Astrocytoma of the brain - causes and treatment, prognosis for life
Brain astrocytoma is a tumor that occurs as a result of disruption of the division and development of glial cells - astrocytes. Visually, in their structure, these cells of the nervous system resemble a five-pointed star, hence their second name - stellate. For more than half a century, scientists have agreed that these are specific cells of the nervous system that perform auxiliary functions.
However, recent research in neurosurgery has shown that the main, and perhaps the only function of astrocytes is protective. It is stellate cells that protect brain neurons from traumatic factors, ensure adequate metabolism, absorb excess waste products of neurons, and participate in the regulation of the blood-brain barrier, as well as in the blood supply to the brain. If at any stage of development these cells undergo pathological changes, then they cannot fully perform their functions, and therefore the entire nervous system suffers.
Causes
Scientists still cannot figure out why brain cancer occurs. Only factors that contribute to pathological transformations are known. This:
- influence of chemicals (mercury, arsenic, lead);
- smoking and excessive alcohol consumption;
- oncology in the family;
- weakened immunity (especially for people with HIV infection);
- traumatic brain injuries;
- genetic diseases. In particular, tuberous sclerosis (Bourneville disease) is almost always the cause of giant cell astrocytoma. Studies of genes that become tumor suppressors have revealed that in 40% of cases of astrocytomas there were mutations of the p53 gene, and in 70% of cases of glioblastomas there were mutations of the MMAC and EGFR genes. Identifying these lesions will prevent the disease from malignant forms of AGM;
- radiation. Long-term exposure to radiation associated with work conditions, environmental pollution, or even used to treat other diseases can lead to the formation of brain astrocytoma.
Of course, if a person, for example, has been exposed to radiation, this does not mean that he will necessarily develop a tumor. But, a combination of several of these factors (work in harmful conditions, bad habits, bad heredity) can become a catalyst for the onset of mutations in brain cells.
Treatment of spinal cord astrocytoma
What type of treatment the patient will need is determined by the attending physician, based on the diagnosis and examination results.
The following methods are used in the treatment of spinal cord glioma:
Surgical intervention
If the tumor is benign, it is removed surgically. Depending on the stage of the disease, complete removal of the tumor is not always possible, so sometimes additional radiation therapy is prescribed.
When diagnosing stage 2–3 astrocytoma, complete surgical removal of the tumor is impossible, so additional methods of therapy are prescribed that destroy the remaining pathogenic cells.
During cancer surgery, endoscopic techniques using miniature instruments can be used. An image of the tumor is displayed on the monitor screen. Endoscopic intervention reduces trauma and the risk of complications.
Radiation therapy is the main or auxiliary method of treating astrocytoma
Under the influence of ionizing radiation, pathogenic cells die in the body, but healthy tissues located next to the tumor also suffer. In cases where surgery is impossible (the astrocytoma is located near vital centers), radiation therapy is used.
Radiation for cancer is carried out in courses to completely kill tumor cells in the body. Treatment is carried out in two ways:
- Internal exposure - radioactive materials are introduced into the tissue where the tumor is located, which has a depressing effect on the mutated cells.
- External exposure - radiation affects the external parts of the body.
Chemotherapy
Treatment of a spinal cord tumor with chemotherapy suppresses the activity of tumor cells. Chemotherapy drugs are available in the form of tablets or injection solutions.
The choice of drug is made by the doctor. He also determines the duration of the treatment course.
A significant disadvantage of chemotherapy is that healthy cells often die along with tumor cells, which worsens health. Chemotherapy drugs damage hematopoiesis and the activity of the nervous system. Their side effects manifest themselves in the patient's vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea. Hair falls out, the patient loses weight. The treatment is painful, but often there is no other way to salvation.
Radiosurgery
Spinal cord astrocytoma can also be effectively treated with radiosurgery. This is a treatment method in which direct radio radiation affects tissues that have undergone mutation. One of the methods of radiosurgery is CyberKnife. The advantage of the technique: the computer carries out special calculations, thanks to which radio radiation acts only on the tumor, without damaging healthy tissue.
In the treatment of astrocytoma, CyberKnife allows you to effectively influence the tumor, speed up the course of treatment and facilitate the rehabilitation period.
Forms of the disease
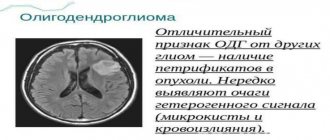
Depending on the cellular composition, astrocytomas are divided into several types:
| Anaplastic astrocytoma. | A malignant tumor (III degree of malignancy), characterized by the absence of clear boundaries and rapid infiltrative growth. It most often affects men over 30 years of age. |
| Piloid astrocytoma | The tumor is benign and has distinct and clear boundaries. It is formed mainly in the area of the brain stem or cerebellum. Children are at risk. The prognosis for treatment of this form of tumor is always favorable, since it responds well to treatment and without complications. But late seeking help increases the likelihood of its degeneration into malignancy in 70% of cases. |
| Glioblastoma | The malignant and most dangerous type of astrocytomas (IV degree of malignancy). It has no boundaries, quickly grows into surrounding tissues and gives metastases. Typically observed in men between 40 and 70 years of age. |
| Fibrillar form | This is a benign type of neoplasm, but the possibility of its transformation into a malignant form increases. The tumor has no definition and grows much faster than pilocytic astrocytoma. Therapy, including surgery, does not give a 100% good result. Most often, this form is detected in young people under 30 years of age. |
Well-differentiated (benign) astrocytomas account for 10% of the total number of brain tumors, 60% are anaplastic astrocytomas and gliomas.
Types and stages of tumor
At stage 1, pilocytic astrocytoma is diagnosed. This is a benign tumor that grows slowly.
At stage 2 - fibrillary astrocytoma. The tumor is also considered benign, slowly increasing in size, but the first symptoms of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm may already appear - the boundaries of the tumor are at some distance from the surrounding tissues.
At stage 3 - anaplastic astrocytoma. A malignant neoplasm, which is characterized by aggressive growth, is difficult to irradiate.
At stage 4, glioblastoma develops. This is the most dangerous tumor among all astrocytomas. The prognosis for treatment at this stage is unfavorable.
According to statistics, benign astrocytomas affect children, while malignant ones develop in adults over 40 years of age.
Symptoms of astrocytoma
All symptoms associated with the development of tumors in the brain are divided into two large groups: general and local. Common symptoms associated with increased intracranial pressure:
- constant headache;
- convulsive syndrome;
- nausea, vomiting in the morning;
- general cognitive impairment (decreased memory, attention, intellectual functions).
Local symptoms are associated with the direct effect of the tumor on brain tissue. Their manifestations depend on the location of the astrocytoma:
- disturbances of speech and its perception;
- problems with sensitivity and movement in the limbs;
- deterioration of vision, smell;
- mood disorders.
Treatment of astrocytoma
Treatment of astrocytoma in Israel and Germany involves the joint participation of neurologists, neurosurgeons and oncologists. When determining the treatment method, the doctor takes into account various factors: the age and general condition of the patient, the presence of contraindications, the degree of malignancy of the tumor, its location and size, and the degree of possible neurological side effects.
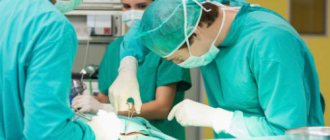
Surgical treatment of astrocytoma
If the diagnosis allows (mainly astrocytomas with grade I malignancy), the priority treatment method for astrocytomas is prescribed - surgery.
The goal of this technique is to remove the maximum amount of tumor tissue without damaging nearby healthy brain tissue.
When the size of the tumor or its location does not allow complete removal by surgery, in such cases, after surgery, chemotherapy and radiation are prescribed to eliminate the remaining pathological cells.
Radiation therapy
Antitumor therapy (radiation of cancer cells), alone or in combination with chemotherapy, is intended after surgical removal of the tumor, the purpose of which is to eliminate the remaining cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
This method of treating astrocytomas involves a course of use of antitumor (cytotoxic) drugs. Chemotherapy is prescribed as monotherapy, depending on the patient’s condition, and also in combination with radiation therapy. Medicines are taken in tablet form orally or intravenously.
A patient diagnosed with low-grade astrocytoma is recommended to have brain implants containing chemotherapy. Implants are small plates that a neurosurgeon places in the area where the tumor is located. Over time, the chemotherapy substance dissolves and actively acts on the remaining pathological tumor cells.
Drug treatment of astrocytoma
In order to reduce swelling of the tissues surrounding the tumor in the brain, patients are prescribed steroid drugs. This treatment is mandatory in cases of increased intracranial pressure in the patient.
Symptomatic therapy is also carried out, which is aimed at improving the general condition of the patient.
Increasingly, patients from the CIS are choosing treatment for astrocytoma abroad. Oncology and neurosurgical hospitals in Israel[/anchor], Germany and other countries have access to the most advanced developments and technologies for the treatment of astrocytoma. It’s easy to request a free consultation - you just need to fill out the request form or send an email to us. Contact us without delay!
Diagnostics
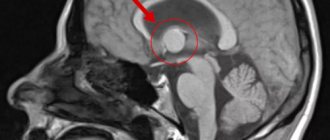
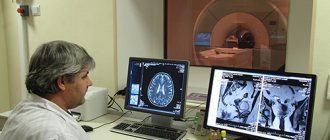
The main way to diagnose a tumor in the brain is to perform a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI is also used during the operation: this helps to monitor the process of node removal.
Sometimes brain astrocytoma is diagnosed using an additional method - magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). This makes it possible to conduct a biochemical analysis of tumor tissue and identify the state of the tumor.
Recurrence of brain tumors is determined using positron emission tomography (PET).
Brain astrocytoma: consequences after surgery
The consequences after surgery for astrocytoma depend on the size of the tumor and its location. Benign astrocytomas, located in an accessible location, give a better prognosis for life expectancy than high-grade astrocytomas or benign astrocytomas, located in a location inaccessible to the surgeon and having a large tumor size. After removal of an astrocytoma, tumor recurrence often occurs, which occurs within two years after surgery. The earlier a tumor is detected, the better the prognosis for its treatment.
Treatment of brain astrocytoma
Depending on the degree of differentiation of brain astrocytoma, its treatment is carried out by one or more of the following methods: surgical, chemotherapy, radiosurgery, radiation.
Stereotactic radiosurgical removal is possible only for small tumor sizes (up to 3 cm) and is performed under tomographic control using a stereotactic frame placed on the patient’s head. For cerebral astrocytoma, this method can be used only in rare cases of a benign course and limited tumor growth. The extent of surgical intervention performed by craniotomy depends on the nature of the growth of the astrocytoma. Often, due to diffuse growth of the tumor into the surrounding brain tissue, radical surgical treatment is impossible. In such cases, palliative surgery may be performed to reduce the size of the tumor or shunt surgery to reduce hydrocephalus.
Radiation therapy for cerebral astrocytoma is carried out through repeated (10 to 30 sessions) external irradiation of the affected area. Chemotherapy is carried out with cytostatics using oral drugs and intravenous administration. It is preferred in cases where brain astrocytoma is observed in children. Recently, active development has been underway to create new chemotherapeutic drugs that can selectively act on tumor cells without having a damaging effect on healthy ones.
Brain astrocytoma
Clinical manifestations that accompany brain astrocytoma can be divided into general, observed at any location of the tumor, and local or focal, depending on the location of the process.
General symptoms of astrocytoma are associated with the resulting increase in intracranial pressure, irritant (irritant) effects and toxic effects of metabolic products of tumor cells. Common symptoms of cerebral astrocytoma include: persistent headaches, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, double vision and/or blurred vision, dizziness, mood changes, asthenia, decreased ability to concentrate, and memory impairment. Epileptic seizures are possible. Often, the first manifestations of brain astrocytoma are of a general, nonspecific nature. Over time, depending on the degree of malignancy of the astrocytoma, there is a slow or rapid progression of symptoms with the appearance of neurological deficits, indicating the focal nature of the pathological process.
Focal symptoms of cerebral astrocytoma arise as a result of destruction and compression of the cerebral structures located next to it by the tumor. Hemispheric astrocytomas of the brain are characterized by decreased sensitivity (hemihypesthesia) and muscle weakness (hemiparesis) in the arm and leg of the side of the body opposite to the affected hemisphere. A tumor lesion of the cerebellum is characterized by impaired stability in a standing position and when walking, and problems with coordination of movements.
The location of brain astrocytoma in the frontal lobe is characterized by inertia, pronounced general weakness, apathy, decreased motivation, attacks of mental agitation and aggressiveness, deterioration of memory and intellectual abilities. People around such patients note changes and oddities in their behavior. When astrocytoma is localized in the temporal lobe, speech disorders, memory impairments and hallucinations of various natures occur: olfactory, auditory and gustatory. Visual hallucinations are characteristic of astrocytoma located on the border of the temporal lobe with the occipital lobe. If a brain astrocytoma is localized in the occipital lobe, then along with visual hallucinations it is accompanied by various visual impairments. Parietal astrocytoma of the brain causes impairment of written language and fine motor skills.
Forecast
Prediction of the disease is made by the doctor based on the following points:
- patient's age;
- degree of malignancy;
- location of the tumor;
- how rapid is the transition from one stage of the disease to another and whether it took place;
- number of relapses.
Based on the overall picture, the specialist makes an approximate prognosis for cerebral astrocytoma. In the first stage of the disease, the patient’s life expectancy will be no more than 10 years.
With the subsequent transition from a benign tumor to a malignant one, the life time will decrease. In the second stage, it can be reduced to 7-5 years, in the third - up to 3-4 years, and in the last stage, the patient can live more than a year if the clinical picture is positive.
Brain astrocytoma: prognosis and consequences
Unfortunately, brain astrocytoma often leads to negative consequences. The lifespan of the first stage, as a rule, does not exceed 10 years. In the second, survival may decrease to 5-6 years, in the third - to 2-3. Once diagnosed with glioblastoma, a person rarely survives the one-year mark.
Pathology entails many negative consequences, which is not surprising. The disease itself is quite serious, and the methods for its treatment have their own characteristics. Possible complications include:
- Loss of vision.
- Inability to move independently.
- Speech impairment.
- Change in taste.
- Decreased sense of touch, etc.
The disease is very serious, therefore, when diagnosing astrocytoma of the brain, one should not delay treatment. The length and quality of future life depends on this.
Prevention
Taking into account how many causes cause the appearance of astrocytoma, as well as how many people have sought medical help in recent years, it is necessary to pay attention to measures to prevent this disease.
Such preventive methods include:
- Strengthening immune defense.
- Elimination of stressful situations.
- Accommodation in environmentally safe areas.
- Proper nutrition. It is important to exclude smoked and fried foods, fatty foods, and canned food. Add more steamed dishes, fruits, and vegetables to your diet.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Preventing head injuries.
- Regular medical examinations.
If a brain astrocytoma is detected, do not despair and give up. It is important to remain optimistic, believe in a good result, and have a positive attitude. Only with such a positive attitude and faith can you defeat oncology.
Classification of anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain
There are several stages. When ranking, the size of the tumor, the nature of its behavior, the intensity of growth, aggressiveness and the manifested clinical picture are taken into account. Staging is important for choosing therapeutic tactics and prognosis.
Astrocytoma grade 1
The neoplasm is small in size. Tissue growth is slow, the neoplasm is well treated. The life prognosis at this stage of pathogenesis is favorable.
Anaplastic astrocytoma grade 2
The tumor begins to grow, however, its development is moderate. The pathological focus is more than 1.5 cm, so pressure is exerted on other brain tissues, which leads to the appearance of a corresponding clinical picture. Signs of malignancy are formed. The boundaries of the neoplasm are located at a certain distance from nearby healthy tissues.
Anaplastic astrocytoma grade 3
In this case, the tumor is cancer, with characteristic negative signs, rapid growth and aggressive behavior. The tumor grows into neighboring tissues, which significantly complicates surgical treatment. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are required. Grade 3 anaplastic astrocytomas generally do not respond well to radiation.
Note. Grade 4 astrocytoma is called gliobalstoma - a dangerous and extremely aggressive type of brain cancer that is difficult to treat.