moving his eyes, and this in turn leads to a certain limitation of activity in a person’s life. In order to look at the object, he has to turn his body, but he cannot achieve the same reaction. Therapy for this condition in most cases includes surgery, as well as the use of local drugs and treatment of the underlying disease, which became the basis of this pathological condition.
- Chemosis of the conjunctiva. This is severe swelling of the tissues of the mucous membrane of the eyeball. This leads to blurred vision, the formation of a “whitish veil” before the eyes, which will ultimately gradually lead to a permanent decrease in visual acuity. A person experiences discomfort even with his eyes closed. In severe cases, the process may be accompanied by the discharge of pus.
Complications of sinusitis and sinusitis are the spread of infection in the brain tissue, and these are very serious conditions that are not always compatible with life and almost always involve abandoning the usual active life and very long and complex rehabilitation.
Finally, increased swelling without appropriate treatment provokes an increase in intraocular pressure, and this is a direct threat to decreased visual acuity and even blindness.
It is impossible not to mention complications from improper therapy. For example, self-administration of diuretics can lead to disruption and even failure of the excretory system. This is a very dangerous condition, which will subsequently require the patient to remain in hospital for a long time, but even in this case there is no complete guarantee that the system will return to functioning.
And of course, for almost every person the aesthetic component of his appearance is important. The presence of puffiness under the eye can give others the wrong idea about this person, which gives limitations (for example, in the professional sphere).
Prevention
The causes and methods of eliminating swelling under the eye can remain just knowledge if you follow preventive measures:
- Keep your eyes and hands clean. This will prevent inflammation not only in the eye tissues, but also systemic diseases such as ARVI or influenza.
- Avoid eye strain and take regular breaks when working with a computer (preferably with special eye exercises). This will prevent various eye pathologies. Even the likelihood of pathogen activation (and possible conjunctivitis) is significantly reduced.
- Eat properly. A lack of vitamins and microelements negatively affects the functioning of all organs and systems, especially vitamin deficiency negatively affects visual acuity. It is advisable not to consume large amounts of salt in foods, so as not to provoke swelling.
- Maintain a daily routine. Sleep duration should be close to 8 hours. Regular lack of sleep aggravates various chronic diseases, and at one point the body will no longer be able to fight against harmful external factors.
- Use protective equipment when working with a welding machine, chemicals and other aggressive substances. The consequences of refusing glasses, masks and gas masks can be fatal.
- If unpleasant sensations appear in the eyes, use drops with a moisturizing effect, and use them as needed. If this method does not help, then urgent consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Swelling under the eye on one side is not only an aesthetic discomfort. This may be a symptom of serious pathologies. The patient may require a complete body scan to make an accurate diagnosis.
Often, for a complete cure, a person has to not just undergo a therapeutic course of taking pharmaceutical drugs, but completely change his lifestyle.
Only such measures can create a reliable foundation for good health.
Source: https://oculistic.ru/bolezni/drugie-zabolevaniya/prichiny-i-sposoby-ustraneniya-otyoka-pod-glazom-s-odnoj-storony
Headache and swelling of the eyelids with conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory eye disease in which the connective membrane is damaged. Its nature can be infectious, viral, fungal, chlamydial, allergic. Inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by mycoses or chlamydia usually occurs in subacute or chronic form. Its symptoms are moderate. Such diseases are usually not accompanied by headaches. The head hurts only with increased visual load, which must be limited during treatment.
Allergic conjunctivitis develops acutely, but it is characterized by severe itching, lacrimation, severe redness of the eye mucosa, and swelling. Cough and runny nose may also bother you. A headache is not a typical sign of an allergic reaction. This symptom often makes itself felt with infectious conjunctivitis.
Blepharitis: swollen eyelid and headache - what to do?
Blepharitis is inflammation of the edges of the eyelids. Often the disease takes a chronic form and often recurs. There are many causes and types of blepharitis, but in most cases inflammation of infectious etiology is detected. The most common types of this
- diseases:
- scaly;
- seborrheic;
- ulcerative;
- acne.
Each of them has its own symptoms. We can briefly list the following signs of all blepharitis:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- itching and burning;
- increased sensitivity of the eyes to light and wind;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- pain in the eyeball area;
- blurred vision;
- discharge of purulent masses;
- sticking and loss of eyelashes;
- the appearance of scales;
- rash on the upper eyelids and skin around the eyeballs;
- accumulations of foamy discharge in the corners of the eyes.
With blepharitis, the upper eyelid usually becomes inflamed. In this case, inflammation can be bilateral or unilateral. Symptoms can be obvious or mild. It depends on the form in which the pathology occurs - acute or chronic. With blepharitis, headaches are not common. This symptom may appear in two cases:
- the patient puts a lot of strain on his eyes by reading or working at the computer during the treatment period;
- the disease has become more complicated, and the inflammatory process has spread to the conjunctiva or cornea.
Blepharitis is treated with eye drops and ointments. The type of drug is determined by the etiology of the disease.
How to treat?
A wet bandage on the frontal area can slightly alleviate a person’s condition.
People are used to dulling this kind of pain with a wet bandage on the forehead or with conventional painkillers, but such methods can only help for a short period of time. First of all, you need to make a correct diagnosis and determine the cause of the deviation from a specialist. You can combat the manifestations of headaches with drugs that can ease the discomfort and remove swelling of the visual organs.
You should choose the right medications only after consulting a doctor, who will make the correct diagnosis and direct treatment to eliminate the root causes of pathologies. Otherwise, therapy will not be effective, but will only worsen the development of the problem.
Treatment with drugs
Anti-inflammatory medications will help patients who suffer from migraines or due to overwork at work. The drugs of choice are not addictive and will not harm the body. If the source of symptoms is the visual organs, then eye drops are prescribed. Such medications protect the mucous membrane from excessive secretion of tears and inflammation of the surrounding eye muscles.
The upper eyelid is swollen with dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The disease develops due to blockage of the nasolacrimal ducts, which can occur due to:
- abnormal structure of the nasolacrimal ducts, their underdevelopment;
- stenosis;
- facial injuries;
- eye infectious diseases;
- inflammation of the paranasal sinuses;
- blepharitis;
- runny nose;
- tuberculosis;
- syphilis.
Atherosclerosis can also lead to dacryocystitis. In other words, there are many causes of pathology. It develops as follows. Due to obstruction of the nasolacrimal ducts, tears accumulate in the lacrimal sac. Invaded bacteria or viruses cause inflammation. The passage becomes even more clogged. This provokes severe swelling. It can cover the lower and upper eyelids. This disease is also accompanied by:
- profuse lacrimation;
- swelling and hyperemia of the conjunctiva;
- pain in the corners of the eyes;
- discharge of mucus or pus;
- high photosensitivity.
The disease occurs on one side of the face. In severe cases, swelling can lead to complete closure of the palpebral fissure. The patient has a fever, headache, and weakness throughout the body. With this development of pathology, there is a high probability of the formation of an abscess, which manifests itself in the softening of the tissues of the lacrimal sac. After opening the formation, an external or internal fistula may occur.
Dacryocystitis is treated with conservative and surgical methods. Initially, they try to eliminate the inflammation with the help of medications. If they do not help, surgical removal of the nasolacrimal duct obstruction is performed.
Swollen eye cold treatment
Swelling due to a cold
With the onset of cold weather, colds await us everywhere. It's very easy to get sick. At work, in the office, or on public transport, there will always be a person with a cold. If you do not take the right measures in time at the first signs of a cold, and do not comply with bed rest, you can get serious complications.
Swelling of the eye due to a cold
Inflammation during a cold can lead to swelling of the eye. On the eye, a cold looks like a painful stye. There is a feeling of pain in the eyes, lacrimation.
During a cold, sinusitis often occurs - inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. As a result, inflammation of the nasal septum causes blockage of the nasal sinuses. Phlegm, which cannot pass freely from the sinuses to the nose, puts pressure on the frontal area and around the eyes.
A purulent formation on the eye cannot be opened. This can lead to further spread of infection and even sepsis and meningitis. If one eye is inflamed, both need to be treated, because the infection easily spreads to the neighboring eye.
The cause of eye swelling during a cold is hypothermia. Ailments can be expressed in the form of weakness, fever. Unpleasant symptoms may be:
- sensation of swelling;
- the appearance of an abscess;
- inflammation;
- redness of the eye
In such cases, an aloe leaf applied to the eye helps.
Swelling of the eyelids due to a cold
When swelling of the eyelids occurs during a cold, redness, increased body temperature, and painful sensations on palpation are observed.
When examining a swollen eyelid, the doctor often detects subcutaneous lumps. They may be caused by conjunctivitis. Vasodilation during edema during the disease leads to swelling.
The disease is caused by viruses that cause colds. The incubation period of the disease is two weeks. The main signs of the disease are:
- pain in the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- conjunctival swelling and redness;
- discharge of pus and sticking of the eyelids;
- fever, weakness, runny nose, headaches, insomnia
This infection occurs quite often. It is contagious and can reach epidemic proportions.
Swollen eyelids due to a cold
Swollen eyelids during a cold should be treated at home with bed rest.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral drugs. Viral inflammation of the eyelids is often accompanied by swelling of the nasopharynx, otitis media or sore throat. If sinusitis appears during a cold, then swelling of the eyelids stands out along with swollen facial tissues.
For the treatment of eyelid edema, traditional medicine recipes are helpful:
- wash your eyes and make compresses from infusions of chamomile and sage. To do this, pour two teaspoons of the herb with a quarter cup of boiling water;
- lubricate your eyelids at night with calendula ointment;
- instill fresh aloe juice diluted with water at a rate of 1:10;
- Rosehip infusion lotions relieve swelling well. Brew two teaspoons of berries with a glass of boiling water. Boil over low heat for five minutes, leave for thirty minutes.
Swelling of the throat due to a cold
Swelling of the throat is not a separate disease and often occurs against the background of colds. The size of the edema depends on the structure of the mucous layer and the causes of its occurrence. When the throat swells, a person feels a feeling of tightness and pain. A sick person feels as if there is a foreign body in the throat.
If the swelling is not extensive, then there may be no sensations of pain, but tension in the throat muscles will be felt. Lying down may make the throat narrowing worse.
When you have a cold, your throat swells
A person with a cold feels as if his sore throat is scratching and burning. This sensation occurs because the virus requires a living cell to live. Viruses that enter the throat penetrate the mucous membranes and destroy it.
Then other viruses appear that capture neighboring healthy cells and also destroy them. This leads to an inflammatory process, increased blood flow and swelling of the throat.
Swelling causes pain - a burning sensation and pain when swallowing.
The throat especially hurts, if ulcers or erosions have appeared. The natural protective barrier of mucosal cells is destroyed, and this further exposes the body to attacks from viruses and bacteria.
Inflammation of the pharynx is called pharyngitis. Inflammation of the larynx - laryngitis.
Source: https://mir-ua.ru/opuh-glaz-prostuda-lechenie/
Stye: swollen eyelid and headache
Barley is a purulent inflammation that develops in the thickness of the eyelid. The disease is always acute. The compaction is localized in the hair follicles or sebaceous glands located in the eyelids. Many people mistakenly believe that stye occurs due to hypothermia. But the real reason for its appearance is a bacterial infection. Hypothermia, weak immunity, and colds can become predisposing factors contributing to the development of this pathology. The following symptoms are typical for barley:
- itching and pain in the eyelid;
- tearfulness;
- redness and swelling of the eyelid;
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Swelling of the upper eyelid and headache with keratitis
Keratitis is an ophthalmological pathology that manifests itself as an inflammatory lesion of the cornea. Common causative agents of inflammation are bacteria, and less commonly, mycoses. A common injury to the eyeball can trigger the development of keratitis. Infection on the cornea also occurs with other eye diseases - conjunctivitis or blepharitis.
The very first sign of keratitis is the appearance of an infiltrate on the cornea. It consists of lymph and plasma. In addition, the disease leads to the development of symptoms such as:
- photophobia;
- pain;
- swelling of the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- tearfulness;
- drop in visual acuity;
- blepharospasm;
- decreased sensitivity of the cornea.
Keratitis is often accompanied by headache. Headache on the side of the affected eye. When the disease is severe, the inflammatory process spreads deep into the cornea. Its tissues begin to die. Scars or ulcers form, which greatly affects vision. But this only happens in the absence of treatment.
The method of therapy depends on the type of keratitis. If it is bacterial, antibacterial drops and antibiotics are prescribed, if it is mycotic, it is treated with antifungal drugs, etc.
Swelling of the upper eyelid and headache with chalazion
Swelling of the upper eyelid can be caused by a chalazion, a benign thickening of the cartilage. This disease develops due to blockage of the excretory ducts of the eyelids. This pathology is very common. It is detected in approximately 7% of patients who come to the ophthalmologist with complaints of inflammation of the eyelids.
Blockage of the excretory ducts of the meibomian glands leads to the accumulation of fatty secretions in them, necessary for wetting the surface of the eye. This occurs against the background of the development of barley, seborrhea, rosacea and other infectious diseases of the eyelids. The likelihood of developing a chalazion increases if:
- viral diseases;
- hypovitaminosis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypothermia;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- poor hygiene, including when using lenses.
A chalazion can be identified by the presence of compaction in the thickness of the eyelid. In this case, pain usually does not occur even with palpation. Gradually the hailstone grows and becomes denser. It can reach 5-6 mm in diameter. The eyelid swells and turns red. This can lead to closure of the palpebral fissure and poor visibility. Lacrimation develops, itching appears, and hyperemia of the connective membrane of the eyeball is observed.
The following symptoms should cause alarm:
- throbbing pain in the eyes and head;
- severe redness of the facial skin;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the upper and lower eyelids at once;
- spread of swelling to the second eye.
These signs indicate a deterioration in the patient’s condition and the need for surgical intervention. At an early stage, chalazion can be eliminated with the help of drug therapy and physiotherapy.
Conjunctivitis due to influenza
Another acute upper respiratory tract disease caused by the influenza virus. It also belongs to the ARVI group, often spreading in the form of epidemics and pandemics. The influenza virus has the ability to constantly mutate. Every year new serotypes appear. Currently, about 2000 varieties of this disease have been identified. Signs of influenza are often similar to those of acute respiratory viral infections: cough, fever, mucus from the nose. However, there is still a difference. It is the correctly identified symptoms of influenza infection that will help cure it faster.
- With ARVI, the temperature rarely rises above 38°C and usually goes away within 2 days, but with the flu it can reach 39-40°C and last up to a week, especially in children.
- Lethargy, weakness and muscle aches, fever, profuse sweating, eye pain, headache, aversion to daylight or artificial light.
- Swelling of the nasal cavity. With ARVI, a runny nose lasts throughout the entire period of the disease, accompanied by copious nasal discharge, and with influenza there is usually only slight congestion in the sinuses.
- The mucous membranes become inflamed in different ways during colds and flu: with ARVI, the throat and nose turn red, with flu - the back wall of the pharynx and the soft palate.
- A severe cough, first dry, then with sputum, is characteristic of both diseases.
- Inflammation and redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes is more typical as a complication of ARVI, however, this is also a common occurrence with influenza. A runny nose and cough, along with conjunctivitis, are three main signs of viral diseases.
Viral conjunctivitis with influenza is a rather dangerous condition, as complications may arise in the form of optic neuritis or keratitis. The inflammatory process in the eyes can develop within a few days after recovery.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in ARVI and influenza
drops and ointments with interferon. When treating any type of conjunctivitis - viral, bacterial, allergic - it is necessary to wash the eyes before administering medications. To do this, you can use weak solutions of various products: boric acid, furatsilin, or special products - for example, “Blefarolion” from the Russian.
Procedures should be carried out with pre-washed hands to avoid introducing dirt. You need to wash your eyes about 5-6 times a day, and then administer drops or ointments. Conjunctivitis is a disease that, if not treated correctly, can lead to many unpleasant consequences for the visual organs. In this case, you should not self-medicate, but strictly follow the doctor’s instructions. If visible improvement in eye condition does not occur within 2-3 days, you should not continue taking the medicine. Contact your specialist again - he will prescribe another remedy. So, how to treat viral conjunctivitis?
Swelling of the upper eyelids and headache: other causes
We have listed ophthalmological ailments in which headache and swelling of the upper eyelids are simultaneously observed. There are other reasons for the appearance of these two signs. Some diseases are very complex and dangerous, for example, cerebral edema, which manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- slow heart rate;
- strabismus (sudden);
- increased blood pressure;
- disturbance of consciousness.
In the future, coma may occur. Thus, headache and swelling of the eyes are just the initial signs. But they can also be a reason to visit a doctor.
Also, headache and swelling of the eyelids can occur with increased intracranial pressure, which is accompanied by:
- pain behind the eyeballs;
- vomiting, sometimes without nausea, suddenly;
- blurred vision, diplopia, temporary complete loss of vision;
- disturbance of consciousness.
The headache is worse when the patient lies down. In this case, painkillers (analgesics), as a rule, do not help.
Swelling of the eyelids and pain in the head are observed in cardiovascular diseases. Swelling occurs in the morning. It goes away during the day. Headaches come and go. Often a person relieves this symptom with medications.
The two symptoms described, if they appear simultaneously and do not go away for several days, should cause concern in any person. Do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor to start drug therapy in a timely manner, if necessary.
Edema, swelling under the eye on one side - causes
Many of us sometimes experience swelling of the eyes, but not everyone knows the danger this can pose to the visual system.
If you are an investigator of medical terminology, then eye swelling should be understood as a pathological process that occurs in the area of the lower or upper eyelid when too much tissue fluid accumulates in the tissue of these anatomical areas.
According to experts, the main reasons that provoke this pathological condition are somatic diseases , as well as external influences, such as fatigue, allergic reactions, etc.
Swelling under the eyes may indicate the development of somatic diseases
People who have a malfunctioning thyroid gland, heart or kidneys are at greater risk of encountering this pathological phenomenon than others.
Another reason for the formation of swelling may be damage to the pituitary gland or improper venous outflow . Edema develops and proceeds differently from most other pathological processes.
Most of them affect the lower eyelid and cause discomfort to a person in the morning.
If kidney function is impaired, swelling may bother a person throughout the day. If unpleasant symptoms make themselves felt in the evening, then, most likely, the person’s cardiovascular system is not all right.
If there are somatic diseases, then swelling under each eye occurs in a symmetrical form.
Inflammatory causes
- Barley. Most often it has unilateral localization. A small round formation appears at the site of inflammation, which causes itching and pain. Sometimes accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
- Conjunctivitis. Inflammation of the conjunctiva with characteristic symptoms: redness and irritation of the skin, purulent mucous discharge that leads to sticking of the eyelids, as well as itching and pain.
- Furunculosis. Accompanied by the appearance of ulcers, severe swelling and pain when touched.
- Erysipelas. A pathology characterized by redness of certain areas of the skin, including the upper eyelids. It is characterized by general intoxication, high temperature (39-40°), as well as rashes, inside of which there is a clear liquid. In severe cases, gangrene and ulcers may appear.
- Endophthalmitis. Inflammatory disease of the inner membranes of the eyeballs. Symptoms include severe pain in the eyes, blurred vision, and swelling of the eyelids.
Swelling under the eye: reasons on one side
Experts name two main reasons that can cause swelling in women:
- pregnancy;
- hormonal imbalance.
Due to the fact that before menstruation, the level of estrogen in the female body increases , this causes fluid retention in the tissues. This is precisely the main reason for the appearance of puffiness under the eyes. Very often this condition is observed during puberty, menopause and during hormonal therapy.
Most pregnant women are concerned about swelling. Most often they make themselves felt during the third trimester.
If edema is present throughout the entire period of pregnancy, and in addition to this, weight gain is clearly visible, then this indicates a certain pathology, and therefore the expectant mother needs to see a specialist.
Based on these signs, it can be assumed that in this case we are talking about a serious somatic illness.
To obtain more accurate data about the patient’s condition, it is necessary to first examine the kidneys , since their improper functioning can provoke dropsy in pregnant women.
Unfavorable genetic background
In some cases, puffiness around the eyes can make itself felt in early childhood. It can be very difficult to explain this condition due to the lack of favorable factors.
But if the parents also have similar signs, then one should be wary. Most likely, it all comes down to the genetic predisposition of the body .
Experts say the main factor that provokes this condition is an excess amount of adipose tissue around the eyes.
Overwork
Prolonged work at a computer, driving a car, reading books in insufficient artificial light, prolonged viewing of television inevitably causes tension in the eye muscles, and this leads to impaired blood supply to the eyelids.
Against the background of general fatigue, a person ’s usual way of life is disrupted . It takes him longer to fall asleep and getting up on time becomes a problem for him.
Without the opportunity to rest properly, a person at some point discovers swelling under his eyes.
Age factor
As people get older, they begin to notice that the skin under the eyes begins to thin, the muscles around the eyes weaken, and the bone tissue becomes more fragile and can no longer support the fatty tissue around the eyes. As people get older, more and more people begin to notice a malfunction of the kidneys and a slowdown in electrolyte balance. Against the background of all this, the likelihood of developing chronic eye swelling in old age increases.
Increased salt content in the body
It has been proven that one of the main reasons for water retention in the body is excess salt. Therefore, doctors recommend limiting its use. It is especially useful to refuse it during dinner. If you do not take precautions when consuming salty foods and canned food, then over time this will lead to the accumulation of fluid in the area around the eyes, and over time, swelling will appear here.
Everyone knows that after eating salty or spicy food you are very thirsty . However, due to the fact that the body contains too much salt, it is only partially eliminated from it.
Lifestyle influence
Experts say that another reason for the appearance of swelling is improper sleep and wakefulness. Those of us who are used to having fun with friends at night are more at risk of seeing puffiness under the eyes in the mirror.
Other factors can lead to swelling:
- abuse of alcohol or drugs, sweet and carbonated drinks;
- bright lighting;
- short sleep.
Experts recommend avoiding drinking strong drinks and coffee a few hours before bedtime. They give the same recommendation regarding smoking and alcohol.
Although many people talk about this, I would like to repeat it again - drink as much fluid as possible during the day.
It is optimal if a person drinks about 2 liters of water per day, and most of it should be drunk before 14:00 .
Experiencing a lack of fluid, the body begins to use its own reserves and switches to an economical mode of operation, trying to stock up on water. And this often leads to the appearance of swelling.
Use of cosmetics
Cosmetics cannot be considered a factor that can cause swelling. It becomes dangerous if used incorrectly. To prevent this from happening to you, you must follow a number of rules:
- A few hours before bedtime, cleanse your body of cosmetics;
- It is recommended to clean the skin on which decorative cosmetics have been applied with special makeup removers;
- After washing, do not rub your face. It is better to blot it with a soft towel;
- Choose your skin care creams carefully. Before purchasing, check out its composition in the store, which should not contain components that cause swelling under the eyes.
What to do if the lower eyelid is swollen
If you notice that your lower eyelids are swollen, the main thing is not to panic and start by determining the cause. Examine the sore spot carefully and determine whether there is a red swelling on the lower eyelid or whether pain is felt when blinking or pressing.
Remember whether the eye has been subjected to mechanical damage, remembering that one eyelid (the damaged one) may swell.
When an unpleasant phenomenon is the result of excess fluid, you need to reduce its consumption and remove excess water from the body (with the help of medications or folk remedies).
If the eyelid under the eye is swollen due to minor mechanical damage or an insect bite, the swelling will soon go away; you can speed up the process by using ointment.
If the swelling does not go away, you need to show the growth on the eyelid to the doctor to make sure that it is not cancer. If the swelling is caused by changes within the body, you need to consult a doctor.
Under no circumstances should the visit be postponed if the lower eyelid is swollen, the eye hurts, or additional symptoms are observed (see above).
Drug treatment
It is possible to treat the disease of patients who find it painful to blink due to edema and swelling only after establishing the cause of the disease and an accurate diagnosis. The therapy is prescribed in a comprehensive manner; as a rule, the following drugs are prescribed:
- a solution of boric acid (5 g of substance per 100 ml of water) and hydrocortisone or tetracycline ointment are used when the eye hurts under the lower eyelid;
- Celestoderm, Levomycetin drops, Prednisolone (these are antibacterial drops that help cure infectious diseases);
- Claritin, Tavegil, Zodak are prescribed for allergic reactions.
We recommend additional reading: How to quickly remove swelling from the face and why it swells
Note! If the problem is related to regular lack of sleep, an eye cream against puffiness and bags under the eyes will be a good help.
Allergic reaction
Swelling and swelling of the lower eyelid is often allergic in nature. It can appear during the flowering period of plants that cause a reaction, after eating certain foods, contact with animals, etc.
Additional signs, besides the fact that the eyelid is swollen and red, indicating an allergic reaction - itchy areas of the skin, the area around the eyes itches.
If you have such symptoms, you need to contact an allergist who will identify the allergen and prescribe medications.
To treat allergies in the lower eyelid, antihistamines are used that have a general (tablets) and local effect (drops). The medications listed above cope well with irritation.
Treatment with folk remedies
In folk medicine, there are also known remedies for swelling, puffiness and bags under the eyes. They are unlikely to help get rid of swelling of a pathological origin, but they do an excellent job with swelling of a physiological nature. Here are some of the most popular recipes:
Source: https://bugmk.ru/glaza-simptomy/opuhlo-vozle-nosa-pod-glazom.html