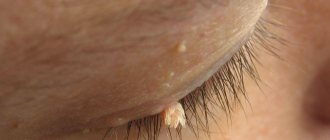
Blepharitis is an eye disease in which the eyelids become very swollen and red. Each type of blepharitis has its own characteristic symptoms. Treatment can take from two weeks to two months, so it is important to contact a specialist in time to prevent complications. We will tell you in the article how different types of this pathology are treated.
In this article
- Signs of blepharitis
- What causes the development of blepharitis of the eyelids?
- What types of blepharitis are there?
- Treatment of blepharitis
- Rules for the use of drugs
- Physiotherapy for the treatment of blepharitis
- What additional measures should be taken when treating blepharitis?
- What are the consequences of untimely treatment?
Blepharitis usually affects the upper and lower eyelids. After diagnosis, the doctor will determine the cause of the disease - based on this, effective medications are prescribed. Too long a course of the disease can lead to unpleasant complications: the appearance of chalazion, barley, the development of keratitis or conjunctivitis, and also deteriorate the quality of vision. When the first symptoms of blepharitis appear, you should immediately begin treatment. How to recognize them?
Signs of blepharitis
This ocular inflammation is characterized by the following clinical manifestations:
- fatigue even with little eye strain;
- thickening and redness of the edges of the eyelids;
- noticeable itching and irritation of the organs of vision;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- sticky discharge or pus that sticks to eyelashes;
- the appearance of scales and crusts on the upper and lower eyelids;
- eyelash loss.
These symptoms apply to many types of blepharitis. If they appear, you should immediately contact a specialist - he will establish a diagnosis and prescribe competent therapy. For a speedy recovery, you must strictly adhere to medical recommendations, observe personal hygiene and the prescribed treatment regimen.
Etiology
Redness of the eyelids can be caused by both external irritating factors and pathological processes of an ophthalmological nature.
External irritating factors that can cause redness of the skin on the upper eyelid include:
- use of inappropriate decorative cosmetics or personal care products;
- lack of sleep;
- prolonged exposure to a room with too dry air, dust, dirt, chemicals.
As for pathological processes in the clinical picture of which this symptom is present, the following should be highlighted:
- barley;
- blepharitis;
- abscess of the eyelid;
- conjunctivitis;
- erysipelas.
It should be noted that redness of the lower eyelid in a child is almost always a sign of a certain disease. If you have such a symptom, you should contact an ophthalmologist and not self-medicate. Timely elimination of the underlying disease will help avoid the development of serious complications.
What causes the development of blepharitis of the eyelids?
Factors that cause non-infectious blepharitis of the lower or upper eyelid are various allergens, including mites. The allergic type of blepharitis begins to develop from the entry into the eye structures of substances that irritate them: cosmetics, household chemical liquids, aerosols, particles of flowering plants. Pet owners can get demodectic blepharitis: it is caused by the Demodex mite, which lives on the fur of pets.
Even visual impairment can cause inflammation of the upper and lower eyelids. Thus, blepharitis often occurs in people diagnosed with farsightedness or astigmatism. The risk group includes people with diseases of the nasopharynx - sinusitis, tonsillitis, as well as general pathologies: diabetes mellitus, gastritis, cholecystitis, etc. Weakened immunity, sensitive and dry organs of vision, chronic intoxication, lack of vitamins important for the eyes can also cause the disease.
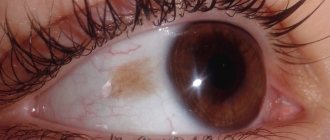
Xanthelasma on the eyelids
Xanthelasma of the eyelids, or flat xanthoma of the eyelids, is a benign formation in the form of yellowish plaques that rise above the skin.
Location: inner corner of the upper eyelid. Sizes can vary from the size of a grain to a bean; plaques can be single or multiple. In this case, they can merge with each other and extend onto the bridge of the nose. The surface of xanthelasma is smooth, the plaques are soft to the touch and do not cause any pain upon palpation.
Such formations are not prone to degeneration. But since they look quite unaesthetic, many would like to get rid of them.
For information: The term “xanthelasma” itself comes from the Greek language. "Xanthos" literally translates as "golden yellow", and "elasma" means plate or plaque.
Such formations are observed in people all over the planet, regardless of race, age and gender. But it is noted that they occur more often in mature women, less often in men, and extremely rarely in children.
It is noted that xanthelasma usually occurs in a pre-infarction state or signals developing atherosclerosis.
Symptoms and causes
Xanthelasma at the initial stage can go unnoticed for a long time. People perceive small yellow spots on the eyelids as natural age-related skin pigmentation. Usually women disguise them with powder and eye shadow. If the plaques are large, many people mistake them for wen and try to remove them using various folk remedies.
It is important not to confuse xanthelasma with wen or warts, since the treatment methods for the two pathologies are completely different
Xanthelasma can be recognized by the following characteristic signs:
- formations from light yellow to light orange on the outer surface of the upper or lower eyelid;
- the size of the spots varies from 0.5 to 1.5 cm;
- may be single, or may merge and move to the bridge of the nose;
- the plaques do not itch, do not hurt, and do not cause any discomfort other than moral discomfort.
Xanthoma is not a pathology in itself; as a rule, it is a sign of a disorder of lipid metabolism in the body. Most often it occurs in people suffering from the following diseases:
How to remove wen under the eye
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- atherosclerosis;
- pancreatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- lipoid nephrosis;
- myxedema.
Why it begins to develop has not been precisely established by medicine. It is generally accepted that the likelihood of xanthoma formation is directly related to a hereditary factor. The fact is that metabolic disorders in the body are inherited. If a child has a disordered fat metabolism, this is usually detected in the first year of life.
The photo shows what xanthelasma of the upper eyelid looks like
Quite often, the cause of formation is the deposition of fat in a specific area, even if the general fat metabolism is not disturbed. However, it is noted that women over 50 years of age who are overweight and have high blood cholesterol levels are at risk.
Note: Xanthelasma is a painless, benign formation, it does not have the ability to become malignant, and does not pose any threat to health, much less human life. This is just a fairly noticeable cosmetic defect.
Since plaques on the eyelids are caused by metabolic disorders, if such a phenomenon is detected, you should contact a dermatologist and endocrinologist. Diagnosis is based primarily on visual examination of the patient. Diascopy is also performed. The doctor presses on the plaque with a glass slide so that the blood drains out and it becomes possible to determine the true color of the formation.
The patient receives a referral for a detailed blood test to determine the level of cholesterol and lipid proteins, and a full examination to determine the quality of fat metabolism in the body.
It is extremely important to carry out a differential diagnosis to exclude pseudoxanthoma, a tumor of the sweat glands or the skin. After making an accurate diagnosis, it is determined what treatment will be and whether it is required.
Treatment methods
There are no specific treatments for yellow plaques on the eyelids. It is necessary to treat the underlying disease - obesity, diabetes or hypertension. The main goal is to restore normal fat metabolism in the body. For this purpose, a therapeutic diet is mandatory.
Its main points are as follows:
- Replacing animal fats with vegetable ones.
- Minimum consumption of salt and spicy seasonings, or better yet, eliminate them completely.
- Exclusion of fatty and fried foods, priority is given to vegetables and fruits, cereals.
- Complete cessation of nicotine and alcohol.
- Limit calories consumed per day to no more than 2000.
In addition, the doctor selects lipotropic drugs, these can be:
- Litenol;
- Cetamifene;
- Lipamide;
- Clofibrate;
- Arachiden.
There are herbal preparations that have the same effect. As a rule, they contain extracts of plantain, birch buds, rose hips, and dandelion root.
Attention! The listed medications also have choleretic properties, so they are prescribed with caution to patients suffering from gallbladder dysfunction. Under no circumstances should you select medications on your own and start taking them; all prescriptions are made only by a doctor.
To support the liver, it is recommended to take hepatoprotectors, for example, Essentiale. What else can a doctor prescribe to get rid of xanthelasma faster:
- choline chloride;
- ascorbic acid;
- a nicotinic acid;
- pyridoxine;
- cyanocobalamin.
Usually, doctors immediately warn the patient that treatment for xanthoma will take a long time and is not always successful. Your health will certainly improve, but there is no guarantee that the plaques will disappear.
For this reason, the patient is informed about the various options for removing the lesions.
Various methods can be used, and the optimal one is determined first of all by the doctor individually, since each of them has its own side effects and contraindications.
- Electrocoagulation. The plaques are cauterized by electric current, which may leave scars. This method is suitable for removing only small plaques.
- Cryodestruction. The formations are cauterized with liquid nitrogen; there is also a risk of scarring after the procedure.
- Surgical excision. The plaques are removed under local anesthesia using scissors or tweezers and then cauterized.
- Laser removal. A directed laser beam destroys the tissue of formations; it is considered the most modern method. But it is not applicable when the eyelid hangs over the plaque; in this case, surgical removal is indicated.
Xanthelasma removal is performed under local anesthesia; it is a simple procedure that does not require hospitalization or long recovery
For information: removing xanthelasma does not mean a complete cure, so that it does not form again, you should continue the treatment prescribed by your doctor, remember a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Traditional medicine for xanthoma on the eyelids
Many patients are prejudiced against the removal of any formations on the skin or cannot undergo it due to contraindications. In this case, treating xanthelasma of the eyelids with folk remedies can help.
Professional doctors do not recognize the effectiveness of traditional medicine methods, moreover, they do not recommend them.
Patients often violate the recipe and dosage of the proposed products and, as a result, only harm their health and add new problems.
However, many are looking for just such recipes to get rid of formations on the eyelids without removal. Below are the most popular and acceptable ones.
- Honey cake. Combine a tablespoon of flour and natural honey, beat in one egg and stir until a fairly dense dough is obtained. Apply the mixture to the affected eyelid for 10 minutes, then rinse with warm water, but without soap. The procedure is carried out every other day until the xanthoma completely disappears. After this, a medicinal ointment can be applied to the eyelid.
- Ointment. Twice a day for 14 days, a thin layer of 1% mercury ointment or zinc-ichthyol ointment is applied to the eyelid. Both drugs have contraindications, so before starting a course of treatment it is recommended to consult with your doctor.
- Herbal collection for oral administration. Mix 100 g of rose hips, 100 g of mint leaves, 75 g of immortelle. Pour the resulting collection with water at the rate of one glass of boiling water for each tablespoon of collection. Close tightly and leave for at least 4 hours. The strained decoction is taken 4 times a day, 150 ml, thirty minutes before meals. The course of treatment lasts thirty days, then a break is taken for sixty days, after which the course can be repeated.
- Infusion of yarrow. Two tablespoons of herbs, dry or fresh, are poured with a glass of boiling water, covered and left for one hour. Then filter and take a quarter glass three times a day before meals.
- In the postoperative period, to eliminate scars and scars, traditional medicine recommends applying 0.5% hydrocortisone ointment to the eyelid.
Whether to try these recipes or not, everyone decides for themselves. Doctors do not deny their benefits in the postoperative period for rapid recovery, as well as for the prevention of relapses. But it is still not recommended as the main method of treatment.
Preventive measures
If a person does not have obvious disorders of fat metabolism, but xanthelasma has formed on the eyelids, he has elevated cholesterol in the blood and local fat deposits are present. This indicates an unhealthy lifestyle and an unbalanced diet. Preventive measures will help avoid the formation of xanthoma or its recurrence.
A healthy lifestyle is the main preventative measure for those with a history of high cholesterol and xanthelasma.
It is recommended to adhere to the following simple rules:
- Diet. Therapeutic nutrition is based on the exclusion of animal fats, spicy and fatty foods, preference is given to vegetable, dairy and cereal products, and it is important to monitor the number of calories consumed per day.
- Monitoring liver function, blood sugar levels, body weight. If deviations are detected, it is necessary to carry out treatment in a timely manner.
- Compliance with the rules of visual and general hygiene.
- Play sports, but without overload and heavy lifting.
- Exercise caution when playing sports or vigorous physical activity: injuries in the eye area can also trigger the development of xanthelasma.
- After 50 years, regular preventive examination by a dermatologist, ophthalmologist, checking blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Reviews
Maria, 52, Volgograd: “I discovered yellow spots on my eyelids ten years ago, but then I didn’t attach any importance to them. I just covered it with foundation and that’s it. But when they began to increase, I realized that something was wrong. And I went to the doctor.
Everything turned out to be very serious! It turned out that my cholesterol was high, my sugar was high, and I urgently needed to start treatment. I want to say that even after two courses of treatment, the xanthomas did not go away; I still had to have surgery. But now I take care of myself, go on a diet, have already lost seven kilograms and feel much better.
So, if you find something similar in yourself, don’t wait, go to the doctor right away.”
Nikolai, 48, Moscow: “There is no need to scare anyone. Yes, xanthomas can appear with high cholesterol, and, of course, you need to monitor this. But they can be easily removed with a laser; it’s not scary or painful. There is no need to panic, nowadays almost everything can be treated without consequences.”
Alexandra, 32, Novgorod: “All these troubles are caused by poor nutrition. My mother is 60, she weighs 90 kg, she eats a lot of meat and potatoes all her life, and loves all kinds of canned food.
Of course, there is arthritis, and hypertension, and obesity, and sugar levels... We also had xanthelasma, we removed it twice, now it appeared for the third time, but nothing was done.
If a person does not think about health and eats everything in sight, then nothing can be done about it and any treatment is pointless.”
Summary: Xanthelasma is not a malignant tumor; it can not be treated, but only perceived as a signal of certain changes in the body. If the plaques grow and cause moral discomfort to the patient, there are various methods for removing xanthoma.
The use of folk remedies in this case is inappropriate due to low efficiency, but a rather high risk of injury to the organs of vision. Reviews recommend finding a good clinic and getting rid of plaques in a safe and modern way.
There is no way to prevent the formation of xanthelasma.
Source: https://gsproekt.ru/simptomy/ksantelazmy-vekah
What types of blepharitis are there?
Depending on the pathogen that caused inflammation of the eyelids, blepharitis is divided into types and, depending on this, medications are prescribed.
Seborrheic or scaly blepharitis
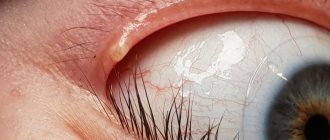
The most common form of the disease. Its symptoms: the formation of dry yellowish scales in the interciliary space, the release of a sticky secretion that glues the eyelashes, swollen and reddened eyelids, profuse lacrimation. With a long course of the disease, some areas of the head may be affected by seborrheic dermatitis.
Ulcerative blepharitis
A severe form of the disease caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Usually difficult to treat. Signs of the disease are the release of pus from the hair follicles of the eyelashes, the formation of ulcers at their roots, and in the acute form - active loss of eyelashes. After recovery, their proper growth may be disrupted, and scars from healed ulcers may remain.
Allergic blepharitis
It develops most often during the flowering period of plants, and can also be a consequence of the reaction of the organs of vision to cosmetics, household chemicals and other components that irritate the mucous membrane. Sometimes drug-induced blepharitis, which occurs as a result of taking certain medications (externally or internally), is also classified as allergic.
Demodectic blepharitis
The causative agent of this form of the disease is the Demodex mite. It causes severe itching and burning, especially in the morning after waking up. Sebaceous secretions and particles of the epidermis accumulate at the edge of the eyelashes.
Meibomian blepharitis
The excretory ducts at the base of the eyelashes become clogged with sticky secretions, the edges of the eyelids become red and inflamed, and purulent blisters form on them. After opening them, small scars remain, which disappear some time after complete recovery. Depending on the location of the affected areas, blepharitis is divided into three categories:
- anterior marginal, in which the inflammatory process spreads to the edges of the eyelids along the ciliary row;
- posterior marginal, affecting the meibomian glands;
- angular, in which inflammation occurs in the corners of the eyes.
If you find any of the listed signs in yourself or your child, you should immediately contact a specialist. If blepharitis of the eyelids goes from a chronic stage to an acute stage, then it will be more difficult to cure it. Effective therapy requires strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene and diet, as well as strict adherence to the prescribed therapeutic regimen and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations.
Spots on the eyelids: causes of white and orange spots
Women constantly monitor the skin of their eyelids, because this is where wrinkles appear first, but age-related changes are not the worst thing that can happen to this delicate area. Under the influence of certain factors, the upper eyelid can be affected by spots of different shapes and colors.
A spot on the eyelid is a fairly rare occurrence, however, it does occur. Unlike formations on other parts of the body, it is impossible to hide it, which causes severe discomfort and spoils the appearance.
Men, women, and even children are equally susceptible to the formation of spots, which is why every adult should know the possible causes of the formation of a defect.
Types of spots on the eyelid
Before prescribing therapy, each doctor will begin to differentiate the neoplasm.
In this area, the skin is very delicate and incorrect diagnosis can provoke poor-quality treatment, which will lead to decreased vision and serious cosmetic defects.
Spots on the eyelids are divided into several types, each of which has its own characteristics and requires an individual approach to treatment:
- freckles are small light spots that appear mainly in blue-eyed, fair-haired and red-haired people;
- chloasma - dark spots that differ from freckles in their larger size;
- vitiligo - white spots caused by a lack of melanin;
- lentigo - convex dark spots that have clear boundaries;
- nevus - neoplasms of a round shape, can rise above the skin, and can differ only in color from the general skin;
- age spots - appear due to skin aging and prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
All of the above forms are classified as pigmented formations, but there are spots that can be caused by diseases and viruses; in medicine they are called acquired. This type of spots in the eye area can be characterized by swelling and severe redness of the skin.
It is categorically impossible to perceive them solely as a cosmetic defect, because they reflect the improper functioning of internal organs, which ones will have to be sorted out by the doctor, based on a thorough instrumental examination and laboratory tests.
Possible causes of stains
The reasons for the formation of spots on the eyelids can be very different. Among the common provocateurs for the development of atypical formations on the skin in the eye area are:
- avitaminosis;
- hereditary disposition;
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- reaction to medication use;
- insect bite;
- reaction to cosmetics and hygiene products.
Very often, neoplasms itch, itch and are characterized by severe swelling. This significantly disrupts the patient’s usual life, and he strives to get rid of the tumor as quickly as possible, but this should not be done at home. Only if you are sure that you have been bitten by an insect, you can take antihistamines and delay visiting the doctor.
In most cases, spots are differentiated by their color, this allows one to eliminate half of possible diseases by visual inspection and speed up diagnosis. In total, medicine knows more than 50 diseases, the symptom of which is spots on the eyelids.
Red spots on the eyes
Red spots may indicate seborrheic dermatitis, allergies, demodicosis and hemangioma. Each of these diseases has accompanying symptoms by which you can recognize it. An allergic reaction, or, as it is commonly called, eczema, can occur due to irradiation, exposure to low temperatures and exposure to chemicals on the skin of the eyelid.
The inflammatory process can also occur as a result of contact with aggressive substances, which are found in cosmetics, washing powders and detergents. Red spots can appear in both children and adults; eczema has no age preferences and manifests itself equally in everyone.
It is painful for a person to blink, the eyelid swells greatly, waters, and the white gas turns red, vision may decrease, but the pathology has a short-term effect.
Violation of the intestinal microflora can manifest itself in the formation of red spots. It would seem very strange, but everything in the body is interconnected and pathogens that enter the intestines can manifest themselves in places with increased susceptibility. The skin on the eyelids is very delicate and thin, it is characterized by low local immunity, and accordingly turns red in the presence of a pathogen.
Among the accompanying symptoms of dysbacteriosis are stool disturbances, abdominal pain, as well as vomiting and deterioration in general condition.
Demodectic mange is a disease caused by a skin parasite called a mite. It settles into the skin, feeds on skin fiber and fat produced by the sebaceous glands.
These mites are orange in color, but it is impossible to see them with the naked eye because they are very small. Redness appears if more than 3 mites infest the skin. One or two mites can live in human skin undetected for several months.
Unsanitary conditions and prolonged exposure to the sun contribute to the spread of ticks.
You can recognize demodicosis by itchy spots that turn into papules with serous contents and do not go away for a long time. Sometimes the skin in the eyelid area may peel off.
Seborrheic dermatitis can develop due to excessive activity of the sebaceous glands and lack of hygiene. The disease is most often observed in infants and men. You can recognize this dermatitis by the spots that are very flaky and peel off in whole layers. The skin around the tumor is very itchy, but does not swell.
Hemangioma is a benign neoplasm. Externally, it resembles a pigment spot or a mole of an unnatural shape. You can recognize a hemangioma by applying pressure.
It becomes white, then gradually regains its former color.
If this factor is present, it is very important to visit an ophthalmologist, because hemangioma can degenerate into a malignant tumor, which requires intensive therapy.
Yellow spots
White and yellow spots are medically called xanthelasma. They are formed mainly in older people. Xanthelasmas are formed against the background of dysfunction of the stomach, liver and intestines. They can be recognized externally by their raised tubercles, soft and smooth to the touch.
The formations have different sizes and shapes, it all depends on the intensity of the disturbance of fat metabolism in the body. The larger the tumor, the more complicated the situation.
People with diabetes, obesity and food lovers with high cholesterol are at risk of developing xanthelasma.
Brown spots
Brown-colored formations are called chloasma; they can be transmitted genetically or develop against the background of diseases of the endocrine system, weak immunity, hormonal imbalance and chronic inflammatory processes in the body. This type of tumor is characterized by severe itching and irritation.
Interestingly, if the spot is caused by pregnancy, then it comes on its own after childbirth without medical intervention. In other cases, the pathology requires careful diagnosis and therapy.
If a spot appears on your eyelids, regardless of its color, you need to go to the doctor, because this is not a healthy signal from the body about a malfunction. Treating such a delicate area at home will not lead to anything good. It’s stupid to lose your sight and become disabled because of your passion for traditional therapy.
Source: https://IDermatolog.ru/dermatity/vidy-pyaten-na-vekax-glaz-i-prichiny-ix-poyavleniya.html
Treatment of blepharitis
To treat infectious types of blepharitis, corticosteroid drugs and antibiotics are used - this regimen is most effective. Antibacterial ointments and drops are presented on the pharmaceutical market in a large assortment. Each remedy has its own active ingredient that suppresses pathogens. Here are some of them that can be prescribed for the treatment of blepharitis.
- "Tetracycline"
An inexpensive, well-known antibiotic that shows good results in the treatment of blepharitis, as well as conjunctivitis, keratitis, barley and other eye diseases. Tetracycline ointment must be used strictly in accordance with the treatment regimen determined by the doctor. It depends on the type of blepharitis, the degree of damage to the visual organs and the individual characteristics of the body.
- "Tobrex"
The active substance, tobramycin, is effective in the treatment of infectious eye diseases. Tobrex is convenient because it has almost no contraindications: it can even be prescribed to children and pregnant women at the discretion of the doctor.
- "Maxitrol"
The active ingredients of these drops are dexamethasone + neomycin + polymyxin B. They are effective in the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis, keratitis, and are also prescribed during the rehabilitation period after eye surgery to prevent the development of infections. May cause increased intraocular pressure and other adverse reactions.
- "Gentamicin", "Dex-gentamicin"
The main active ingredients are gentamicin, gentamicin + dexamethasone. Ointments have antiallergic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. They are used in the treatment of many eye diseases, including blepharitis of the upper and lower eyelids. Contraindicated for viral inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva, increased intraocular pressure and a number of other conditions.
- "Normax"
Antibacterial agent from the group of fluoroquinolones. The active ingredient is norfloxacin. Not recommended during pregnancy, lactation, or children under 18 years of age. Adverse reactions: nausea, headache, dizziness and others.
- "Levomycetin" (ointment, drops)
The ointments and drops contain broad-spectrum antibiotics, including chloramphenicol. Used for conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis and other eye diseases.
- "Erythromycin"
The main components of the ointment are broad-spectrum antibiotics. Used for various eye diseases. Sometimes they may not act effectively enough due to the fact that some pathogenic bacteria have developed resistance to them, since drugs based on erythromycin have been used for several decades.
- "Signitsef"
Antibacterial drops from the fluoroquinolone group. It is used to treat conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratitis and other diseases, as well as to prevent complications after eye surgery. Sometimes it can cause decreased visual acuity, discomfort, dry eye syndrome and a number of other side effects. Contraindicated during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and children under 1 year of age.
- "Oftocipro", "Tsiprolet" "Tsipromed", "Ciprofloxacin"
The active component of these drugs is ciprofloxacin. Used to treat blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, bacterial corneal ulcers, chronic dacryocystitis (inflammation of the lacrimal sac) and barley. Contraindicated in viral keratitis, pregnancy, lactation, and children under 1 year of age.
Spots on the eyelids: what they are, photos of formations and treatment methods
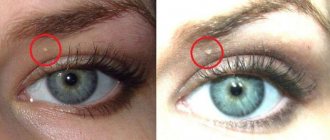
The appearance of yellow spots on the eyelids is called xanthelasma.
The formations are frightening to patients because they may indicate serious systemic diseases.
Such manifestations can be single or multiple. As the disease progresses, their number increases. Also, neighboring formations can merge with each other. To identify the true causes, it is recommended to undergo diagnostic tests, and then receive the necessary treatment from a doctor.
Xanthelasma on the eyelids
Xanthelasma of the eyelids, or flat xanthoma of the eyelids, is a benign formation in the form of yellowish plaques that rise above the skin. Location: inner corner of the upper eyelid.
Sizes can vary from the size of a grain to a bean; plaques can be single or multiple. In this case, they can merge with each other and extend onto the bridge of the nose. The surface of xanthelasma is smooth, the plaques are soft to the touch and do not cause any pain upon palpation.
Such formations are not prone to degeneration. But since they look quite unaesthetic, many would like to get rid of them.
For information: The term “xanthelasma” itself comes from the Greek language. "Xanthos" literally translates as "golden yellow", and "elasma" means plate or plaque.
Such formations are observed in people all over the planet, regardless of race, age and gender. But it is noted that they occur more often in mature women, less often in men, and extremely rarely in children.
It is noted that xanthelasma usually occurs in a pre-infarction state or signals developing atherosclerosis.
Rules for the use of drugs
In order for the prescribed drops and ointments to act purposefully to achieve a faster effect, they must be administered correctly. So, it is more convenient to do this with a special spatula - it can be purchased at any pharmacy. You should squeeze out about 5-6 mm of ointment from the tube onto your shoulder blade, carefully pull back the lower eyelid and place the ointment there, being careful not to touch the eye tissue with the tip of the tube. Then you need to close your eyelids for a while so that the product is evenly distributed inside.
When instilling drops, make sure that they fall exactly into the conjunctival sac. Do not exceed the recommended dosage of medications, acting strictly as prescribed in the prescription. Excessive amounts of medication may harm your eyesight. It is better to instill in a horizontal position so that the liquid does not leak out.
The duration of use of antibacterial drugs is determined by the attending physician. However, a visible effect should occur within 3-4 days from the start of their use. If this does not happen, then you need to seek advice from a specialist - you may need to change your medication. It should be remembered that if antibiotics are used for too long, there is a risk of developing superinfection - the growth of pathogenic microorganisms that are immune to them, including fungi.
It contains mild, soothing herbal ingredients: green tea, chamomile, witch hazel extract, and effectively cleanses the eyelid skin of impurities. Apply a little lotion to a cotton swab and lubricate their edges at the base of the eyelash row, trying to remove all traces of discharge. After this, medications can be administered.
In the allergic form of blepharitis, moisturizing preparations that imitate natural human tears will help relieve dryness, itching, and irritation: Hilo-chest of drawers, Systane, Artelak Balance and others.
You should not make a diagnosis yourself and self-medicate by seeking advice from friends or using information from the Internet. Only a specialist, after a competent diagnosis, will select effective medications to eliminate inflammation of the eyelids. An inappropriate remedy for a particular type of blepharitis can only aggravate the course of the disease and thereby delay recovery.
Effective methods for treating eyelid pigmentation
In general, age spots do not pose any danger to the human body, but they cause aesthetic discomfort that one does not want to put up with.
That is why dermatologists, together with cosmetologists, offer several ways to solve the problem:
- Cream with whitening effect. If you use budget funds, you can use hydrogen peroxide as an example, but you need to be careful with it, since there is a high probability of damaging the skin. Zinc ointment is an equally effective remedy, because it not only eliminates wrinkles, but also perfectly whitens the skin. Mercury cream - its use is not recommended without consulting a doctor, especially in the eye and eyelid area.
- Help from a cosmetologist. The most common procedure for getting rid of eye pigmentation is chemical peeling. The process uses acids that can block the action of melanin. Laser peeling is the second most popular procedure. It is enough to do 3 procedures to remove superficial spots from the eyes, but only a few will undertake a session in the eyelid area. Phototherapy - infrared rays act on hyperpigmented spots, thereby removing them.
- Cosmetics can also eliminate age spots in the eyelid area. For example, Retin-A cream can reduce the concentration of pigment in the skin. "Achromin MAX" destroys melanin and forms a protective barrier around the eyes. VC-IP has the power to inhibit the growth of melanin.
Traditional methods:
- Add a tablespoon of chopped parsley to 250 ml of vodka, leave for a week and wipe your face twice a day.
- Mix the juice from squeezed lemon with a full dessert spoon of honey, spread it on your face and wait half an hour, then wash it off.
- Chop the dandelions and fill them with 1.5 cups of water. Boil for a quarter of an hour, strain and lubricate your face three times a day.
- Wipe your face with lemon every day.
- Apply old kefir or expired sour cream to your face for half an hour.
Pigmentation of the eyelid is a rather sensitive problem, since not many products can give a positive result and not harm the skin of the face.
In most cases, this problem can be resolved at home. But there are often situations when even a qualified doctor cannot cure a disease, since the cause is not fully understood. In this situation, you need to be patient and undergo a full examination to identify the root causes of eyelid pigmentation.
Physiotherapy for the treatment of blepharitis
If the disease changes from chronic to acute or the prescribed medications have a slow effect, additional physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed. Treatment with devices will help eliminate inflammation and redness of the upper and lower eyelids, improve metabolic processes, and accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues. For this use:
- UHF therapy;
- darsonvalization - exposure to high-frequency pulsed current;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy and other methods.
Washing the conjunctival cavity and applying anti-inflammatory compresses to the eyelids also have a good result. The list of necessary procedures is determined by the ophthalmologist, and he also regulates their duration and period of implementation.
What additional measures should be taken when treating blepharitis?
During therapy, you should strictly adhere to certain rules that will speed up the results.
It is important to follow a strict diet, excluding too spicy, salty, fatty, smoked foods, and alcoholic drinks from the diet. You need to consume more foods containing healthy vitamins - retinol, riboflavin, ascorbic acid, zinc, selenium:
- retinol - wild garlic, broccoli, garlic, viburnum berries, fish oil;
- riboflavin - beef liver, cod liver, quail eggs;
- vitamin C - citrus fruits, greens, sour berries;
- selenium - nuts, legumes, some cereals, for example, buckwheat;
- zinc - seafood (kelp, shrimp), hard cheeses.
By following a diet that includes the consumption of these foods, you can significantly speed up the healing process. It will also be useful to take vitamin complexes for the eyes. The development of any infection in the body is a consequence of weakened immunity, and it needs to be strengthened.
During the treatment period, you need to change bed linen more often, especially pillowcases, and also get a separate towel for the patient. It is better to gently blot the affected eye with a disposable napkin after washing, and do not rub it with your hands. Women should avoid using decorative cosmetics. It can clog the excretory ducts, prevent the release of pus and increase inflammation. In addition, cosmetics during illness cause an allergic reaction in the eyes. A large percentage of success lies in observing simple hygiene rules and following the doctor’s recommendations.
What are the consequences of untimely treatment?
Blepharitis, if there is a delay in starting treatment or improper therapy, can go from chronic to acute, and then it will be much more difficult to cure it. If you have symptoms that may indicate blepharitis, you should not waste time and consult a doctor. He will find out the etiology of the disease and prescribe effective medications.
There is no need to search for a diagnosis on your own and use drops and ointments based on information from the Internet. The symptoms of different blepharitis may be similar, but they may require different medications. When carrying out treatment, the patient must responsibly follow all instructions - only careful adherence to them guarantees a successful result.
Yellow spots on the eyelids
The appearance of yellow spots on the eyelids is called xanthelasma.
The formations are frightening to patients because they may indicate serious systemic diseases.
Such manifestations can be single or multiple. As the disease progresses, their number increases. Also, neighboring formations can merge with each other. To identify the true causes, it is recommended to undergo diagnostic tests, and then receive the necessary treatment from a doctor.
We recommend reading: Yellow circles under the eyes
Causes
There is fat metabolism in the human body. It refers to the movement of lipids throughout the body, their absorption and breakdown. If any stage is disrupted, xanthelasmas may form. There are also other reasons for the appearance of such segments on the skin of the eyelids:
- lipoid nephrosis – damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys, which forms swelling of the subcutaneous fat;
- obesity – an increase in body weight above normal volume, which disrupts fat metabolism in the body,
- inflammatory liver diseases, including hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis;
- complications of diabetes mellitus leading to disruption of various types of metabolism.
This means that the formation of xanthelasma is a sign of a systemic disease. If you just eliminate fatty deposits on the skin of the eyelids, they will return again within some time. Therefore, the doctor needs to identify the root cause.
Symptoms
If the cause of the condition is inflammatory liver disease, the following clinical symptoms may be detected:
- sharp or dull pain in the right hypochondrium;
- the formation of spider veins under the skin;
- exhaustion of the body;
- nausea, vomiting, flatulence, heartburn;
- thickening of the phalanges of the fingers.
If the yellowing of the skin is a benign formation called xanthelasma, a small bulge in the form of a plaque forms in a person’s eyes. It has a yellow tint and there is no pain when pressed.
Benign yellowing can occur in people of both sexes, but most often it appears after 45 years of age.
Diagnostics
If the patient consults a doctor, he will conduct several diagnostic tests to confirm or refute the presence of systemic diseases:
- Patient interview. The doctor asks if he has a history of diabetes, kidney disease, or other pathologies. Also learns about his heredity. Perhaps the patient will independently complain to the doctor about the symptoms that appear.
- Examination of a person. The doctor examines the affected skin surfaces on the eyelids. During palpation, the patient will not experience pain or other discomfort.
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine, blood biochemistry. With the help of such tests, it is possible to identify the norm or abnormality in the cellular composition of the blood. If liver pathology is observed, biochemical markers will increase. These include ALT, AST.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Perhaps a disturbance in fat metabolism appeared as a result of inflammatory diseases of the liver, kidneys, pancreas and its ducts.
- Biopsy of material from a fatty formation on the eyelid. Subsequently, it is subjected to histological examination. It determines the normal or malignant process in cells.
We recommend reading: Red circles under the eyes
After receiving all the data from the study, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. Only after this does therapy begin.
Treatment
The method of therapy depends on the diagnosis that caused the disease. Most often, doctors use the following treatment methods:
- a diet with which the patient loses weight, normalizing lipid metabolism, eliminating excess cholesterol in the blood;
- elimination of bad habits that affect the condition of internal organs, including the liver and kidneys (drug addiction, alcoholism);
- drugs that reduce the concentration of lipids in the blood;
- adjustment of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus;
- hepatoprotectors that prevent the destruction of the liver cell membrane when exposed to negative environmental factors or internal toxins of the body;
- surgical removal of xanthelasma, after which the resulting wound is cauterized;
- cauterization of the formation using electrocoagulation, that is, exposure to electric current discharges;
- laser removal, considered the highest quality method for eliminating xanthelasma, which does not require pain relief, damages tissue in small quantities;
- removal with liquid nitrogen, used for small sizes of xanthelasma, which is carried out under the influence of low temperatures and freezing.
If the formation has been eliminated using various surgical methods, the patient then undergoes a rehabilitation period. A person needs to stick to a diet and not be in direct sunlight often. Daily treatment with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drops is necessary to prevent the development of a pathological process on the thin skin of the eyelids.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of yellowing on the skin of the eyelids, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- high-quality nutrition that does not overload the body, especially various parts of the gastrointestinal tract;
- drinking a large amount of water per day, at least 2.5 liters per day, to saturate the body with fluid and prevent dehydration;
- if there are not enough nutrients in food, it is recommended to use multivitamin preparations, which contain all the necessary vitamins, minerals, and trace elements;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases, if they cannot be completely cured, it is necessary to take them under control with the help of medications;
- periodic visits to doctors, especially if the patient has pathology of the skin with the appearance of inflammation and benign formations on the surface.
The use of all preventive measures will not be able to completely prevent the risk of developing diseases, but will significantly reduce them.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 2 5.00
Source: https://proglazki.ru/simptomy/zheltye-pyatna-na-vekah-glaz/