The organs of vision are negatively affected not only by reading in the wrong position, using a computer, but also by frequent use of a smartphone.
With its help, people not only make calls, but also use it for games, reading books, and browsing the Internet.
All this negatively affects vision function if the smartphone is used for a long period of time. To eliminate this action, you need to know a number of important rules and procedures.
Why does the computer hurt my eyes?
While in front of the screen, the user views digital and alphabetic images, which, unlike pictures on paper, constantly flicker. The organs of vision strive to capture the image, so they begin to work in an unusual mode and get sick. The muscles of the organs of vision remain motionless for a long time, which provokes myopia and decreased sensitivity of vision.
The eyes hurt because they work under stress, so the blood flow inside them slows down. In tissues that turn into collections of metabolic products, a lack of oxygen begins.
Trying to replenish it, the eye vessels expand and often burst from tension. Lack of oxygen also harms a person’s brain, which is why he gets headaches, back, and neck pain from the computer.
Watch an interesting video about the causes of eye pain associated with the choice of monitor:
What diseases cause eye pain?
Many people have eye pain due to ophthalmological and systemic diseases. The reason may be in the organs of vision or in other disorders. The choice of specialist and treatment depends on the cause of the pain; in order to identify it, laboratory and instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
There are a number of ophthalmological diseases and conditions that can affect soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves located in the organs of vision.
They cause acute and chronic pain:
- Increased eye strain. It occurs in people who spend a long time in front of a computer, phone, TV, or tablet. Pain occurs when reading books frequently in poor conditions, for example, in low light.
- Entry of a foreign body. It can penetrate the cornea due to strong winds, sparks from a welding machine, or for other reasons. Acute pain, redness, photophobia, increased sensitivity, and spasm of the eyelids occur.
- Conjunctivitis. It can be of an allergic, bacterial, viral nature. This is a disease in which the conjunctiva of the eye becomes inflamed. Redness, swelling, pain, and photophobia appear. With bacterial conjunctivitis, purulent exudate is released.
- Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. It can develop due to the proliferation of fungi, viruses, bacteria, parasites (eyelash mites). The eyelids swell and an abscess filled with fluid may form under the skin.
- Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea. The inflammatory process begins as a result of mechanical damage, burns, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. If the disease lasts a long time, the cornea becomes cloudy and visual acuity decreases.
- Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure due to impaired outflow of secreted fluid. There are anterior and posterior chambers in the eyeball, and fluid constantly circulates inside them. If it accumulates but does not come out, the pressure increases. This can lead to damage to the optic nerve, retinal detachment, and blindness.
- Retinal diseases. They develop due to burns, mechanical damage, and malnutrition through blood vessels. If the retina detaches, the person goes blind.
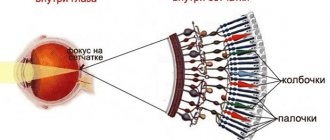
- Diseases of the optic nerve. Light streams pass through the eyes, hitting the rods and cones of the retina. From them, information in the form of nerve impulses passes through the nerve, entering the brain. The nerve is damaged due to malnutrition through blood vessels, mechanical damage, and infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Strabismus, amblyopia. If both eyes see the picture in front of them incorrectly, this leads to increased strain. As a result, not only your eyes hurt, but also your head.
There are diseases that develop not in the eyes, but in peripheral organs; with their prolonged development, complications arise from the organs of vision, this also leads to pain:
- Diabetes. A large amount of glucose accumulates in the patient’s blood, which is not distributed to the tissues, but binds to cholesterol and forms plaques. They are transported through large and small vessels, including the microcirculation of the eyes. This leads to blockage, severe pain, decreased or complete absence of vision.
- Atherosclerosis. Cholesterol accumulates in the patient’s blood, which spreads through the vessels, clogging their lumen. The mechanism of the disease is the same as for diabetes mellitus.
- Arterial hypertension. Increased pressure puts stress on the endothelium. This leads to rupture of the vessel wall and hemorrhage inside the eyeball. With chronic hypertension, the function of the visual organs decreases, and constant headaches and eye pain occur.
- Ischemic disease. A person experiences spasm of peripheral vessels. If this happens in the eyes, nutrition is disrupted. Gradually, the visual organs will stop working. Severe spasm causes severe pain.
- Vasculitis, increased fragility of blood vessels. If the endothelium is fragile, this leads to hemorrhage in any part of the body. Painful sensations appear during spasms, which causes a decrease in vision function.
- Neuropathy. The inflammatory disease can spread to the optic nerve, this is dangerous because it connects to the brain. This causes a decrease in its functionality and constant pain.
For each disease, a separate treatment is determined. Therefore, diagnostics are initially carried out, identifying the nature of pain, decreased vision function and other symptoms.
Symptoms
Monitor syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms:
- eyes hurt and get tired after working at the computer;
- the outlines of silhouettes are blurred;
- tingling sensation;
- eyes water;
- there is a feeling of discomfort, as if sand had gotten into it;
- double image;
- eyes become red from the computer;
- vision decreases in the absence of glasses or contact lenses;
- My spine and my head hurt from the computer.
If you have severe eye pain from using a computer, you need to visit an ophthalmologist who will give a correct assessment of the condition and make a diagnosis.
Consequences of ignoring eye pain
VCS cannot be treated with disdain. This is a modern disease that needs to be treated promptly, otherwise it will lead to complications.
Possible consequences of ignoring eye pain:
- violation of the accommodative abilities of the lens;
- dry eye syndrome due to a constant lack of tear fluid, which also leads to serious complications;
- headaches and migraines;
- myopia due to constant looking at small details due to pain;
- increased sensitivity to brightly lit objects.
VCU is the only condition that doctors are unable to treat on their own. It’s not just the lack of treatment methods; against the background of this problem, ophthalmological diseases develop, causing more serious complications.
My eyes hurt after using the computer, what should I do?
A complete examination by an ophthalmologist, including a patient interview, examination, and examination of the anterior segment of the eyeball helps determine what needs to be done if the eyes hurt from the computer.
Folk remedies
If you are not a supporter of traditional medicine, effective folk remedies for eye pain will help you:
- An infusion of birch leaves, which is filled with water and brewed for 6-7 hours. Moisten a piece of gauze with the resulting product, apply it to the eyelids, hold for 20 minutes, after which the compress is renewed and the procedure is repeated.
- Blue cornflower decoction. The flowers are poured with boiling water and after 20 minutes a compress with the infusion is applied to the eyelids for the same time. The product not only relieves irritation and fatigue, but also restores lost shine to the skin.
- Potato juice. Helps cope with inflammation and swelling. A mask is made from it like this: mix the juice with crushed cucumbers, apply to the face, leave for 20 minutes, and then wash off with chamomile infusion.
Traditional medicine techniques are sometimes not enough to stop your eyes from hurting from using a computer. Then you need to use stronger means.
Medicines
The first signs of eye fatigue from working at a computer can be relieved with drops that are sold over-the-counter at an average price. You can find the drugs yourself in a regular pharmacy, but it is better to consult a doctor, since there may be an intolerance to the components or an allergy to them, the signs of which are not immediately visible.
Drops for pain in the eyes, blocking nerve patency:
- "Artelak";
- "Oxial";
- "Hilozar-chest of drawers."
Drugs for eye fatigue:
- “Pure Tear” from Vizin;
- "Systane";
- "Vidisik."
As a rule, the pain goes away 2 minutes after instillation, the effect lasts for a long time.
To select a safe remedy, the ophthalmologist observes changes in the condition after 30 days of using the drops. If your eyes continue to hurt from the computer or side effects occur, your doctor will prescribe another drug.
People who use contact lenses should know how medications are combined with them. There are drops that are used without removing the lenses, for example, Oxial. Other drugs are instilled after removing contact optics, which can only be put on after 20 minutes.
When working at a computer every day, it is necessary to keep the eye muscles in good shape, and there are special techniques for this.
Gymnastics for the eyes
It is important to take breaks while working in front of the computer, otherwise your vision will begin to hurt. This is where a few eye exercises will come in handy when working at a computer:
- Rotating in a circle. The gaze is moved clockwise and back around the visual axis.
- Relaxation of the eyes. Close your eyelids and imagine a positive moment in your life. Having rested, the organs of vision will not hurt much.
- Diagonal gaze movement. Direct your gaze towards the imagined angles.
- Blinking. To stop dryness, take intervals between working and blinking repeatedly.
- Moving the gaze up and down vertically.
- Sideways glance. Lower your gaze to your nose, as if you were making faces in childhood.
- Concentration on near and distant objects. Go to the window, first look at a point on the glass (you can draw it), and then move your gaze into the distance to another object.
After a simple warm-up against eye fatigue, it is recommended to wash your face with cool water to increase blood flow to the eyeballs. Then they will not get sick for a long time.
Nutrition and vitamins
The risk of eye soreness from the computer will be reduced if the user receives nutrients through food or vitamin complexes:
- Vitamin A. Component of the vision pigment - rhodopsin. Its deficiency causes weakened visual function and decreased dark adaptation. Contained in carrots, greens, rowan, pumpkin, liver.
- Vitamin C. Helps strengthen eye blood vessels. Can be consumed from citrus fruits, sauerkraut, rose hips, black currants, kiwi.
- Vitamin E. Normalizes the condition of the cell membranes of the eyeball, protects against ultraviolet rays. Included in sea buckthorn oil, meat, liver, eggs.
- B vitamins promote oxygen exchange between eye tissues. Contained in brewer's yeast, cereals, bran.
Look at the photo for products that are good for your eyesight:
What to do
There are a number of measures that can help cope with the causes of SCD and alleviate or completely eliminate symptoms.
If a person constantly suffers from discomfort when working at a computer, you need to consult a doctor, despite existing knowledge about the problem. Other causes must be excluded. In addition, only a doctor can recommend optimal measures and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Even if there are no acute eye problems, visiting an ophthalmologist will not hurt. An annual eye examination is recommended for all people who regularly work on a PC for 3 or more hours a day.
Eye drops
Ocutiarz - quickly copes with episodic dryness and pain in the eyes, which occurs at the end of the day, after prolonged work at the computer. The basis of the drops is hyaluronic acid, a component naturally present in the tissues of the eye, due to which it is close in action to natural tears. Ocutiarz can be used when wearing soft and hard contact lenses, and the drops also have a long shelf life - months from the moment the bottle is opened.
Cationorm - the only cationic emulsion in Russia is prescribed to people with severe complaints of redness and dryness throughout the day, even in the morning. The emulsion is evenly distributed and retained for a long time on the ocular surface, helping to eliminate redness and dryness of the eyes. Cationorm protects and heals the ocular surface, restores all layers of the tear film and prevents further development of the disease.
Oftagel is a gel with carbomer in maximum concentration, suitable for people with complaints of periodic dry eyes, redness and lacrimation and with the reluctance or inability to instill drops more than once a day; it can be instilled once before bed to achieve long-term hydration and protection of the eyes.
Drops or artificial tears are prescribed for immediate relief. Medicines help prevent the mucous membrane from drying out. Korneregel, Lakrisifi, Vizin and Vial have no medical indications. They should be instilled up to 10 times a day as needed. But before use, consult your doctor.
The most effective for SCZ are ophthalmic drugs that quickly eliminate pain. However, doctors do not recommend immediately switching to their use. It is advised to eliminate the syndrome with gymnastics and artificial tears.
Ophthalmic products:
- Ephralia;
- Aloe extract according to Fedorov;
- Diclofenac;
- Visoptic;
- Hypromellose;
- Inocaine;
- Lakrisifi.
Vitamins for eyes
Eye pain during prolonged use of a PC occurs due to a lack of vitamins. For such disorders, it is recommended to take courses of vitamin complexes.
The following substances are useful:
- Vitamin A. Improves vision in the twilight, eliminates discomfort and restores color reproduction.
- Vitamin E. Restores visual cells and protects against electromagnetic radiation emanating from the PC screen.
- Vitamin C. Strengthens blood vessels and prevents the premature onset of asthenopia.
Useful vitamins for the eyes: SuperOptic, Okuwait Forte, Systein Ultra, Taufon, Oftan Katahrom.
Eye exercises
Gymnastics is performed standing or sitting; it is better to stand up and do gymnastics for the whole body.
Exercises:
- Go to the window. Find a distant object and a spot on the glass. Focus your gaze on the second, then move to the first, and vice versa.
- Blink for 2 minutes. Sometimes squeeze tightly and open your eyes.
- Make rotational movements with your eyeballs without moving your head. Look in different directions, draw diagonal stripes and follow the second hand of the clock with your eyes.
- Extend your hand in front of you, raise your index finger up. Fix your gaze and slowly move your finger towards your nose, then move it away without looking away.
- Close your eyes, lightly press your index and middle fingers on the pupil. Alternate a second of pressure with rest.
The correct mode of working at the computer
Continuous work time at the computer is 60 minutes. After an hour, take a break, during which they perform eye exercises or Palming.
After 4–5 hours, it is recommended to go out into the fresh air. Walk in the park for 1–2 hours or go to the store. Then the work continues.
Persons working in offices should discuss this point with their employer. An employment contract must comply with labor protection requirements (Article 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The duration of work on a PC is an essential working condition if it exceeds 50% of working time.
Adjusting monitor brightness and contrast
The monitor itself offers many ways to influence the contrast and brightness of the image. These are partly the settings on the monitor itself, partly the operating system functions that affect the construction and output of the image.
Optimally adjust brightness and contrast. Adjust the screen brightness so that your eyes can easily switch between the monitor and the environment without strain.
The contrast always matches the selected brightness. Select a screen resolution higher than the default one. The higher the resolution, the finer the structures and the sharper, more focused the image. If the user interface is too small at high resolution, fix it using the operating system's on-board tools.
As a result, the texts and symbols are again just as large, but more subtle. Basically, current operating systems such as Windows offer the ability to make the screen content larger or smaller. Applications, icons, fonts, etc. are enlarged by the specified factor.
This doesn't always work 100% in all applications, but system programs and many standard applications support this feature.
Select the appropriate screen size. If you need to open a lot of data with large tables at the same time, a PC with a large monitor will do. It displays more required pages of the same size. However, this solution does not always help. The larger the screen, the more the extraocular muscles work. Consequently, they get tired faster and overexert themselves.
We recommend reading: Distance from the monitor to the eyes
Workplace optimization
People underestimate the impact of a computer and proper workspace optimization. The optimal location of the monitor is important, not only for the eyes, but also for posture and, therefore, for the back and neck:
- Place the monitor parallel to the windows and lighting in the room. Light sources are located to the side of the screen, not in front of/behind it. The monitor is placed in the center of the field of view so that the person can see it without twisting the neck or turning the head. Located at a distance of 60–70 cm from the eyes. Select the height so that the top line is just below the organs of vision. If more than one monitor is used, place it side by side.
- Use the same picture settings for both PCs.
- Minimize reflections on the screen surface. In principle, it is recommended to use monitors with a matte surface, which eliminate reflections to a large extent. Anti-reflective film is installed on glossy screens.
- Adjust ambient light. Ideally, the brightness of the screen does not differ significantly from the brightness of the environment.
Special glasses for working on a computer
Special glasses have a coating that neutralizes electromagnetic radiation from the monitor. They protect your eyes from constant screen flickering. Glass diffuses contrast and regulates the uniform incidence of light on the retina.
Benefits of glasses:
- efficiency increases;
- eyes do not get tired quickly;
- dry eyes disappear;
- blood circulation increases;
- Photophobia does not develop.
Visually, computer glasses are no different from regular glasses that are sold for vision correction. But multi-layer coating is applied to the glass, thanks to which a positive effect is achieved.
Glasses - monofocal, bifocal and progressive. Such optics are worn not only to protect against PC radiation, but also on the street.
How to choose glasses
An ophthalmologist prescribes glasses when working at a computer if the following is detected:
- myopia (myopia) (see glasses for myopia);
- farsightedness;
- presbyopia (glasses must be worn most of the time);
- astigmatism (see glasses for astigmatism).
There are monofocal lenses with one optical power and multifocal lenses with several optical zones for different distances.
Typically, glasses are chosen taking into account the characteristics of the person, since not only the type of lenses is important, but also their comfortable focusing, as well as the absence of eye muscle strain when using optics.
Special glasses for computers, unlike regular glasses, block blue light rays due to:
- tinting – brownish tint of lenses;
- blue blocker reflective coating that completely blocks blue rays from the screen.
The described glasses reduce the brightness of the screen and the main room lighting, and therefore prevent your eyes from overwork and pain. They do not transmit color 100%, which slightly distorts the shades on a computer monitor, but this is not very noticeable.
The most effective optical devices for working on a computer or laptop are glasses from Fedorov or Gunnar.
Arrangement of the workplace
Your eyes will not hurt from working at the computer if you organize your working conditions correctly. Experts give several recommendations on this matter.
Monitor settings
If the user's eyes hurt from being in front of the monitor, the settings on the monitor may be incorrectly adjusted. Therefore, it is important to adjust the screen to your feelings and remember what brightness to set on your PC monitor so that your eyes don’t hurt.
The brightness should not be very low, as a pale screen surface increases eye strain. The default monitor screen settings set the minimum frequency, but it is better for the user to select the maximum.
Not only the parameters are important, but also the convenient placement of the screen. Its upper border should be below eye level, and its lower border should be at an angle, next to the user.
You should use dark letters on a light background for contrast, but not vice versa.